Chapter 2 Biochemistry of Life
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Matter
Anything that takes up space
Element
Substance that can’t be broken down by chemical means into other substances
90% of life consists of
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
Atom
Smallest piece of an element that retains the characteristics of the element
The 3 subatomic particles
Protons, neutrons, electrons
Protons
Positive charge, mass of 1, found in the core
Electrons
Negative charge, no mass, floats around the core
Neutron
No charge, 1 mass, found in core
Atomic number
Number of protons
Charge
P-e
Atomic weight
P+n
Isotope
Atom with different neutrons, affects the weight
Chemicals bonds do what
Link atoms together
Atoms form
Molecules
Valence shell
Outermost shell of an atom
Ion
Charged atom
Cation
Positively charged atom
Full valence shell
Stable, won’t bond
Not full valence shell
Unstable, reactive
Period
Rows, number of electron orbits
Group
Columns, number of valence electrons
the 3 chemical bonds
Nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, ionic
Covalent bond
Each atoms unpaired electrons are shared by both nuclei
Non polar covalent bond
Electrons are evenly shared between 2 atoms, the bond is symmetrical
Polar covalent bond
Electrons are asymmetrically shared
Ionic bond
Electrons are transferred from 1 atom to another
Electronegativity
Measure of an atoms ability to attract electrons, helps determine the type of bond
Period table arranged atoms by electronegativity
Low to high
Elements with similar electronegativities will form
Nonpolar covalent bonds, right
2 elements with moderately different electronegativities will form
Polar covalent bonds, middle
Elements with very different electronegativities will form
Ionic bonds, left
Hydrogen bond
Atom with a partial negative charge attracts a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge. These bonds form between adjacent molecules or between different parts of a large molecule.
Water is
cohesive, adhesive, an excellent solvent, only dissolves selected molecules, regulates temperature, expands when it freezes, has a neutral pH, is necessary for chemical reactions for life
Water is cohesive
this creates high surface tension
Cohesion
tendency of water molecules to stick to one another
surface tension
caused by cohesion between molecules on the surface
Adhesion
water bonds from hydrogen bonds with other molecules
Transpiration
cohesion, adhesion, condensation, evaporation, and surface tension allow water molecules to climb from a trees roots to its leaves
hydrophillic
water loving (polar solutes, ions)
water does what when it freezes
expands
Why does water have unique properties
hydrogen bonds pull water molecules close to eachother
Why is water an excellent solvent
it dissolves hydrophillic substances
hydrophobic
doesnt dissolve (nonpolar)
Excellent solvent for salt
slight negative charge on water attracts positive charges
solution
liquid mixture
solvent
liquid portion
solute
stuff in solvent
Water regulates temperature
it heats and cools slowly (hydrogen bonds make it resist changes in temperature)
ice is
less dense than water
Water has a neutral pH
7
acidic
0-6, more left you go more acidic. Adds H to the solution
Basic
8-14, more right you go more basic. OH exceeds H.
Buffer solution
Helps maintain a constant pH by absorbing and releasing H into a solution
Organic molecule
contains both hydrogen and carbon
(methane, glucose, Carbs, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids)
Water is essential in many chemical reactions
photosynthesis, respiration, dehydration, hydrolysis
Macromolecules
Carbs, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
Monomer
single unit
polymers
multiple monomers
Dehydration synthesis
Joins monomers together
Hydrolysis
breaks polymers apart
Carbohydrates (polysaccharides)
Provide quick energy, simple sugars/monosaccharides
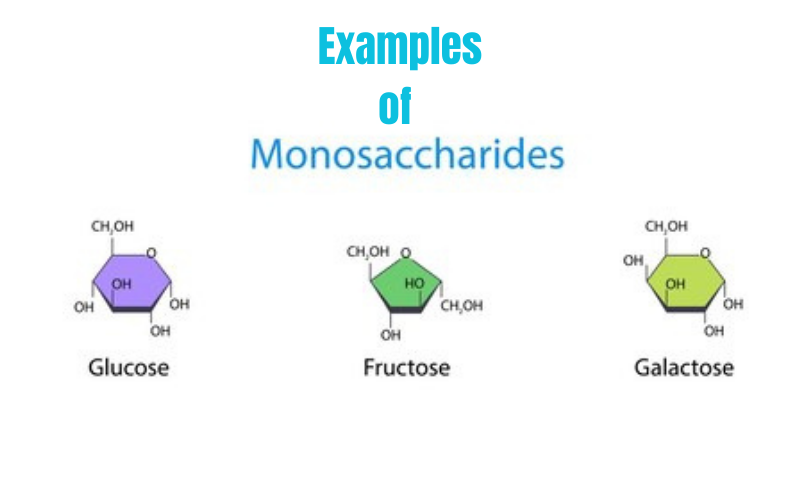
Monosaccharides
simple sugars (ribose, glucose, fructose)
Disaccharides
contain 2 monosaccharides, joined by dehydration synthesis (Lactose and Sucrose)
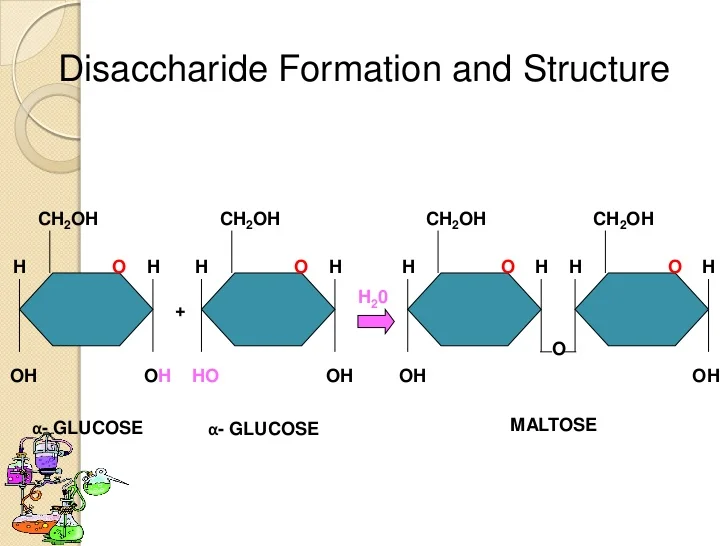
Lactose
composed of galactose and glucose. Found in milk.
Sucrose (carb)
table sugar. Composed of glucose and fructose.
polysaccharides (carbs)
multiple monosaccharides joined together. (starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin, and peptidoglycan)
starch
Carb; provides energy storage in plants
glycogen
protein; provides energy storage in animals
cellulose
Carb; found in cell walls of plants
Chitin
Carb; found in cell walls of fungi and exoskeletons of some animals
Peptidoglycan
Carb; found in cell walls of bacteria
Proteins
Have many different structures of functions. Made of amino acids .
protein structures
defense antibodies, storage (hemoglobin), structural (collagen), transport, contractile (actin and myosin), enzymes
Collagen
Structural protein; creates cellular structures
actin and myosin
produce muscle contractions
Dipeptide
2 amino acids binded together by dehydration synthesis
polypeptide
long chain of amino acids
What determines a proteins function
its shape
Denature
removes its nature, changing the shape of something (irreversible)
5 sugar carbs (pentose)
ribose, deoxyribose
6 sugar carbs (hexose)
glucose, fructose
R groups
each amino acid has its own
Protein primary structure (sequence)
amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
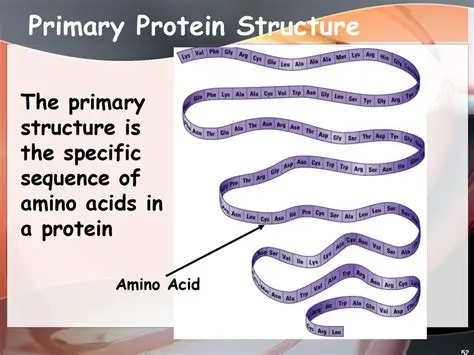
Protein secondary structure (substructure)
Localized areas of coils, sheets, and loops within a polypeptide (amino acids change position to go where they are attracted)
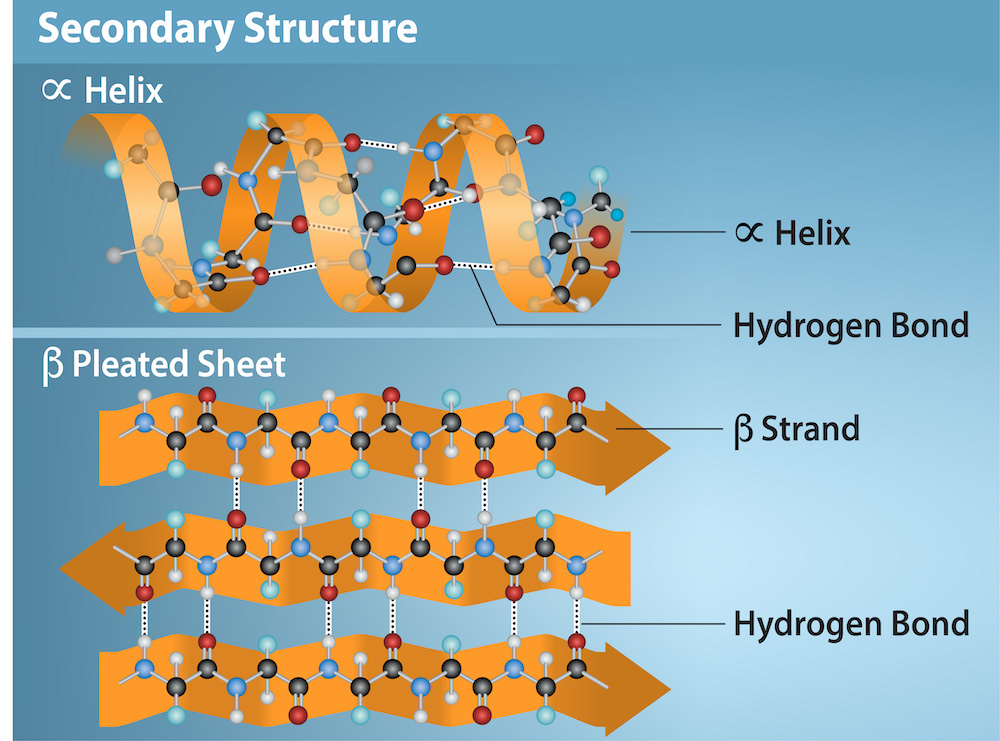
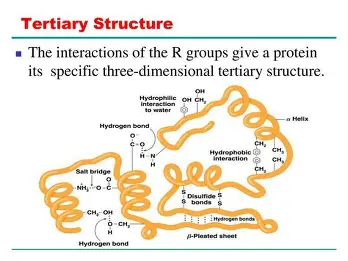
Tertiary structure
overall shape of the protein
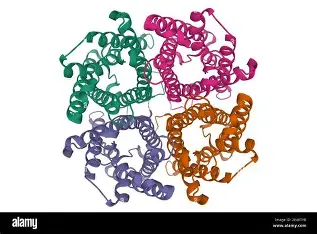
Quaternary structure (protein shape)
overall protein shape of multiple polypeptides all interacting
Lipids
collection of different hydrophobic molecules not built from monomers
Lipids include
fats, oils, phospholipids, steroids, waxes
fats
long term energy storage and insulation in animals
oils
Lipid; Triglyceride; 3 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule; Unsaturated fatty acid; long term energy storage in plants and their seeds
phospholipids
Lipid; derived from triglycerides; has 2 fatty acids attatched to a phosphate group; component of plasma membrane
steroids
Lipid; component of plasma membrane/ sex hormones; ex cholesterol for animals
waxes
Lipid; composed of fatty acids combined with alcohols; protection, prevent water loss
Triglycerides (fats and oils)
3 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule.
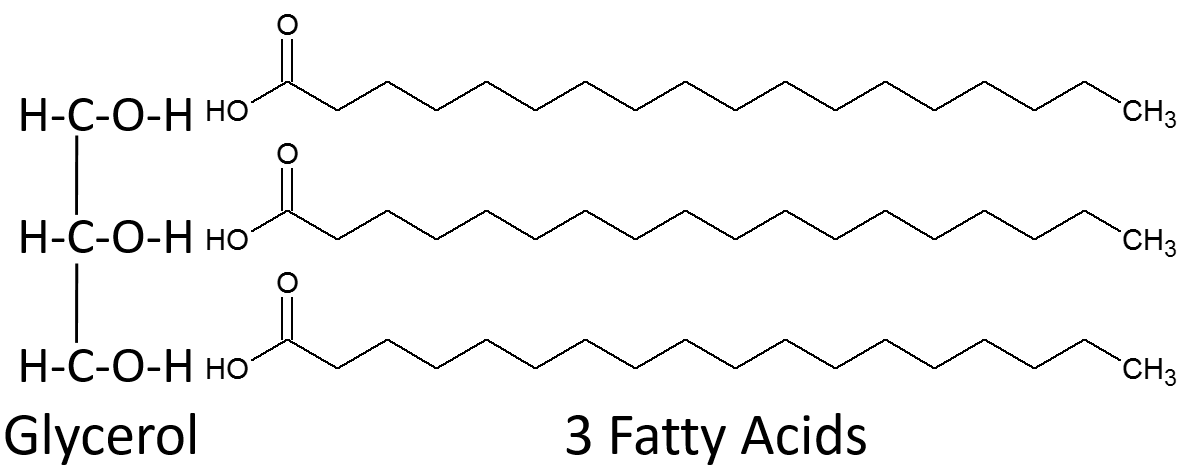
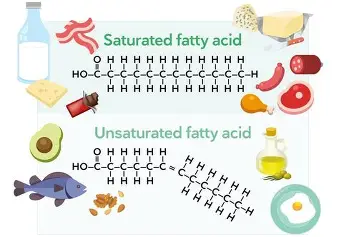
Fatty acids are either
saturated or unsaturated
Unsaturated fats
one or more double bonds between carbons (liquid at room temp)
saturated fats
No double bonds between carbons; solid at room temperature
Phospholipids
derived from triglycerides. 2 fatty acids attached to a phosphate group
Fatty acids are
nonpolar and hydrophobic
phosphate groups are polar and hydrophillic