Lecture 2: Fungal Structure and Morphology (9/4/24)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Differentiate Molds and Yeasts
Molds: Grows in multicellular filaments, thread-like tubular structures (hyphae)
Yeast: Grows/reproduces as a single cell through BUDDING
Describe hyphae
Multicellular filaments, thread-like structures
Describe budding of a yeast
In a parent yeast cell, the nucleus will copy/divide
Bud forms (bud receives a copy)
Cytoplasm divides
Chain of yeast forms (connected to parent yeast)
Both molds and yeasts are considered “__”
Fungi
What is mycelium?
Matlike network of hyphae
What is the area above the surface of substrate called? What about below?
Aerial hyphae
Vegetative hyphae
What is conidia?
Asexual reproductive elements
What grows on the aerial hyphae?
Reproductive hyphae and conidia (“fluffy stuff”)
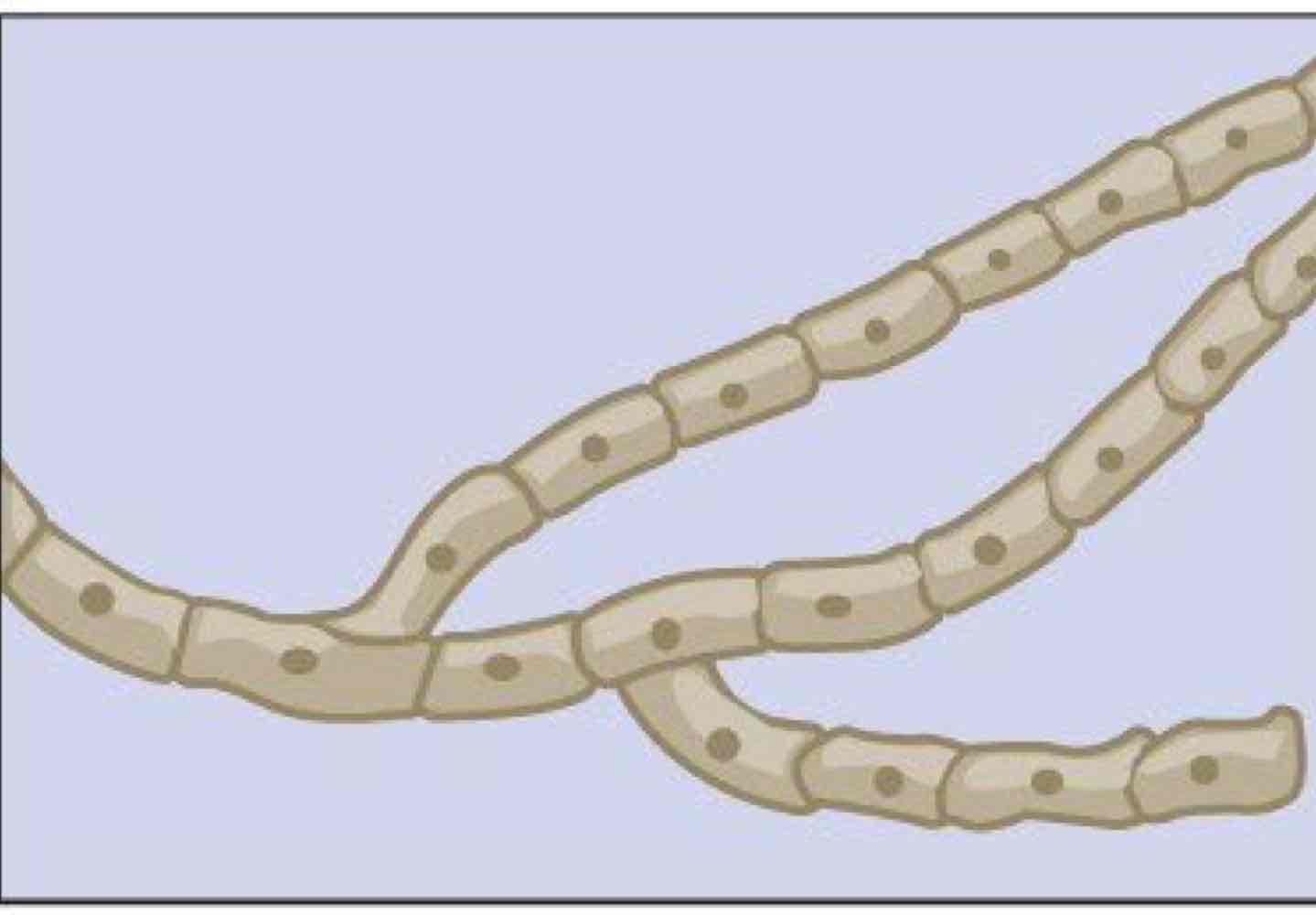
What is septate hyphae? Draw if possible.
One hyphae separated by septum
What is coenocytic hyphae? Draw if possible.
Multiple hyphae in one area (separations are spread out)
What is septate hyphae w/ clamp connections? Draw if possible.
One hyphae separated by septum w/ a small bump
What is hyphae w/ arthroconidia and disjunctor cells? Draw if possible.
Hyphae surrounded by arthroconidium (may break apart and infect) and separated by disjunctor cells (space between the hyphae)
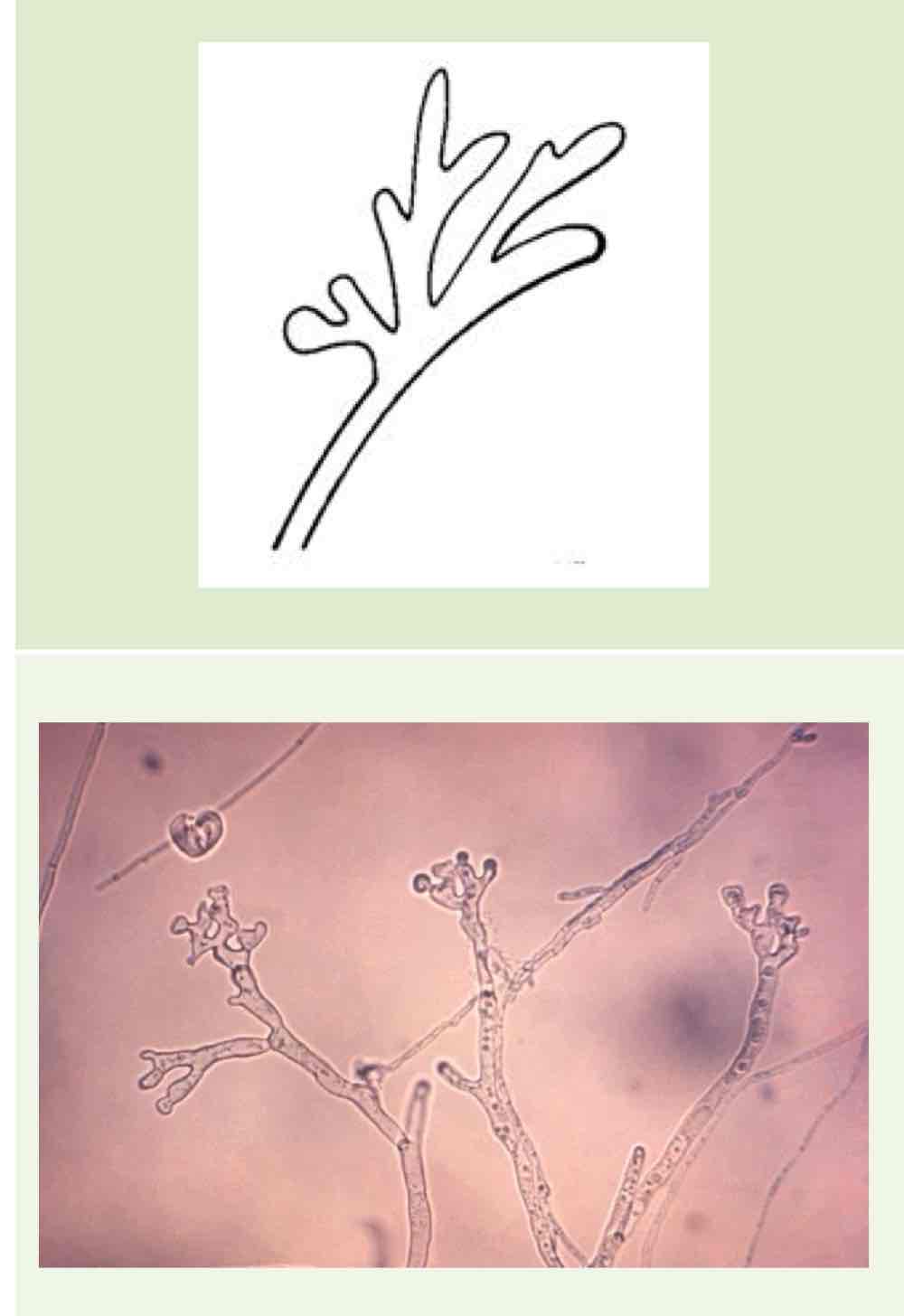

Name this hyphae
Antler hyphae
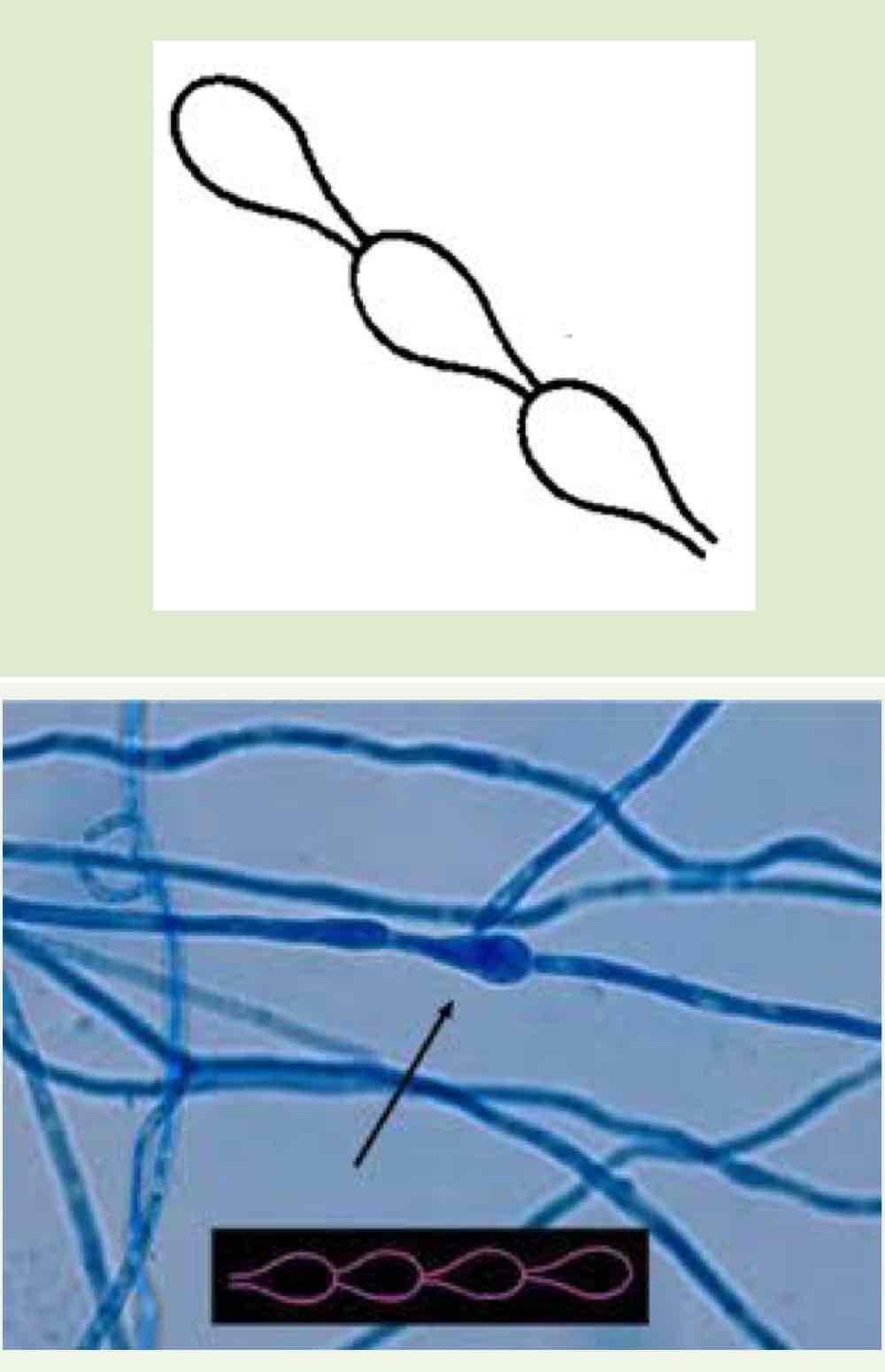
Name this hyphae
Modular hyphae (swelling)
Name this hyphae
Pectinate body
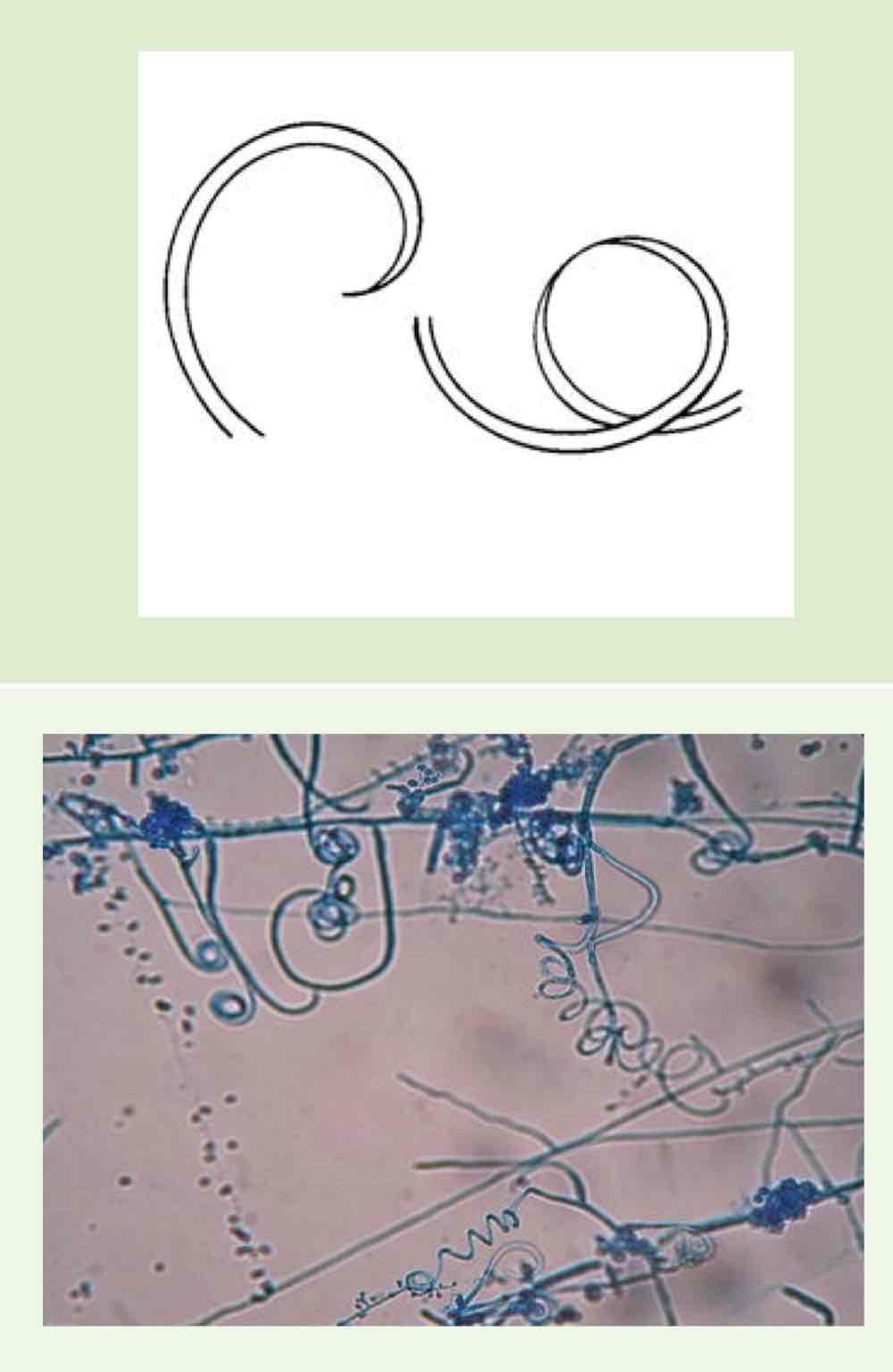

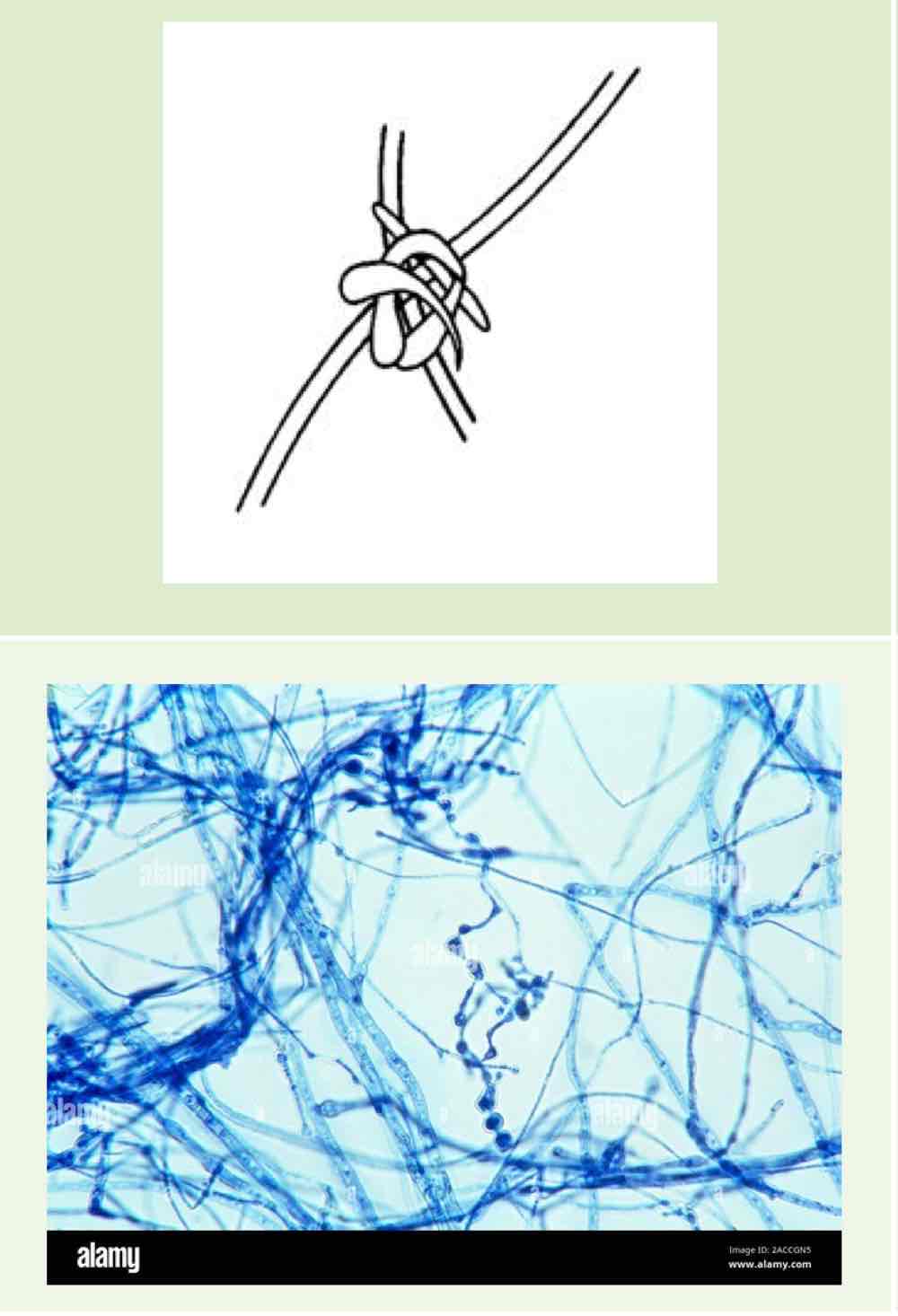
Name this hyphae
Spiral (coiled) hyphae
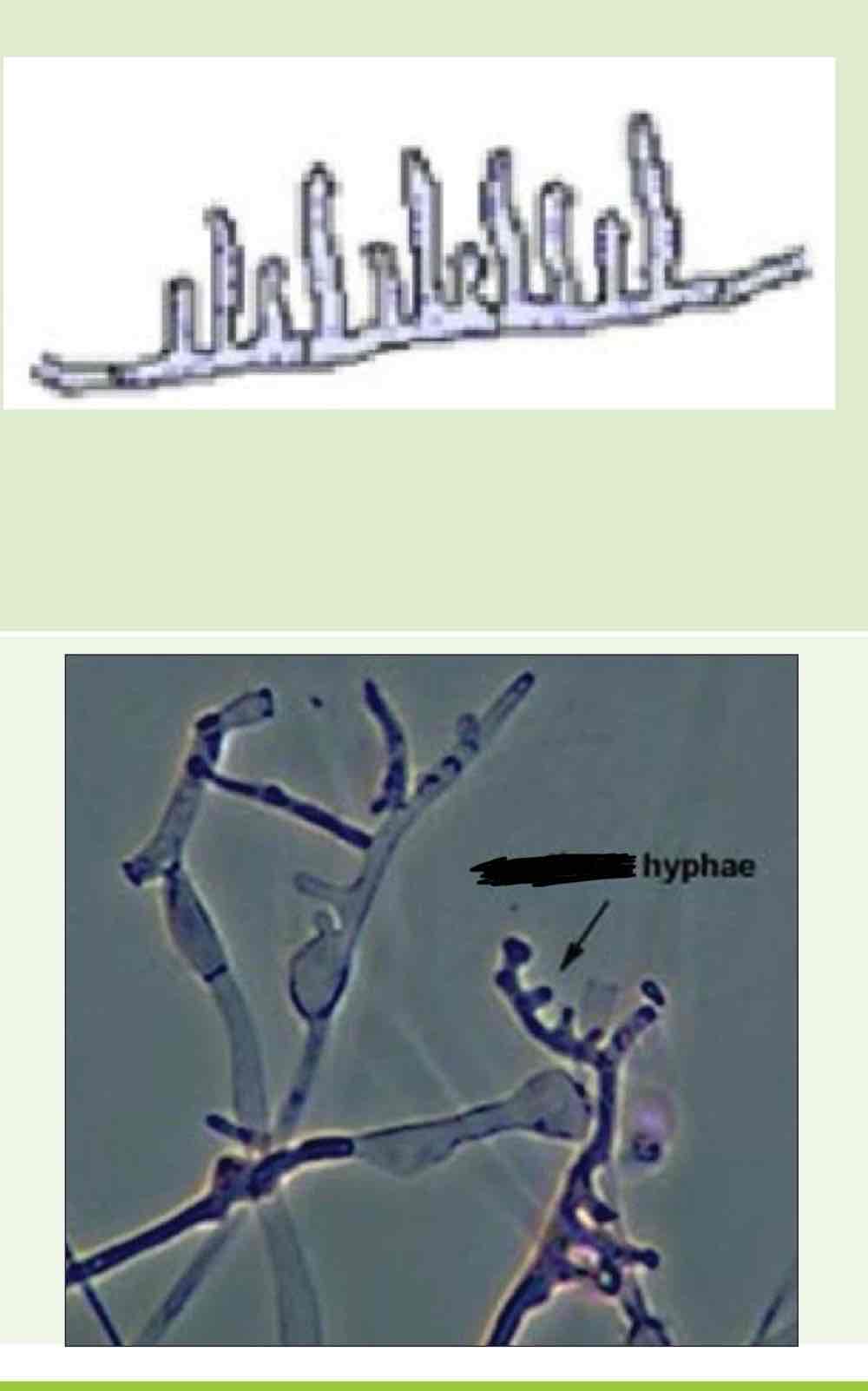
Name this hyphae
Racquet hyphae
Name this hyphae
Septate hyphae

Name this hyphae
Coenocytic (nonseptate) hyphae
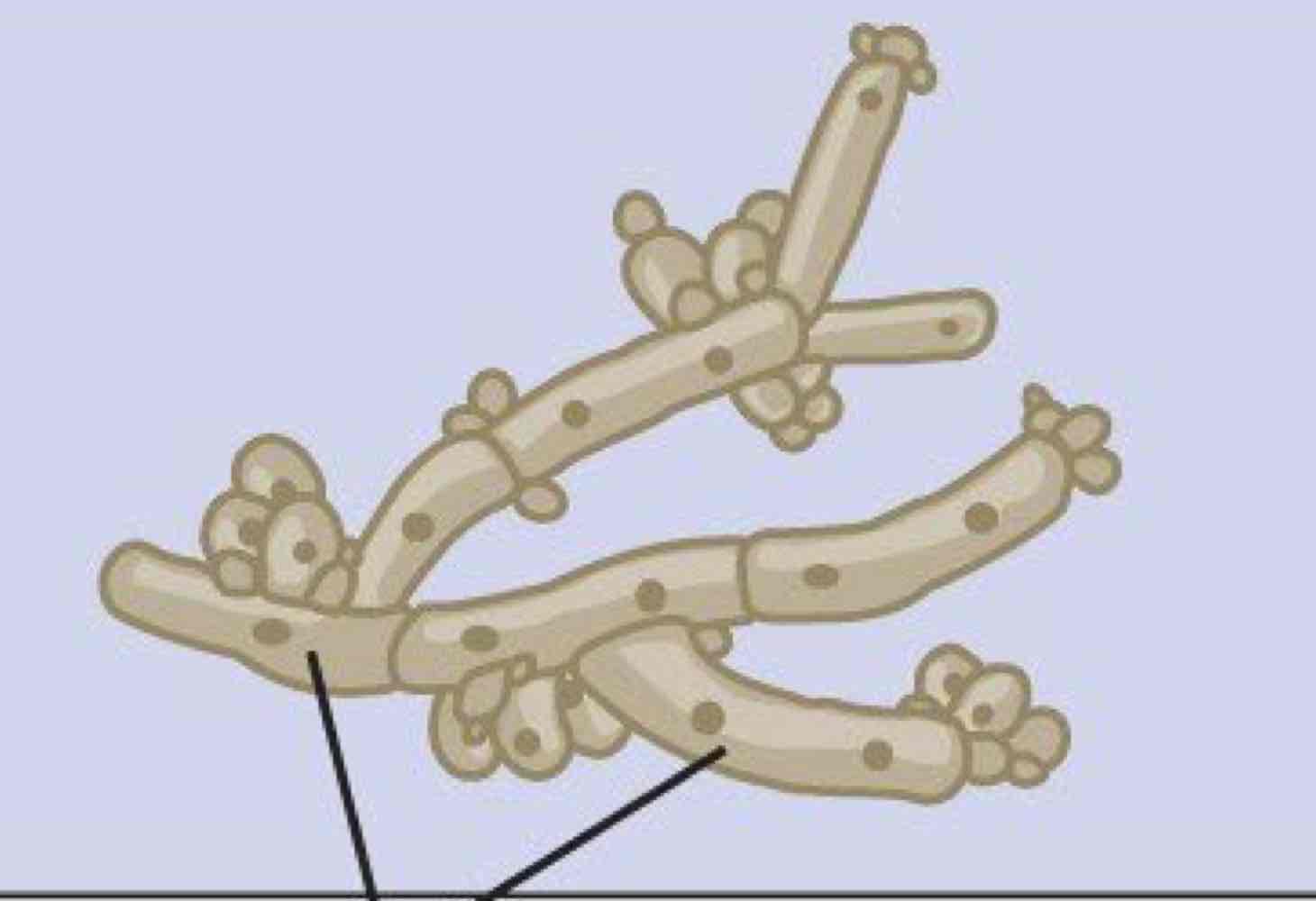
Name this hyphae and its structures
Pseudohyphae
Yeast cells
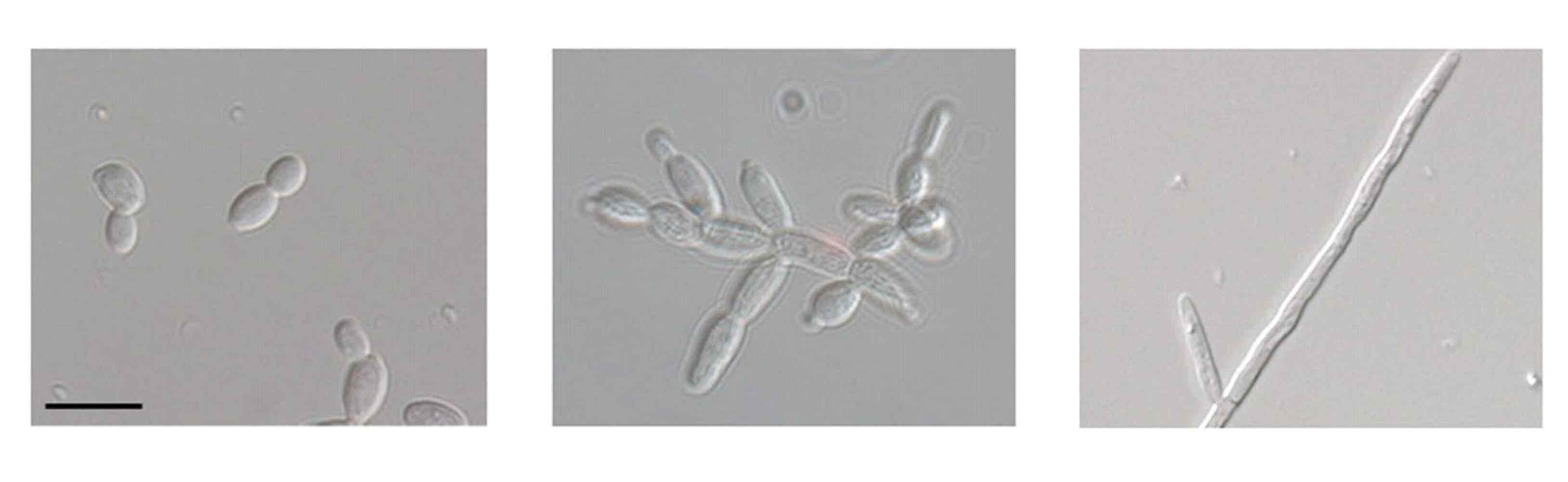
What are these?
1: Yeast
2: Pseudohyphae
3: Hyphae
Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction in Fungi (Starting from spores)
Asexual: Spores → Germination → Mycelium → Mitosis → Start again at spores
Sexual: Spores → Germination → Mycelium → Plasmogamy → Heterokaryocytic stage → Karyogamy → Zygote → Meiosis → Start again at spores
Fungal Spore Characteristics
Means of fungal reproduction
Microscopic
Sexual or Asexual
Major source of fungal infection: Inhalation of spores or skin contact w/ spores
Types of Sexual Spores
Basidiospore
Ascospore
Zygospore
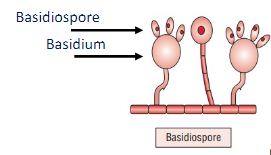
Characteristics of Basidiospore
Produced by basidiomycetes
Born in a club-shaped structure called basidium
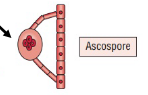
Characteristics of Ascospore
Produced ascomycetes
Produced in a sac called an ascus
Usually 4-8 ascospores in ascus (varies by species)
Characteristics of Zygospore
Thick walled spores formed when two sexually compatible hyphae of certain fungi fuse together
Asexual spores are also known as:
Conidia
Types of Asexual Spores
Sporangiospore
Conidiospore
Arthrospore
Chlamydospore
Blastospore
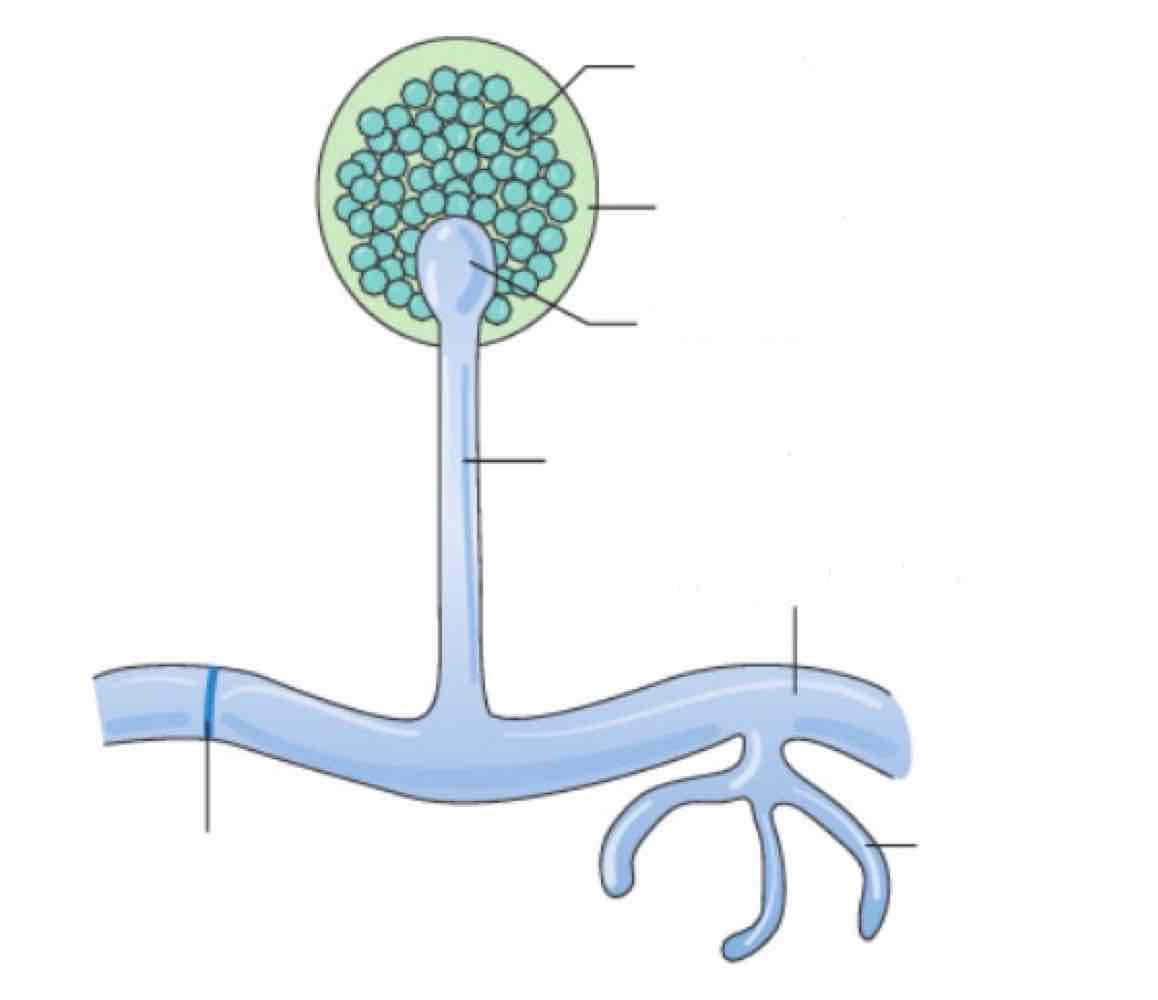
Name the spore and its structures:
Sporangiospore
Sporangium: Sac where asexual spores are produced
Columnella
Sporangiophore
Pausi-septate hyphae
Septum (rare)
Rhizonds (roots)
Where are the asexual spores of the sporangiospore produced?
In a sac called sporangium
Where is the sac (sporagium) located and what is it called?
At the end of the aerial hyphae and is called sporangiophore
Examples of Sporangiospore
Rhizopus
Mucor
Absidia
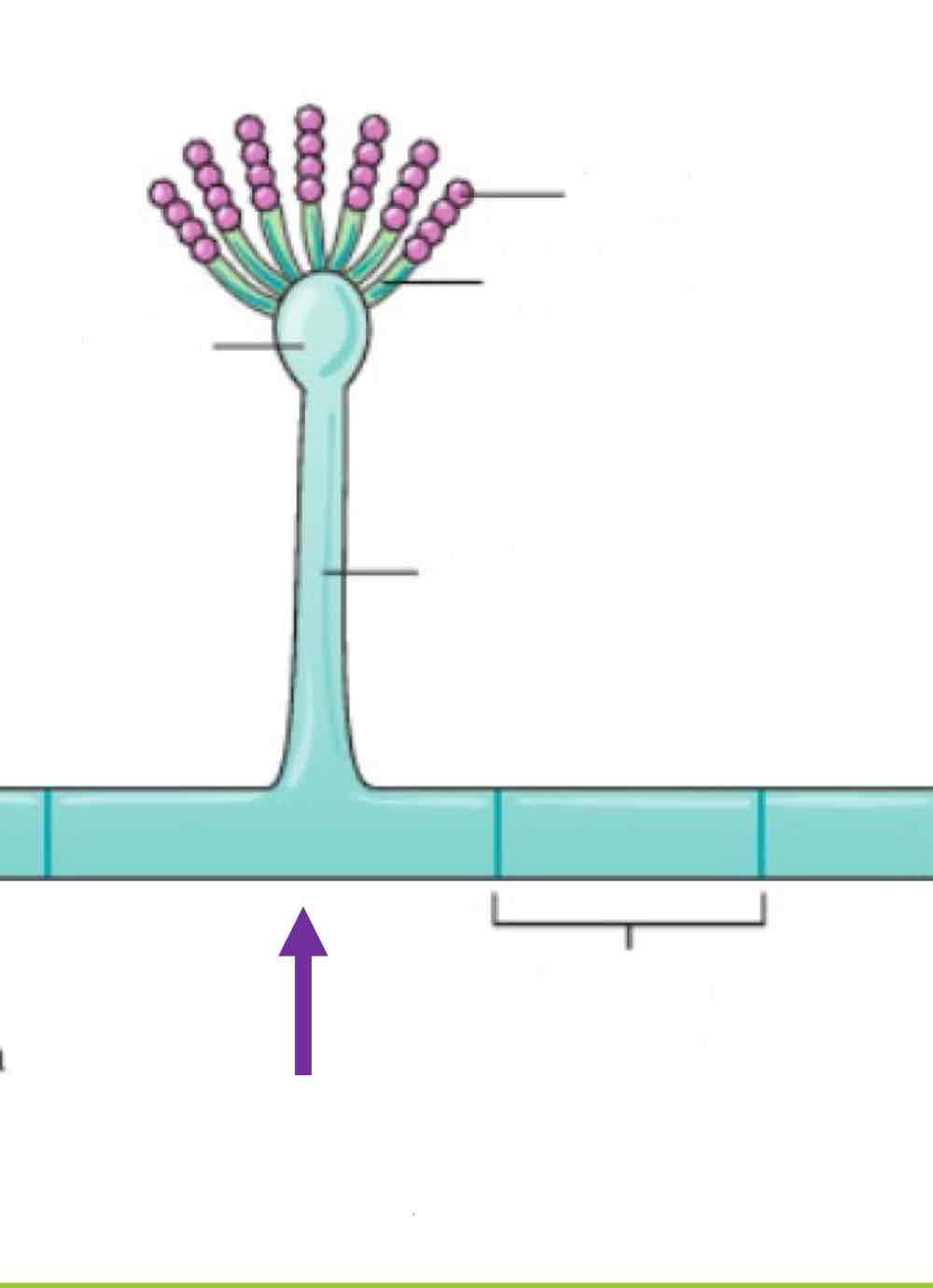
Name the spore and its structures:
Conidiospore (“Conidia”)
Phialides
Vesicle
Conidiophore
Foot cell (vegetative)
Septate hyphae
Characteristics of Conidiospore
Single celled/multi-celled spores born on tip or side of aerial hyphae (conidiophore)
Can be found singly or in chains
Difference between Sporangiospore and Conidiospore:
Conidias are not produced inside any sac-like structure, unlike sporangiospores
Difference between a uniserate and biserate conidiospore:
Uniserate: 1 layer
Biserate: 2 layers (metulae = 1st layer)
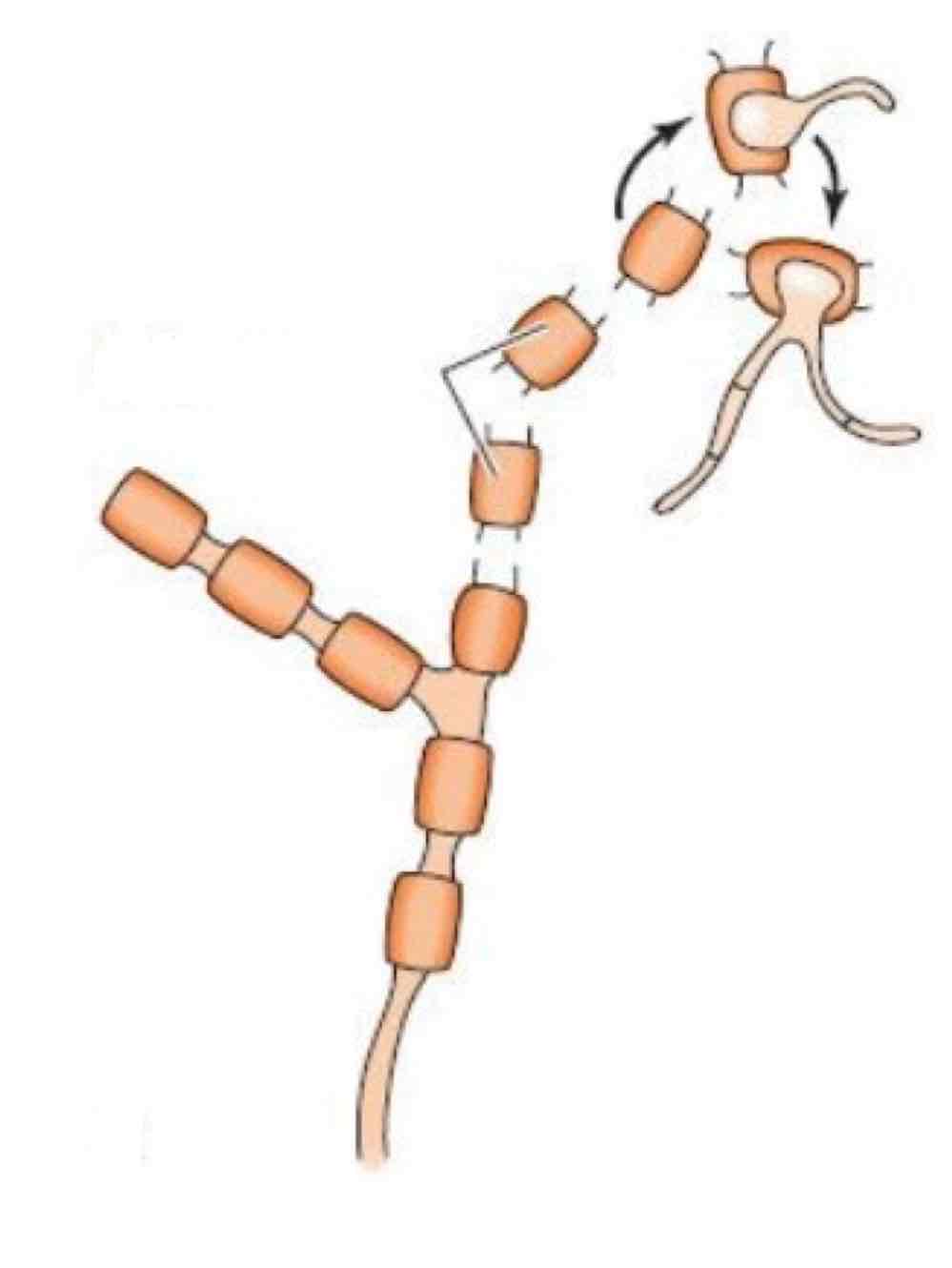
Name the spore and its structures:
Athroconidia
Arthrospores
Characteristics of Arthroconidia
Primitive spore
Made by breaking up the fungal mycelium → hyphae separate, then fragment into arthrospores
Examples of Arthroconidia
Trichosporon
Geotrichum
Coccidioides immitis **
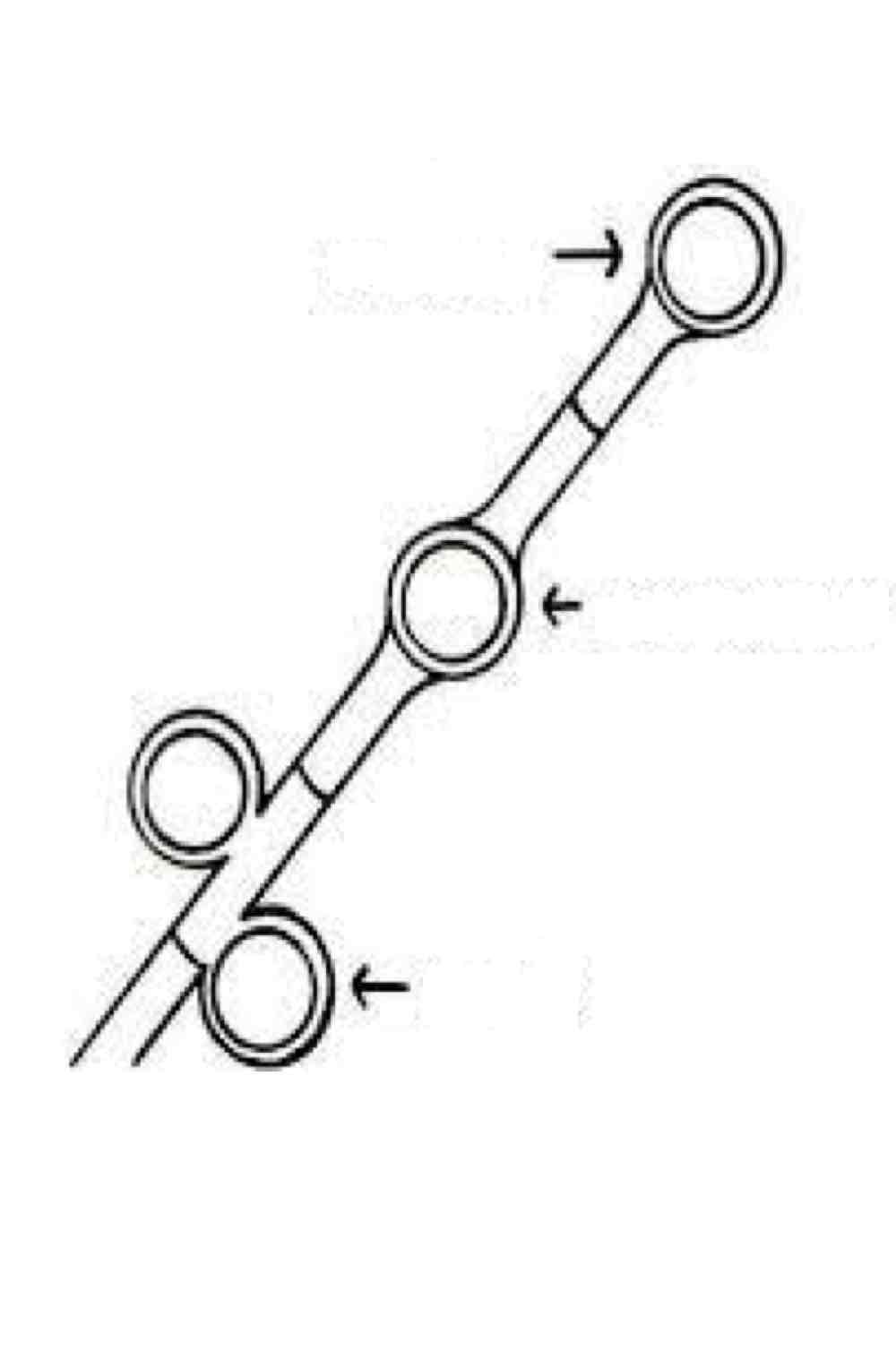
Name the spore and its structures:
Terminal (end)
Intercalary (middle)
Sessile (outside)
Characteristics of Chlamydospore
Often formed during unfavorable conditions (too dry/hot)
Purpose: Perennation (survival), not dissemination
Thick-walled, single cell
Hyphae contacts → Loses water → Condenses cytoplasm → Thick-walled chlamydospore
Will eventually germinate into new fungi when environmental conditions improve
Examples of Chlamydospore
Candida albicans
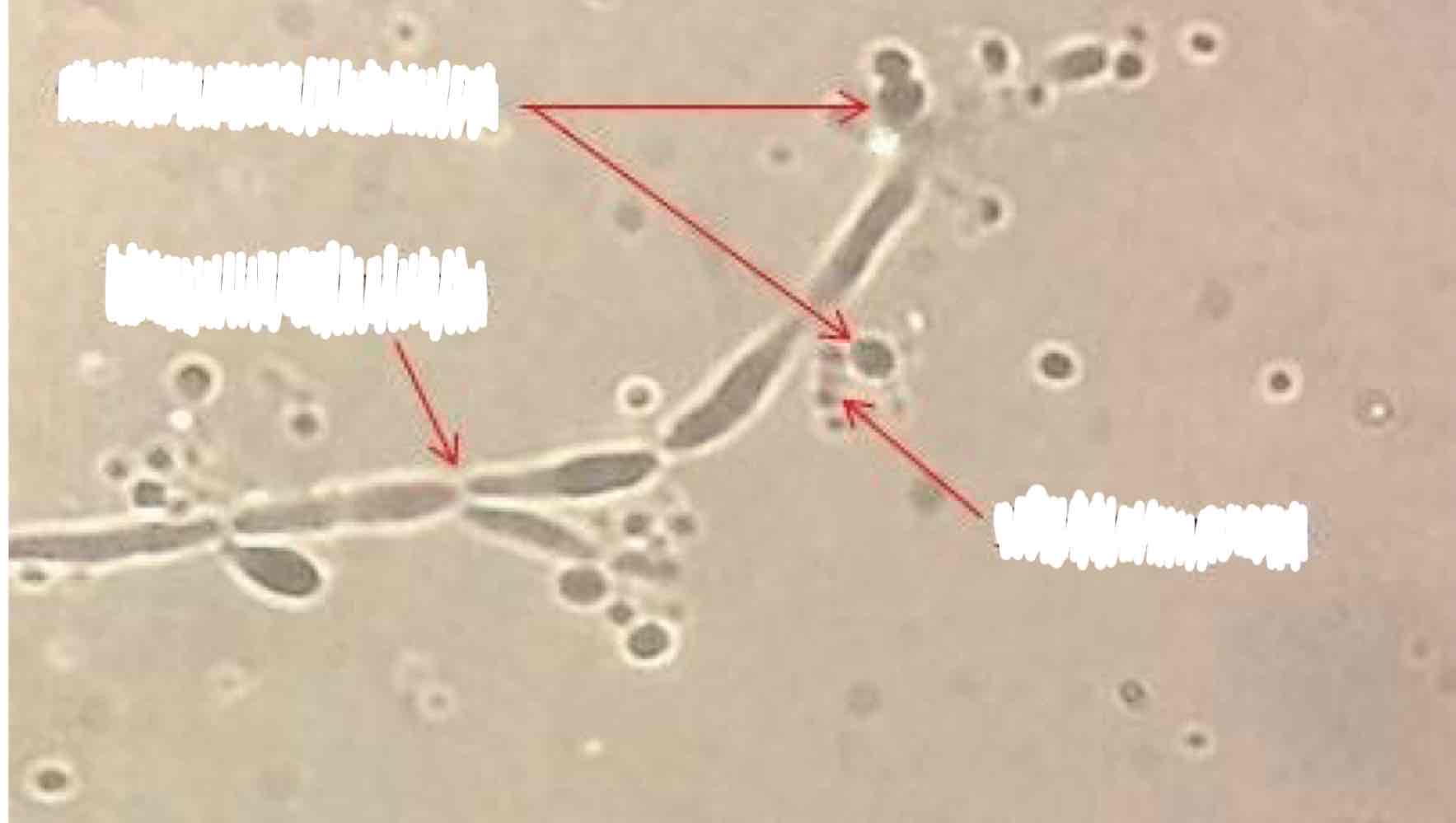
Name the spore and its structures:
Blastospore
Clusters of chlamydospores, psuedohyphae, blastoconidia
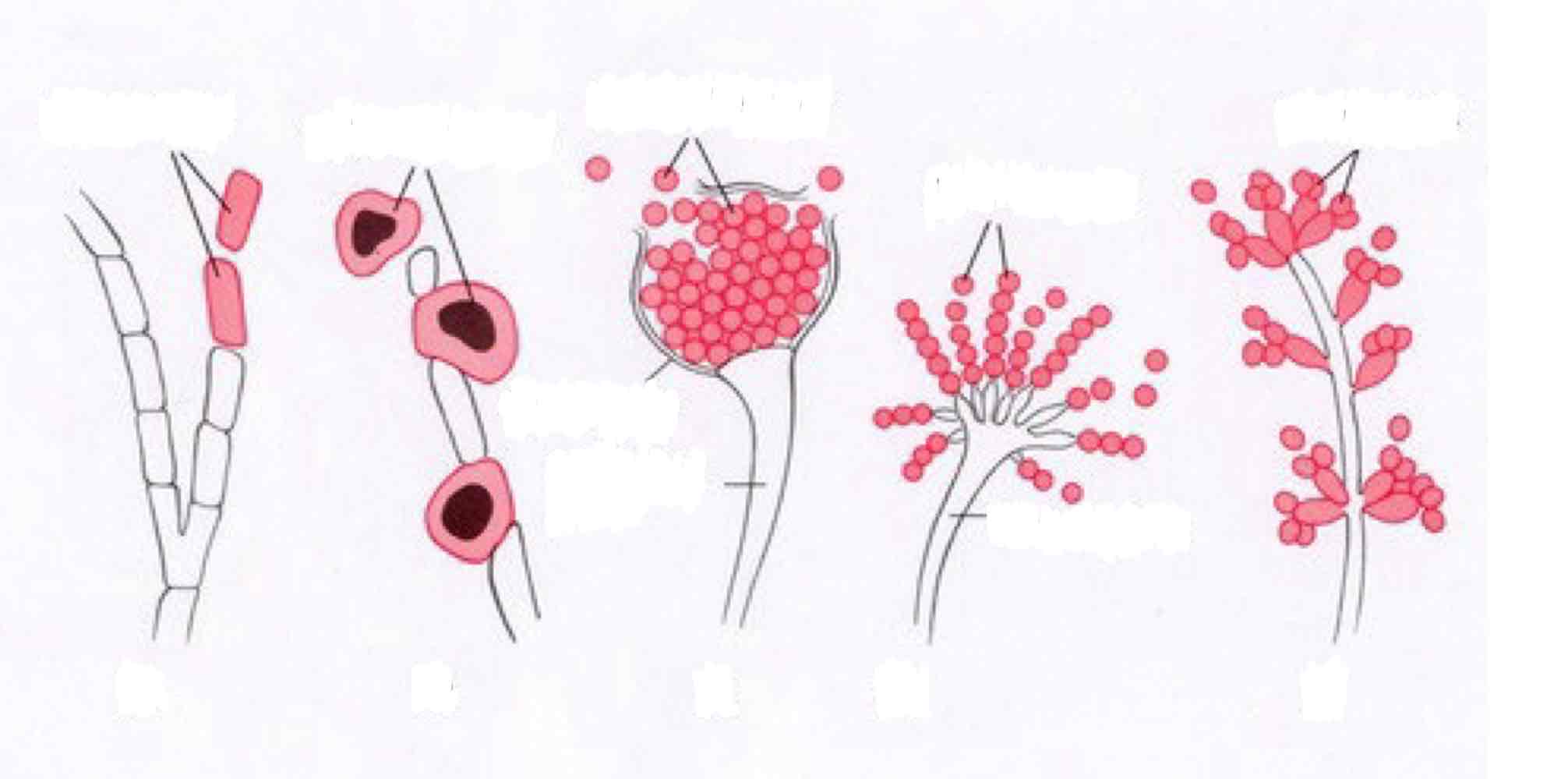
Name these asexual spores
Arthrospores
Chlamydospores
Sporangiospores
Conidiospores
Blastospores
Characteristics of Blastoconidia
Results from the budding of a yeast:
Asexual reproduction
Results in bud from a parent cell
Asexual Spores of Ascomycetes: Macroconidia vs. Microconidia
Macroconidia
Large asexual structures
Thick/thin/smooth/rough walled
Divided into cells w/ transverse septa
Different shapes in ID: spindle, boat, pencil, cigar
Microconidia
Small asexual structures
Amount and arrangement aids in ID: May appear singly or in clusters
More often the infectious form, not always