AP Psychology Ultimate Guide
1/736
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
737 Terms
Psychology
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes.
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to see events as having been predictable after they have already occurred.
Overconfidence
The tendency to overestimate one's abilities, knowledge, or chances of success.
Confirmation Bias
The tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one's preexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
Evolutionary Perspective
A theoretical approach in psychology that examines how human behavior and mental processes have evolved over time, emphasizing the role of natural selection.
Biological Perspective
A viewpoint in psychology that focuses on the physiological and genetic factors that influence behavior, thoughts, and emotions.
Cognitive Perspective
An approach in psychology that emphasizes mental processes such as perception, memory, and problem-solving, exploring how people understand and think about the world.
Humanistic Perspective
A psychological approach that emphasizes personal growth, self-actualization, and the inherent goodness of individuals, focusing on subjective experiences.
Psychodynamic Perspective
A theory in psychology that explores the influence of the unconscious mind and childhood experiences on behavior and personality, often associated with Sigmund Freud.
Behavioral Perspective
A psychological approach that focuses on observable behaviors and the ways they are learned through interaction with the environment, often emphasizing conditioning and reinforcement.
Socio-Cultural Perspective
A psychological approach that examines how cultural and social factors influence behavior, thoughts, and emotions, highlighting the role of societal norms and practices.
Biopsychosocial Perspective
A comprehensive approach in psychology that integrates biological, psychological, and social factors to understand mental health and behavior.
Hypothesis
A testable prediction or statement about the relationship between two or more variables, foundational for scientific research and experimentation.
Falsifiable
A characteristic of a hypothesis that means it can be proven wrong through experimentation or observation.
Operational Definition
A specific and measurable definition of a variable or concept used in research. It outlines how the variable will be manipulated or measured in a study.
Reliability
The consistency of a research study or measuring test, indicating the extent to which results can be replicated over time.
Population
The entire group of individuals or instances about whom researchers seek to draw conclusions, often represented by a sample in studies.
Sample
A subset of individuals selected from a population to participate in a research study, used to represent the larger group effectively.
Convenience Sample
A type of non-probability sample where participants are selected based on their easy availability and proximity to the researcher, rather than through a random selection process.
Representative Sample
A subset of a population that accurately reflects the characteristics of the larger group, often achieved through random selection.
Random Sample
A sampling method where each member of a population has an equal chance of being selected for a study, ensuring that the sample is unbiased and representative.
Peer Review
A process in which scholars evaluate the quality and credibility of each other's research before publication to ensure academic standards are met.
Replication
The process of repeating a study to verify its results and ensure reliability, often used to confirm or refute findings.
Experimental Methodology
A systematic approach used in experiments to test hypotheses by manipulating variables and observing effects, ensuring scientific rigor and validity. Cause and Effect between variables.
Non-Experimental Methodologies
Research methods that do not involve manipulation of variables, such as observational studies, surveys, and case studies, used to explore relationships and gather data.
Case Study
An in-depth examination of a single individual or group to explore complex issues, often used to gather detailed qualitative data.
Correlational Study
A research method that examines the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them, allowing researchers to identify patterns and predict outcomes, but not establish causation.
Naturalistic Observation
A research method where behavior is observed in its natural environment without interference, allowing researchers to gather data on spontaneous actions.
Meta-Analysis
A statistical technique that combines the results of multiple studies to identify overall trends and effects, providing a comprehensive understanding of a particular phenomenon.
Survey
A research method that gathers information from a sample of respondents through questionnaires or interviews, allowing researchers to analyze attitudes, opinions, or behaviors.
Self-Report Bias
A tendency for respondents to provide inaccurate or misleading information about themselves, often due to social desirability or recall issues, which can skew research results.
Social Desirability Bias
The tendency of survey respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others, leading to distorted or biased results.
Quantitative Measurement
A method of measurement that focuses on quantifying variables and obtaining numerical data, often through surveys or experiments, enabling statistical analysis.
Qualitative Measurement
A method of measurement that focuses on understanding qualities or characteristics, often through interviews or open-ended questions, providing rich descriptive data.
Likert Scales
A type of rating scale used to measure attitudes or opinions by asking respondents to indicate their level of agreement or disagreement on a symmetric agree-disagree scale for a series of statements.
Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated or changed in an experiment to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
The variable that is measured or observed in an experiment to assess the impact of the independent variable.
Control Group
A group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment or intervention, allowing for comparison to the group that does.
Experimental Group
The group in an experiment that receives the treatment or intervention being tested, allowing researchers to assess its effects.
Confounding Variable
A variable that influences both the dependent and independent variables, potentially skewing the results of an experiment.
Random Assignment
The process of randomly allocating participants to different groups in an experiment to ensure each group is similar at the start, minimizing bias.
Single-Blind Procedure
A research design where participants are unaware of whether they are in the experimental or control group, reducing bias in their responses.
Double-Blind Procedure
A method where neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving a particular treatment, helping to eliminate bias in experimental results.
Placebo
A substance with no therapeutic effect, often used in control groups to assess the effectiveness of new treatments.
Placebo Effect
The phenomenon where individuals experience real changes in their condition due to their expectations of a treatment, even when given a placebo.
Experimenter Bias
The tendency for researchers' expectations or preferences to influence the outcome of their study, potentially skewing the results.
Correlation
A statistical measure that describes the extent to which two variables are related, indicating how they may change together.
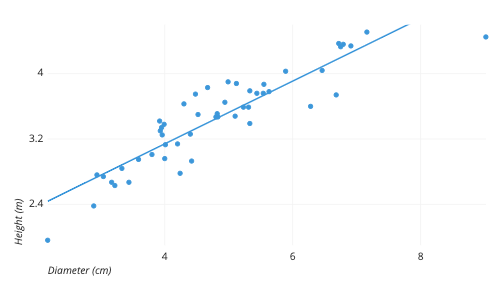
Scatterplots
A graphical representation of two variables that shows the relationship between them, where each point represents an observation in the dataset.
Third Variable Problem
The issue that arises when a third variable influences both variables in a correlation, making it unclear if the relationship between the two variables is direct or due to this external factor.
Directionality Problem
The difficulty in determining the causal direction of a relationship between two correlated variables, as it's unclear which variable influences the other.
Positive vs. Negative (Correlation)
Correlation describes the relationship where increasing values of one variable correspond to increasing (positive) or decreasing (negative) values of another variable.
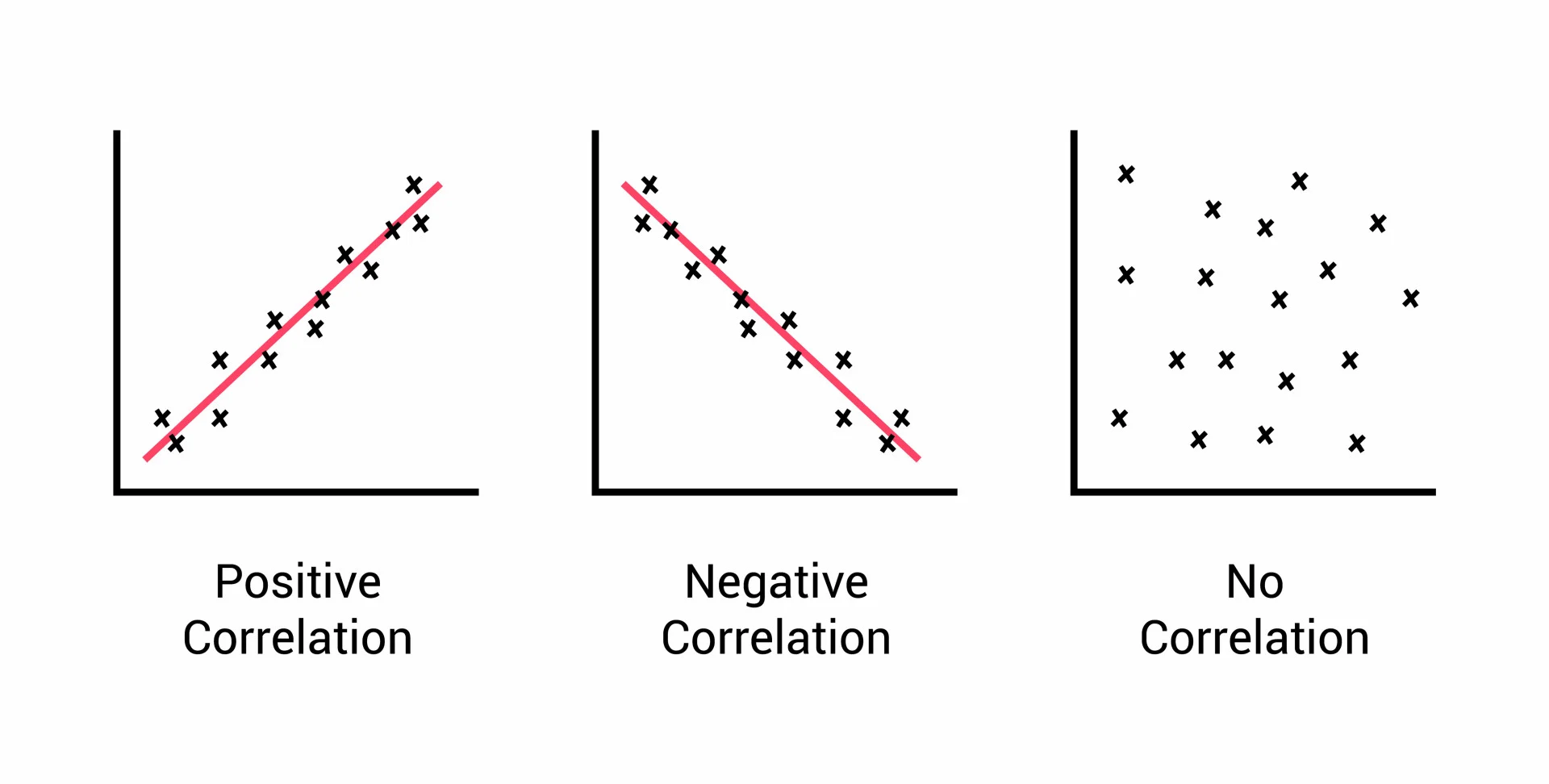
Correlation Coefficients
Numerical values that measure the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables, ranging from -1 to +1.
Illusionary Correlation
The perception of a relationship between two variables when none actually exists, often influenced by cognitive biases.
Measures of Central Tendency
Statistical measures that summarize a set of data by identifying the central point within that data set, commonly including mean, median, and mode.
Mean
The average of a set of numbers, calculated by adding all values and dividing by the total count. It's a measure of central tendency. It is sensitive to outliers, which can skew the result.
Median
The middle value in a data set when the values are arranged in ascending or descending order. It is a measure of central tendency that is less affected by outliers than the mean.
Mode
The value that occurs most frequently in a data set. It is a measure of central tendency that can be used with nominal data.
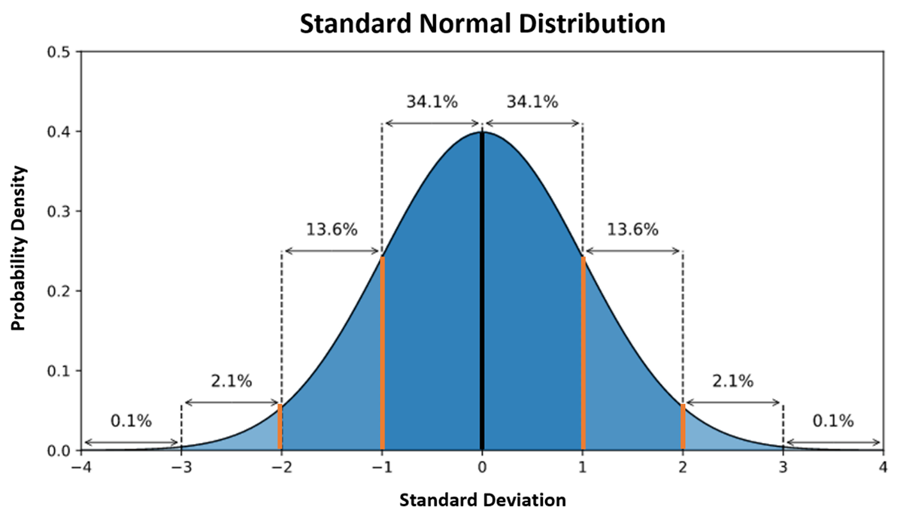
Normal Curve
A graphical representation of a distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showcasing that most values cluster around this central peak and probabilities for values further away from the mean taper off equally in both directions.
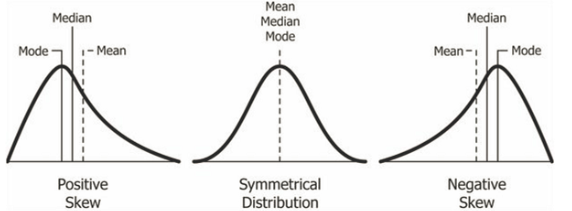
Skewed Distribution
A probability distribution where values are not symmetrically distributed, causing the data to cluster more on one side of the mean than the other.
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest values in a data set, providing a measure of variability.
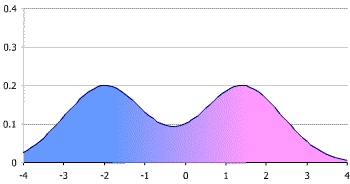
Bimodal Distribution
A probability distribution with two distinct modes or peaks, indicating that the data set has two prevalent values or groups.
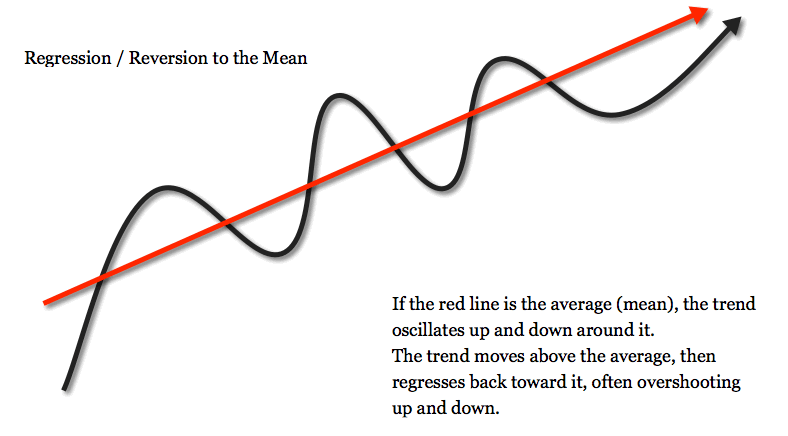
Regression Toward the Mean
The phenomenon where extreme scores on a variable tend to be closer to the average on subsequent measurements, showing a statistical tendency toward the mean.
Measures of Variation
Statistics that describe the spread or dispersion of a data set, including range, variance, and standard deviation.
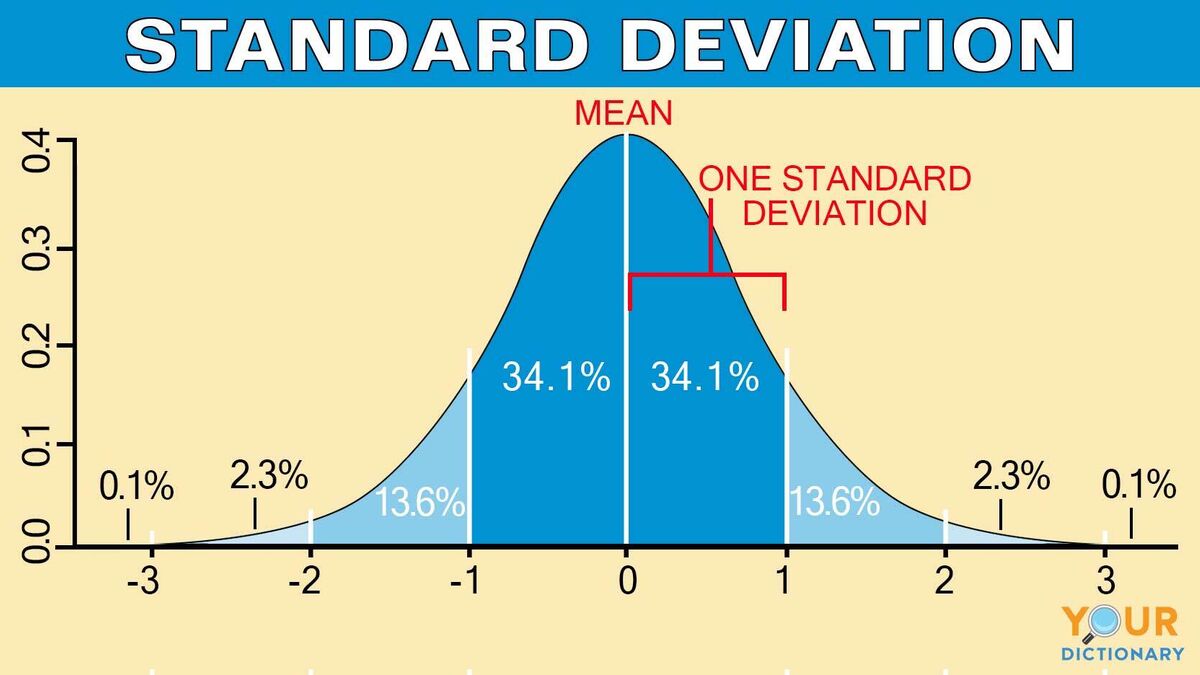
Standard Deviation
A measure that quantifies the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values, indicating how spread out the numbers are from the mean.
Statistical Significance
The likelihood that a result or relationship is caused by something other than mere chance. In psychology, it is typically evaluated using a p-value to determine if findings are meaningful. A commonly used threshold for statistical significance is p < 0.05, meaning the data is unlikely to occur more than 5% of the time under the null hypothesis.
Generalizability
The extent to which research findings can be applied to settings, people, or situations beyond the specific study sample. It assesses how well the results of a study can inform broader conclusions.
Percentile Rank
The measurement of a score's position within a distribution, indicating the percentage of scores that fall below it. For example, a percentile rank of 90 means that 90% of the scores are below that score.
Effect Size
A quantitative measure of the magnitude of a phenomenon or the strength of a relationship in research. It helps to determine the practical significance of findings beyond just statistical significance.
Institutional Review Board
A committee that reviews research proposals to ensure ethical standards are met, protecting the welfare of participants.
Informed Consent
The process of obtaining approval from participants before they engage in research, ensuring they are fully aware of the study's purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits.
Informed Assent
A process similar to informed consent, but specifically involving minors or individuals unable to give full consent, ensures their understanding and agreement to participate in research.
Confidentiality
The ethical principle that requires researchers to keep participants' information private and secure, ensuring that their identities are not disclosed.
Protection from Harm
An ethical guideline in research mandates that researchers to minimize any potential physical or psychological risks to participants, ensuring their well-being during and after the study.
Debriefing
A process following research participation where researchers inform participants about the study's purpose, methods, and any deception involved, allowing for questions and ensuring understanding.
Research Confederates
Individuals who are part of a study but act as though they are participants to manipulate or observe the behavior of genuine participants without their knowledge.
Avoiding Deceit
An ethical principle in research that emphasizes transparency and honesty, ensuring that participants are not misled about the nature of the study and its procedures, unless deception is justified by significant scientific value.
Nature
The inherent characteristics or fundamental qualities of a phenomenon, often contrasted with nurture, indicating the biological aspects that influence behavior and traits.
Nurture
The environmental factors and experiences that shape individual behavior and traits, often contrasted with nature, referring to biological influences.
Heredity
The genetic transmission of traits from parents to offspring, influencing physical characteristics and psychological attributes.
Environment
The surrounding conditions, circumstances, and influences that impact an individual's development and behavior, often contrasting with heredity.
Natural Selection
The process through which certain traits increase in a population due to individuals with those traits being more likely to survive and reproduce in their environment, leading to evolutionary changes over time.
Eugenics
A social philosophy advocating the improvement of human genetic traits through selective breeding and sterilization. It has a controversial history associated with unethical practices.
Research Studies (Twins, Adoption, Family)
Scientific investigations that explore the influences of genetics and environment on behavior by comparing similarities and differences among twins, adopted individuals, and family members.
Central Nervous System
The part of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information and coordinating activity throughout the body.
Peripheral Nervous System
The part of the nervous system that includes all the nerves outside the central nervous system, connecting the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. It is responsible for relaying information between the central nervous system and limbs or organs.
Autonomic Nervous System
The part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
Somatic Nervous System
The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movements by transmitting signals from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles. It is responsible for activities such as walking, talking, and other movements that require conscious control.
Sympathetic Nervous System
A division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations, often referred to as the "fight or flight" response.
Neurons
The basic building blocks of the nervous system, neurons are specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body, playing a crucial role in communication between the brain and other body parts.
Glial Cells
Specialized cells in the nervous system that support, protect, and maintain neurons, involved in various functions such as nutrient transfer and waste removal.
Depolarization
The process by which a neuron's membrane potential becomes less negative, leading to the generation of an action potential.
All-or-Nothing Principle
The principle stating that a neuron either fires an action potential fully or does not fire at all, regardless of the strength of the stimulus.
Sensory Neurons
Neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system, allowing for perception of stimuli such as sight, sound, and touch.
Interneurons
Neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons within the central nervous system, playing a crucial role in reflexes and complex processing.
Resting Period
The state in which a neuron is not actively firing an action potential, characterized by a negative internal electrical charge relative to the outside.
Myasthenia Gravis
An autoimmune disorder that leads to weakness in skeletal muscles. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the communication between nerves and muscles, impairing muscle contraction.
Motor Neurons
Neurons that transmit signals from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles to facilitate movement.
Reflex Arc
The neural pathway that mediates a reflex action, consisting of a sensory neuron, an interneuron (in some cases), and a motor neuron, enabling quick responses to stimuli without direct involvement of the brain.
Reuptake
The process by which neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron after being released into the synaptic cleft, terminating the signal between neurons.
Multiple Sclerosis
A chronic autoimmune disorder affecting the central nervous system, characterized by the degeneration of myelin sheaths surrounding neurons, leading to impaired communication between the brain and the rest of the body.