Rivers
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
A waterfall is formed when a river flows on top of a band of hard rock e.g. granite and a band of soft rock e.g. limestone.
2
As the river flows over the bands, processes of hydraulic action and abrasion erode the soft rock. This causes vertical erosion down into the river channel forming a waterfall
3
At the base of the waterfall, a plunge pool is formed. As water is falls into the plunge pool, it splashes against the back wall eroding it even more. This causes undercutting
4
Undercutting erodes the soft rock and leaves an overhang of the hard rock, which collapses
5
This process repeats and the waterfall retreats upstream
Example
Torc Waterfall, Co. Kerry
Source
The beginning of a river
Course
The route a river takes to the sea
Confluence
The point at which two rivers join
Tributary
A small river
Mouth
Where a river ends
Drainage basin
The area of land drained by a river
Watershed
Area of high land that separates two drainage basins
Estuary
The tidal part of a river
Hydraulic Action
The physical force of moving water that breaks down rocks from the riverbed and banks
Abrasion
Small stones carried by the river wear away riverbeds and banks
Attrition
Small stones collide into each other and break into smaller pieces
Solution
Acids in the water dissolve rocks e.g. limestone
Feature of a youthful stage & explain what it is
A waterfall is a vertical drop in the youthful stage
Example of a waterfall
Torc Waterfall, Co Kerry
What is a feature of river deposition?
A levee is a long ridge of alluvium that runs along the edge of a river
Formed in the Old Stage of a river
What is HEP?
-Hydroelectric Power is the creation of electricity by using the force of falling water
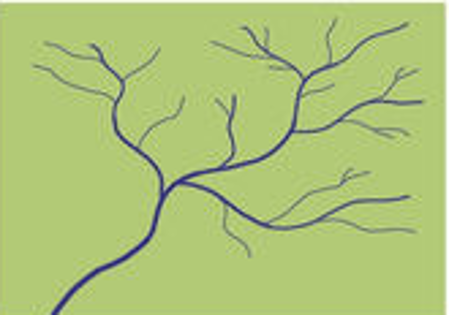
Dendritic
Where tributaries combine before joining the main river.
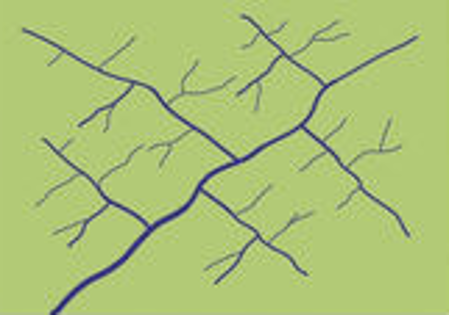
Trellis
Where tributaries join another tributary or the main river at a 90° angle.
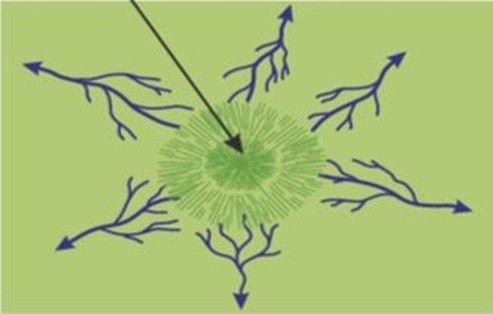
Radial
This is where streams flow down from a central high point. It looks like the spokes on a bicycle wheel.
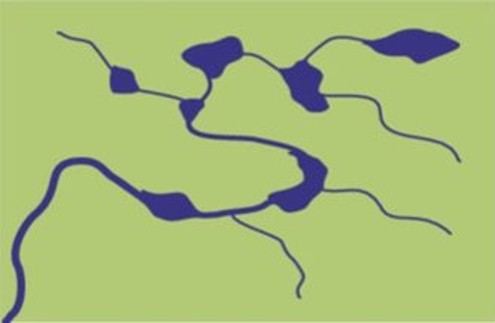
Deranged
There is no clear pattern.
Why did the River Shannon flood?
Unusually high levels of rainfall, lack of planning and buildings on flood plains
What were the immediate impacts of the flood?
Agricultural land covered in water
Livestock lost
Thousands of homes flooded
Roads/infrastructures damage
Businesses shut during Chrismastime
Water unsafe to drink
What were the government responses to the flood?
Army deployed with sandbags & pumps
Emergency accommodation was set up
Local councils were given €16m
€85m was given to repair roads/infrastructures
It cost €106m overall
What were the long term solutions?
Flood defenses were put to prevent future floods
The river was dredged to deepen the river channel
A national flooding forecast was set up with a waring service
Shannon Flood Risk Group created to control floods for the Shannon
Advantages of HEP
Provide cheap and clean energy which is renewable & sustainable.
Helps control flooding also.
What is the The Gorges Dam?
A dam built on the Yangtze in China at 185m in height and 1.6km in width. Provides cities such as Shanghai with energy but prevent floods.
Name an example of a dam.
Ardnachrusha, Co. Clare
Disadvantages of HEP
Damming the river prevents the fertile alluvium transporting downstream, meaning farmers need to used artifical fertilisers. Much of the Shannon’s volume is diverted to the HEP station which means water flowing downstream is reduced and fish stock are being depleted.
Name an example of a delta.
Mississippi Delta (USA)