Introduction to Medical Devices, Physical Agents and Safety Culture
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Health Technology definition
An intervention developed to prevent, diagnose or treat medical conditions; promote health; provide rehabilitation; or organize healthcare delivery
Intervention definition
a medical test, medical device, pharmaceutical, biologic (e.g., vaccine), procedure, program or system
Biology
Biologics - vaccines
Chemistry
Pharmaceuticals
Physics
Medical Devices
Physical Agents example
sources of energy such as x-rays, magnetic fields, laser, UV sources, electricity etc.
medical device role
Protection from deleterious effects of associated Physical Agents
Medical Physicists role
act as a knowledge transfer bridge between medical device providers / medical device research literature and the medical and healthcare professions
Medical device definition
any instrument, apparatus, appliance, software, implant, reagent, material or other article intended by the manufacturer to be used, alone or in combination, for human beings for one or more of the following specific medical purposes
specific medical purposes (7)!!
- diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, prediction, prognosis, treatment or alleviation of disease
- diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, alleviation of, or compensation for, an injury or disability
- investigation, replacement or modification of the anatomy or of a physiological or pathological process or state
- providing information by means of in vitro examination of specimens derived from the human body, including organ, blood and tissue donations
- which does not achieve its principal intended action by pharmacological, immunological or metabolic means, in or on the human body, but which may be assisted in its function by such means.
- devices for the control or support of conception;
- products specifically intended for the cleaning, disinfection or sterilisation of devices
Regulations definition
binding legal force throughout every Member State and enter into force on a set date in all the Member States
Directives definition
lay down certain results that must be achieved but each Member State is free to decide how to transpose directives into national laws.
Decisions definition (2)
- EU laws relating to specific cases and directed to individual or several Member States, companies or private individuals.
- binding upon those to whom they are directed
Recommendation definition (2)
- not binding
- allows the institutions to make their views known and to suggest a line of action without imposing any legal obligation on those to whom it is addressed.
Opinion definition (2)
- not binding
- instrument that allows the institutions to make a statement without imposing any legal obligation on those to whom it is addressed.
type of EU Legal Acts (5)
- regulation
- directive
- decision
- recommendation
- opinion
active device definition
any device, the operation of which depends on a source of energy other than that generated by the human body
implantable device definition (2/4)
1. any device (also partially or wholly absorbed) which is intended:
- to be totally introduced into the human body
- to replace an epithelial surface or the surface of the eye, by clinical intervention and which is intended to remain in place after the procedure
2. Any device intended to be partially introduced into the human body by clinical intervention and intended to remain in place after the procedure for at least 30 days
invasive device definition
any device which, in whole or in part, penetrates inside the body, either through a body orifice or through the surface of the body
in vitro diagnostic medical device definition
any medical device which is a reagent, reagent product, calibrator, control material, kit, instrument, apparatus, piece of equipment, software or system, whether used alone or in combination, intended by the manufacturer to be used in vitro for the examination of specimens, including blood and tissue donations, derived from the human body, solely or principally for the purpose of providing information
in vitro purpose of providing information about:
- concerning a physiological or pathological process or state
- concerning congenital physical or mental impairments
- concerning the predisposition to a medical condition or a disease
- to determine the safety and compatibility with potential recipients
- to predict treatment response or reactions
- to define or monitoring therapeutic measures
- Specimen receptacles
Specimen receptacles definition
a device, whether of a vacuum-type or not, specifically intended by its manufacturer for the primary containment and preservation of specimens derived from the human body for the purpose of in vitro diagnostic examination
Basic Devices (In vivo Diagnosis - physiological med. dev.) (2)
- Thermometers
- blood pressure monitors
Cardiology Devices (In vivo Diagnosis - physiological med. dev.) (4)
ECG (electrocardiograph)
Doppler flowmeters
Doppler ultrasound
exercise stress testing
Neurophysiology Devices (In vivo Diagnosis - physiological med. dev.) (2)
EEG (electroencephalograph)
EMG (electromyograph)
Gastrointestinal Devices (In vivo Diagnosis - physiological med. dev.) (2)
electrogastrograph (an ECG for the stomach!)
naso-gastric sensors
naso-gastric sensors role
measure pH to assess gastro-oesophageal reflux
Audiometry Devices (In vivo Diagnosis - physiological med. dev.)
measurements of hearing
Optometry Devices (In vivo Diagnosis- physiological med. dev.)
measurements of vision
Respiratory physiology Devices (In vivo Diagnosis- physiological med. dev.) (2)
spirometers
pulse oximetry
Urodynamics Devices (In vivo Diagnosis - physiological med. dev.) (2)
uroflowmeter
cystometrograph
cystometrograph role (CMG)
measures bladder capacity, bladder pressure, how full bladder is before you feel the urge to urinate
uroflowmeter role
measures the amount of urine and flow rate
Diagnostic Radiology (in vivo Diagnosis) (6)
X-ray projection imaging (XRI)
Computerised Tomography (CT)
Ultrasound
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Thermography
Medical image processing software
endoscopy definition
visual examination of a body cavity or canal using a specialized lighted instrument (endoscope)
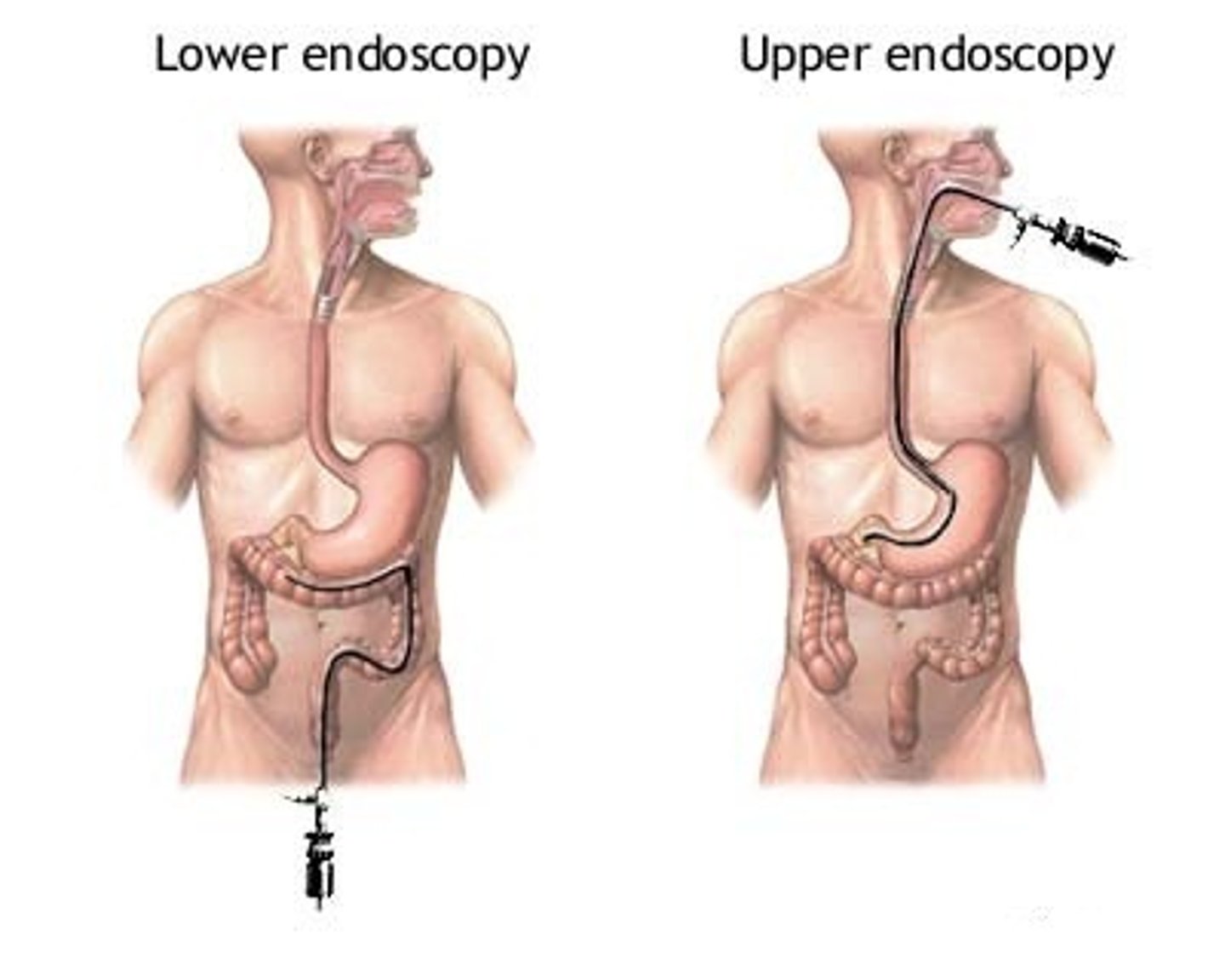
capsule endoscopy definition
examination of the small intestine made by a tiny video camera placed in a capsule and then swallowed as traditional endoscopy cannot completely access the small intestine because of its length and complexity

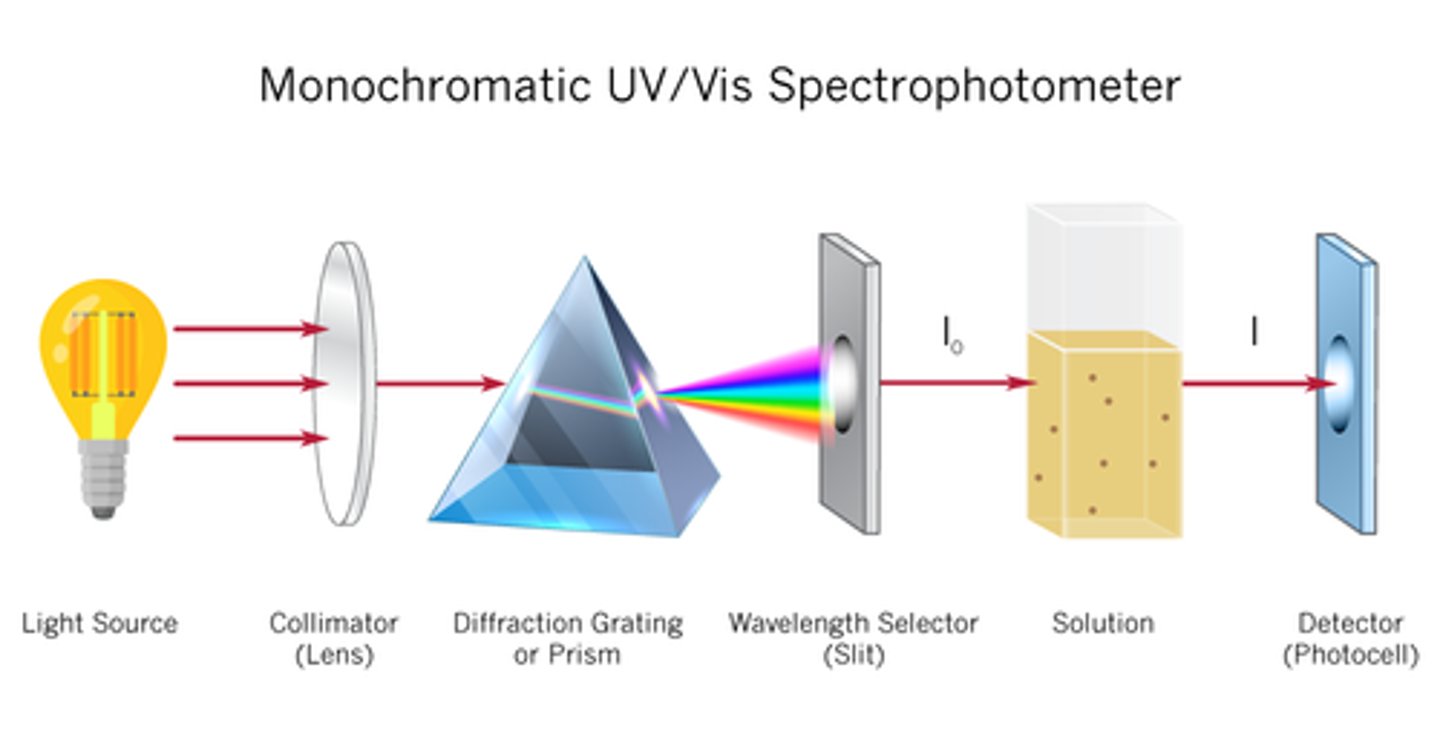
Spectrophotometers (UV, VIS, IR) definition
measurement of concentrations (fx.: blood to see the amount of bilirubin, haemoglobin, and glucose in the serum of blood)
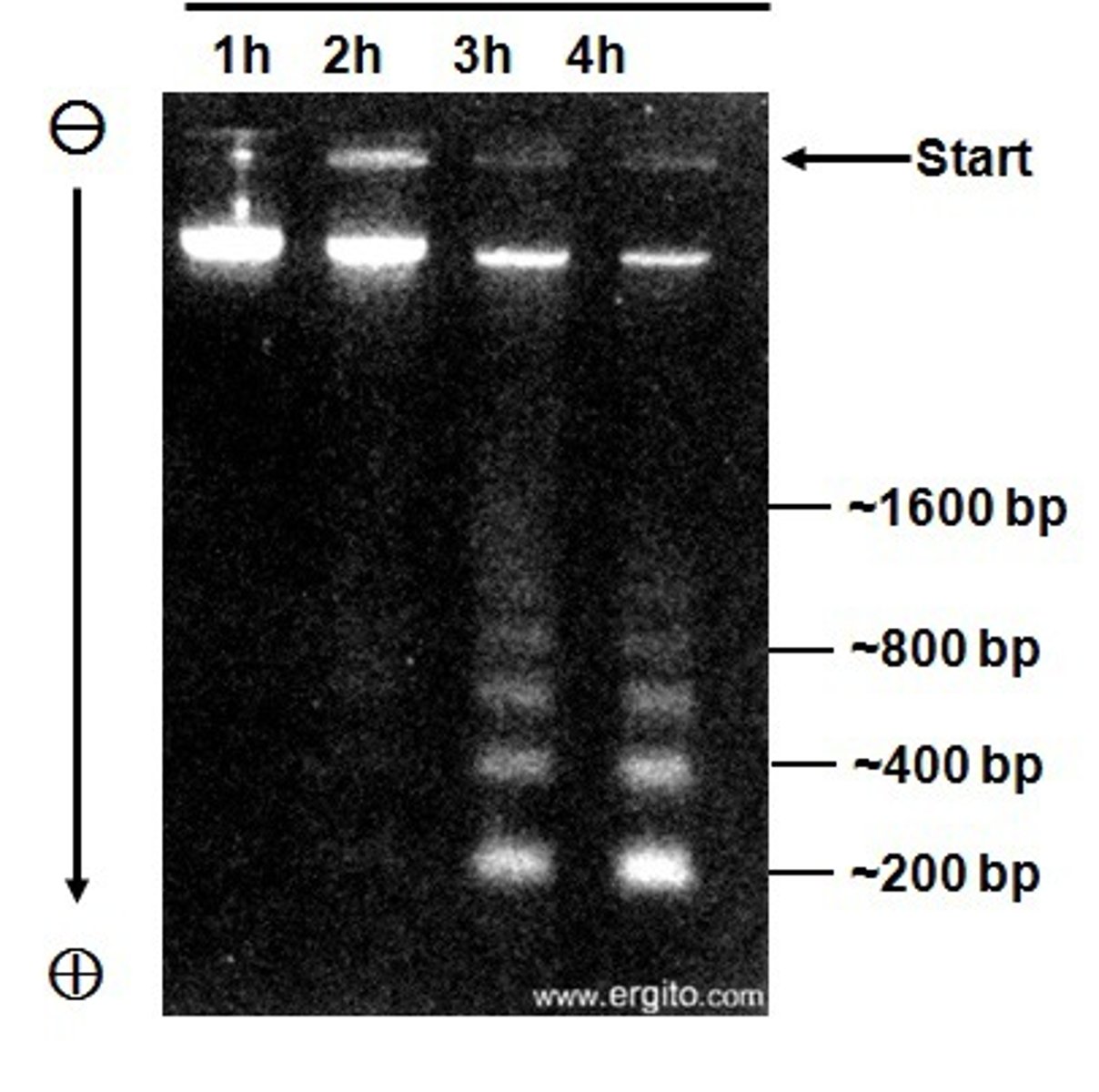
Electrophoresis definition
a technique by which molecules are separated and measured (fx.: proteins, DNA, or RNA fragments)
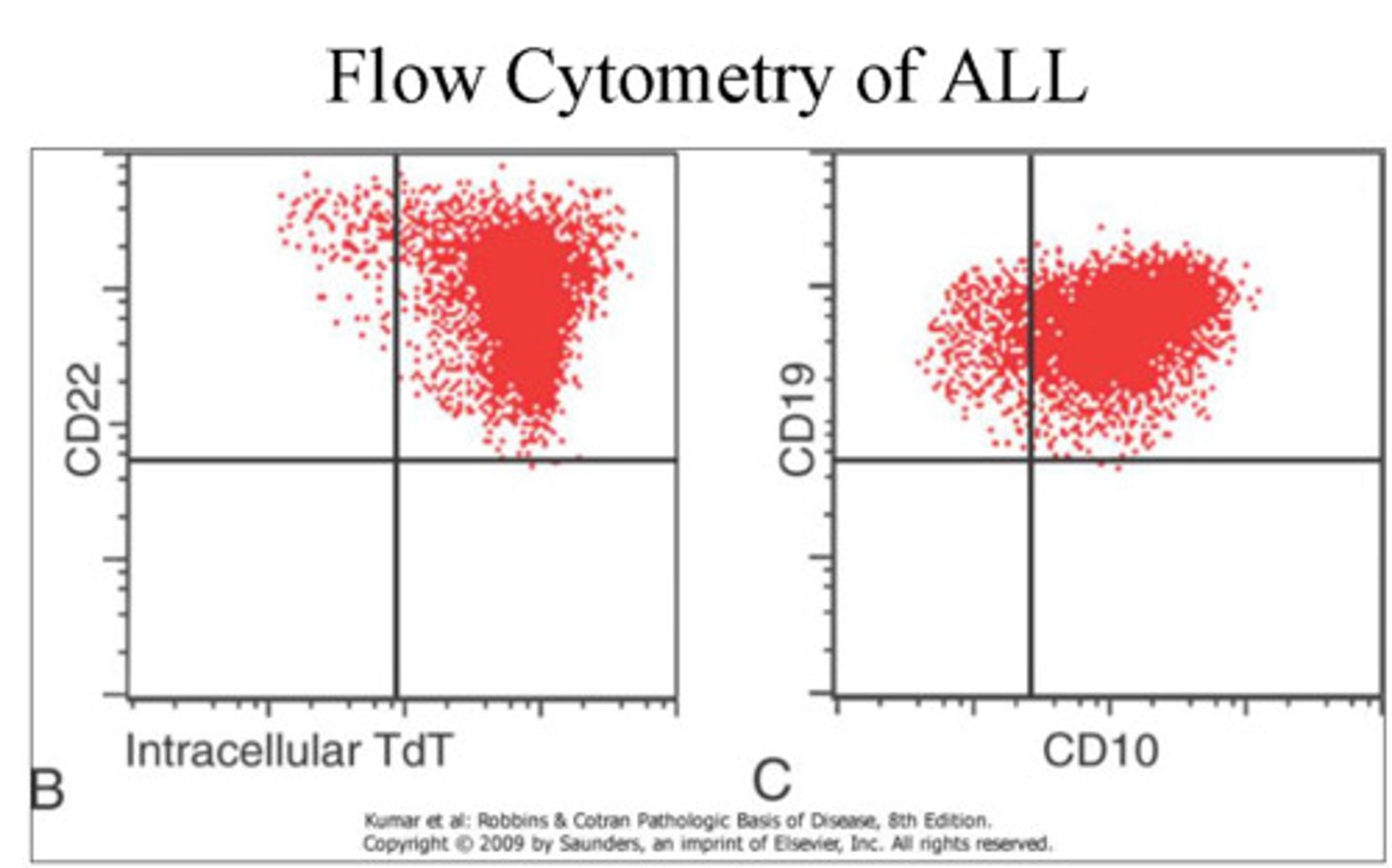
Flow cytometry definition
a technique for counting cells suspended in fluid as they flow past a light beam
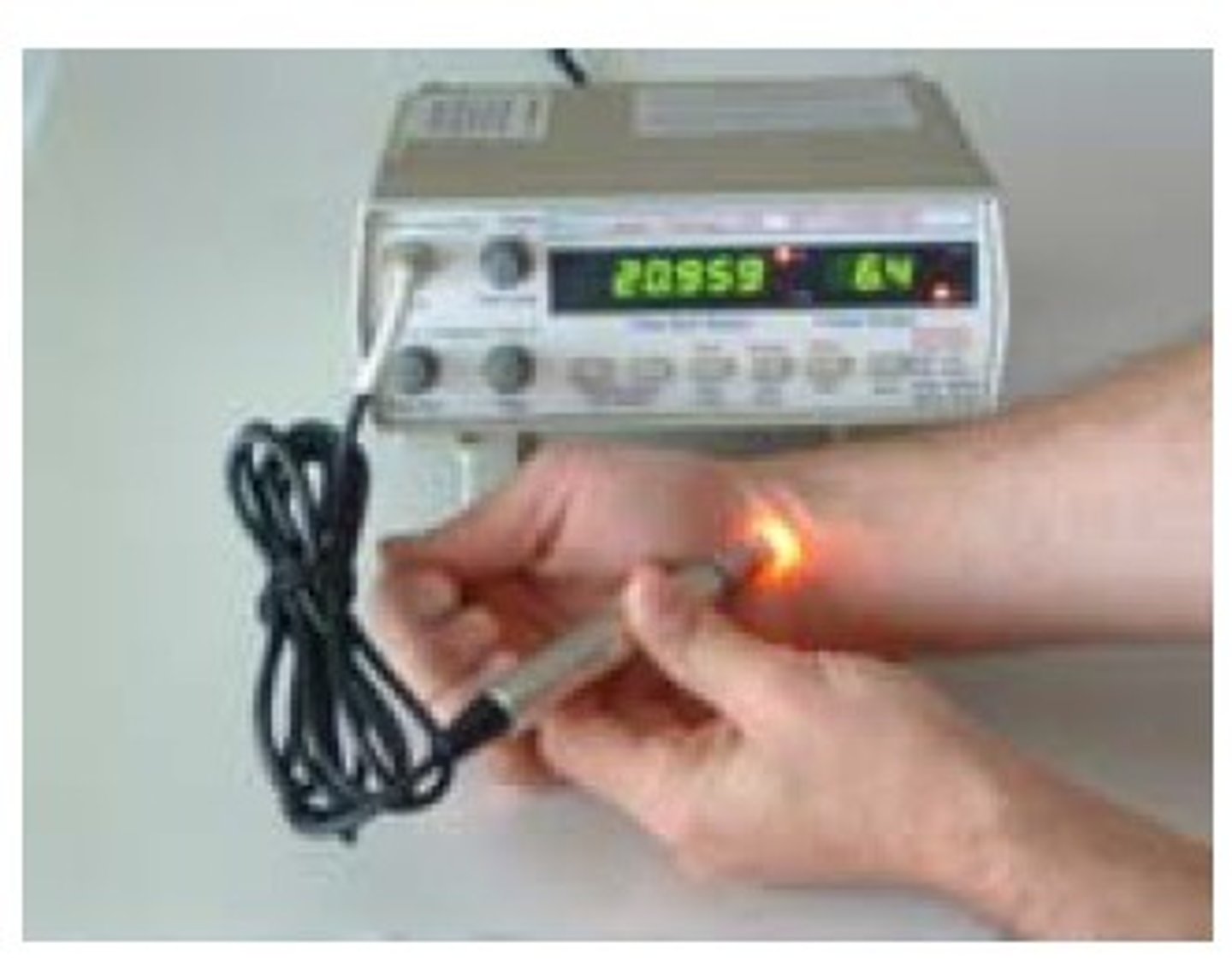
pH / ISE meters definition
ion selective electrode for measuring ion concentrations
Medical Laboratory Devices (5)
- Spectrophotometers
- Electrophoresis
- Flow cytometry
- pH / ISE meters
- Medical microscopes
Drug Delivery Devices (Therapy)
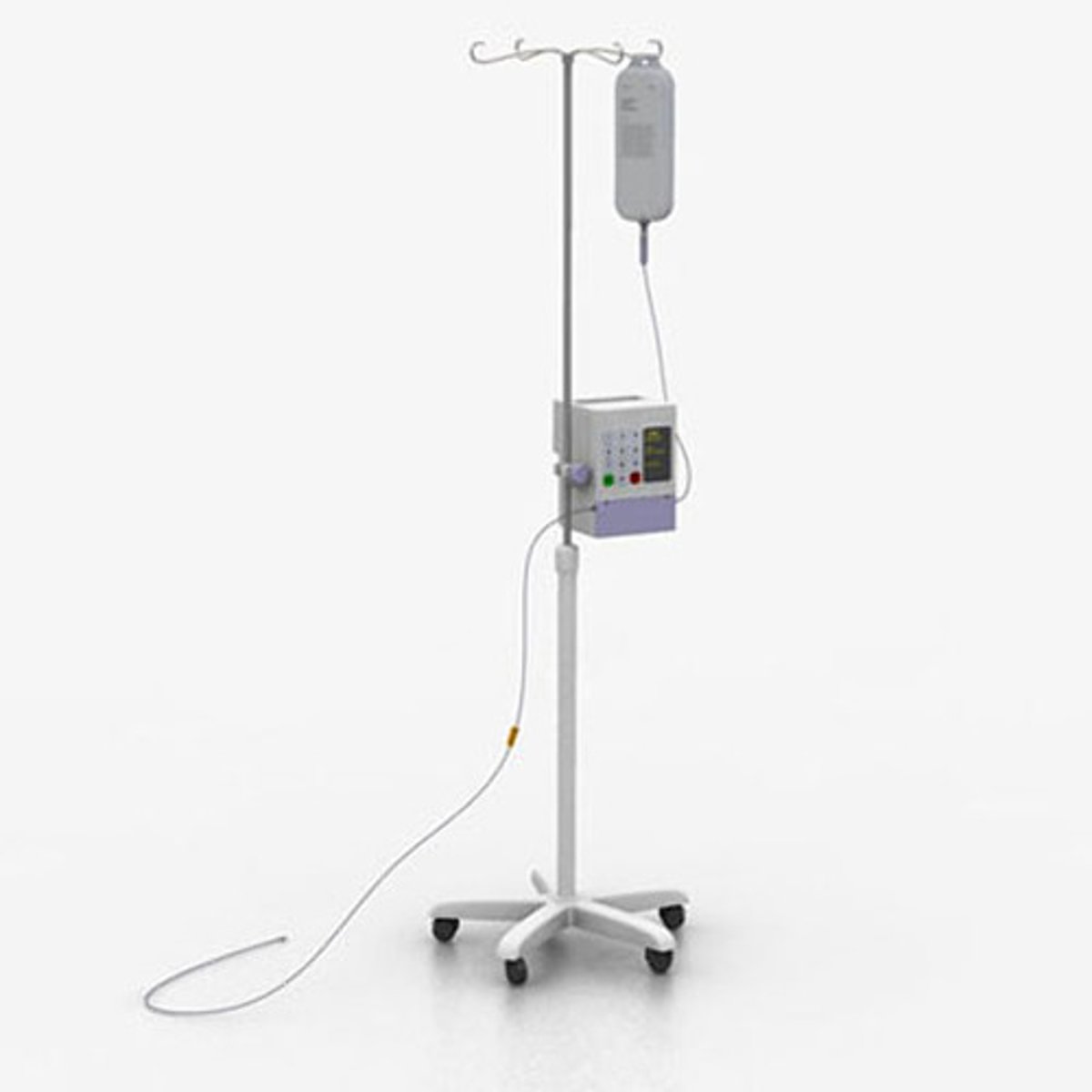
Infusion pumps
syringe driver (a small infusion pump)
Physiotherapy Devices (Therapy) (5)
UV and IR therapy
Shortwave diathermy
Ultrasound therapy
Laser therapy (wound treatment: faster healing, pain relief)
Muscle stimulator
laser therapy
wound treatment: faster healing, pain relief

Shortwave diathermy
SWD
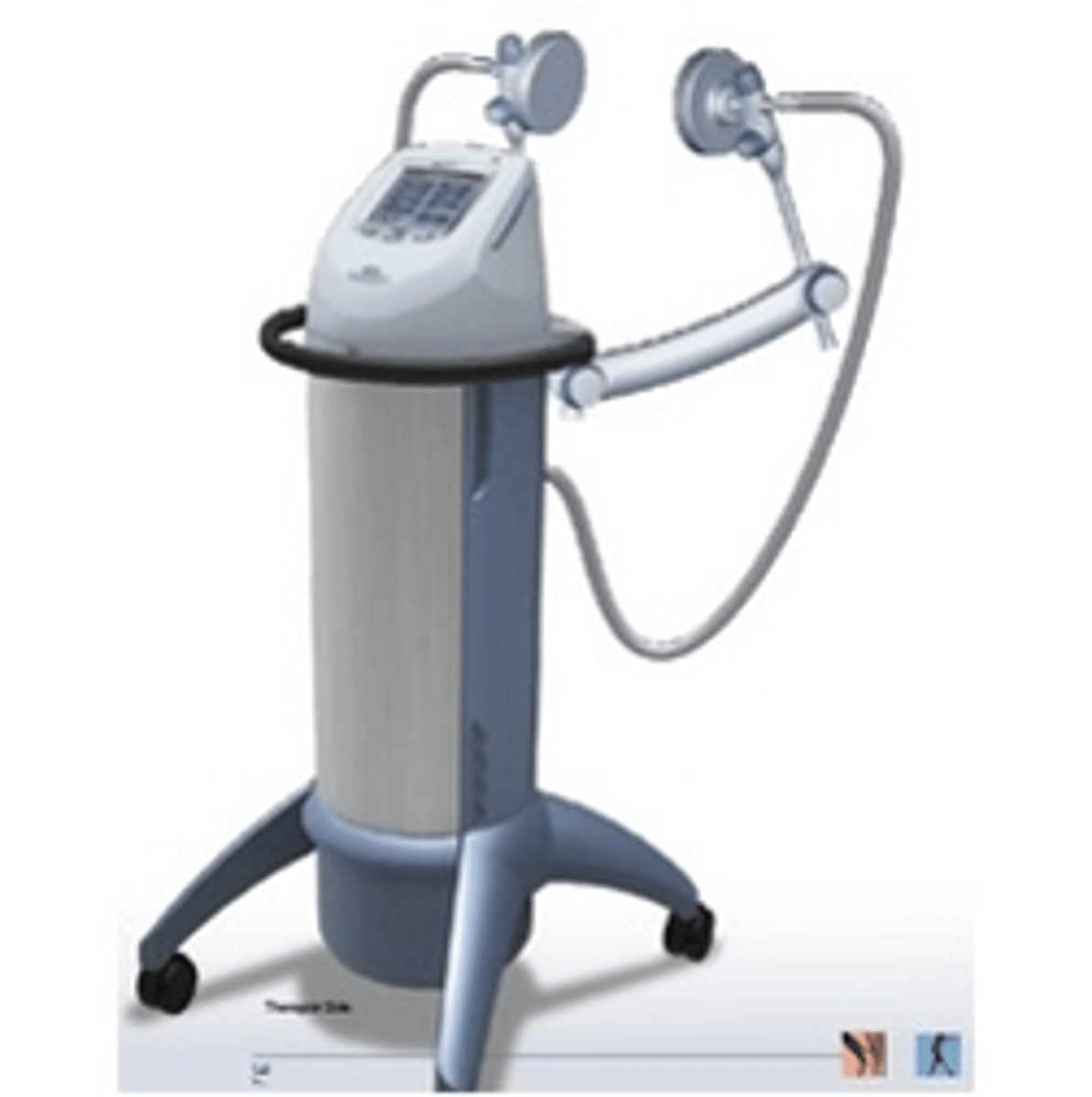
Ultrasound therapy
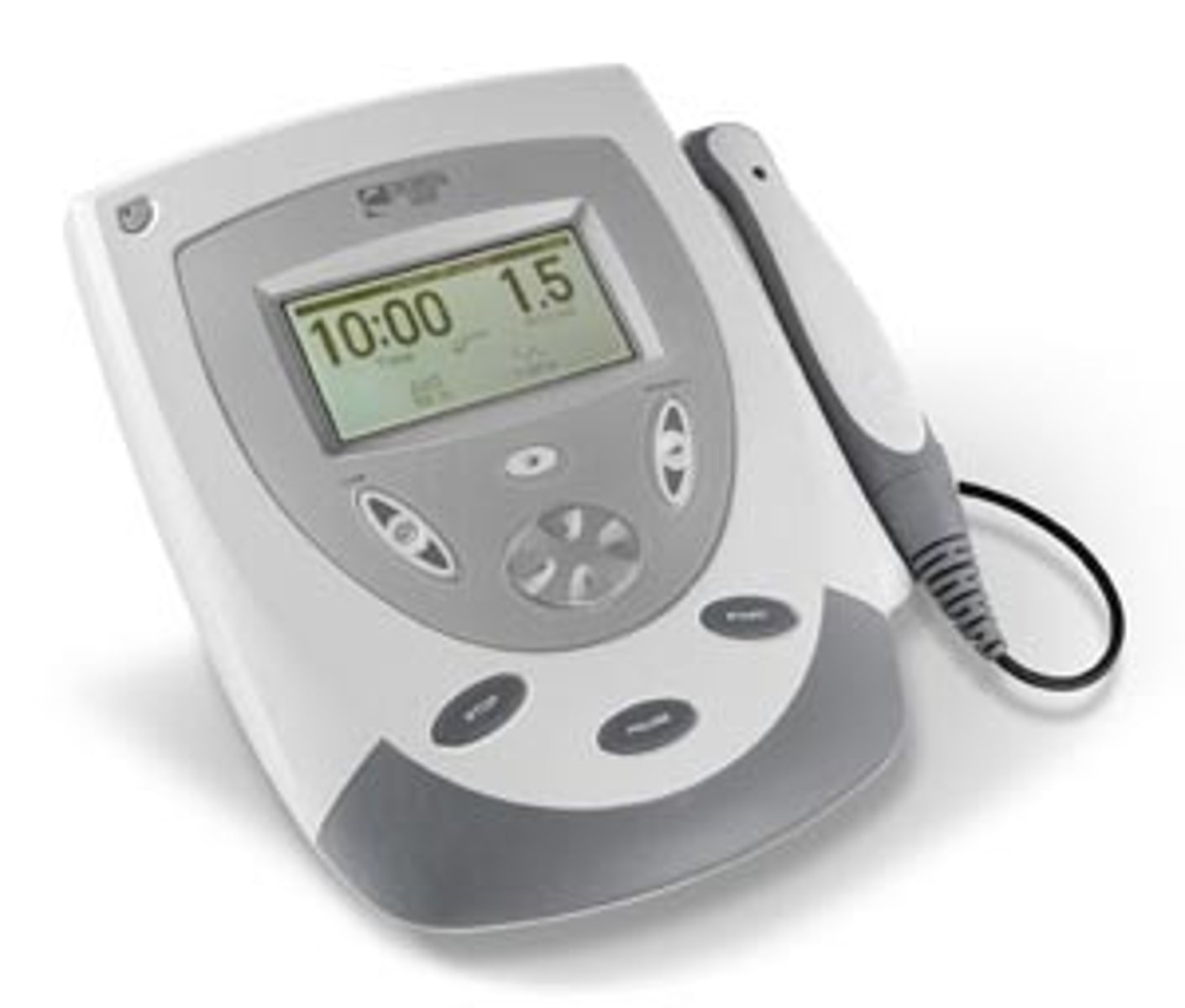
Muscle stimulator
creates steady electric impulses that stimulate muscle contractions
syringe driver
a motorized device that injects medication/drugs into the body
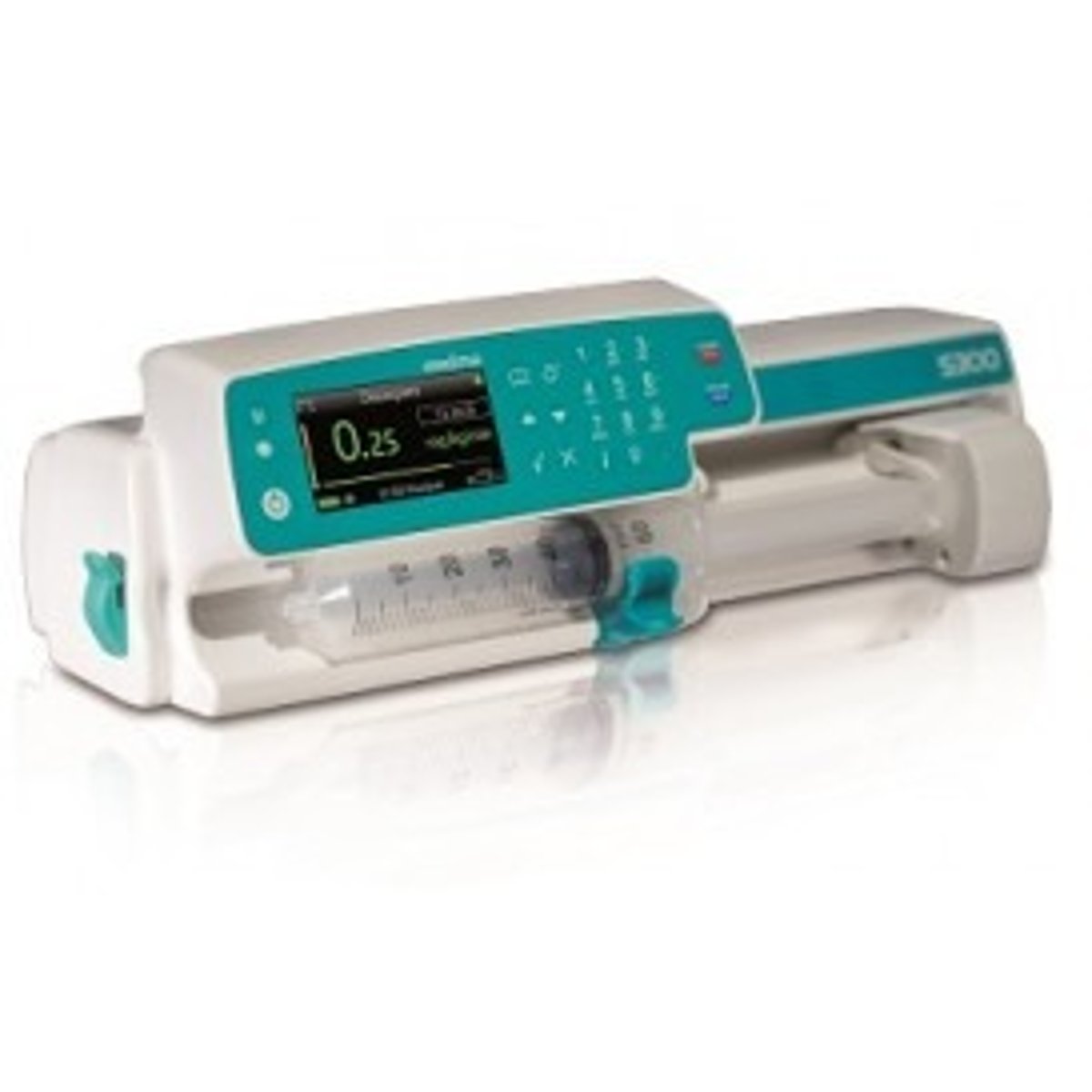

Infusion pumps
regulate the flow of medication into a patient
Surgical Theatre Devices
devices used in surgical field - clamp, light etc
Prosthetic Devices
artificial replacements for human machine

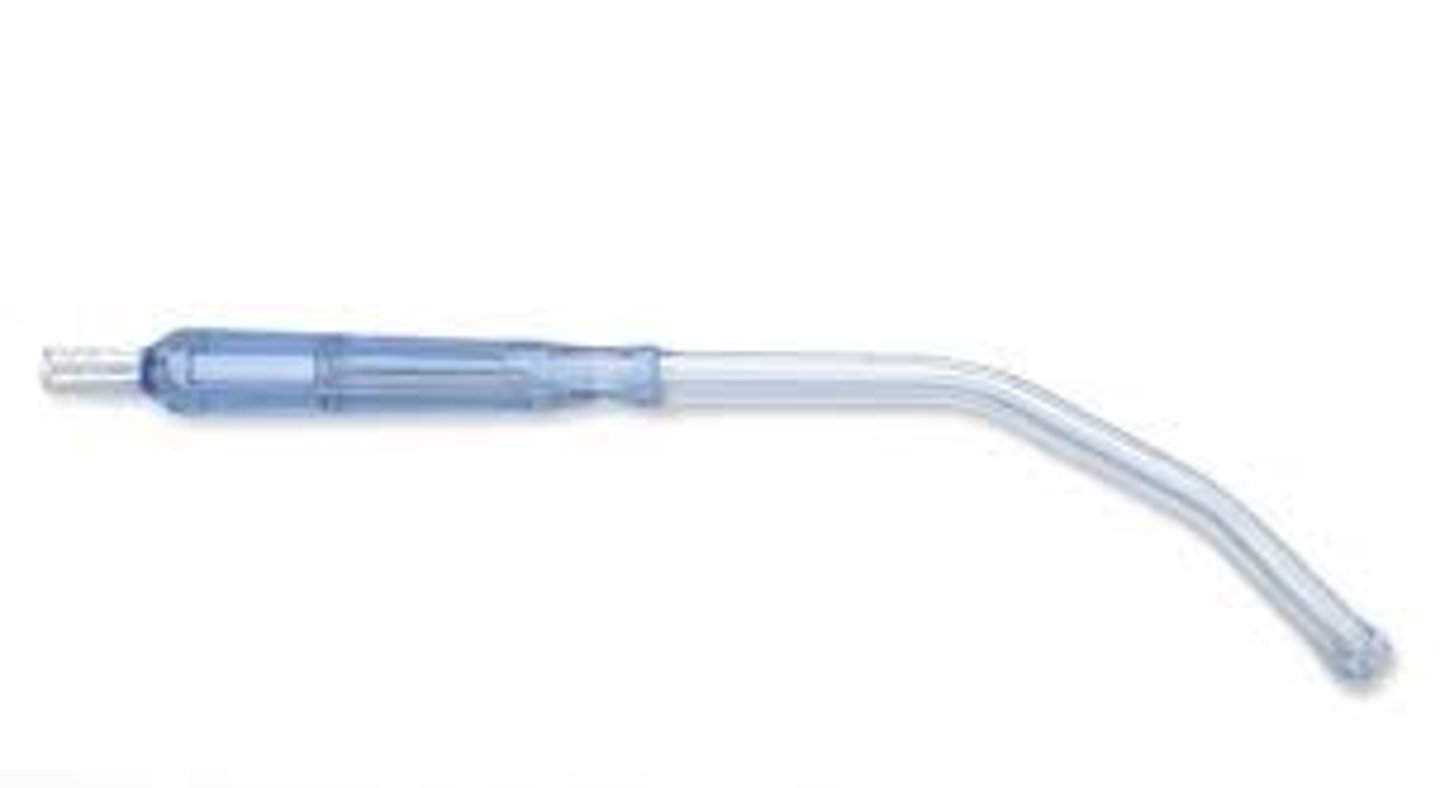
Disposable Medical Devices examples (3)
Suction catheter
I.V. cannula
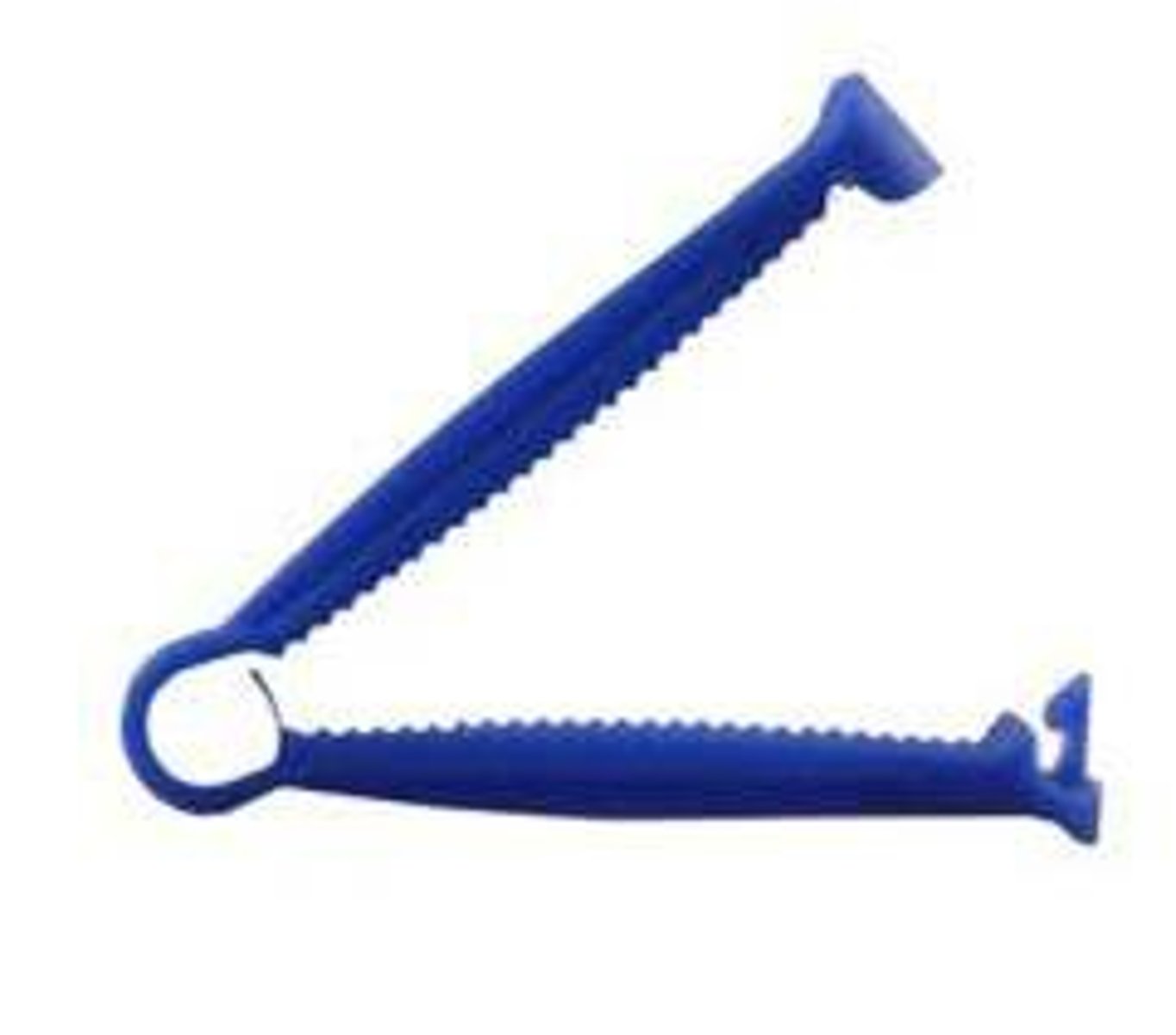
Umbilical cord clamp
Suction catheter

IV cannula
Umbilical cord clamp

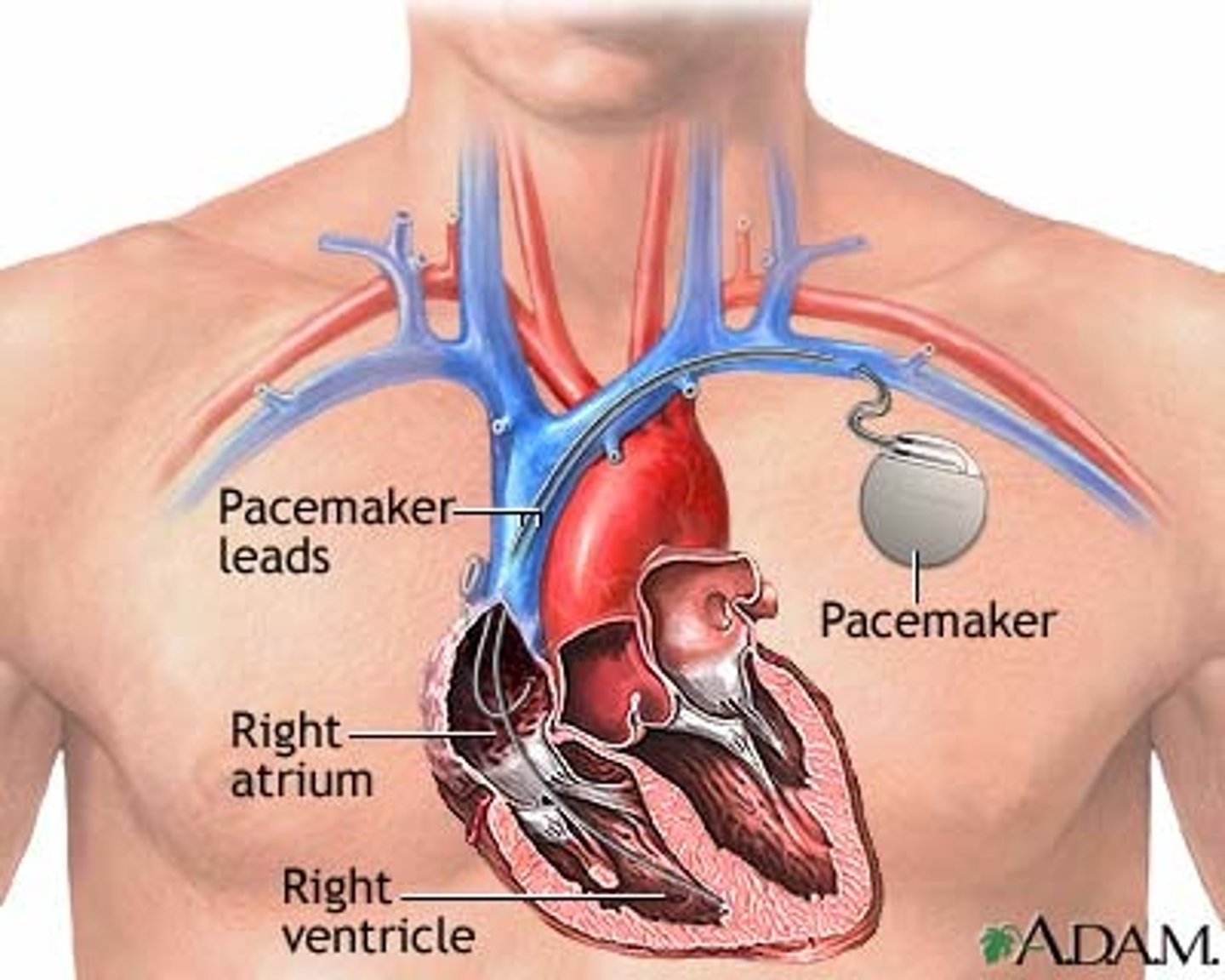
Pacemaker
delivers electrical impulses to heart to regulate heart rate
- lead fed through vein to right atrium
- detect missed heartbeat
cardiac defibrillator
An external or implantable device that provides an electric shock to the heart to restore a normal sinus rhythm.
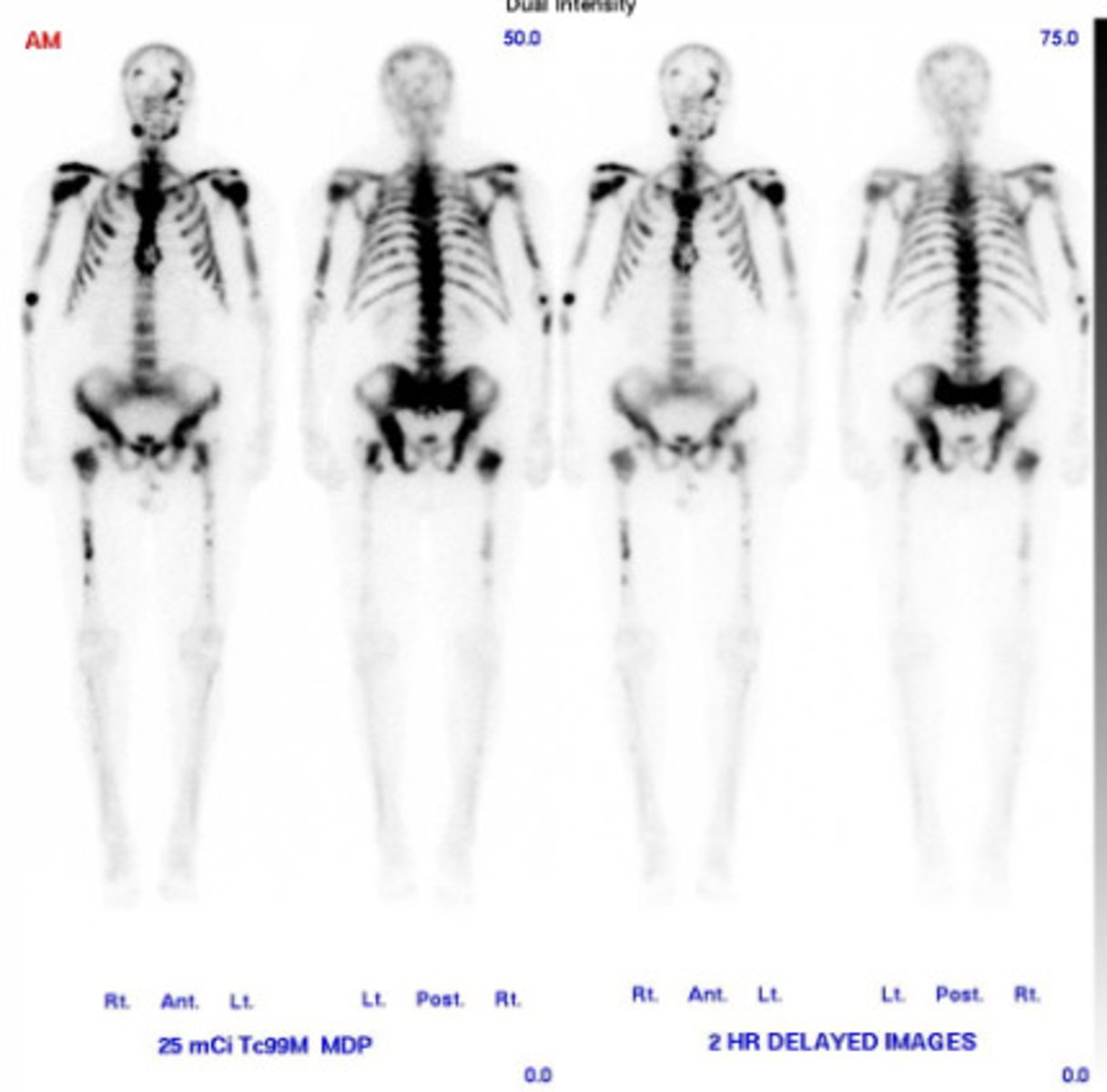
Nuclear Medicine
Uses radioactive materials either to image a patient's body or to destroy diseased cells
Thyroid gland location and structure
made up of two halves (2 tyroid cell) on the side of the trachea
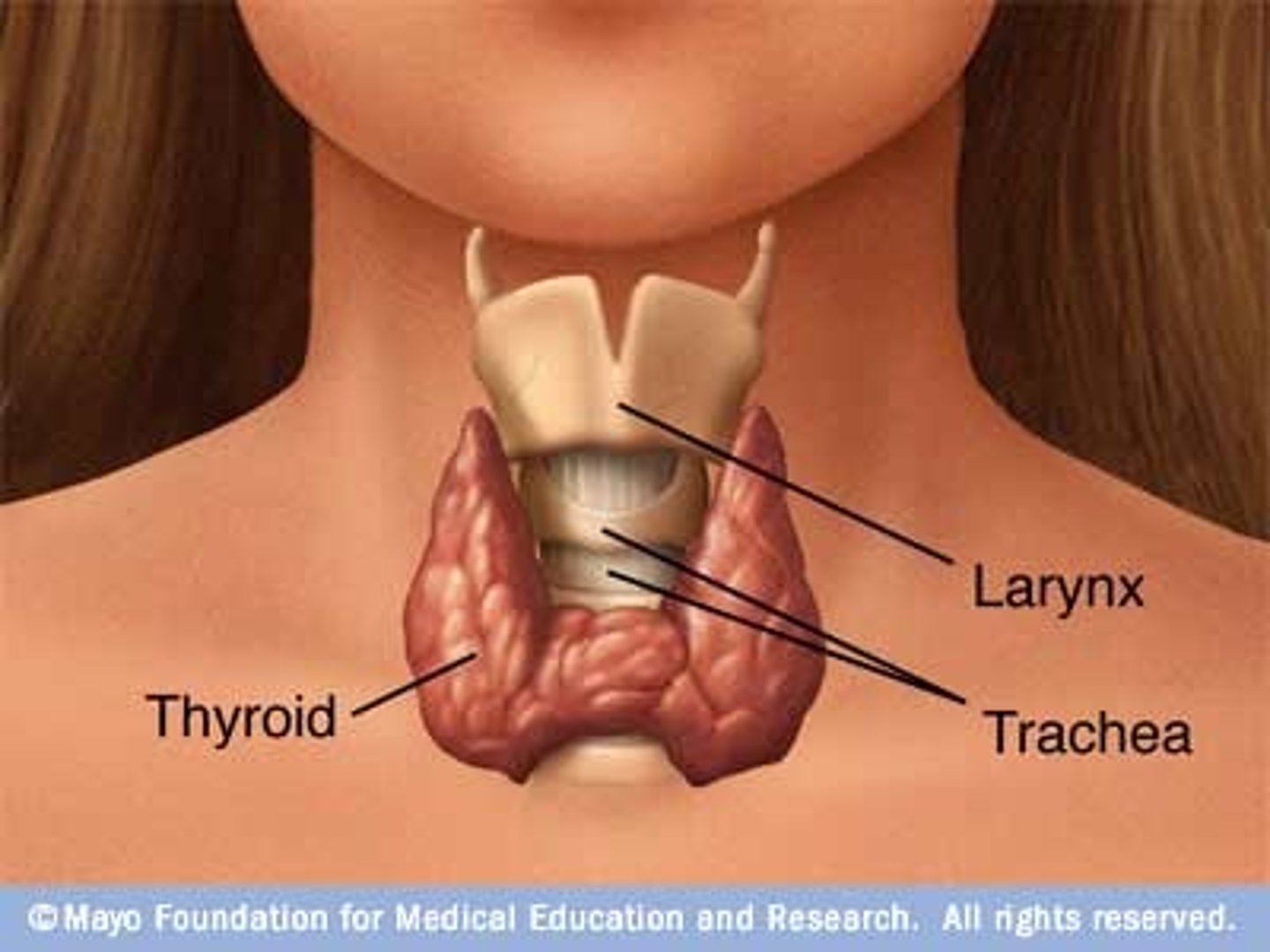
function of thyroid gland
combine iodine and the amino acid tyrosine to make thyroid hormones
- only cells in the body which can absorb iodine
Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4)
thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
I-123
used for diagnosis
I-131
used for therapy
Self-testing 'home' Devices (3)
-thermometers
-pressure measuring instruments
-test kits (pregnancy test kits, glucose levels in blood)
Point-of-care devices definition (POC)
allows for patient testing and analysis near the patient (at the bedside)
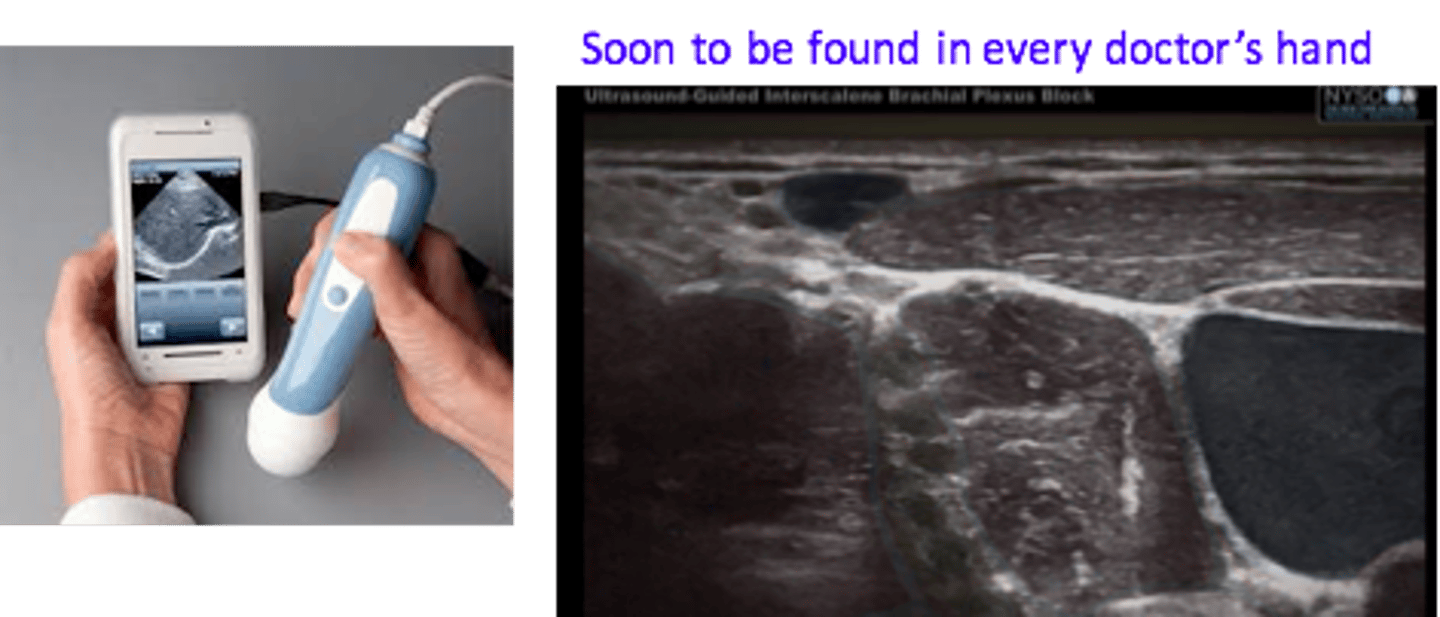
POC Devices: Miniaturization examples
Blood analysis system
ultrasound system
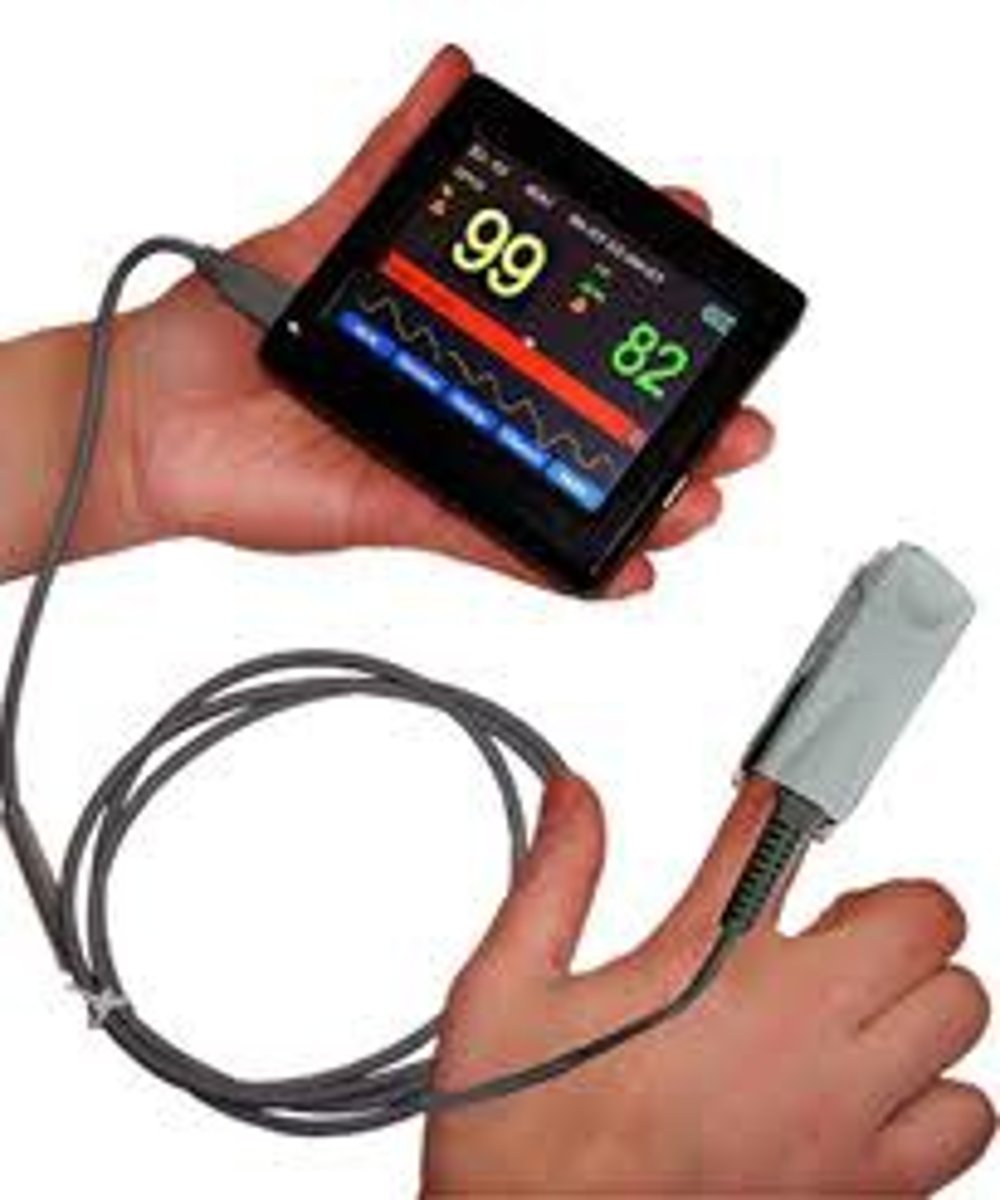
Pulse oximeter
Blood analysis system

ultrasound system
Pulse oximeter
shows blood oxygenation level, pulse rate
CE Mark
A product safety standard of the European Union

Classes of devices order
increasing order of increasing risk
Device Classification
according to risk level and level of regulatory control proportionate to the level of risk
Class I (5)
-Urine collection bottles
-Cervical collars
-Walking aids and wheelchairs
-Non-invasive electrodes
-Medical imaging monitors
Class IIA (7)
Tubing used with infusion pumps
Dental bridges and crowns
Muscle stimulators
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) devices MRI,
Gamma cameras ECG,
EEG
Class IIB (7)
X-ray sources
gas-machine
Anaesthesia machines
Dialysis machines
Insulin pens
Infusion pumps
External pacemakers and defibrillators
Class III (5)
pacemaker
artificial-heart
implanted neuromuscular stimulator kit
transducer
electrode