QUIZ-2_THE SKELETAL AND ARTICULATION SYSTEM
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
BONE/OSSEOUS TISSUE
is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton, the support structure of the body
CARTILAGE
in the areas of the skeleton where bones move (for example, the ribcage and joints), — , a semi-rigid form of connective tissue.
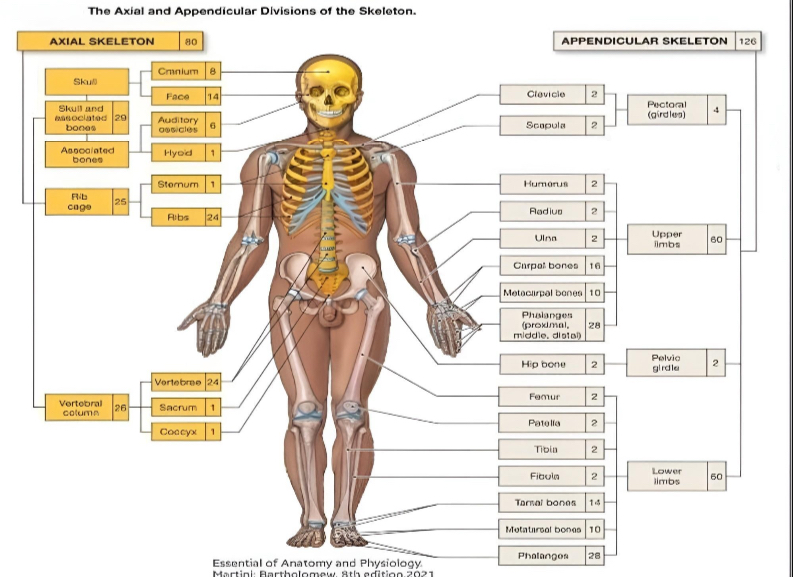
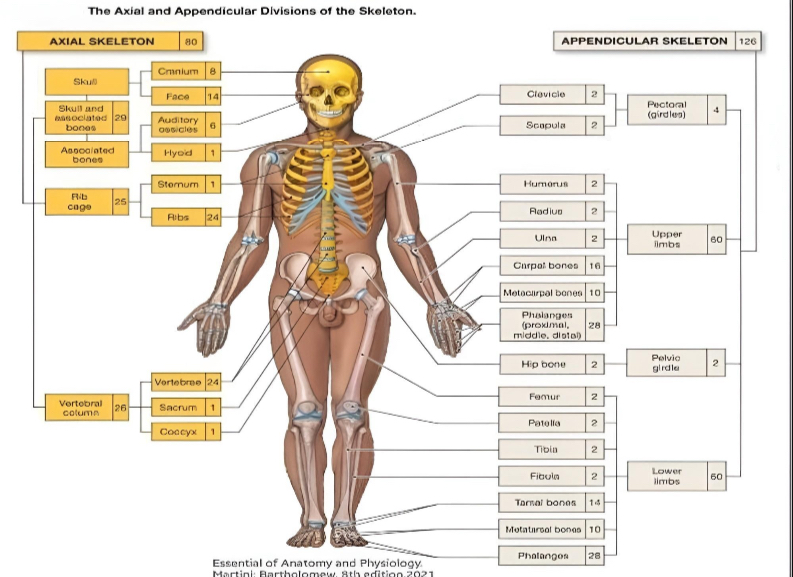
206
the adult human skeleton usually consists of — named bones.
80 BONES
axial skeleton (how many)
126 BONES
appendicular skeleton (how many)
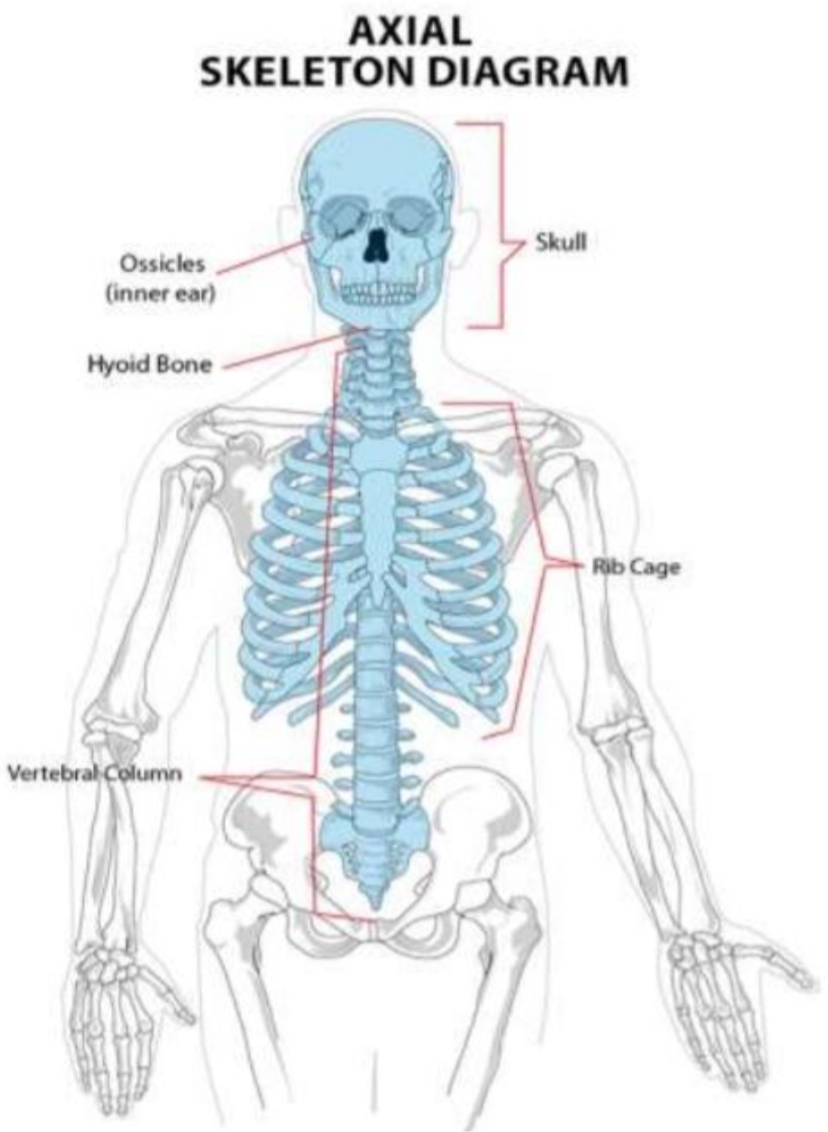
AXIAL SKELETON
lie along longitudinal axia
skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles
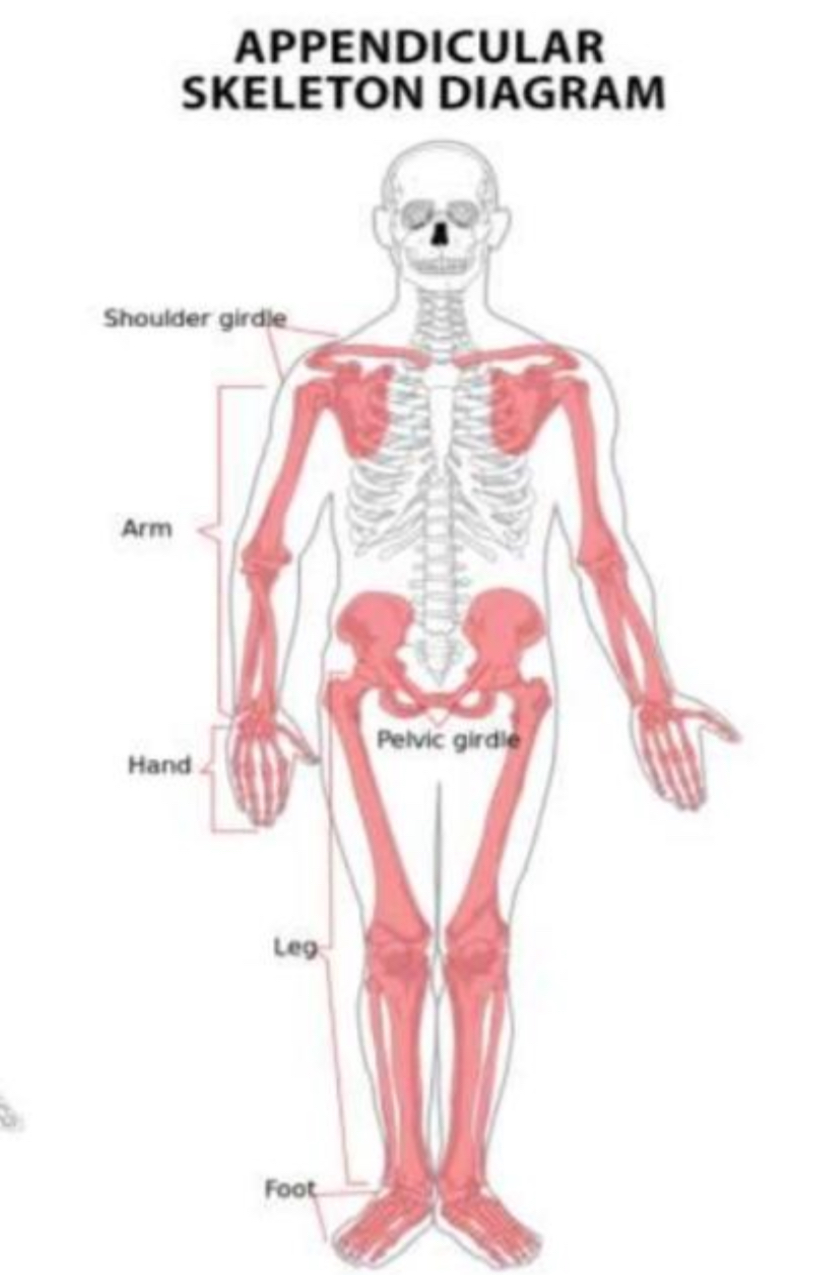
APPENDICULAR SKELETON
upper & lower limbs
pelvic & pectoral girdles
AXIAL
the — skeleton of the adult consists of 80 bones, including the skull, the vertebral column, and the thoracic cage.
SKULL
— formed by 22 bones. Also associated with the head are an additional seven bones, including the hyoid bone and the ear ossicles (three small bones found in each middle ear).
VERTEBRAL COLUMN
— consists of 24 bones, each called a vertebra, plus the sacrum and coccyx.
THORACIC CAGE
— includes the 12 pairs of ribs, and the sternum, the flattened bone of the anterior chest.
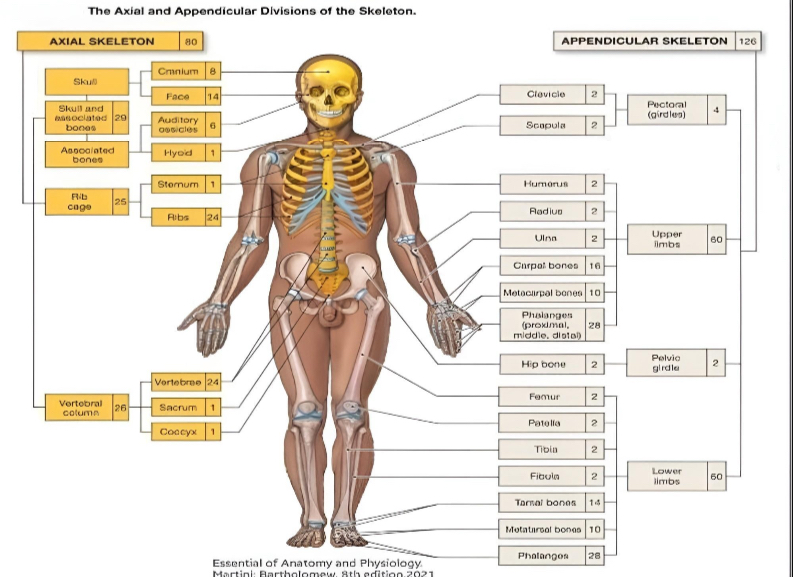
APPENDICULAR
the — skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton.
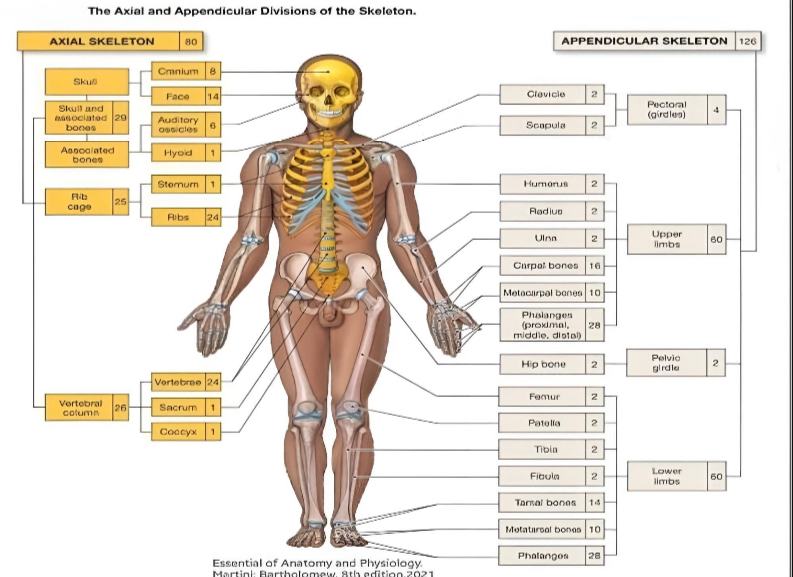
PECTORAL GIRDLES
clavicle (2)
scapula (2)
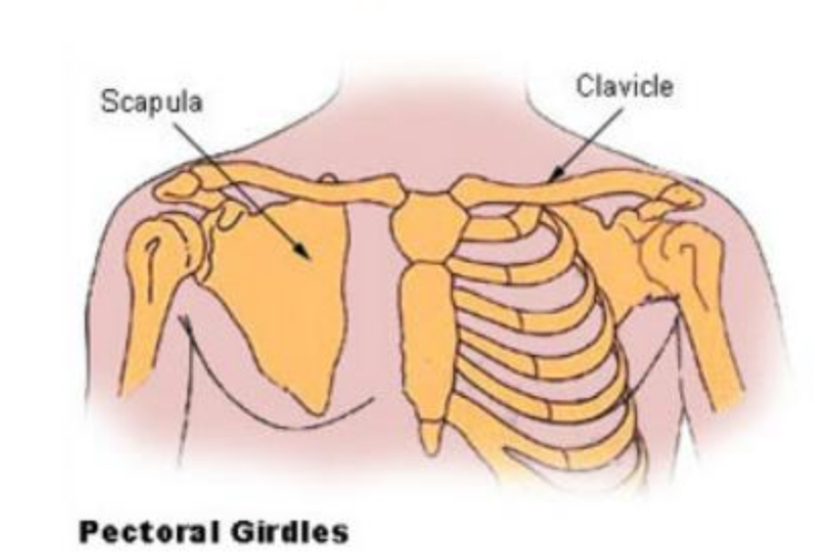
UPPER EXTREMITY
humerus (2)
radius (2)
ulna (2)
carpals (16)
metacarpals (10)
phalanges (28)
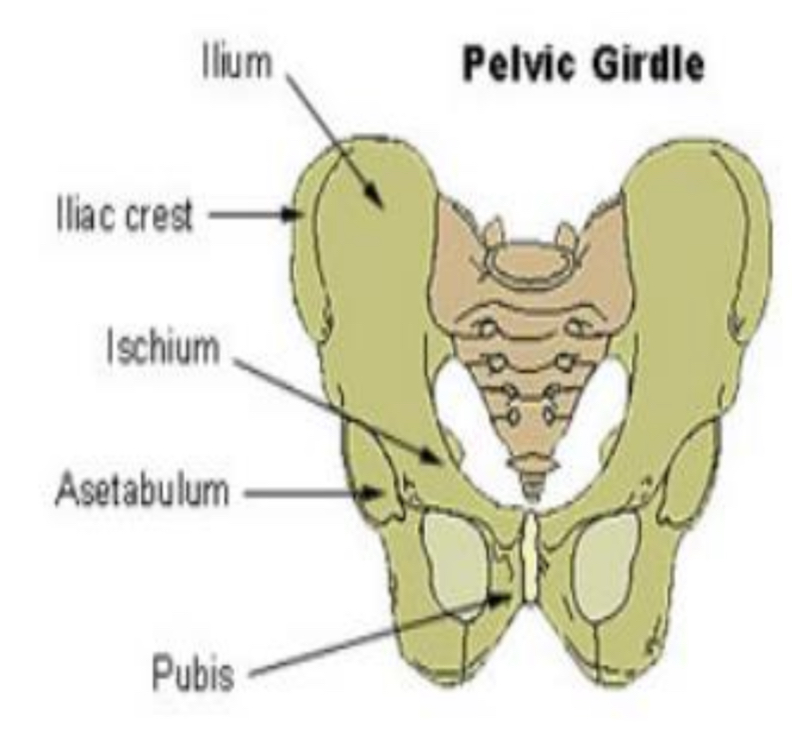
PELVIC GIRDLE
coxal, innominate, or hip bones (2)
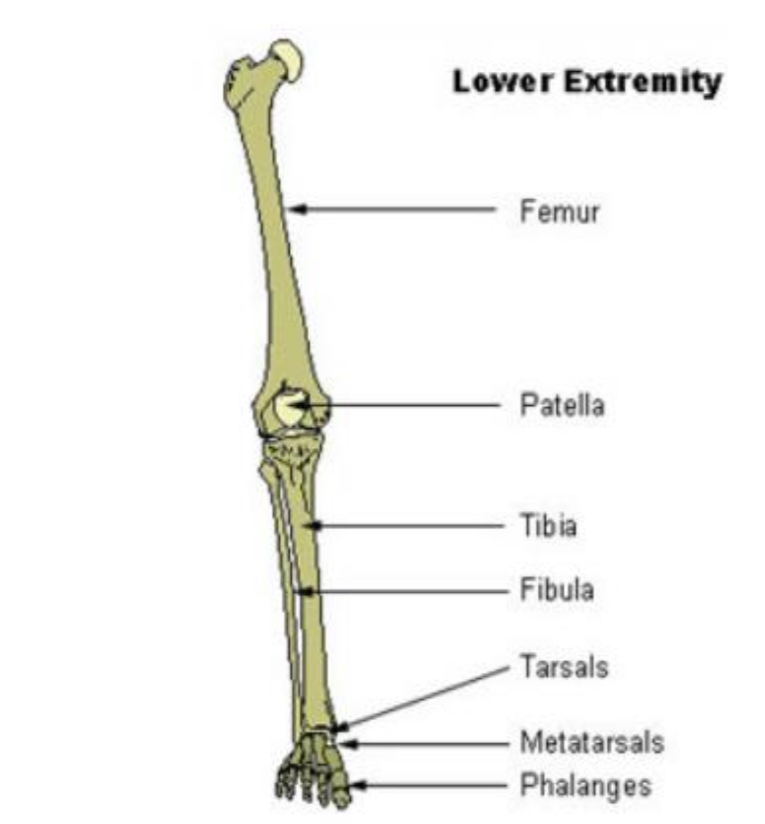
LOWER EXTREMITY
femur (2)
tibia (2)
fibula (2)
patella (2)
tarsals (14)
metatarsals (10)
phalanges (28)
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
bones are made of — reinforced with calcium and specialized bone cells. Most bones also contain bone marrow, where blood cells are made.
MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
bones work with muscles and joints to hold our body together and support freedom of movement. This is called the —
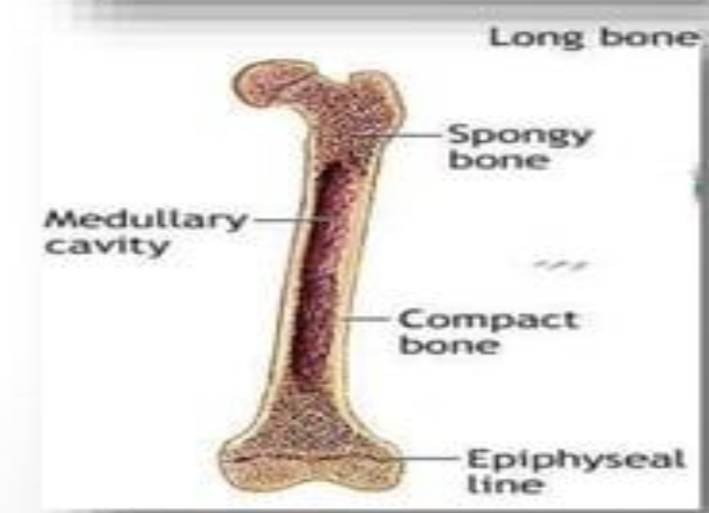
LONG BONE
composite bone
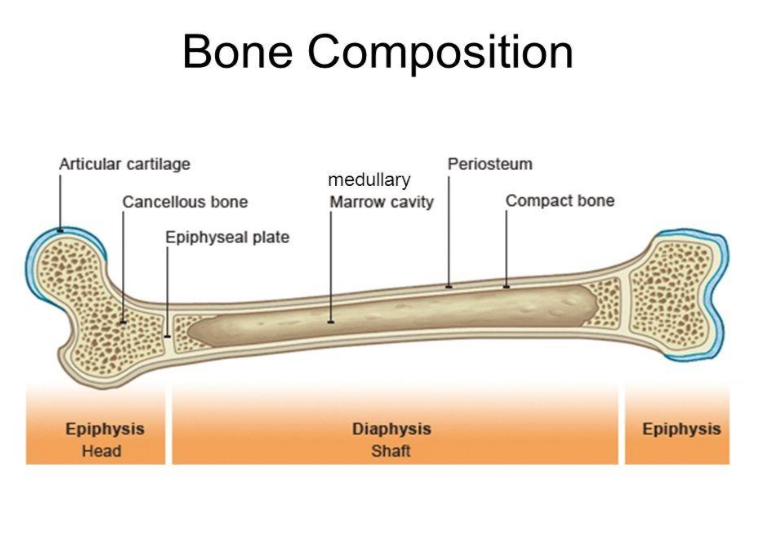
DIAPHYSIS
shaft
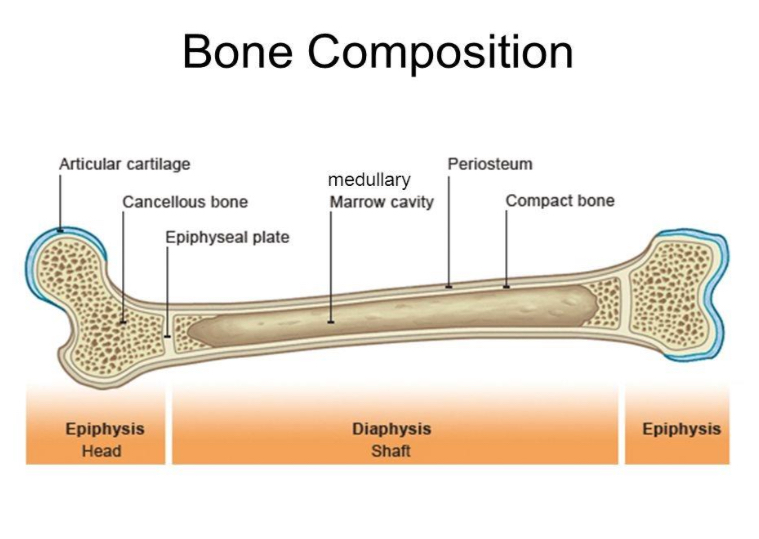
EPIPHYSIS
expanded portion at the end is
Articular Cartilage.
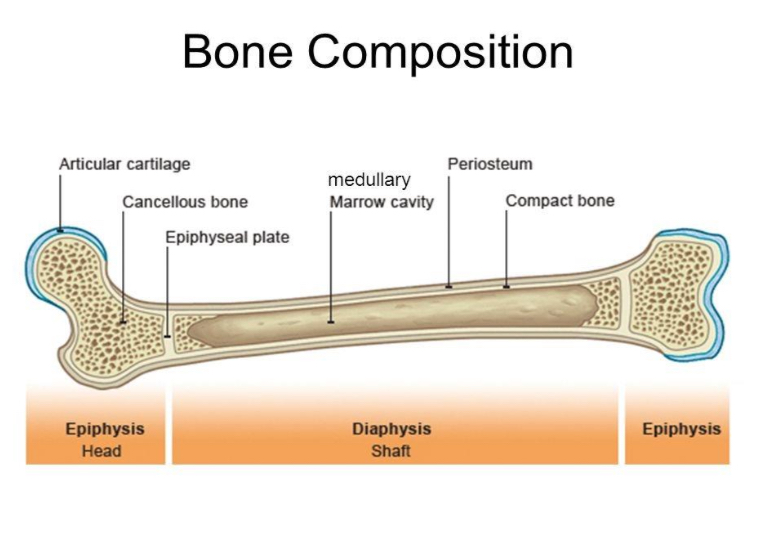
EPIPHYSEAL LINE
where the two meet is called Epiphyseal Plate (Growth Plate) becomes —
MEDULLARY CAVITY
within diaphysis is a hollow space called —
LONG
like the femur and forearm
SHORT
like the wrist and ankle
FLAT
like the skull
IRREGULAR
like the spine (referred to as long or short)
SESAMOID BONES
teeth or small bones found within tendons called —
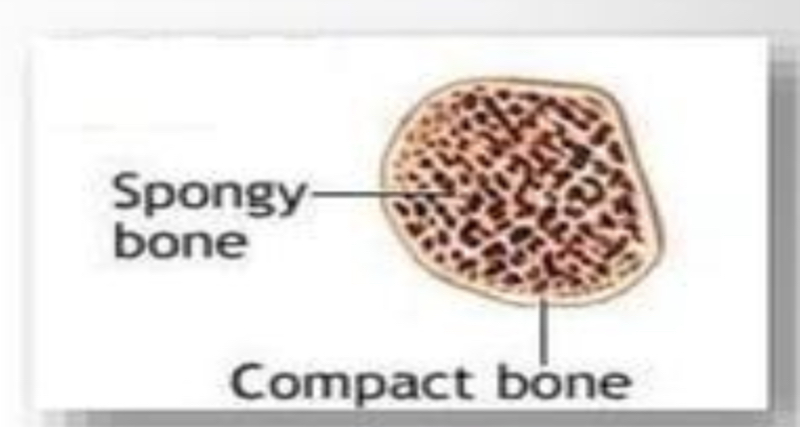
SPONGY BONE
also called cancellous or trabecular bone
it is found in the long bones and it is surrounded by compact bones
COMPACT BONE
also called cortical bone
surrounds a spongy bone. They are heavy, tough and compact in nature
LIVING TISSUE
bone is — that makes up the body's skeleton
SHORT BONES
(tarsals in the foot, e.g)
cancellous bone in the center;
compact bone recoating all peripheral surface
FLAT BONES
(cranium, e.g)
two thin livers or compact bone
enclosing between them: variable quantity of cancellous bone.

BONE MARROW
interstices of the cancellous bone and the medullary cavity in the diaphysis of the long bones are occupied by —
COMPACT TISSUE
is the harder, outer tissue of bones.
CANCELLOUS TISSUE
is the sponge-like tissue inside bones.
SUBCHONDRAL TISSUE
the smooth tissue at the ends of bones, which is covered with another type of fissue called cartilage
PERIOSTEUM
the tough, thin outer membrane covering the bones is called the —
TUNNELS & CANALS
under the hard outer shell of the periosteum are —
BLOOD & LYMPHATIC VESSELS
through these, — carry nourishment for the bone
MUSCLE, LIGAMENTS, & TENDONS
— may attach to the periosteum
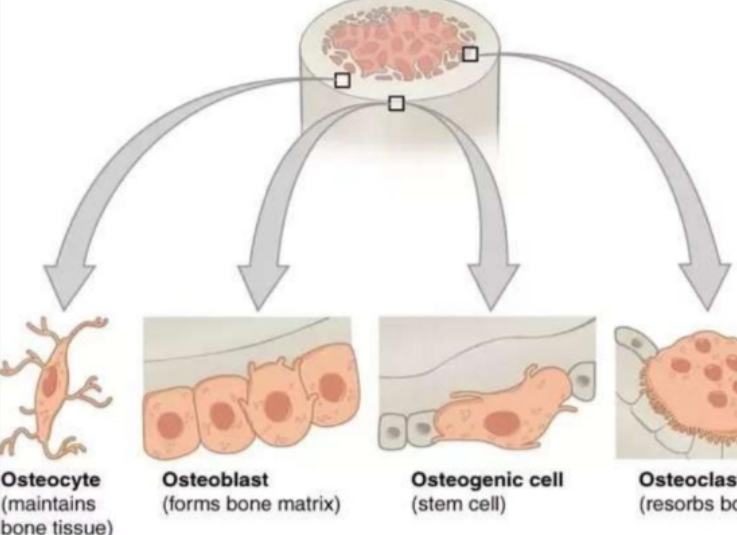
OSTEOCYTE
is a type of cell within the bone which helps to maintain bone as living tissue
OSTEOBLAST
is a type of cell within the bone which is responsible for the formation of new bone tissue
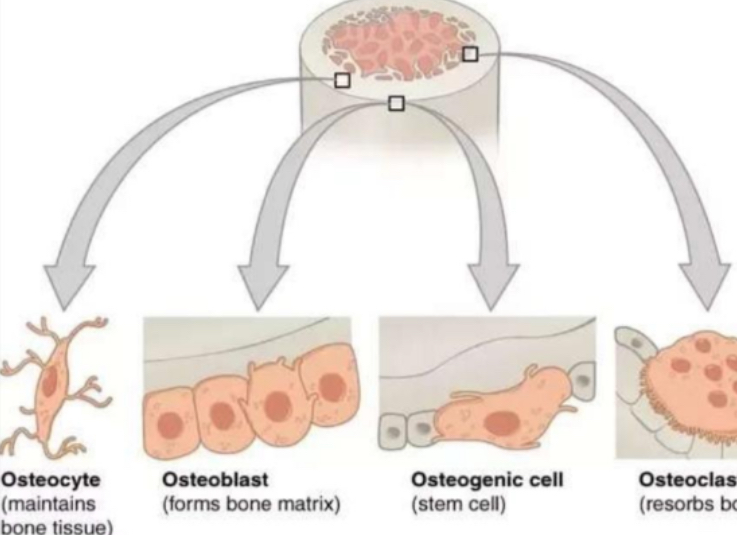
OSTEOPROGENITOR
also known as osteogenic cells
are stem cells in the bone that play a prodigal role in bone repair and growth
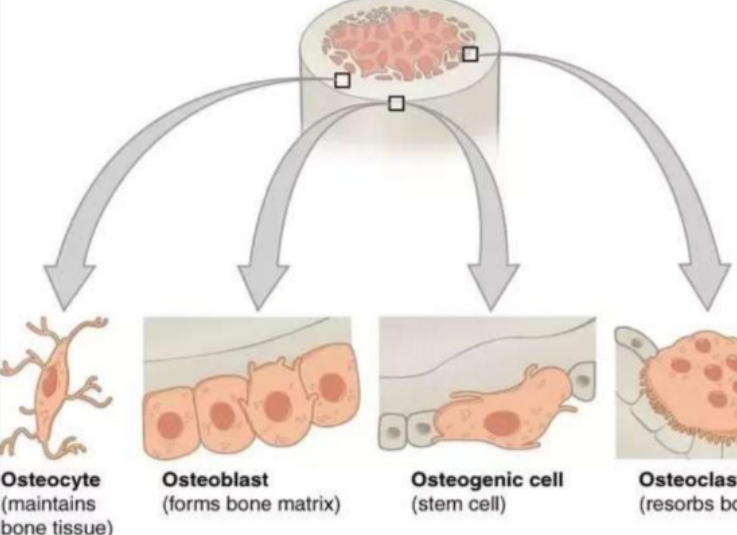
OSTEOCLAST
is a very large cell formed in bone marrow which is responsible for the absorption and removal of unwanted tissue
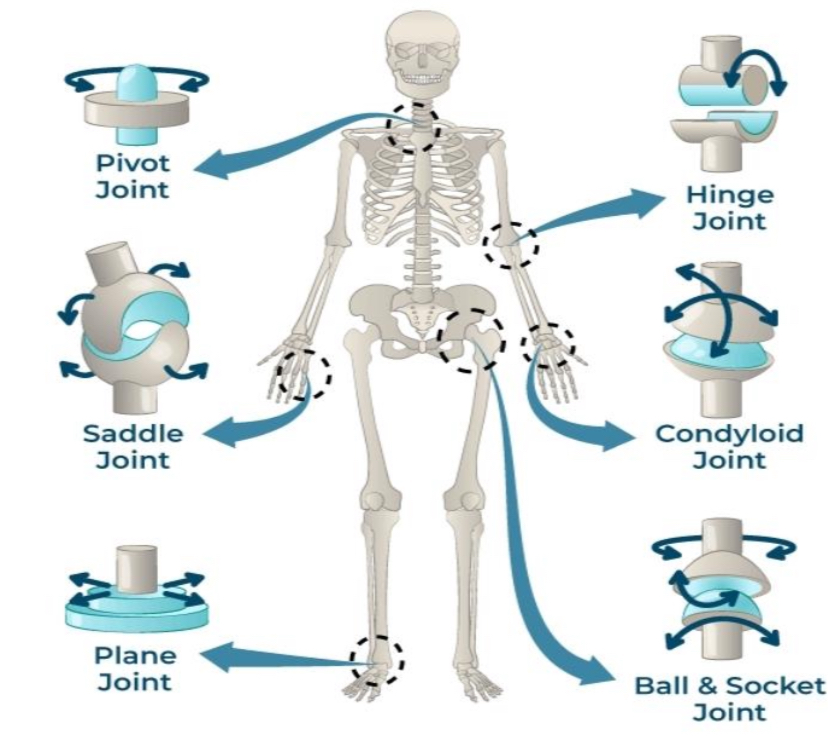
PIVOT JOINT
joints that permit rotatory movement of bones, around a single axis
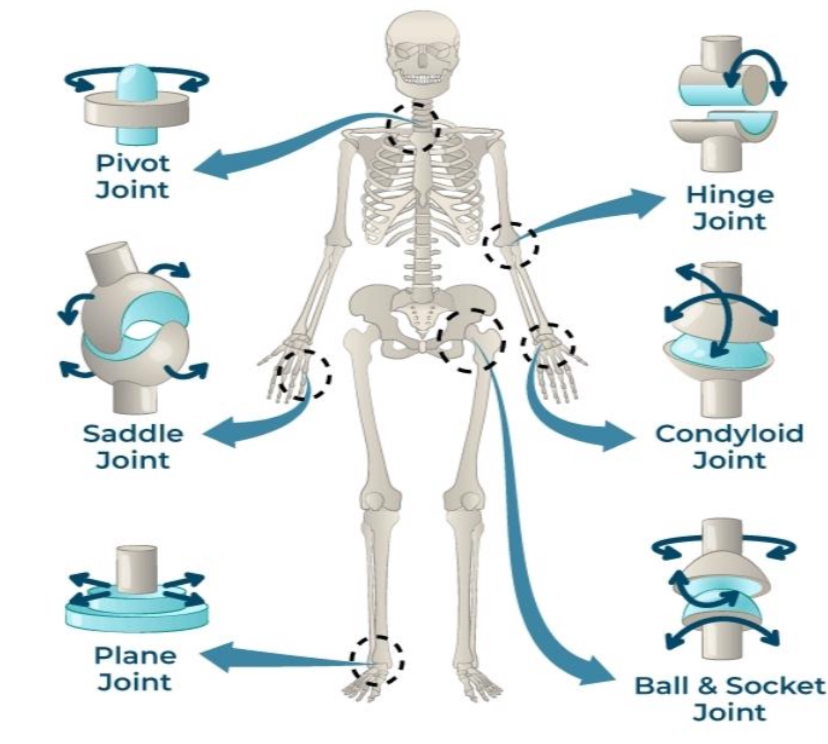
SADDLE JOINT
type of biaxial and movable joint that allows movements on two planes-flexion or extension and abduction or adduction
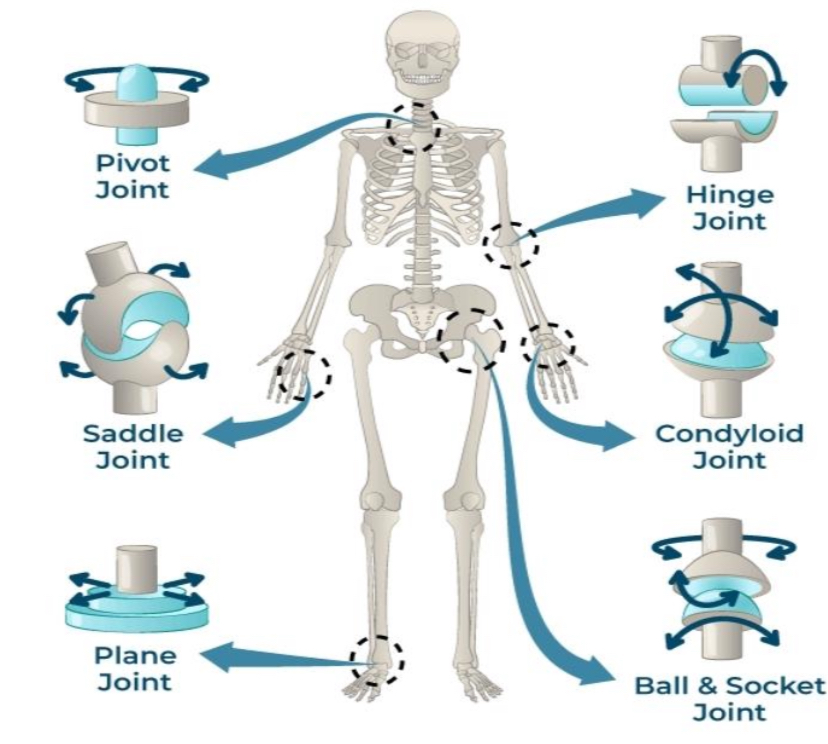
PLANE JOINT
type of structure in the body formed between two bones in which the articular, or free, surfaces of the bones are flat or nearly flat, enabling the bones to slide over each other
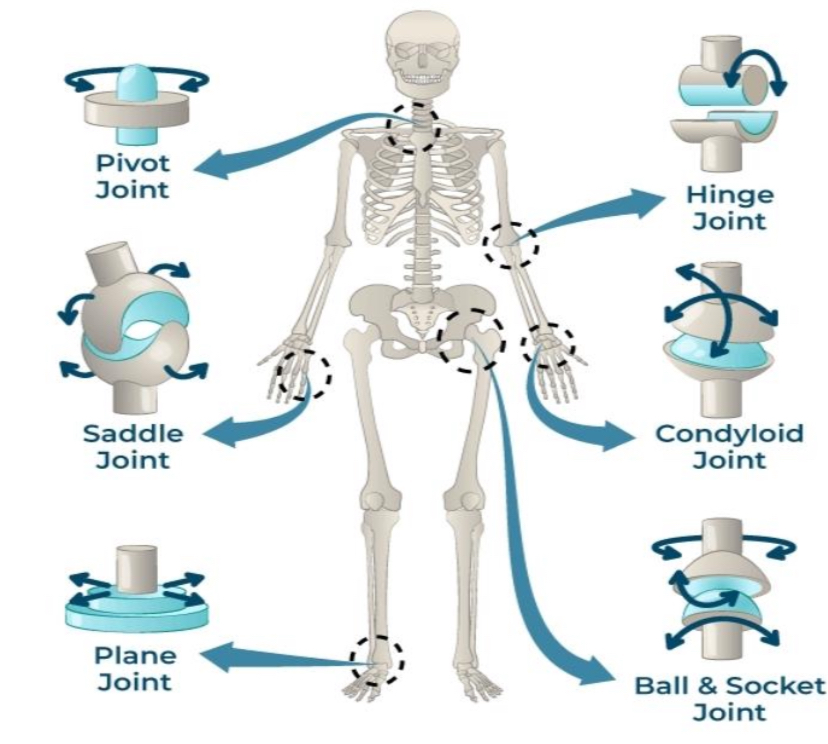
HINGE JOINT
type of synovial joint that exists in the body and serves to allow motion primarily in one plan
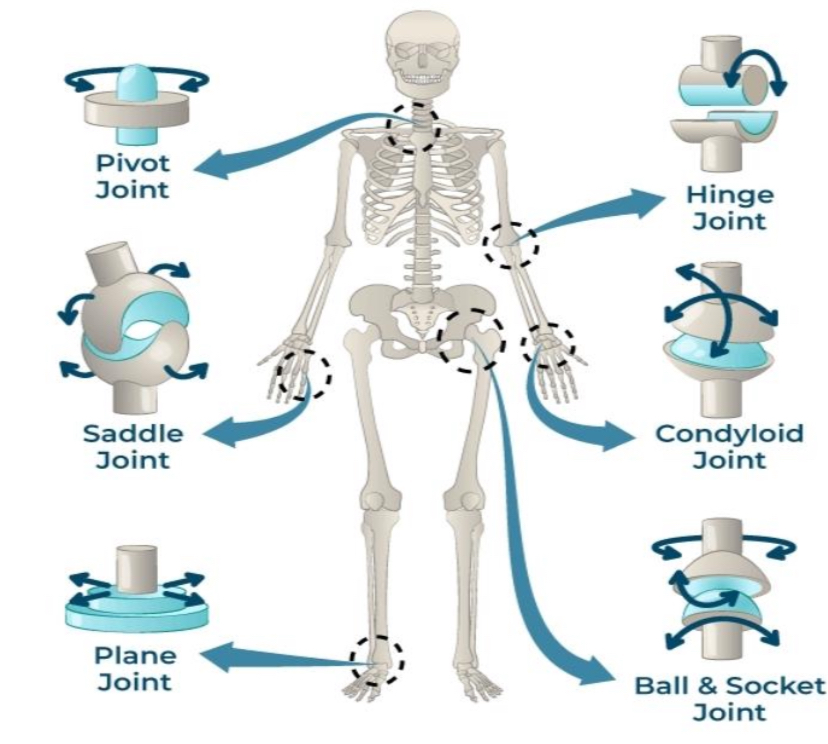
CONDYLOID JOINTS
also known as ellipsoid joints
composed of an egg-shaped bone known as a condyle that fits into a similarly shaped cavity.
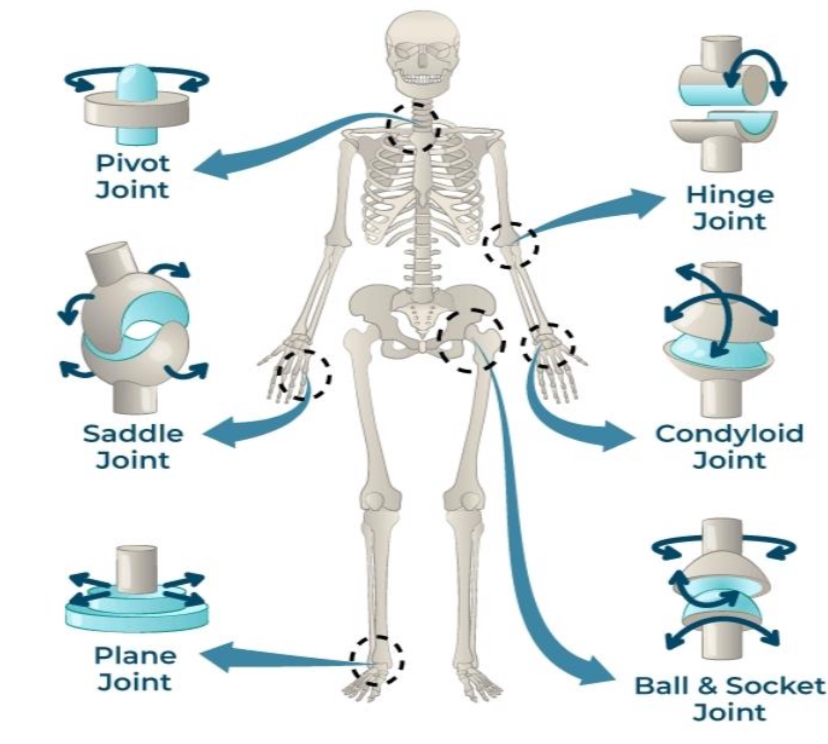
BALL & SOCKET JOINTS
type of synovial joint that
moves throughout three or more planes of motion into multiple directions
SYNOVIAL JOINT
— of joint capsule
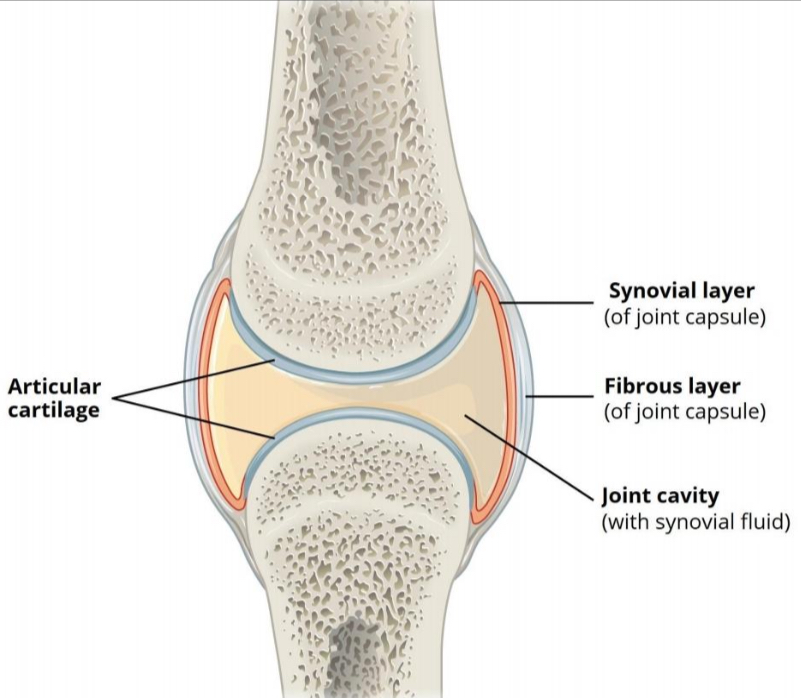
FIBROUS LAYER
— joint capsule
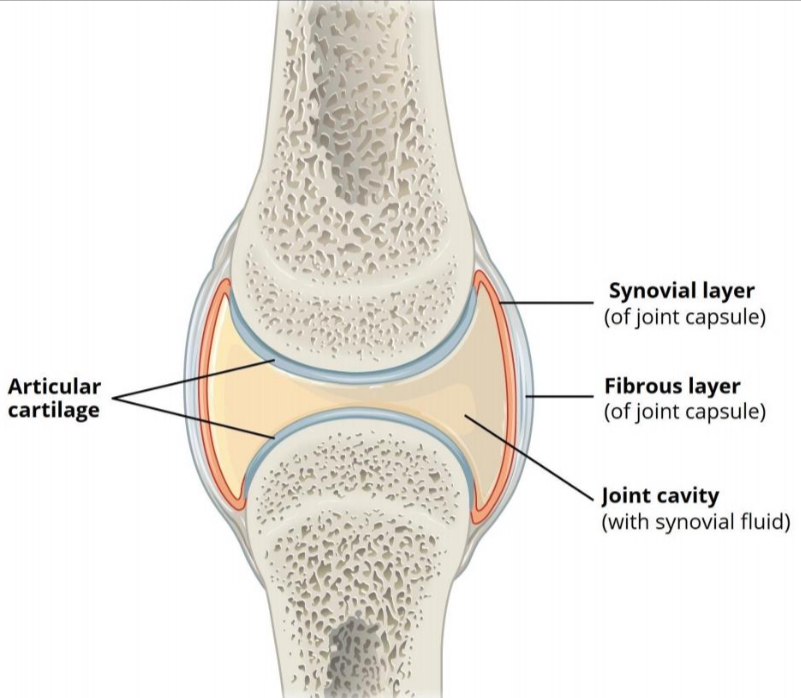
JOINT CAVITY
— with synovial fluid
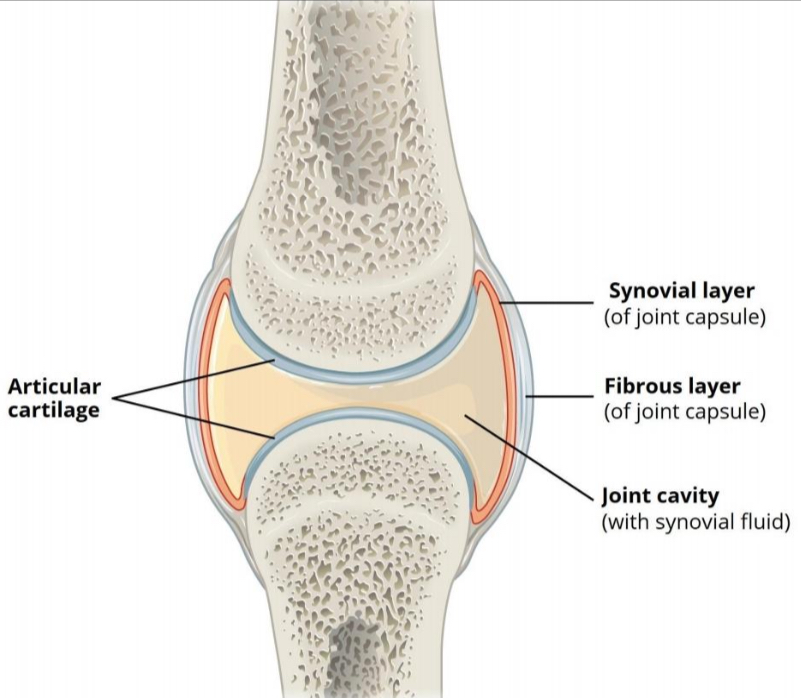
ARTICULAR/HYALINE CARTILAGE
prevent friction between articulating bones
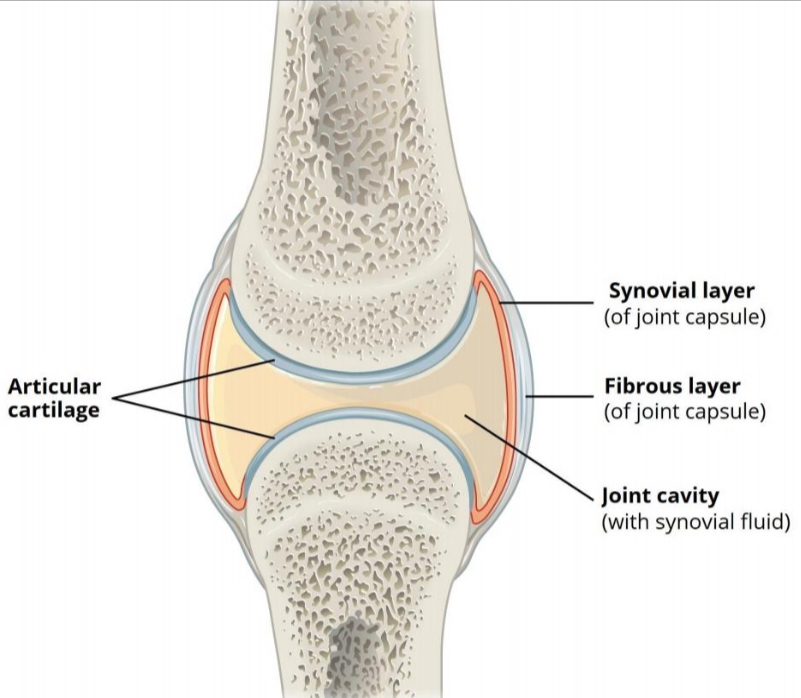
TWO-LAYERED JOINT CAPSULE
outer Layer - Strengthen joint
inner Layer - To secrete synovial fluid
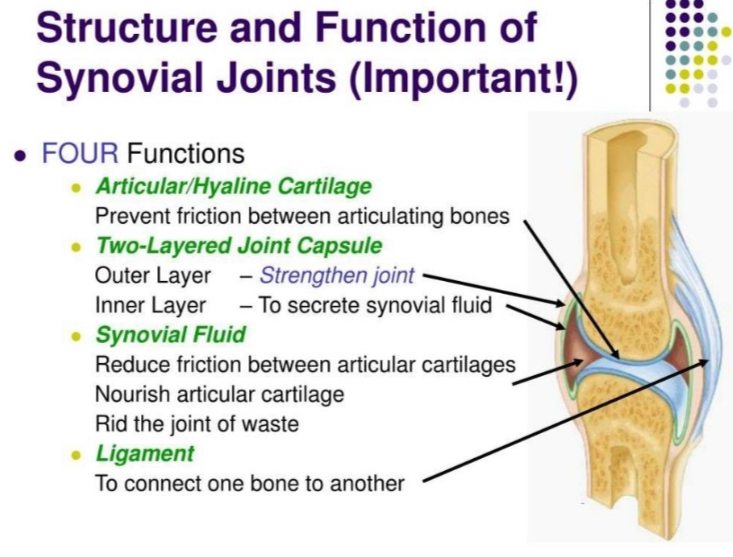
SYNOVIAL FLUID
reduce friction between articular cartilages
nourish articular cartilage
rid the joint of waste
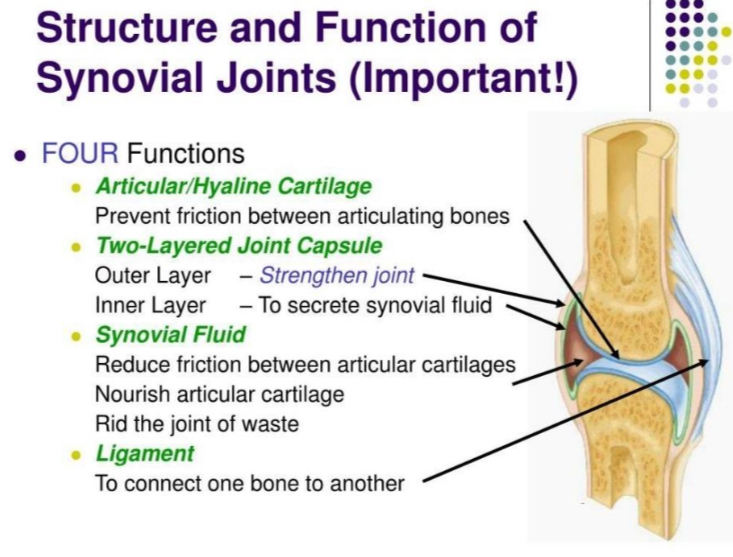
LIGAMENT
to connect one bone to another