FORESTRY K2 '25 Flashcards
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Primary cavity excavators
birds that dig cavities into snags for food or habitat (woodpeckers, sapsuckers)
Secondary cavity users
depend on primary excavators or natural decay for nesting
what % of birds in forest are cavity dependent
20-40%
snags make up _% of mixedwood
5-10%
give 4 benefits of snags for wildlife
cavity nesting
insects under wood provide food source
perches for raptors
bats roost under bark
Increased fragmentation decreases
small mammal populations like voles
Martens
used to be most abundant small mammal in eastern North America, now extirpated in eastern canada and threatened across their range due to habitat loss and trapping
5benefits of downed deadwood for wildlife and plants
provides threatened American marten with habitat for natal dens, protection from predators, and subnivean (below snow) habitat during winter months
amphibians rest there to protect from thermal drought
increases bryophite, lichen, and moss biodiversity
provides moist, nutrient-rich germination bed for spruces
deadwood fallen into spreams provides critical amphibian breeding habitat
what aged forests have the most deadwood? The least? List three in order
old-growth > young > economically mature
higher species richness was observed when
fine woody debris was mixed with coarse woody debris than when it was just coarse woody debris
Coarse woody debris (CWD)
decomposing logs on the forest floor, provides nutrients for plants, habitat, food
what wildlife nests in coarse woody debris?
snowshoe hare, ruffed grouse, bobcats, black bears, lynx, shrews
beneftis of CWD on forests and carbon storage
recycles nutrients like potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus
holds in moisture during small droughts
can store. and release carbon slowly in logs of rot-resistant trees
how to create CWD
leave stumps when harvesting
either cut dying trees and leave logs or let them stand to become snags
allow natural disasters, fire, and disease run their course
define forest health
the ability of a forest to sustain itself while providing for society’s economic, spiritual, and social needs
define ecological processes
the interaction between organisms and their environment
list the stages of forest succession
0) fire, insect, disease, or human removes older trees and almost all vegetation and recycles nutrients
1) grasses, wildflowers, trees and shrubs
2) shade-intolerant species like trembling aspen and lodgepole pine come
3) shade-tolerant species like white spruce grow under canopy
4) climax community grows old and becomes old growth
who manages forest health in Alberta?
Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development and Forest Health Officers
give benefits of forest insect and diseases when at natural levels
kill dead and dying trees, insects provide food source for birds
Disorders
non contagious, non living elements of the environment that damage trees (hail/ice storms, drought, pollution, nutrient deficiencies, mechanical injuries)
how can mammals and birds act as forest pests?
overgrazing and harming regeneration and growth, also can create wounds for pathogens to enter
define ecosystem service
something the environment provides to people for free
trees slow the flow of water. How does this help the ecosystem?
reduces flooding by letting some water infiltrate and slowing the rest
reduces erosion into waterways, keeping fish gills from clogging and rock bottoms from getting mucky
allow pollutants to settle out and absorb some pollutants directly
what makes trees especially good among plants at watershed protection
larger and more extensive root systems such that even after tree dies, roots in soil decompose and leave behind pores, increasing permeability
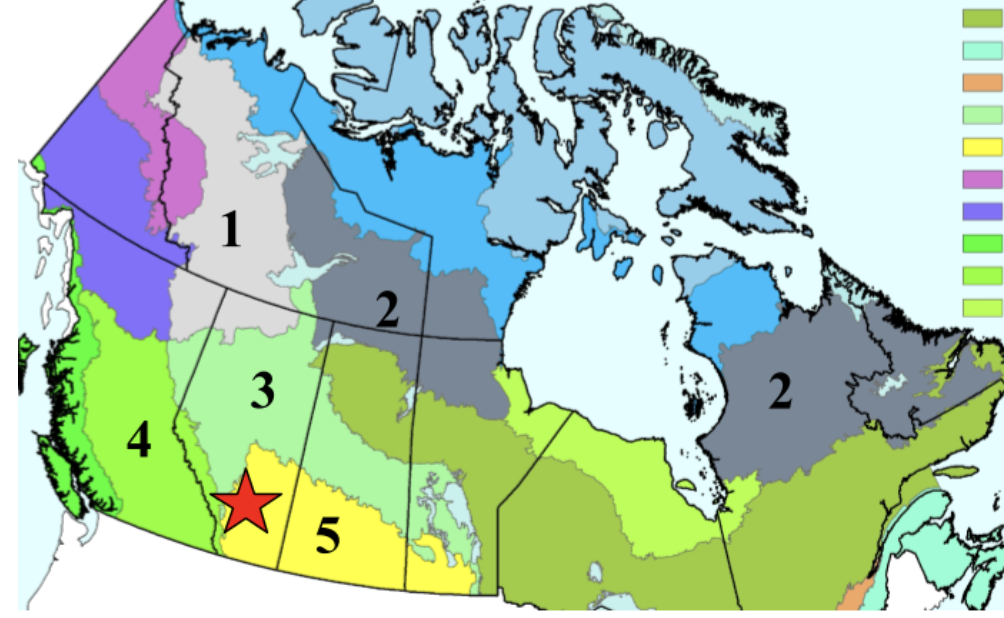
Name all 5 ecoregions
1) taiga plains
2) taiga shield
3) boreal plains
4) montane cordillera
5) prairie
Taiga plains key characteristics and indicator plants
short, cool summers and cold winters
little rain
permafrosted soils and sedimentary rock
fire-dominated
paper birch, willows, aspen, black spruce, balsam fir, lodgepole and jack pine
Taiga shield key characteristics and indicator plants
cold, long winters, mild summers
oldest bedrock in world, very boggy, waterlogged land
black spruce, tamarack, jack pine, alders birches willows, balsam fir, white spruce
Boreal plains key characteristics and indicator plants
short, warm summers, cold winters. Dry
flat with thick soil
fire-adapted
Jack pine, spruces, firs, tamarack, manitoba maple and water birch
heavily loged
Prairie key characteristics and indicator plants
hot summers, cold winters
dry due to rainshadow
flat fertile plains with oil deposits
95% converted to farmland, but existing trees are white spruce, balsam fir, lodgepole pine, aspen and poplar
many endangered animals
Montane cordillera key characteristics and indicator plants
milder climate
located between rockies and coast mountains, so double rainshadow creates ombre of dry to wet
high elevation plants and animals: lodgepole pine, engelmann spruce, ponderosa pine, western hemlock, redcedar, aspens and poplars and birches