pathophys
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
what are the pH and [H+] ranges for acidosis and alkalosis

primary altercations and secondary responses to acidosis and alkalosis

respiratory acidosis causes
disturbance of neural respiratory control
disorders of thoracic cage
airway obstruction and severe pulmonary disease e.g. COPD, pneumonia asthma attack
metabolic acidosis causes
excessive HCO3- loss via kidneys or GI
Non ion gap
Diahhroea
RTA 2 - failure pf proximal tubule to reabsorb HCO3-
RTA 1 - disorder of acid excretion in tubules
RTA 4 - reduced ammonia excretion secondary to hypoaldosteronism
High anion gap
diabetic ketoacidosis
lactic acidosis
organic acid accumulation in blood
reparatory alkalosis causes
hyperventilation
fever
hypoxia
panic attack/hysteria
increased metabolism
pregnancy
hyperthyroidism
pheochromocytoma
metabolic alkalosis
GI loss - excessive vomiting
hypokalemia - causes movement oh H+ into cells
hypercalcemia + milk alkali syndrome
Explain the anion gap

consequences of acidemia
recued cardiac output
low blood pressure
arrythmias
hyperventilation - respiratory muscles fatigue
insulin resistance, inhibition of glycolysis
hyperkalemia
altered mental status + coma
consequences of alkalosis
arteriolar constriction
reduced coronary artery perfusion
arrythmias
hypoventilation
glycolysis
hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia
reduced cerebral blood flow = seizures
ICF meaning
fluid in the cells
main constituents = Calcium, magnesium, phosphate, potassium
ECF meaning
fluid outside the cell = interstitial fluid + blood plasma
main constituents = sodium, chloride, bicarbonate
electrolyte concentrations can only be measure from the blood plasma but its a good representative of ICF as well
normal serum sodium conc
135 - 145 mmol/L
controlled by aldosterone, insulin, angiotensin, renin, cortisone
normal serum potassium conc
3.5 - 5.5mmol/L
responsible for acid base balance and for kidneys to concentrate urine
normal serum magnesium conc
0.75 - 1.25 mmol/L
normal serum calcium conc
2.1 - 2.6 mmol/L
normal serum phosphate conc
0.8 - 1.45 mmol/L
types of hyponatremia
isotonic: occurs when there are elevated levels of other ECF constituents
hypertonic: other osmotically active substances like glucose or mannitol cause ICF to move ECF space, diluting sodium
hypotonic: higher TBW relative to sodium
types of hypotonic hyponatremia
the volemia refers to the quantity of [Na]
![<p>the volemia refers to the quantity of [Na]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0775c7d3-0549-4019-8533-df0a673e8b74.png)
types of hypernatremia
the volemia refers to the quantity of [Na]
![<p>the volemia refers to the quantity of [Na]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/65fa4e1e-638a-4187-a383-3ca06c6a0cbf.png)
hypokalemia causes
dietary deficiency
drugs: catecholamines
acute leukemias
GI or renal losses
hypokalemia clinical manifestation
flattened T waves
ST depression
U waves
arrythmias
cramps, weakness, paralysis
hyporeflexia, hypo excitability
hypokalemia therapy
repletion of potassim
hyperkalemia causes
increased intake
drugs - beta blockers
acidemia
burns, rhabdomyolysis, hemolysis
decreased renal excretion
hyperkalemia clinical manifestation
peaked T waves, wide QRS, loss of p waves
arrythmias
hyperreflexia, hyperexcitability
increased release of aldosterone, insulin
hyperkalemia therapy
calcium to stabilize cell membrane
insulin to shift potassium into cells
role of magnesium?
essential for enzyme activity
acts antagonistically with calcium
magnesium deficiency causes and effects

magnesium excess/toxicity causes and effects

calcium function
99% in bone, most of the remaining 1% is in the ICF
absorbed from intestines under influence of vitamin D
calcium stimulated release of neurotransmitters, hormones and exocrine glands
PTH stimulates movement from bone to ICF
hypocalcemia causes and effects

hypercalcemia causes and effects

phosphate function
is not bound by plasma proteins
PTH reduces plasma phosphate
calcitriol increases plasma phosphate
hypophosphatemia causes and effects

hyperphosphatemia causes and effects

osteopenia
reduced bone mass
osteoporosis
clinical state resulting from osteopenia
causes: excess glucocorticoids, insulin deficiency, low estrogen (menopause), inactivity
osteomalacia (rickets)
mineralisation of bone matrix for growth plates
effects: stunted growth, bow legs, delayed closure of fontanelles, Larson sulcus
atelectasis
alveolar sacs or whole segments do not expand fully → lung collapse
leads to VQ mismatch = poor ventilation, normal perfusion → hypoxia
can be acute or chronic
2 types, absorption and compression
signs: dyspnea, asymmetry in respiration, abolished/diminished breath sounds, clubbing, cyanosis
absorption atelectasis
caused by intrinsic or extrinsic bronchial occlusion (often from mucus plugs)
and by impaired surfactant production
compression atelectasis
caused by extrinsic compression which drive air out -→ lung collapse
eg trauma, rib fractures, obesity - inhibits full expansion of thoracic cage or makes breathing painful
bronchiectasis
chronic abnormal dilation of the bronchioles
types: cylindrical, fusiform, saccular
bronchiectasis pathophysiology
causes: repeated damage to bronchial walls, abnormal mucou-cilliary clearance → breakdown of supporting tissue adjacent to airway
mucus stagnation leads to increased risk of infections and increased bronchial pressure which causes mucosal injury
bronchiectasis symptoms
productive cough, clubbing fingers, sputum, hemoptysis, crackles, diminished breath sounds
often seen in CF patients and Kartagener syndrome
hyperacpnia
increased CO2 conc in arterial blood caused by hypoventilation
causes:
depression of respirator system by drugs
neurologic disorders affecting brain stem
thoracic cage abnormalities
airway obstruction like sleep apnea, tumour
increased work of breathing - emphysema
symptoms: respiratory acidosis, electrolyte imbalances, arrythmias, headaches, coma seizures, shortness of breath
cyanosis
5g of desaturated hemoglobin in blood regardless of Hg conc
not all patients will necessarily present with blue tinge
central and peripheral cyanosis
central cyanosis
low Oxygen saturation in arterial blood
observed in central parts eg buccal membranes and lips
periphrral cyanosis
slowed circulation to fingers and toes, nail beds
hypoxemia

restricitve vs obstructive lung diseases

COPD pathophysiology
chronic bronchitis and emphysema
smoking impairs ciliary action and macrophage function
inflammation increase mucus production
destruction of alveolar septa -→ peribronchiolar fibrosis
chronic bronchitis

emphysema

asthma
chronic reactive airway disorder, a massive overreaction to allergens
bronchospasm constricts airway, histamine stimulate excess mucus production
on inhalation the narrowed lumen can expand slightly
on exhalation increased intrathoracic pressure closes the lumen completely so air cannot escape
patient will become hypoxic which triggers hyperventilation → CO2 retention an alkalosis
intrinsic and extrinsic triggers of asthma
extrinsic
dust, pollen, food additives, mold, animal hair
intrinsic
cold, stress, exercise, severe respiratory tract infection, cough laugh, genetics, anxiety
symptoms of asthma
paroxysmal dyspnea,
dry cough that becomes productive at the end of attack
wheezing on ascultation
pneumothorax pathophysiology
accumulation of air in pleural cavity
types: open, closed, tension
a rupture in visceral or parietal pleura leads to air accumulation in the pleura and separation of the 2 layers
negative pressure is lost
the lung recoils up to hilus
every breath the patients takes the air passes through the rupture and into the pleural space
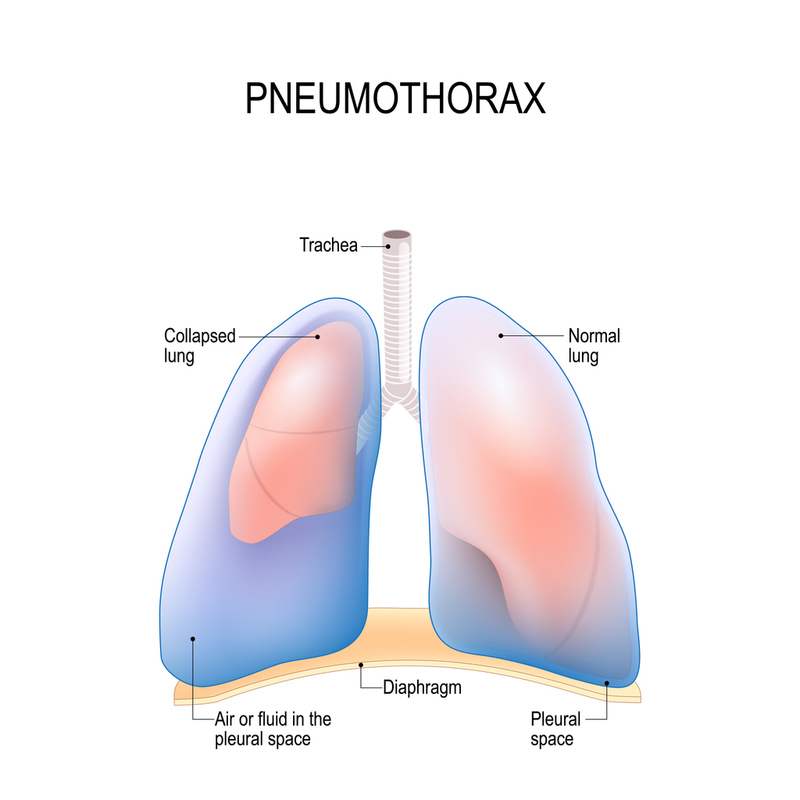
closed pneumothorax causes
air from inside the lung enters pleura
blunt chest trauma
air leakage from blebs (atelectasis)
rupture from barotrauma (pressure differences diving high attitude)
high intrathoracic pressure during mechanical ventilation
cancerous or tubercular lesions that erode pleura
interstitial lung disease
open pneumothorax causes
atmospheric air enters wound
penetrating chest wound
sucking chest wound
insertion of central line catheter
chest surgery
thoracentesis
transbronchial biopsy
tension pneumothorax causes
results when air in the pleural space is under higher pressure than air in the adjacent lung, Increasing air pressure pushes against the recoiled lung, causing compression atelectasis
penetrating chest wound treated with an air-tight dressing
fractured ribs
mechanical ventilation
high-level positive end-expiratory pressure that causes alveolar blebs to rupture
chest tube occlusion or malfunction
pulmonary edema

respiratory failure
when the lungs can maintain arterial oxygenation or eliminate CO2
impaired gas exchange → resp. failure
alveolar hypoventilation → low O2 sats and hypercapnia → resp, acidosis
V/Q mismatch → hypoxemia
untreated V/Q mismatch → right to left shunting → hypoxia → lactic acidosis
lactic acidosis causes tachycardia, increased stroke volume and increased risk of heart failure
ARDS causes
massive inflammation that injure alveolar capillary membrane
a form of pulmonary edema that can quickly lead to respiratory failure
causes:
sepsis
trauma
anaphylaxis
aspiration of gastric contents
near drowning
drug overdose
pulmonary contusions
ARDS pathophysiology
direct (aspiration of gastric juice) or indirect (inflammatory mediators) injury to pulmonary capillary endothelium
injury stimulates platelet aggregation, microthrombus formation, neutrophils and macrophages
this causes extensive damage to alveolar capillary membrane → increased permeability → pulmonary edema
reduced lung compliance and V/Q mismatch
alveolar injury: increased membrane permeability, increased susceptibility to infection, decreased surfactant production
resp. failure
acute kidney injury
a sudden decline in GFr and increase in urea and creatinine
prerenal aki
caused by reduced blood flow to the kidneys
eg shock, renal artery stenosis, heart failure
prolonged lack of blood flow causes injury to the structures inside the kidney and will begin to cause intrinsic injury
intrinsic AKI types
glomerular nephritis
tubulointerstitial nephritis
pyelonephritis
glomerular nephritis
lesions on the wall of the glomerular capillaries means it cannot filter macromolecules
so blood and proteins are not reabsorbed and pass into the urine
hematuria and proteinuria
small lesions - loss of small proteins up to albumin
extensive lesions - loss of albumin and IgGs
loss of proteins → hypoproteinemia → lower colloid osmotic pressure → edema
nephritic syndrome (glomerular capillary wall injury)
hematuria
azotemia (increased urea and creatinine) → oliguria
salt and water retention → edema
reduced GFR
unaffected area will hyper filtrate to compensate and maintain GFR but in the long run it will cause damage and sclerosis
nephrotic syndrome (podocyte injury)
proteinuria = hypoproteinemia and hypoalbuminemia
hypoproteinemia stimulates protein synthesis in the liver → increased lipoproteins → hyperlipidemia
hyperlipidemia → lipiduria
causes of nephrotic syndrome
minimal change diseases - children
focal segment glomerulosclerosis - adults
membranous nephropathy
diabetes lupus, amyloidosis, infections, drugs, cancer
RPGN
severe form of glomerular nephritis that can lead to irreversible renal failure
immunologically mediated
chronic glomerular nephritis
end stage glomerular disease → develop into chronic renal failure
signs: HTN, edema hematuria
tubulointerstitial nephritis pathophysiology

tubulointerstitial nephritis causes
Acute | chronic |
drugs - most common infections diseases - lupus, sjorgen’s, sarcoidosis idiopathic | long term exposure to lithium, NSAIDs, heavy metals chronic infections obstructive uropathy metabolic diseases eg hypercalcemia |
acute pyelonephritis
acute suppurative inflammation of the kidney caused by bacterial infection
uncomplicated, complicated, ascending
uncomplicated pyelonephritis
often occurs in young healthy women with no structural or urinary tract obstructions
complicated pyelonephritis
children/adults with functional urinary tract abnormalities of predisposing conditions
how is spread pyelonephritis
ascending from lower urinary tract
or
hematogenous spread
symptoms of pyelonephritis
abrupt onset
fever + chills
pyuria
dysuria
pollakiuria
lumbar pain radiating anteriorly
chronic pyelonephritis
recurring infection superimposed on urinary tract , obstruction or urine reflex
signs: polyuria, nocturia, signs of CKD, ultrasound - kidney decreased dimensions
Chronic kidney disease CKD
presence of kidney damage > 3 months
GFR < 60 for > 3 months
chronic and progressive even after initial cause is gone
uremia
accumulation of urine products that should’ve been excreted “urine in the blood”
CKD consequences

renal artery stenosis

nephrolithiasis

obstructive uropathy
structural or functions defect in urinary tract that blocks flow the flow of urine
obstructive uropathy may impair renal function = obstructive nephropathy
the blocked urine can get backed up and cause hydronephrosis
heart failure
when the heart is unable to generate adequate cardiac output
leads to inadequate perfusion of tissues/ increased diastolic pressure on left ventricle
leads to increased pulmonary pressure
SNS increases HR
PSNS deceases HR
preload
the volume of blood that stretches the ventricle at the end of diastole
afterload
the force that contracting heart muscle must generate to eject blood from the ventricles
compensatory mechanisms of the heart
frank starling forces - increase preload to help sustain cardiac performance
cardiac hypertrophy and remodelling
RAAS activation
alterations in myocyte regenerations and death
systolic left heart failure
inability to generate adequate contractility (most commonly caused by MI)
increased preload
excess plasma volume = edema, mitral valve disease,
diastolic left heart failure

right heart failure
inability to provide adequate blood flow to pulmonary circulation and normal venous pressure
often caused by left heart failure, increased LV pressure backs up into pulmonary circulation
peripheral edema and hepatosplenomegaly
high output failure
inability of the heart to supply blood and nutrients to tissues despite adequate blood volume and normal/increased contractibility
causes: anaemia, septicaemia, hyperthyroidism, beriberi
HTN
primary HTN - HTN without evidence of other diseases
primary HTN can evolve to secondary as renal function decreases
secondary HTN - HTN resulting from other diseases eg kidney disease
primary hypertension

mechanisms of primary HTN
sympathetic overactivity
acquired or inherited defect in the kidneys’ ability to excrete the excessive sodium load
Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
impaired release of endothelium-derived relaxing factors e.g. nitric oxide
mechanisms of secondary HTN

Target organ damage in HTN
atherosclerosis
subcortical white matter demyelination
left ventricular hypertrophy
nephrosclerosis
Dementia and cognitive impairment
circulatory shock
acute failure of the circulatory system to supply peripheral tissues with oxygen, cellular or cells inability to use oxygen
shock gradually progresses to multisystem organ failure, initially reversible but becomes irreversible if prolonged
shock often presents with hypotension and hypoperfusion but can also present with normal vitals (SNS compensates initially)