ORGMED LAB 8: ETHANOL
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
give synonyms of ethyl alcohol
ethanol
grain alcohol
drinking alcohol
alcohol
give chemical formula of ethyl alcohol
C2H6O
ethanol is (CLOUDY OR VIVID / CLEAR OR COLORLESS)
clear or colorless
ethyl alcohol has a ______ odor
wine-like
spgr of ethyl alcohol:
____________ at _____
0.7892 at 10C
give boiling point of ethyl alcohol:
___ C (___F)
78.32 C (172.81 F)
give melting point of ethyl alcohol:
_____ C (____F)
-114.1 C (-173.45 F)
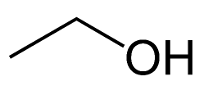
name this structure:
ethyl alcohol
Ethyl alcohol is one of the most commonly used __________ or ________ for many years
antiseptics or disinfectants
a use of ethyl alcohol in which its purpose is to kill or inhibit growth of microbes on living tissues
antiseptics
a use of ethyl alcohol in which its purpose is to kill or inhibit growth of microbes on inanimate objects
disinfectants
ethyl alcohol acts by __________ and ____________ proteins within the _______________ of microorganisms.
this causes disruption of the ______________ of the microbes, ultimately leading to _________ and ______
denaturing and coagulating proteins
within the cell walls and membranes
membrane
cell lysis and death
the length of the aliphatic carbon chain in an alcohol (DIRECTLY / INVERSELY) influences its bactericidal effectiveness, up to____# carbons only.
directly influences
8 carbons
If an alcohol molecule contains 9 or more carbons, they are considered as _____________, in which are _______ liquids
higher alcohols
viscous liquids
higher alcohols tend to be (MORE / LESS ) soluble and have (LOWER / HIGHER) boiling points compared to shorter-chain alcohols due to (INCREASED / DECREASED) molecular forces
less soluble
higher BP
due to increased molecular forces
SAFE bactericidal effect of ethanol at conc between:
_________________
60-85%
For 60%–70% ethanol, exposure times of ______ are necessary
≥5 min
For 80-85% ethanol, exposure times of ______ is effective
≤0.5 min (below 30secs)
Ethanol's primary sources are _________ and _______
sugars and starches
Ethanol is primarily derived from crops like:
_________ (CN) + ____________ (SN)
_________ (CN) + ____________ (SN)
_________ (CN) + ____________ (SN)
_________ (CN) + ____________ (SN)
sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum)
sugar beets (Beta vulgaris)
corn (Zea mays)
wheat (Triticum aestivum)
Ethanol is COMMONLY produced through hydration of _______
ethene
ethene when hydrated, undergoes an _______ reaction with _______ as catalyst to produce ethanol
addition reaction
phosphoric acid
other known method of producing ethanol: ________
fermentation
_____________ (SN) is an example of microorganism that conver carbohydrates into ethanol and carbon dioxide through the (AEROBIC / ANAEROBIC) respiration
Saccharomyces cerevisieae
anaerobic respiration
the ethanol produced from fermentation then undergoes ________ to increase its concentration and remove byproducts
distillation
IN THE 1ST STEP OF FERMENTATION:
A _____ molecule is broken down via ______, yielding ___# _______ molecules.
glucose; via glycolysis
2 pyruvate
IN THE 2ND STEP OF FERMENTATION:
The two pyruvate molecules are broken down, yielding ___# _______ and giving off _____# molecules of carbon dioxide.
2 acetaldehyde
2 carbon dioxide
IN THE 3RD STEP OF FERMENTATION:
The two molecules of ________ reduces the two acetaldehyde molecules to ____# molecules of ethanol.
NADH
2 ethanol
Ethanol, undergoing complete combustion, will yield an (ENDOTHERMIC / EXOTHERMIC) reaction
exothermic
give the reaction of ethanol undergoing complete combustion
C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O + heat
when undergoing oxidation, ethanol first produces __________ (_______), and then with further oxidation, forms __________ (_______)
acetaldehyde (ethanal)
acetic acid (ethanoic acid)
when undergoing oxidation, the solution color of ethanol changes from ____________ to ________
orange to green
the orange color of ethanol solution is characteristic of the ________ ion
dichromate(VI) ion
as ethanol undergoes oxidation and thus changing color, the green color is characteristic of ________ ion
chromium (III) ion
Esterification of ethanol involves a reaction with a ______, typically in the presence of a ______ like _______, to produce an __________ and ______
carboxylic acid
catalyst; sulfuric acid
ester and water
_______ is the sweet and fruity-smelling ester produced when ethanol undergoes esterification
ethyl ethanoate
_________ can be used as a substitute for ethanol, with similar antiseptic properties.
isopropyl alcohol
isopropyl alcohol is aka ________
2-propanol
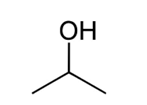
name this structure:
isopropyl alcohol
Put the following steps in the correct order by writing the appropriate procedure step number (1–9) in each blank.
_____ Add 20 ml of nutrient solution (which contains 0.55 g of yeast) for fermentation.
_____ Weigh the product and compute for the percentage yield.
_____ Shake the mixture thoroughly and attach a bent tube, fitted to a stopper for the purpose of bubbling the evolved carbon dioxide in lime water.
_____ Attach a water condenser, distill the mixture and collect 3 ml and 7 ml fractions separately.
_____ Place a cotton swab on top of the test tube.
_____ Dissolve 10 g of glucose in 140 ml of water in a 250-ml Erlenmeyer flask.
_____ Lead the bent tube into the test tube which contains 10–15 ml of lime water.
_____ Do not shake at the end of fermentation. Decant the liquid into a 125-ml distilling flask.
_____ Allow the mixture to stand for one full week at room temperature.
2
9
3
8
5
1
4
7
6