NEUR305: Vision
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are rods?
low light levels
low spatial acuity (grainy)
black/white vision
peripheral vision
What are cones?
high light levels
high spatial acuity (sharp images)
color vision
center/focal vision (many in the fovea)
What is the opponent-process theory?
Our minds can only register the presence of one color of a pair at a time because the two colors oppose one another.
blue/yellow
green/red
black/white
ex. the cell that activates when you see red will deactivate in green light
The eye is part of the…
central nervous system
Function of iris and pupil?
The iris controls how much light the pupil lets in!
What does pupil size correlate to?
Arousal
What is sensory adaptation?
A gradual decrease over time in responsiveness of the sensory system (decreased sensitivity).
SENSORY NEURON LESS RESPONSIVE, don’t detect the stimulus.
What is sensory habituation?
As a result of repeated exposure to a stimulus.
INTERNEURONS LESS RESPONSIVE, still detect the stimulus.
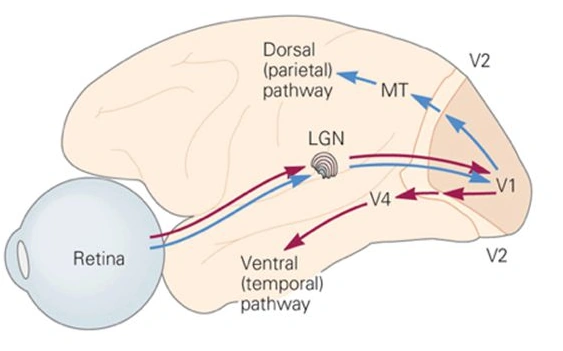
Outline visual pathway (WHAT/ventral)
Retina → Lateral Geniculate Nucleus → V1 → V2 → V4
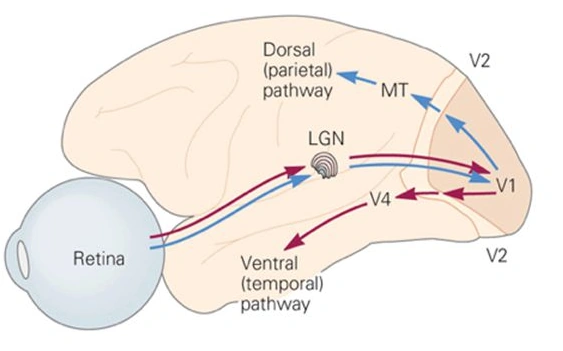
Outline visual pathway (WHERE/dorsal)
Retina → Lateral Geniculate Nucleus → V1 → V2 → MT/V5
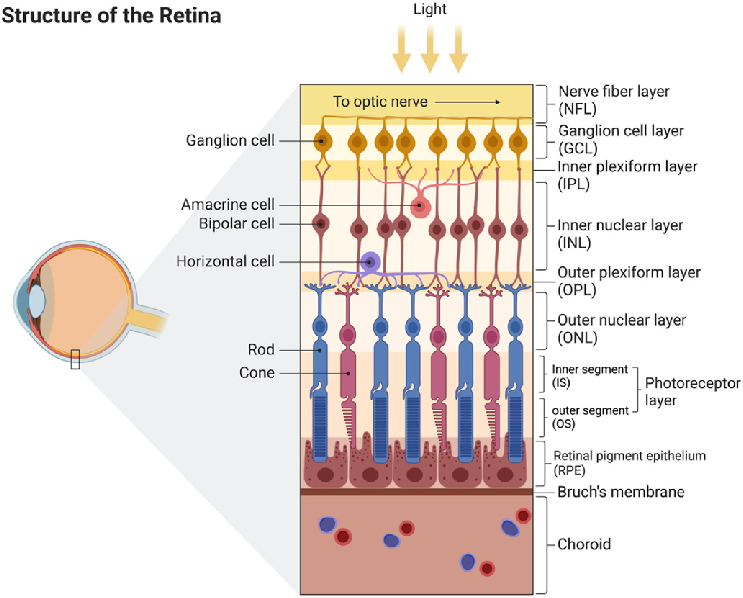
What’s the structure of the retina?
Ganglion cells
Interneurons (amacrine cells, bipolar cells, horizontal cells)
Photoreceptors (rods & cods)
The retina is organized INSIDE OUT (photoreceptors are all the way in the back of the retina when they need to process the light first).
Can rods and cones send action potentials?
NO
Only graded potentials, which involve slight changes in potential but no action potential firing (possibily due to short axons)
Where are there no photoreceptors?
On the optic nerve!
We can only see color by comparing…
activity of different cones; cones come in flavors of wavelengths
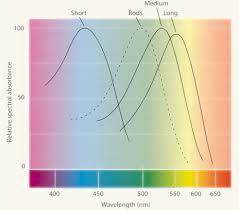
Why do we perceive color different?
Variability of cone distribution (absorbing long, medium, and short wavelengths)!
What’s the difference between rods and cones (think covergence)?
1:1 degree of convergence for cones!
1 cone for each ganglion cell.
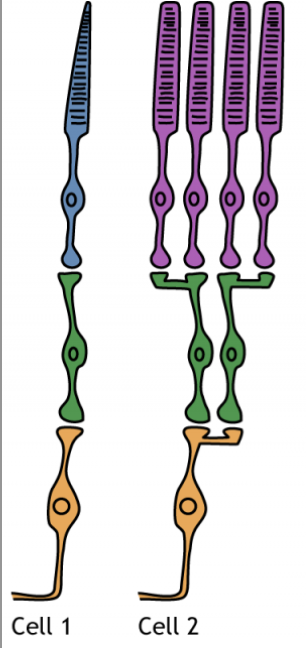
What’s the size of the receptive field for cones?
Small! To allow for better visual acuity.
What’s the size of the receptive field for rods?
Large! Visual acuity isn’t as good.
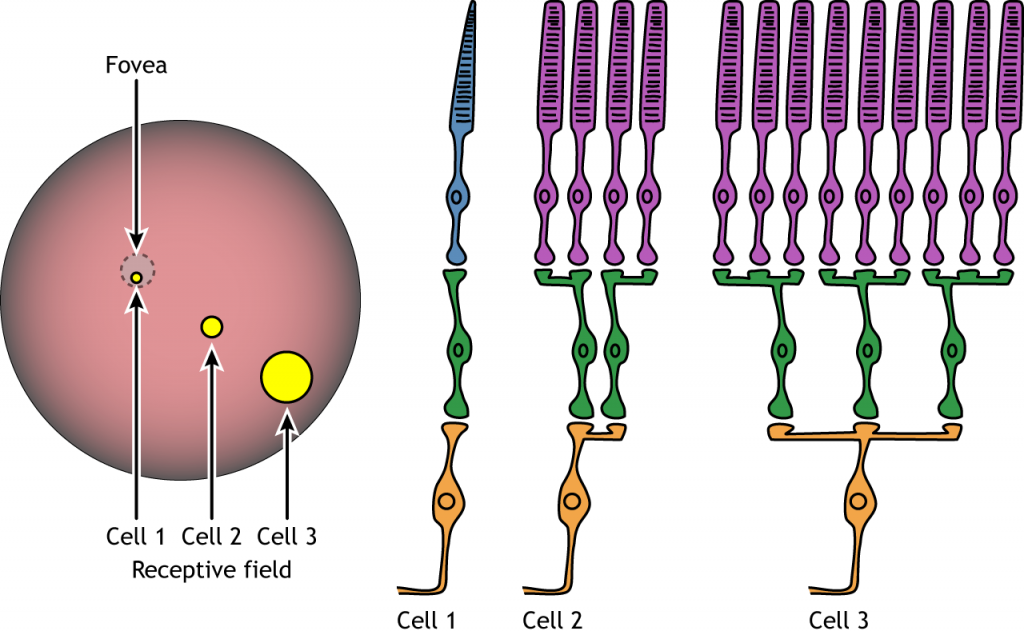
What does receptive field correlate to?
Level of convergence!
If information is gathered from a large # of photoreceptors, which converges into one ganglion cell it’s a large receptive field. Ganglion cells combine information from bipolar cells.
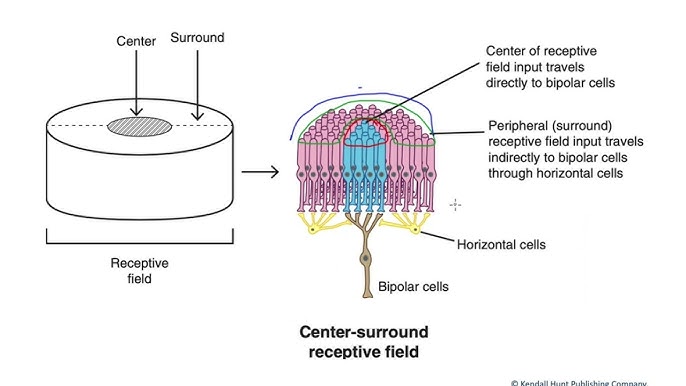
What are center-surround receptive fields?
They are sensitive to their edges (excitatory center, inhibitory surround).
Neuron’s response to a stimulus is inhibited by the excitation of a neighboring neuron.
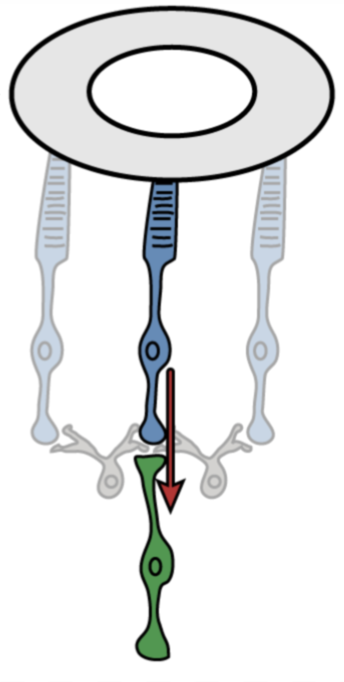
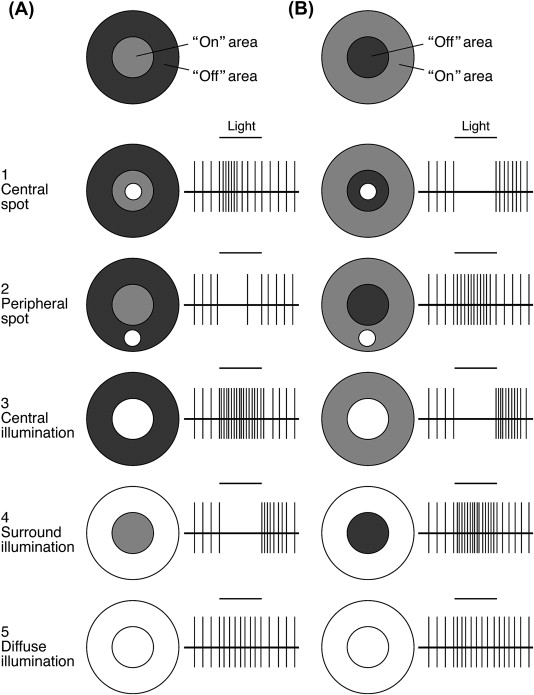
What are on-center ganglion cells?
Depolarizes (turns on) with light
Lateral inhibition when surround is hit with light.
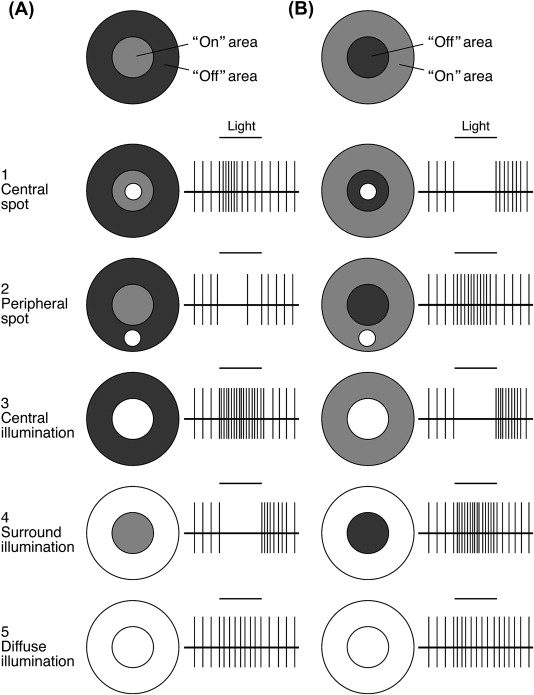
What are off-center ganglion cells?
Depolarizes (turns on) in dark
Outline on-center response levels
Center partially illuminated - SOME response
Center fully illuminated - LARGEST response
Surrounding partially illuminated - REDUCED response
Surrounding fully illuminated - No response
Everything illuminated - Base line activity
Outline off-center response
Center partially illuminated - NO response
Center fully illuminated - NO response
Surrounding partially illuminated - Some response
Surrounding fully illuminated - LARGEST response
Everything illuminated - Base line activity
Ganglion neuronal subtypes
Midget (parvocellular)
high spatial acuity (very small surface area)
object detection and detail
Parasol (magnocellular)
low spatial acuity (large surface area)
motion detection
Projections to the LGN come from 3 kinds of ganglion cells that encode for…
high resolution
large receptive field motion
color (koniocellular)
Function of superior colliculus?
Head orientation
What cells don’t need rod/cone input to express color?
Intrinsically photosensitive ganglion cells (ipRGCs); modulate responses to light in absence of rod/cone input; involved in circadian rhythm; express melanopsin
What do projections from ganglion cells to the pretectum do?
Encode luminance and motion
Tonic mode of LGN neuron shows…
Animal is alert
On graph: spike in, spike out multiple times
Burst mode of LGN shows…
Animal is out of focus
On graph: A singular brust
Which layers of the V1 correspond to magnoceullar?
1 and 2
Which layers of the V1 correspond to parvocellular?
3 to 6
Which part of the LGN corresponds to koniocellular?
Spaces in between the layers
How do cells in V1 respond?
Simple cells are sensitive to a specific orientation
Receptive fields stack up to form bars
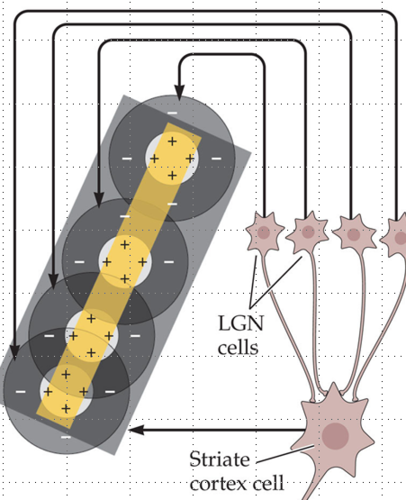
What’s the organization of V1 columns?
Forms into pinwheels (activity moves around a center); blobs are color sensitive and interblobs are orientation sensitive
Orientation columns and ocular dominance columns intersect at right angles
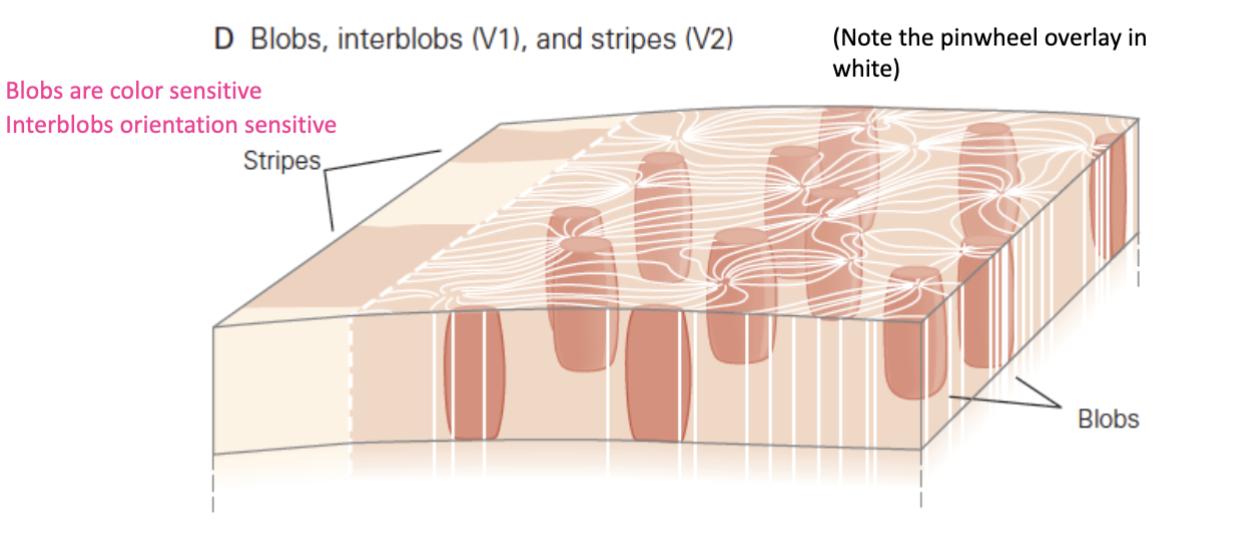
What is stereoposis?
The ability to view perception from both eyes; layers 2/3
What is the range of wavelengths that we perceive as light?
400 to 700 nanometers
What does the V2 process?
Thin stripes → color
Pale/inter stripes → spatial form
Thick stripes → motion
What can V2 do that V1 can’t?
Respond to “boundary ownership”, which side is part of the background and which is the object!
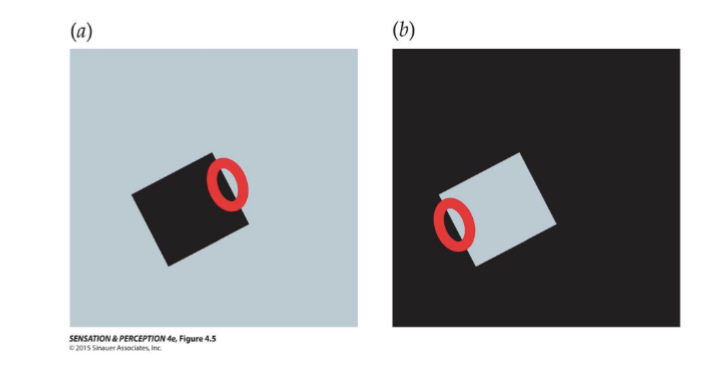
What is good continuation?
Function of V2
Two elements will tend to group together if they lie on the same contour

How do gestalt group rules apply to V2?
If objects are located in the same region we see them as being grouped together.
Dorsal stream of visual processing?
stimulus location
motion
sends information to motor
areas of frontal cortex
where and how
Ventral stream of visual processing?
color, form, details
facial recognition
object recognition
What role does the V4 play?
It plays a role in shape perception and contours (damage cannot see abstract art)!
What role does the V5 play?
Motion
What does damage to the V5 do?
View the world as snapshots, called alkinetopsia “motion blindness”
What is object constancy?
Ability to recognize an object as the same regardless of the viewing position and illumination (color, shape, size, etc.)
V4 plays a role in size constancy!
What is the role of lateral occipital cortex?
Looks into shape/object perception
What is the role of the fusiform face area?
Recognition of faces