L10 New from old - metamorphism
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Subduction, contact and regional metamorphism
Igneous intrusion → contact metamorphism (in contact with e.g. basalt heat + temp)
Subduction metamorphism → subduction zone’pre
Regional metamorphism → continental plate (himalayas outstrecthed)

Metamorphism
‘pre-existing rock (protolith) undergoes solid-state change in response to modification of its environment.’
change in temperature and/or pressure
compression
reaction with ‘‘hydrothermal fluids’’
Different protoliths - different metamorphic rocks
(in this case illustrated by contact metamorphism associated with igneous intrusion)
Original rock i.e. what you start with (protolith)
What you do to it (T and P + fluids)
Outputs can be extremely complex
Emphasis in this course is on processes not products
N.B. Remember ‘shale to schist’, ‘limestone to marble’, ‘sandstone to quartzite’.

Are there textures in hand specimen that are diagnostic of metamorphism
protolith → metamorphic rock
metamorphic minerals (indicative of P/T condition)
metamorphic textures (e.g. foliation - alignment of minerals, in this case micas, has a silvery shine)
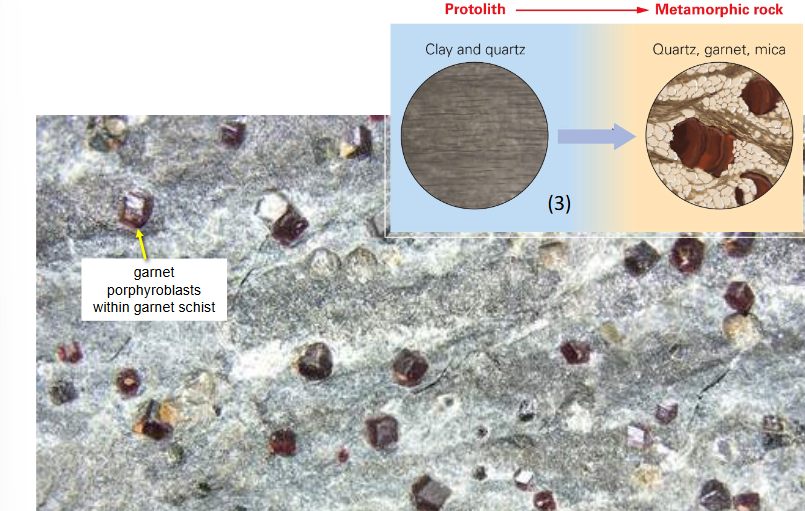
garnet porphyroblasts..
metamorphism often results in foliation
planar foliation is the parallel alignment of play minerals (e.g. clays/micas)
minerals oriented perpendicular to compression
sometimes with alternations of differently coloured layers

non-foliated texture
no preferred orientation of the minerals in the rock
when deformation is low and clay/mica content is low

processes involved in forming metamorphic rocks?
recrystalization
phase change
neocrystallization
pressure solution
plastic deformation
Recrystallization
changes shape and size of grains
no change in mineral identity
when changed large crystals and new grains are made
solid state process where atoms of mineral are reorganised mainly by solid-state diffusion.
Phase change
one mineral transformed into another with the same composition but different crystal structure.
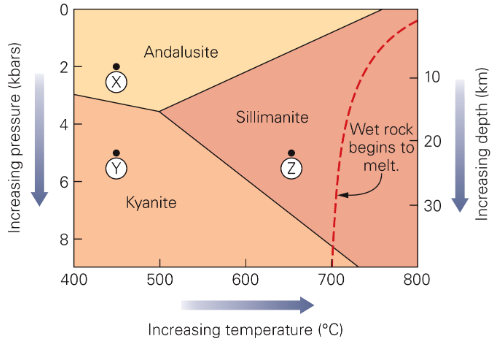
Three polymorphs of Al2SiO5
Andalusite- low T and P = contact pressure
Kyanite- low T, high P = subduction zone
Silimanite- high T and P = lava becoming a rock
Both T and P change with depth in the Earth
Mineral stability, which is highly dependent upon T and P, can be graphed on phase diagrram.
Andalusite → Killiney
neocrystallization
growth of new minerals different from protolith
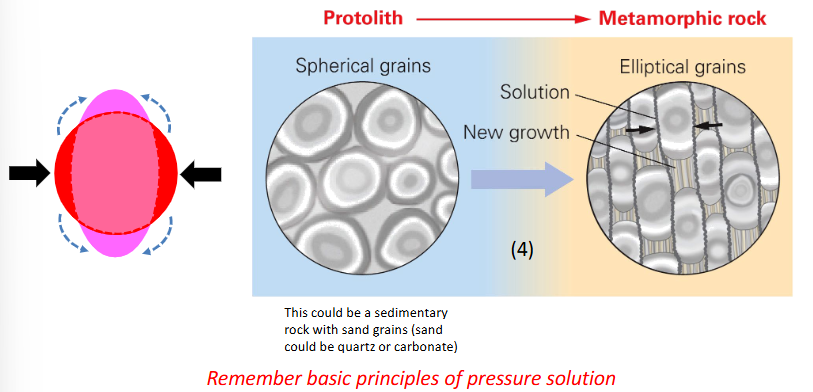
Pressure solution
minerals grains dissolve where their surfaces are pressed against other grains
ions produced migrate (water-assisted diffusion)
precipitation where grains under less pressure
can shorten grains in one direction and lengthen them in another
also occurs under non-metamorphic conditions
plastic deformation
rock sheared/squeezed at high temperature/pressure
minerals change shape without breaking: plastic behaviour
can occur without change to composition or crystal structure
or occur when metamorphic reactions are happening
During plastic deformation, the grains change shape internally without breaking or dissolving - by internal deformation of the atomic lattice.

metamorphism is the result of heat and/or pressure
Heating
atoms vibrate
chemical bonds between them stretch and break
atoms detach
results in rearrangement of atoms within grains and migration of atoms into/out of grains
recrystallisation and/or neocrystallisation
Pressure
greater pressure = closer packing of atoms
density increases
phase changes and/or neocrystalisation
Role of compression, shear and the development of preferred orientation
differential stress: stress applied unequally in all directions
(1) normal stress: applied perpendicular to a surface
how does preferred orientation form?
at elevated temperatures rock changes shape without breaking
internal texture changes in sympathy with the stresses applied
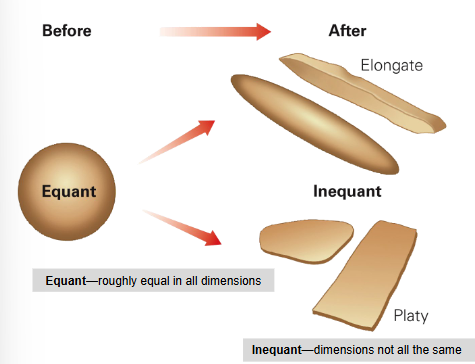
preferred orientation develops via alignment of inequant grains.
inequant grains may be pre-existing (i.e. geometry before metamorphism) or may form during the metamorphic episode
Elongate (cigar shaped):..
Pressure solution, neocrystallisation, plastic deformation
pressure solution occurs on faces perpendicular to direction of compression i.e. grains shorten in that direction
often accompanied by neocrystallization: precipitation occurs where rock is stretching
plastic deformation at high T accompanied by differential stress
…
plastic deformation and rotation
foliation
role of hydrothermal fluids in metamorphism
hot water, steam, supercritical fluids*
* under high temp and pressure
characteristics of fluid and gas
very pervasive
accelerate reactions (atoms migrate faster through fluids than solids
provides water that becomes absorbed by minerals during metamorphism
metasomatism: chemical composition of rock is altered by introduction and/or removal of chemical components by water-rich fluids
source of water
Types of metamorphism and their settings
Burial - deep burial in a basin
Dynamic - shearing in a fault zone
Contact (i.e. thermal) - heating by an intrusion
Hydrothermal - alteration by hot water leaching..
Burial metamorphism (diagenesis)
Pressure (P) and Temperature (T) increase as sediments are buried ina basin due to…
Get diagenesis (i.e. cementation/dissolution of sediments rather than classic metamorphism..
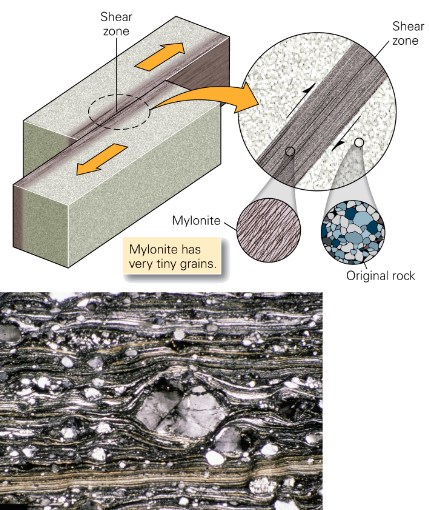
Dynamic metamorphism
Breakage of a rock by shearing within a fault zone
at deeper levels rocks are ductile. rocks in fault zones smear\ to form mylonite.
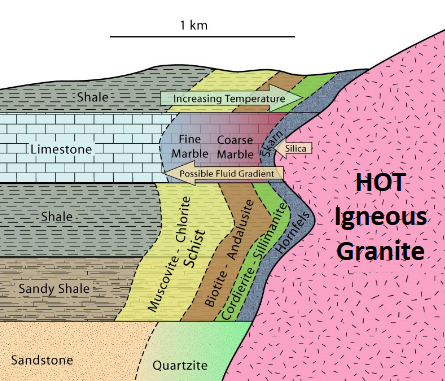
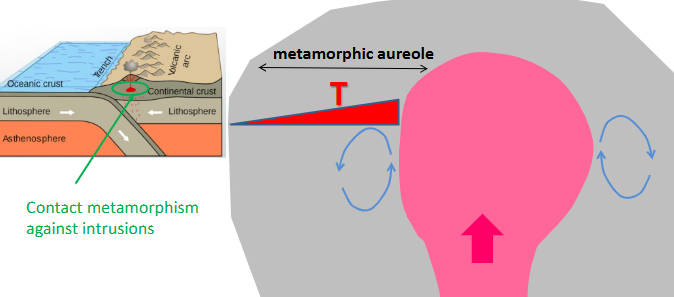
Contact (thermal) metamorphism
contact - position adhacent to an igneous intrustion
thermal - develops in response to heat without change in pressure
magma intrusion affects ‘country rock’
heat transferred and hydrothermal fluids ciruclated
metamorphic aureole generated
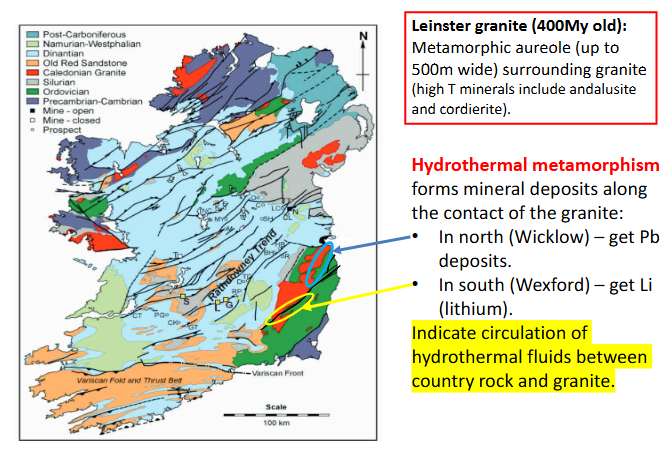
Example of contact metamorphism in Ireland
Leinster granite (400 millions year old)
Metamorphic aureole (up to 500m wide) surrounding granite (high T minerals include andalusite and cordierite)
Long crystals → andalusite (slightly high temp rock)
original rock was an oceanic mudstone (deposite on south side of lapetus ocean seperating north and south of Ireland)

Hydrothermal metamorphism in Ireland - EXAMPLE
Forms mineral deposits along the contact of the granite:
North (wicklow) - get Pb deposits
South (Wexford) - get Li (lithium)
Indicated circulation of hydrothermal fluids between country rock and granite.
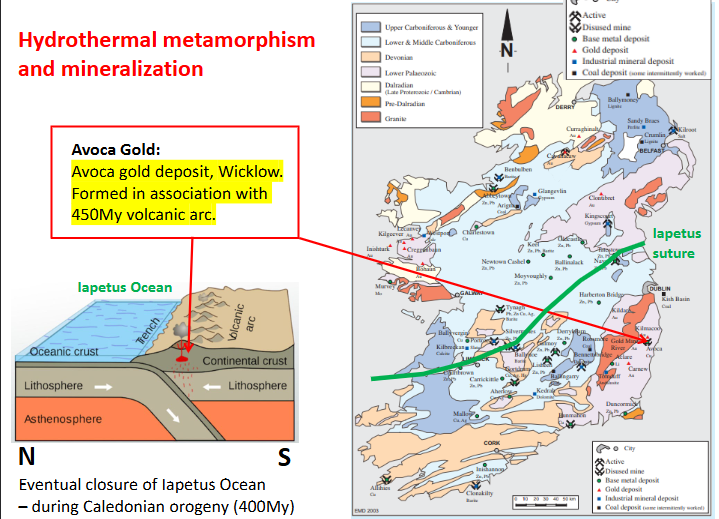
Hydrothermal metamorphism and mineralization
Avoca Gold:
Avoca gold deposit, Wicklow
Formed in association with 450My volcanic arc.Ireland’s gold → was from volcanic arc, the subduction zone in the likes of avoca gold deposits
convection currents stripping those rocks.
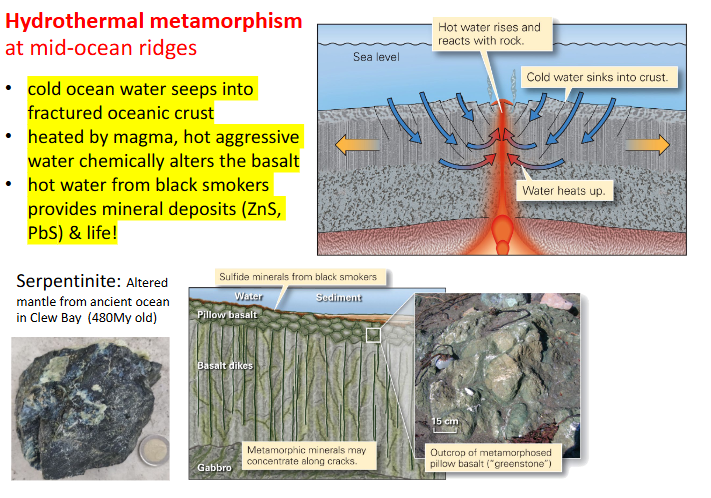
Hydrothermal metamorphism at mid ocean ridges
cold ocean water seeps into fractured oceanic crust
heated by magma, hot aggressive water chemically alters the basalt
hot water from black smokers provide mineral deposits (ZnS, PbS & life)