HSP3U1 : Psychology Unit Test
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Cognitive Development Theory
A theory proposed by Jean Piaget that explains how children's thinking evolves through stages from infancy to adulthood.
Sensorimotor Stage
Birth to 2 years of age, mental development mainly includes sensation and motor skills. Such as biting, moving, chewing etc.
Preoperational Stage
Ages 2-7, this where children struggle with logical thinking and being able to understand how other people think and their perspectives.
Concrete-Operational Stage
7-11, child becomes better at using logical thinking rather than intuitive thought and can visualize other people’s perspectives and views.
Formal-Operational Stage
11-Adulthood, we understand hypothetical problems and think of the world in a more scientific way. We can think of many different solutions to problems and are able to compare them.
Psychosocial Theory
Theory by Erik Erikson that believes that life happened in 8 different stages throughout your life that help to develop your identity.
Maslow’s Heirarchy of Needs
Psychological theory by Abraham Maslow. It categorizes human needs into five levels: physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization.
Classical Conditioning
Ivan Pavlov’s theory on type of learning where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a reflexive response through repeated association. For example, a dog being conditioned to drool at the sound of a bell since a bell is associated with meal time.
Operant Conditioning
Similar to classical conditioning, this theory by B.F. Skinner uses positive and negative reinforcements and punishments in order to be able to condition behaviors.
ABCs of Behavior
Antecedent - something that comes before a behavior and may trigger that behavior
Behavior- Anything an individual does
Consequence- Something that follows this behavior
Psycho Sexual Theory
Sigmund Freud's theory that personality development is influenced by childhood experiences and conflicts related to different erogenous zones.
These are oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital.
Oedipus Complex
Freudian theory where children desire the parent of the opposite sex and view the same-sex parent as a rival. Resolved through identification.
Psychoanalytic Theory
Sigmund Freud’s theory that personality is made up of 3 components. These develope one’s personality in a variety of ways.
Superego
Aims to avoid acting on instant gratification and is morally driven.
Ego
Part of personality that balances the other two parts, aiming for pleasure but avoiding negative consequences
Id
Impulsive part of the psyche that seeks pleasure and avoids pain. Instant gratification is core to this part, and is heavily desired. Seen to be the biggest part of our personality.
Social Learning Theory
Albert Bandura’s theory that children learn through observation of others, and whether these things are received positively or negatively determines whether or not they will imitate that action.
Primary and Secondary Emotions
Theory by Robert Plutchik to describe emotions. Primary emotions are basic, instinctual feelings like joy or fear, while secondary emotions are more complex and arise from a combination of primary emotions.
Fight or Flight
Response to stress: body's automatic reaction to danger; prepares for fighting or running away. Triggers release of adrenaline for quick response.
Harlow’s Study of attachment
Harlow's Study of Attachment: Experiment with infant monkeys showing the importance of contact comfort in attachment formation, choosing comfort over basic needs such as food.
Harlow's study revolutionized our understanding of attachment theory, highlighting the critical role of contact comfort in forming secure and healthy attachments. It emphasized the importance of emotional bonding.
Triangular Theory of Love
Robert Sternberg’s theory that states love consists of three components: intimacy, passion, and commitment. Different combinations of these components result in different types of love.
Defense Mechanisms
Psychological strategies used to cope with anxiety and protect the ego from distress. Examples include denial, projection, and repression.
Biological Perspective (School of Thought)
School of thought that studies psychological issues by researching the brain, system, nervous system and genetics to help explain human behavior, personality, and mental states.
Psychodynamic Theory (School of Thought)
This school of thought tries to explain personality in terms of conscious and unconscious theories, often maintaining that childhood experiences shape our personalities.
Behaviorists (School of Thought)
These individuals beelieve that human believe can be explained by how we are conditioned or taught to act. They believe that psychological disorders are best treated by changing behavior patterns through stimulus and response
Cognitive Theories (School of Thought)
School of thought with theories that personalities are affected by how we think. These theories emphasize that our thought processes affect the way we behave.
Humanistic Psychologists (School of Thought)
Individuals in this school of thought look at human behavior both as the observer and through the eyes of the person doing the behavior. This approach is often used to study phenomenons, for its focus on the influence of direct experience.
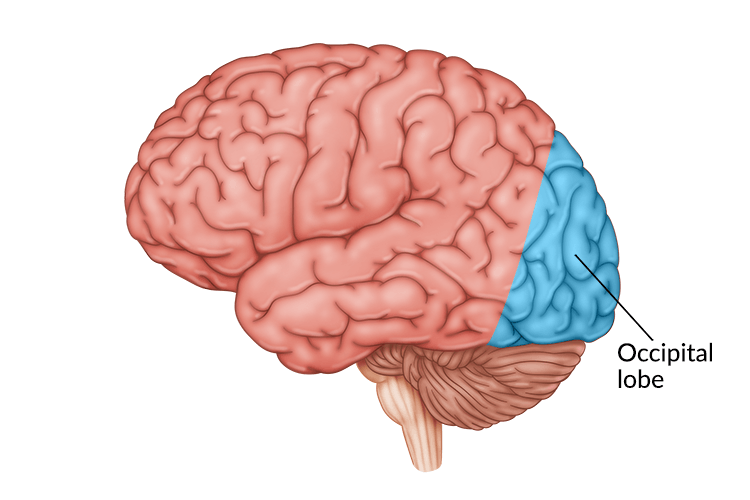
Occipital Lobe
Part of the brain that is responsible for visual perception and information, such as color, form and motion.
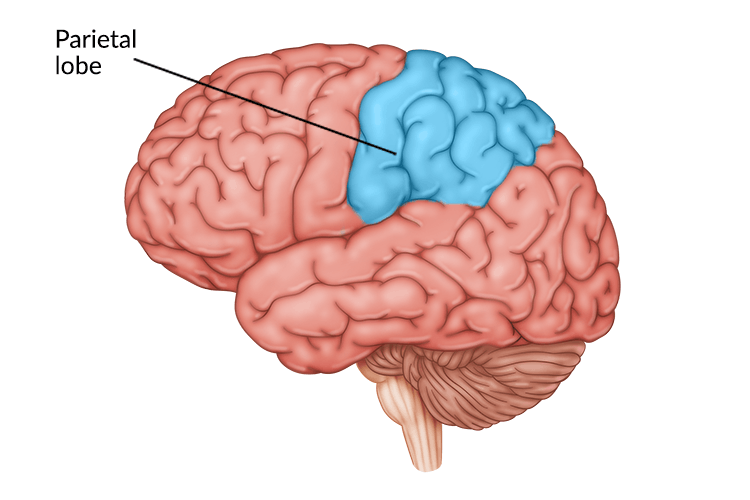
Parietal Lobe
Part of the brain that receives and processes senses. This helps us to be aware of our surroundings and work on spatial tasks, such as imagining rotating objects.
This part of the brain is usually larger in men.
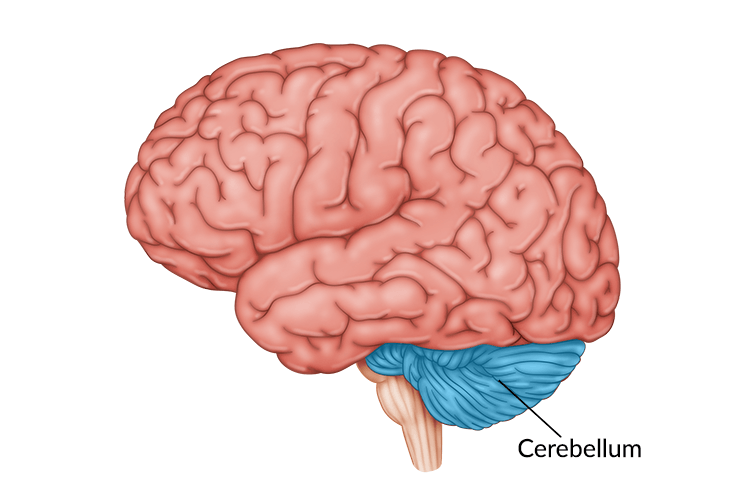
Cerebelium
Part of the brain that is responsible for controlling muscles. Helps with balance control, gait and posture.
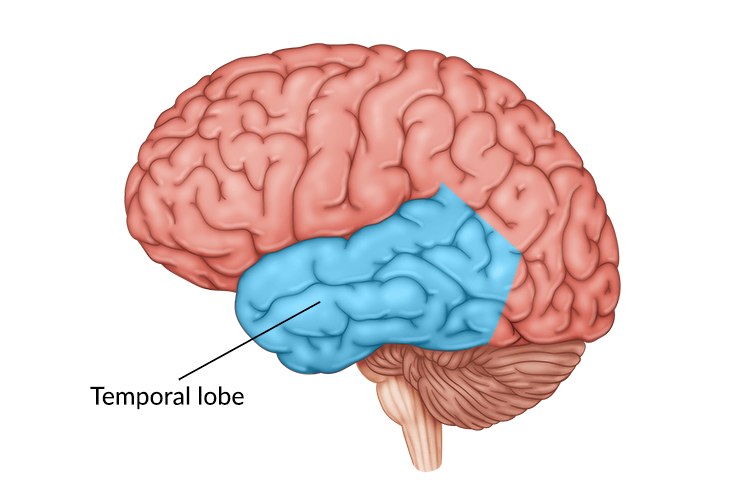
Temporal Lobe
One of the major parts of the brain that deals with language understanding and expression, object and facial recognition, emotional reactions and processing, and memory storage and recall.
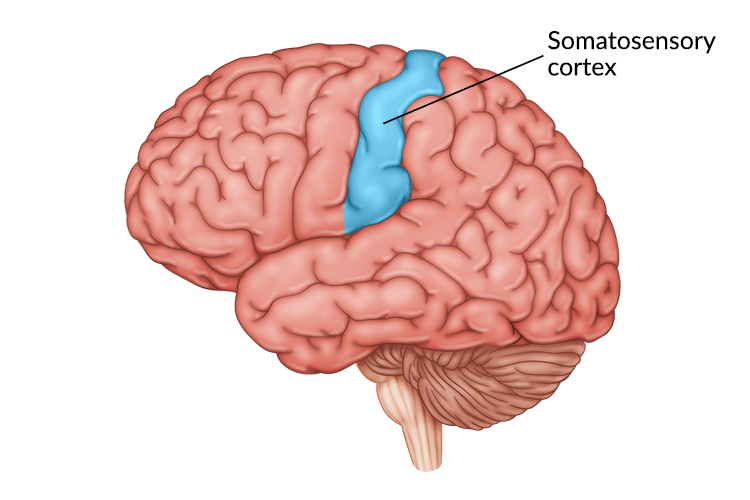
Sensory Cortex
Part of the brain that deals with processing and interpreting sensory stimulus. For example, identifying an object based on its texture, temperature and shape.
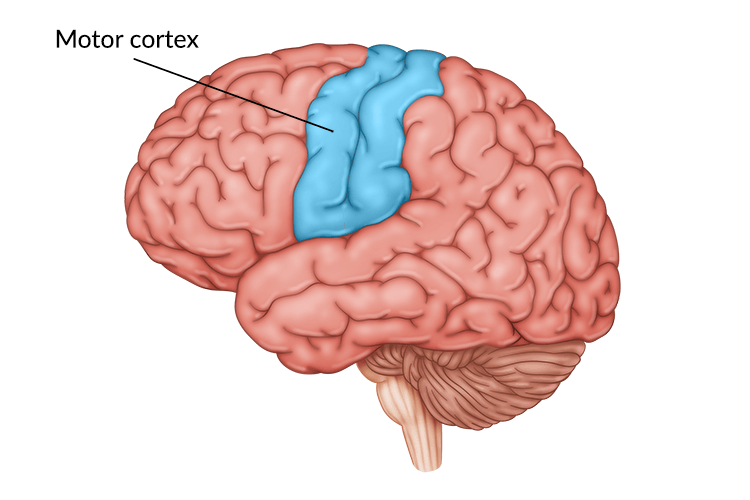
Motor Cortex
Part of the brain that generates signals to direct the body’s movement.
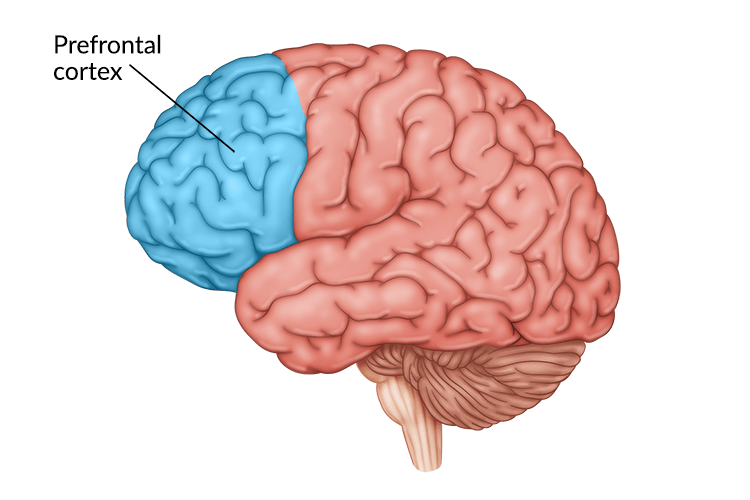
Pre-frontal cortex
One of the last places in the brain to mature and regulates our thoughts, actions and emotions through extensive connections with other brain regions. This part of the brain plays an important role in controlling stress and decision-making, avoiding impulsive decisions.
Neuroplasticity/ Brain Plasticity
Ability for the neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization. An example of this being used would be changing how we have learned to operate a bicycle.
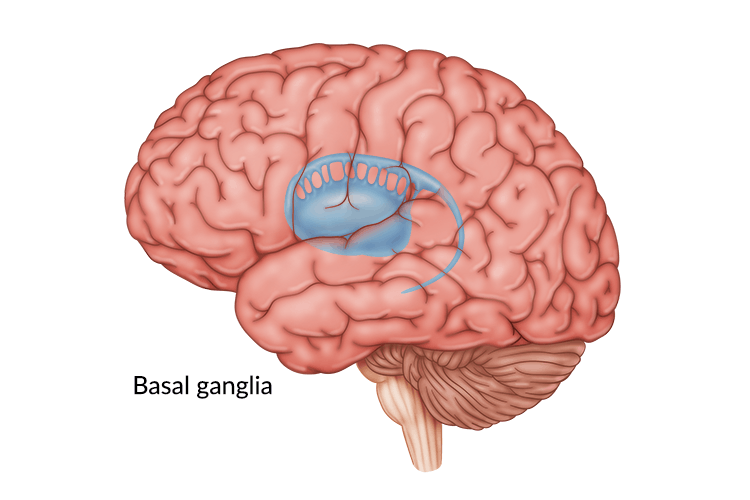
Nucleus Accumbus (Apart of the Basal Ganglia)
A part of the Basal ganglia, this structure in the brain works as a “reward circuit”. When we do something that is considered rewarding the dopamine levels in this structure increase. This is often called the “reward system”
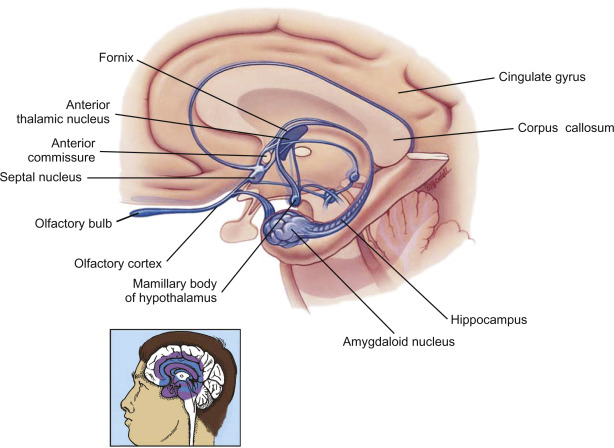
Limbic System
Part of the brain involved in behavioral and emotional responses, regulating emotion and memory while also dealing with sexual stimulation and learning.
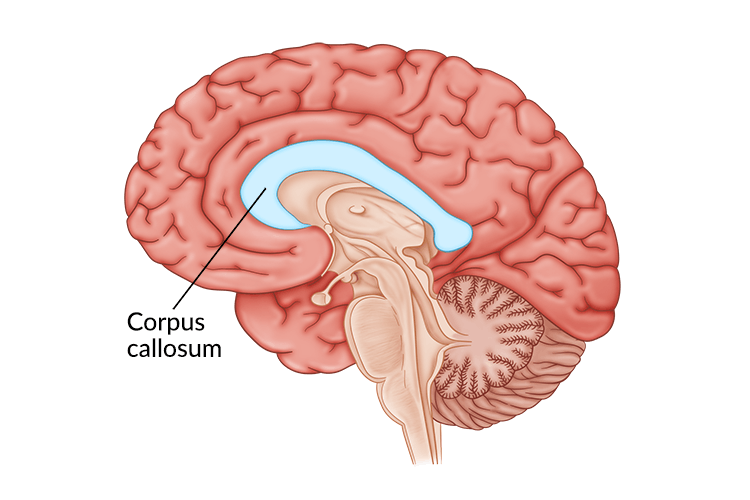
Corpus Colloseum
Part of the brain that allows for information to transmit from both sides of the brain. It is hypothesized to have a big part in physical coordination, vision, and cognitive functions.
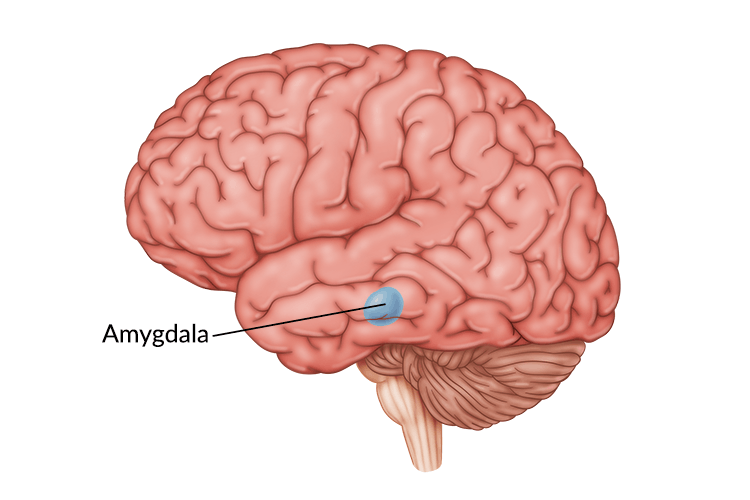
Amygdala
Structure in the brain that is responsible for emotional and behavioral regulation, specifically the body’s response to fear. This is a part of the limbic system, which helps to automatically detect danger.
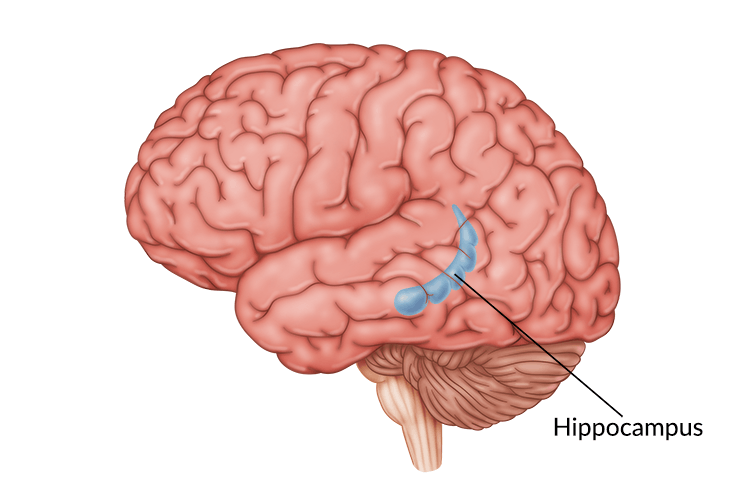
Hippocampus
Structure in the temporal lobe that has a major role in learning and memory. It stores short-term memories and then transfers them to long-term storage in our brains. It also helps to process emotions such as anxiety and avoidant behavior.
Women’s are bigger than men’s when adjusting for the overall difference in brain size (~10%).
Looking-Glass Self
Charles Horton Cooley’s idea that our sense of self and identity is developed through how others perceive us.
George Herbert Mead and Roletaking
Self develops through social interaction with others during childhood.
Stage 1- Imitating those around them
Stage 2- Acting out these roles
Stage 3- Stage-play group games/ roleplay
Wish Fulfillment in Dreams
Wish fulfillment refers to the idea that dreams are a way for the unconscious mind to fulfill repressed desires or wishes. It suggests that dreams serve as a symbolic representation of our deepest desires, often in a disguised form.
Jungian Archetypes
According to Jung, personality appears in the form of archetypes, or universal patterns of thought and behavior that affect what we focus on and how we interact with the world. Jungian archetypes categorize people in terms of various personality patterns.
Melissa Hines
Psychologist that specializes in human gender development, known for her work in showing typical sex differences in the brain
Nature vs. Nurture
Debate on whether genetics or environment has a greater influence on behavior and development.
The Nurture side of this argument is part of the behavioral school of thought, and genetics is part of the biological school of thought.
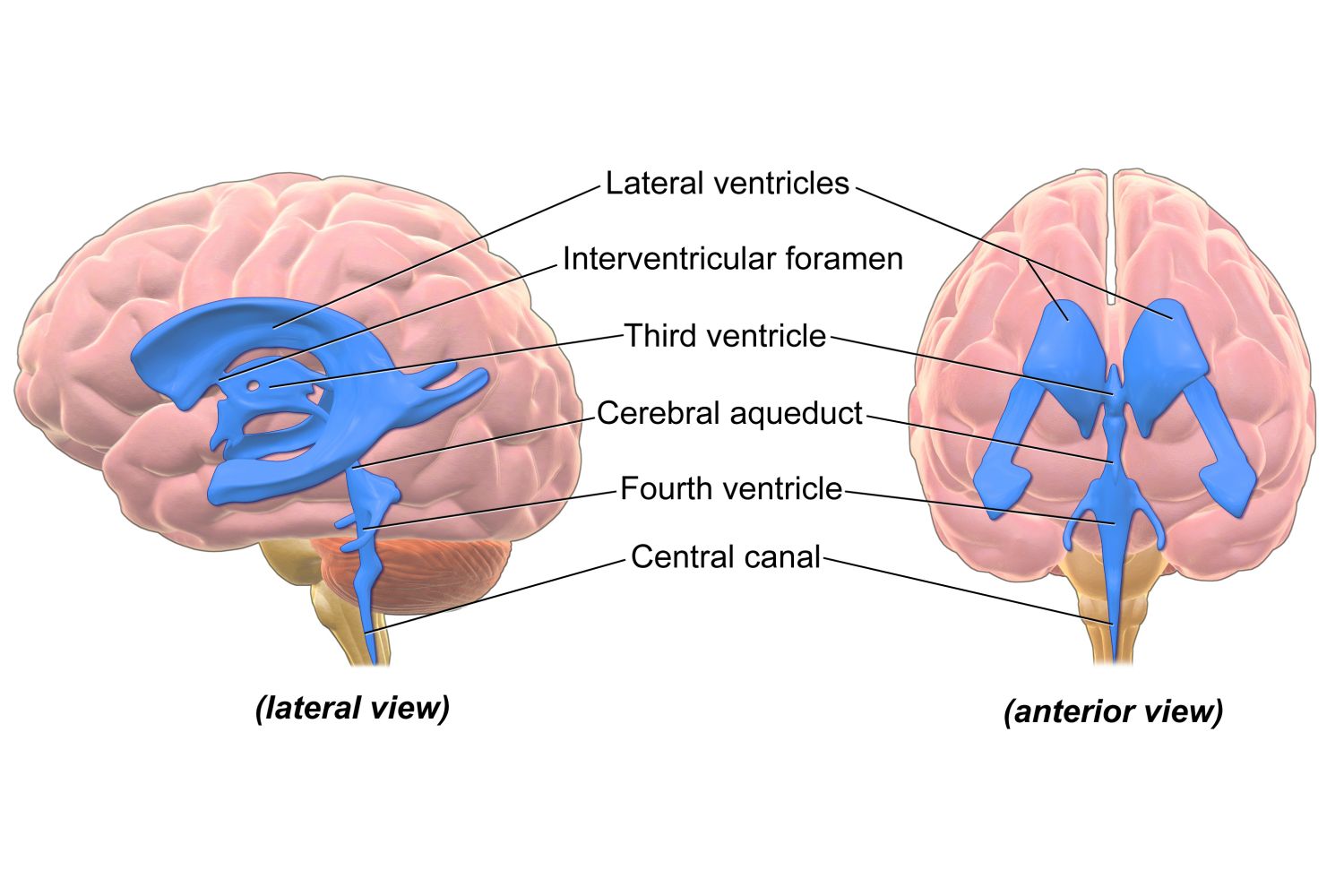
Ventricles
Communicating network of cavities in the brain, helping to keep the brain cushioned and bouyant.
Chomsky
Mountain Experiment
Experiment by Jean Piaget to demonstrate whether a child’s thinking was egocentric (assuming that other people will see things the way that they do).
Little Albert Experiment
An experiment by John B. Watson where a baby was exposed to multiple objects but has conditioned to be extremely afraid of rats by associating the loud sound of a pan with one.