The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
Protein
Polymers of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
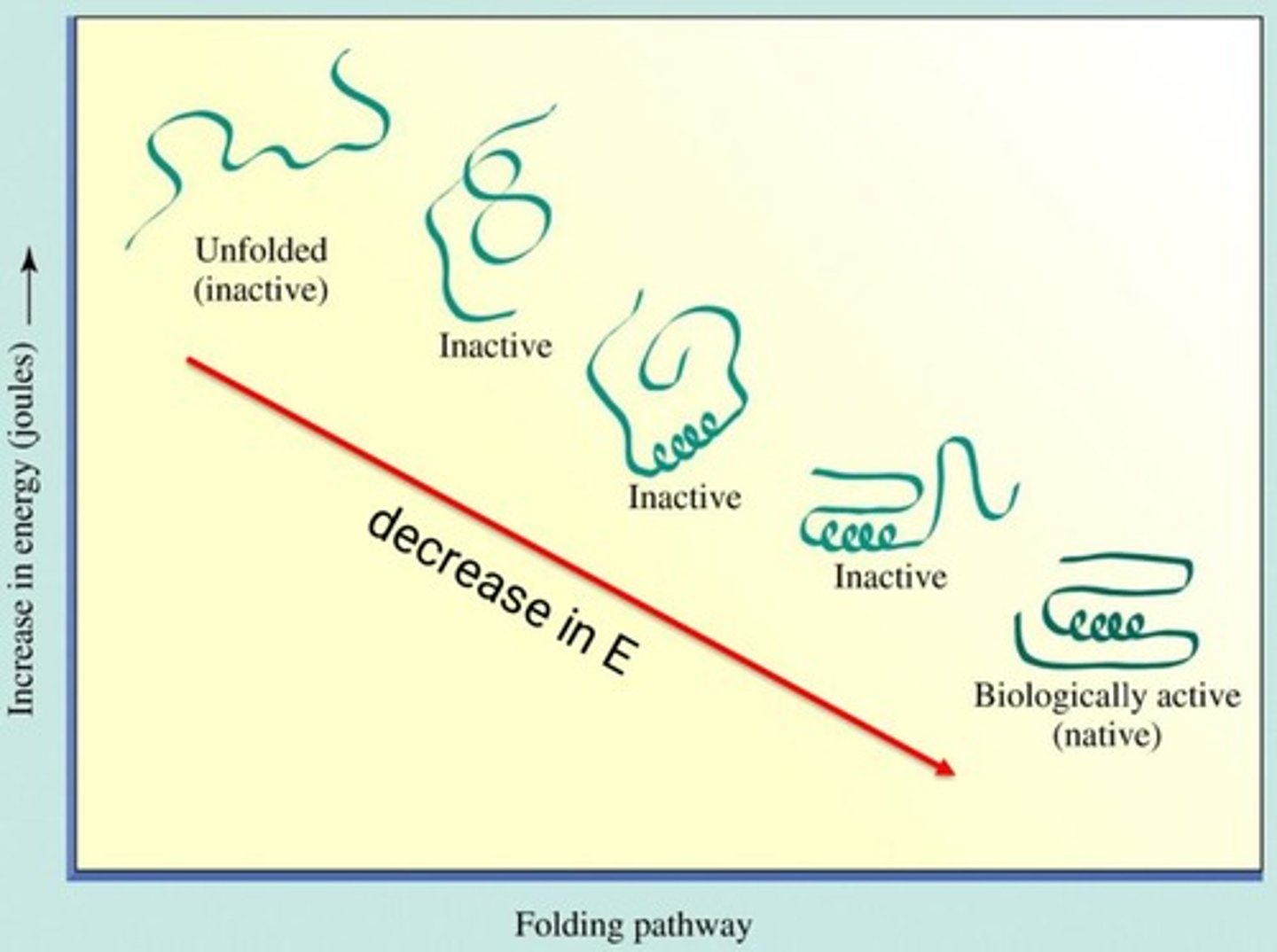
Native Conformation
3-D shapes of proteins with biological activity.
Random Coil
Proteins lacking a regular repeating structure.
Molecular Mass
Calculated by amino acid residues times 110.
Polypeptide
Chain of amino acids forming a protein.
Amino Acid Residues
Building blocks of proteins, typically 100-1000 per protein.
Monomeric Protein
Protein composed of a single polypeptide chain.
Oligomeric Protein
Protein made of multiple polypeptide chains.
Conjugated Protein
Protein attached to other macromolecules.
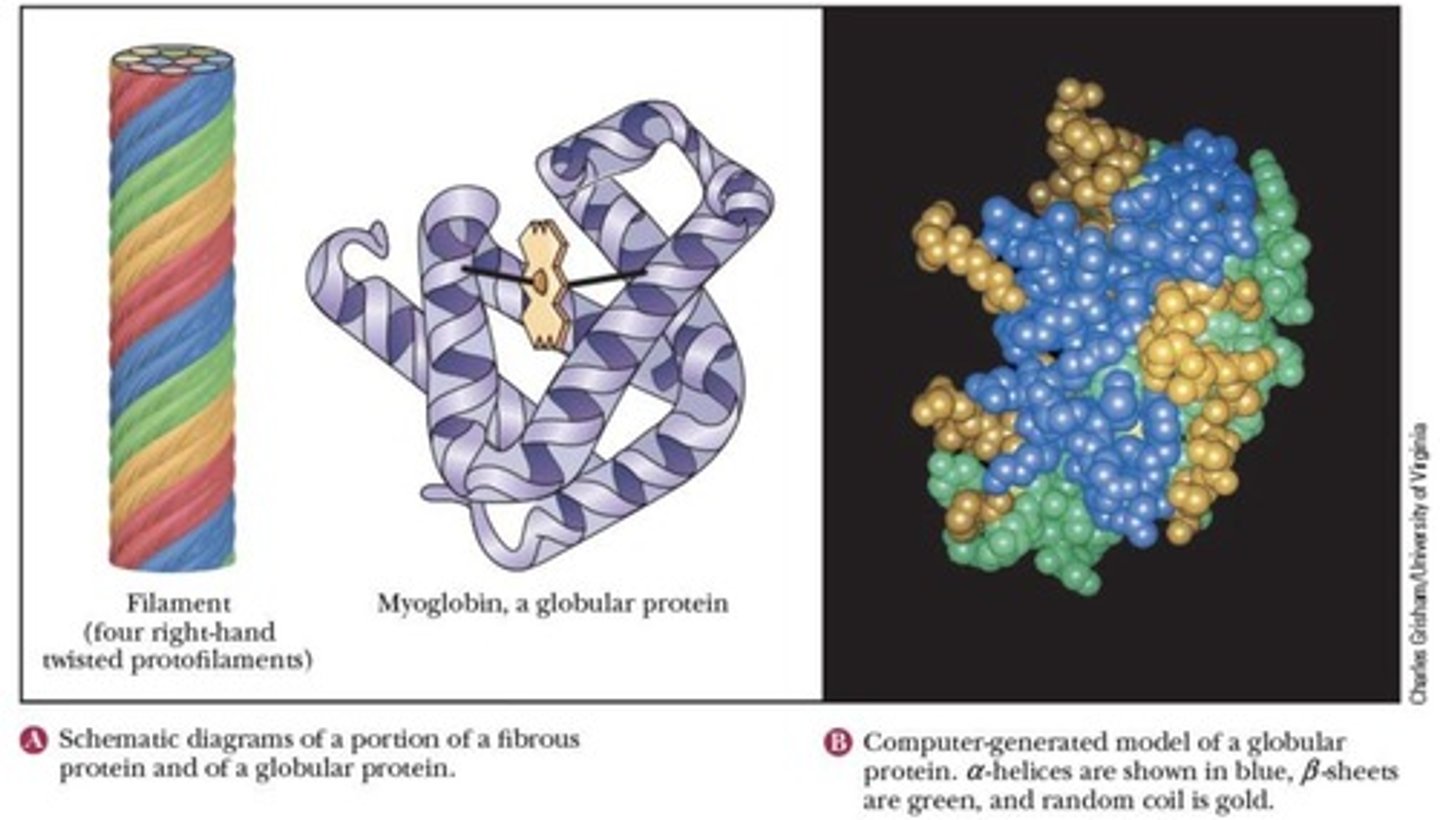
Globular Proteins
More soluble proteins with diverse functions.
Fibrous Proteins
Less soluble proteins providing structural support.
Enzymes
Biological catalysts facilitating biochemical reactions.
Amylase
Enzyme that digests carbohydrates in the mouth.
Structural Proteins
Provide mechanical support to cells and organisms.
Collagen
Fibrous protein giving strength to bones and skin.
Immune Proteins
Antibodies that bind and destroy foreign substances.
Transport Proteins
Carry small molecules through the bloodstream.
Lipoproteins
Transport insoluble biomolecules in the blood.
Ferritin
Protein used for nutrient storage.
Hormones
Regulatory proteins like insulin and prolactin.
G Proteins
Transmit hormonal signals inside cells.
Receptor Proteins
Mediates transmission of nerve impulses and signals.
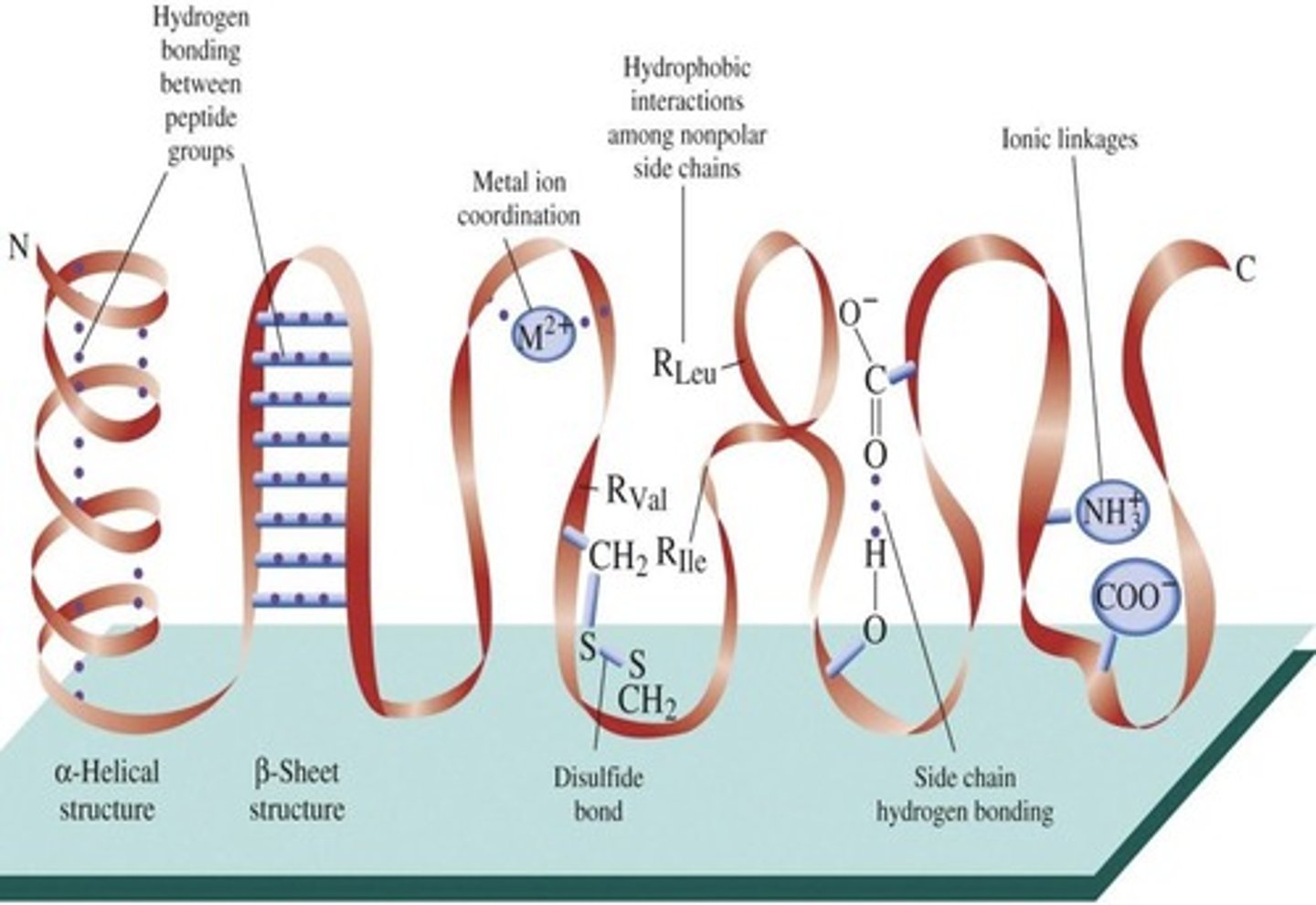
Primary Structure
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
N-terminal End
Start of the polypeptide chain sequence.
C-terminal End
End of the polypeptide chain sequence.
Secondary Structure
Localized 3-D arrangements of polypeptide chain.
Alpha-helix
Common secondary structure formed by hydrogen bonds.
Beta-pleated Sheet
Another secondary structure with hydrogen bonding.
Domains
Clusters of secondary structural motifs in proteins.
Super-secondary Structure
Specific clusters of secondary structures in proteins.
Tertiary structure
3-D arrangement of all atoms in a protein.
Prosthetic groups
Non-amino acid portions of proteins.
Quaternary structure
Arrangement of multiple polypeptide subunits.
Subunits
Individual polypeptide chains in a protein.
Primary structure
Amino acid sequence of a protein.
Sickle-cell anemia
Condition caused by a single amino acid change.
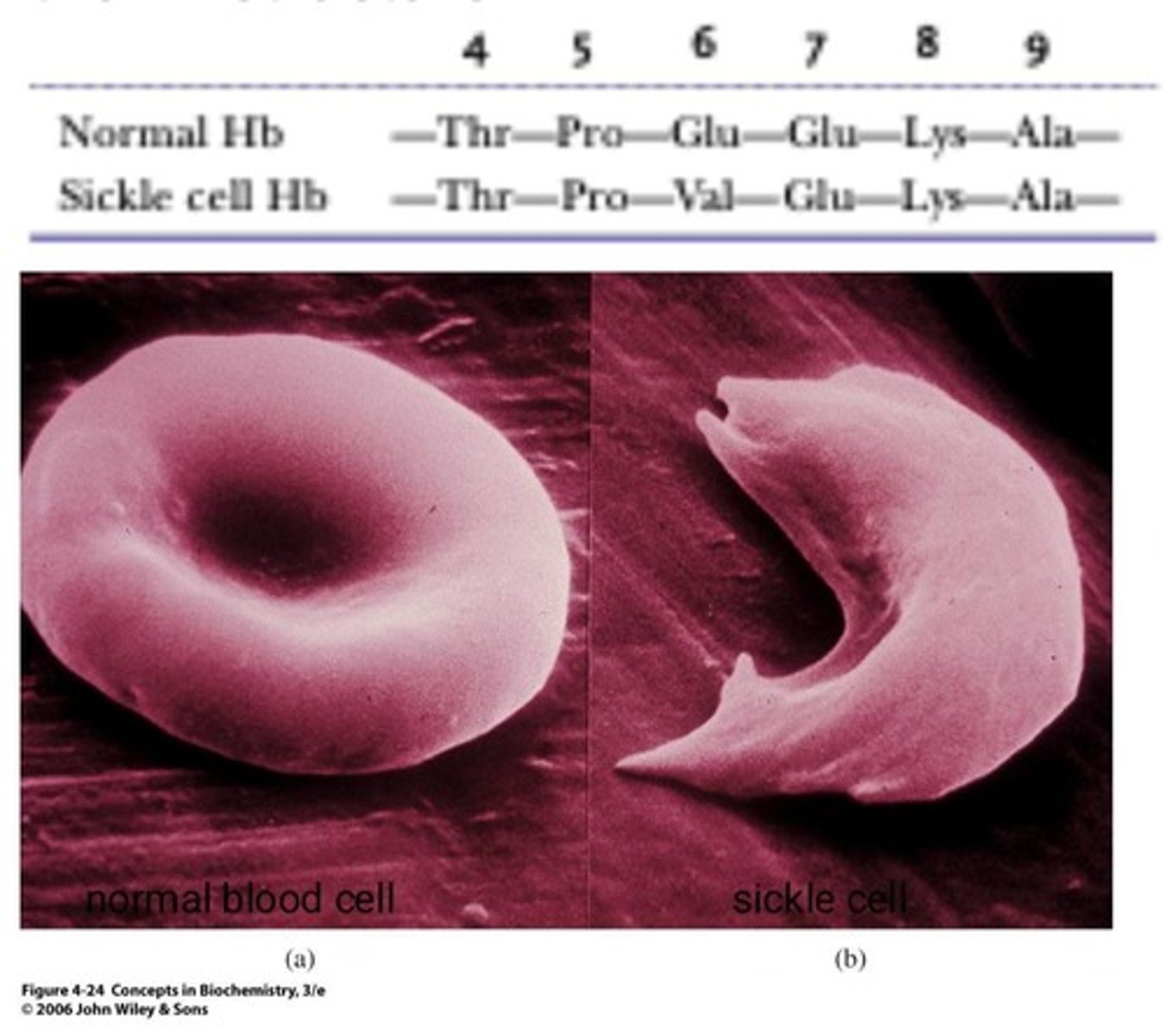
Red blood cells
Cells that transport oxygen in the body.
Site-directed mutagenesis
Technique to replace specific amino acid residues.
Secondary structure
Hydrogen-bonded arrangement of polypeptide chains.
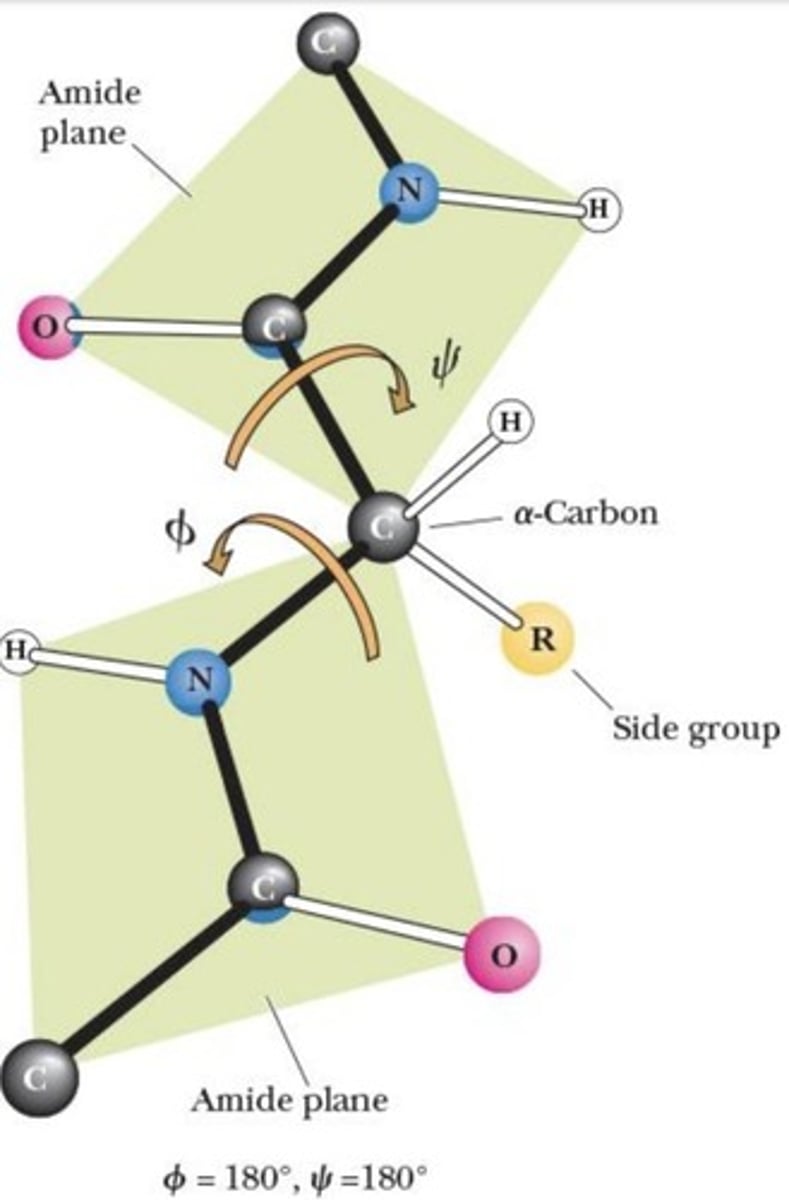
Ramachandran angles
Angles phi and psi for peptide bond rotation.
a-Helix
Right-handed helical structure stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
B-pleated sheet
Secondary structure with parallel or antiparallel strands.
Hydrogen bonds
Attractive forces between hydrogen and electronegative atoms.
Pitch
Linear distance between corresponding points on helix turns.
C-O group
Part of peptide bond involved in hydrogen bonding.
N-H group
Part of amino acid involved in hydrogen bonding.
Proline
Amino acid that disrupts a-helix structure.
Cyclic structure
Proline's structure restricts backbone rotation.
Intrachain hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding within the same polypeptide chain.
Bond strength
Stability of interactions between atoms in proteins.
Amino acid residue
Individual amino acid within a protein sequence.
Conformation
Three-dimensional shape of a protein.
Biological activity
Function of a protein based on its structure.
Helical conformation
Arrangement allowing linear structure in proteins.
Maximum bond strength
Optimal stability in protein folding patterns.
3.6 residues
Number of amino acids per turn in a-helix.
5.4 Å
Distance between turns in an a-helix.
R groups
Side chains of amino acids extending outward.
Electrostatic Repulsion
Repulsion from like-charged side chains proximity.
Steric Repulsion
Crowding from bulky side chains proximity.
𝝰-Helical Conformation
Side chains lie outside the helix structure.
𝝰-Carbon
Carbon atom adjacent to amino acid side chain.
Lysine (Lys)
Positively charged amino acid side chain.
Arginine (Arg)
Positively charged amino acid side chain.
Glutamate (Glu)
Negatively charged amino acid side chain.
Aspartate (Asp)
Negatively charged amino acid side chain.
Valine (Val)
Bulky side chain causing steric repulsion.
Isoleucine (Ile)
Bulky side chain causing steric repulsion.
Threonine (Thr)
Bulky side chain causing steric repulsion.
B-Pleated Sheet
Extended peptide backbone with zigzag structure.
Hydrogen Bonds
Bonds between peptide chains in B-sheets.
Interchain Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds between different peptide chains.
Intrachain Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds within the same peptide chain.
Parallel B-Sheet
Chains aligned in the same direction.
Antiparallel B-Sheet
Chains aligned in opposite directions.
R Groups
Side chains alternate above and below the plane.
S-Trans Peptide Bond
Planar bond configuration in peptide chains.
310 Helix
Helix with three residues per turn.
B-Bulge
Irregularity in antiparallel B-sheets.
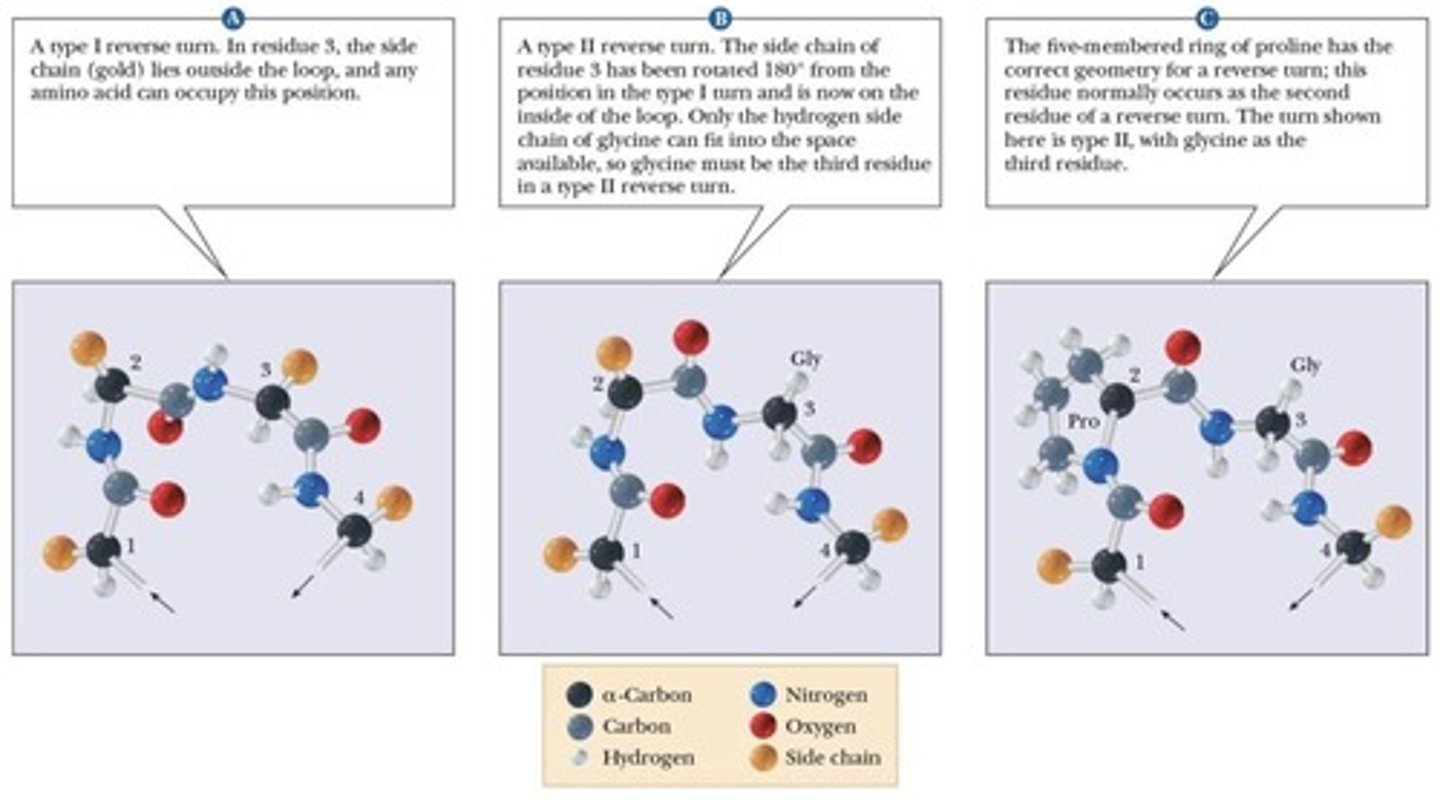
Reverse Turns
Regions where polypeptide chain folds back.
Glycine
Amino acid commonly found in reverse turns.
Proline
Cyclic amino acid found in reverse turns.
Supersecondary Structures
Combination of a and B strands.
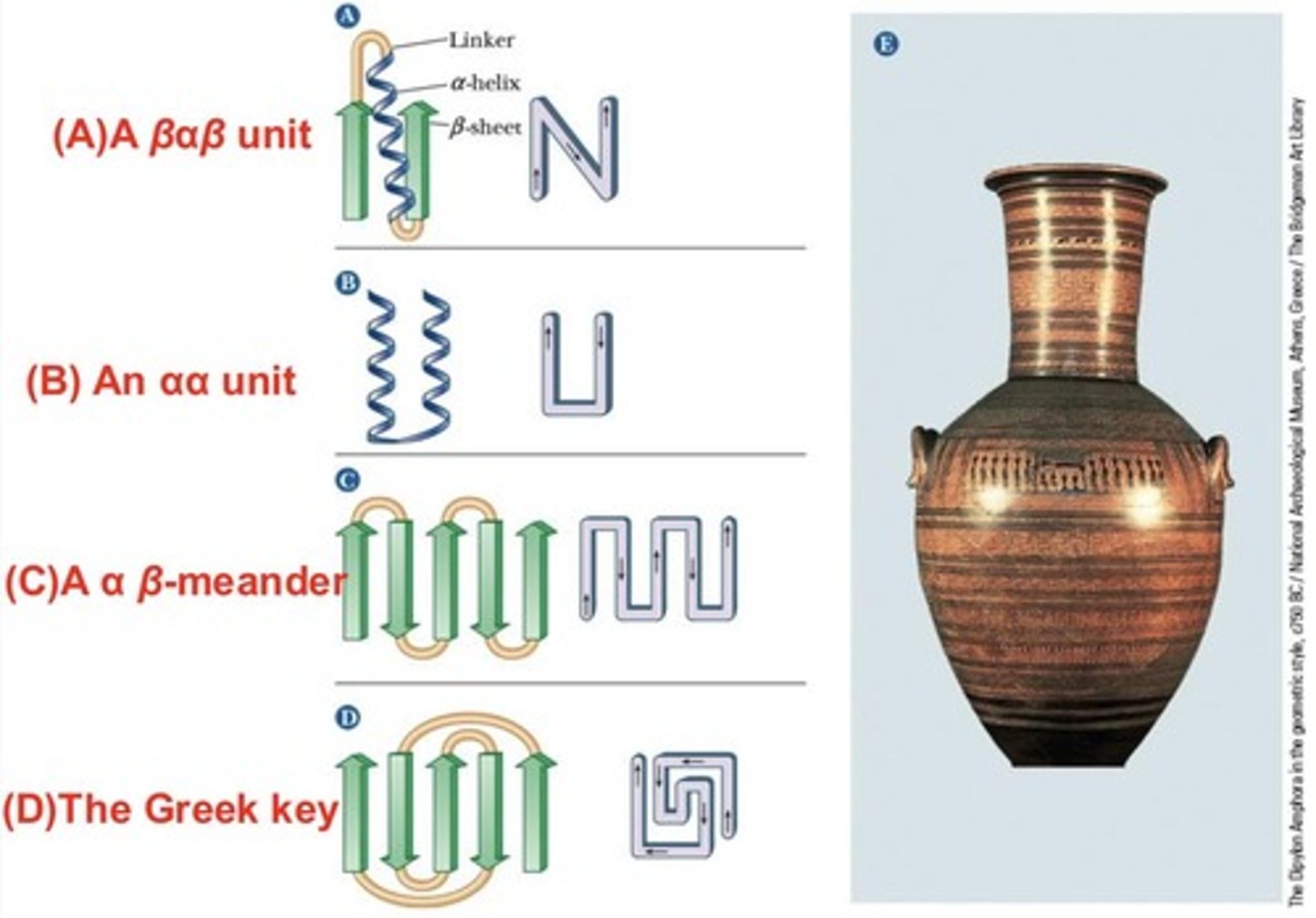
BaB Unit
Two parallel B-strands connected by a-helix.
aa Unit
Contains two antiparallel a-helices.
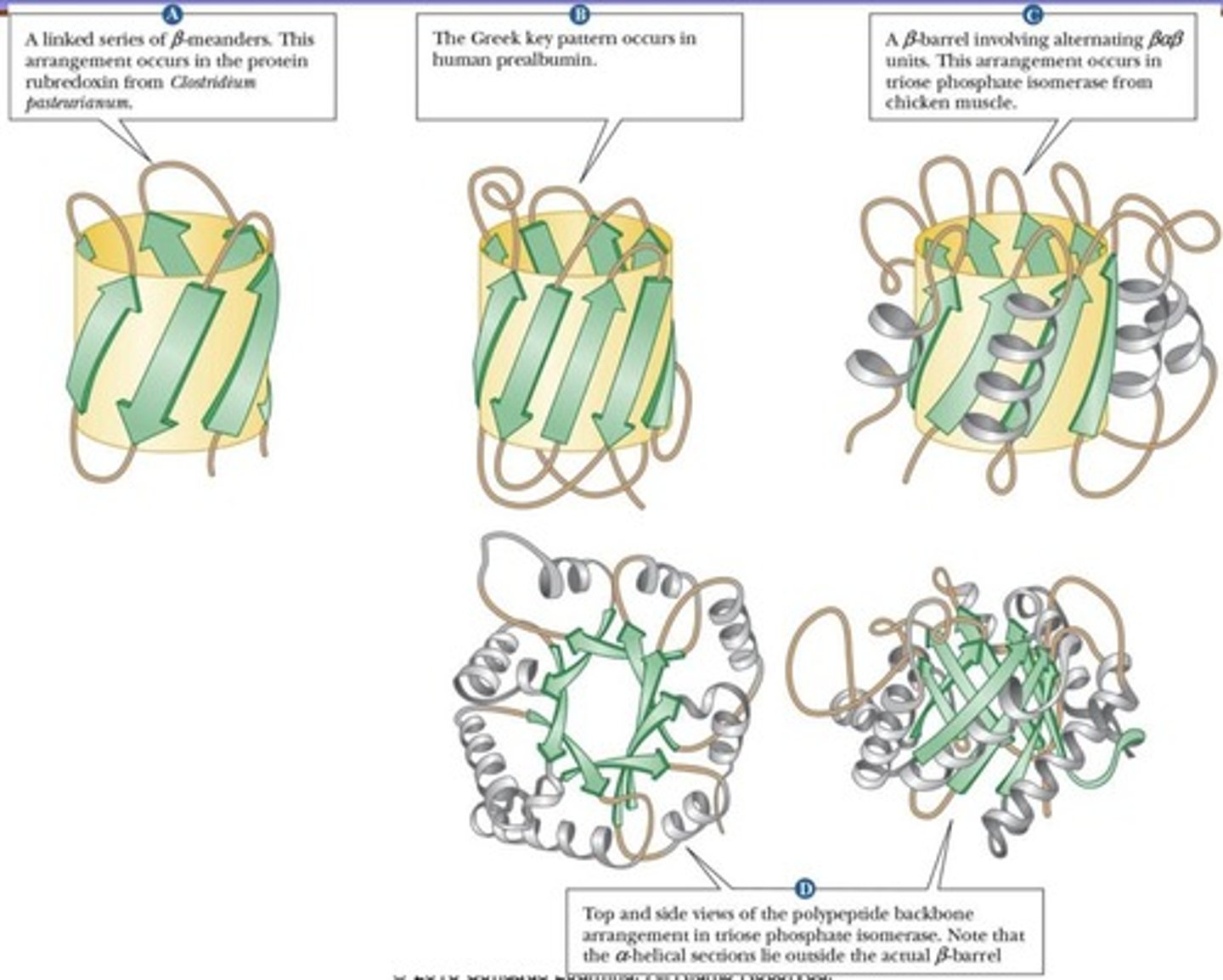
B-Meander
Antiparallel sheet formed by tight reverse turns.
Greek Key
Polypeptide chain doubles back on itself.
Motifs
Repetitive supersecondary structures in proteins.
B-Barrel
Extensive B-sheets folding back on themselves.
Motifs
Patterns in proteins that do not predict function.
Protein Sequences
Similar sequences indicate similar protein functions.
Domains
Structural units associated with specific protein functions.
Collagen
Most abundant protein in vertebrates, found in tissues.
Triple Helix
Structure of collagen formed by three polypeptide chains.
Tropocollagen
Basic unit of collagen, molecular weight 300,000.
Amino Acid Sequence
Collagen has repeating X—Pro—Gly or X—Hyp—Gly.
Hydroxyproline
Modified proline essential for collagen stability.
Glycine
Every third residue in collagen, allows tight packing.
Superhelical Arrangement
Collagen chains twist to form a stiff rod.
Hydrogen Bonds
Stabilize collagen chains via hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine.