reflection of light
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
reflection
light travelling in a medium encounters a boundary leading to a second medium. part of the incident light ray returns back to the first medium. this is reflection
mirrors
can be plane or curved
mirrors redirect light rays and form an image of objects
- mirrors are made on a thin layer of aluminium on a polished surface
what are the two types of reflection
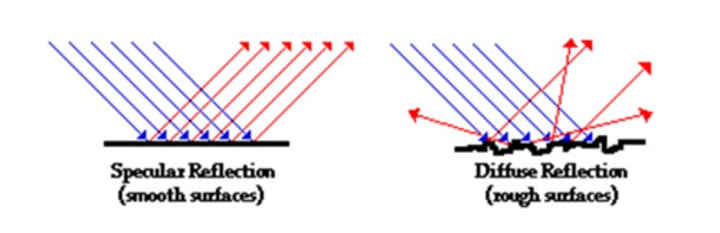
1. Specular (regular) Reflection
2. Diffuse Reflection
specular (regular) reflection
when a parallel pencil of rays is incident on a highly reflected surface, the light rays are reflected in a single direction
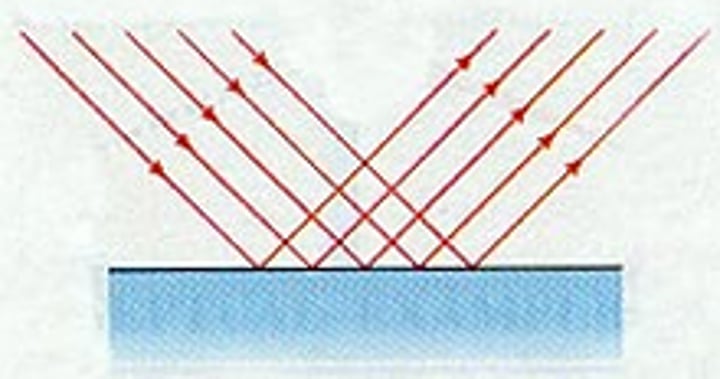
diffuse reflection
when a parallel pencil of rays is incident on a irregular or rough surface, the light rays are reflected in all directions (e.g. paper)
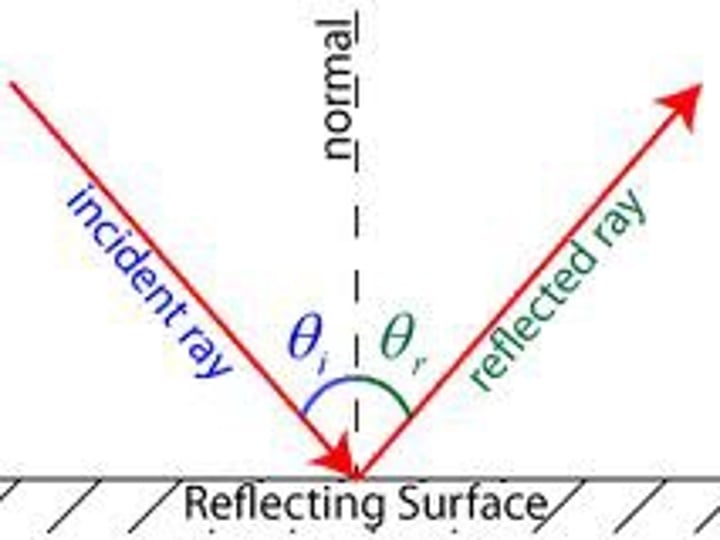
laws of reflection
1) incident angle is equal to the angle of reflection
2) incident ray, reflected ray and normal ray are all in the and plane, which is perpendicular to the surface
plane mirror distance
for a plane mirror the image distance behind the mirror is the same as the object distance from the mirror
characteristics of images formed by plane mirror
1. Image is virtual;
2. Same size as the object;
3. Same orientation as the object UPRIGHT laterally inverted
4. Same distance from the mirror as the object.
the sight testing chart
1) uses a plane mirror
2) letter chart should be 6m away from patient 3m testing room and plane mirror makes the total distance 6m
3) letters on chart are inversed so that they appear lateral to patient in mirror
what are the 2 types of mirror?
1) convex
2) concave
convex mirror
light rays will diverge
concave mirror
light rays will converge
