Endocrine Critique
1/206
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
Endocrine glands _____ and ______ hormones
produce and secrete
What is a Right to left shunt
hole in right ventricle to the left ventifcle
deoxygenated blood enters left side and goes systemic circut
causes numerous issues - espeically in brain and kidneys
What is one of the biggest disadvantages of the dual-tracer parathyroid imaging compared to dual-phase?
patient has to stay on camera, and stay still for method to work well
What is the first test typically performed when evaluating thyroid function?
blood draw (blood work)
What is the function of hormones?
regulate body’s growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function
What shape is the thyroid commonly compared w/?
butterfly
What hormones does the thyroid produce?
T-3 and T-4 hormones
What is the function of the thyroid hormones?
regulates cellular activity - e.g. metabolism of cells
Describe the physiological process of the thyroid’s conversion of iodine into hormones (start from how iodine gets to the thyroid)
iodine absorved into bloodstream from digestive tract
blood transport iodine in form of iodide to thyroid gland, where it’s trapped and organified by thyroid follicular cells
iodide oxidized to form:
MIT (monoiodotyrosine
DIT (diiodotyrosine)
T-3 = 1MIT moluecule and 1 DIT molecule
T4 = 2 DIT molecules
T/F: All endocrine cells can absorb iodine
False
What endocrine cells can absorb Iodine?
thyroid cells only
T/F: the majority of all release thyroid hormones is in the form of T4
True
T/F: The majority of release thyroid hormones is in the form of T3
False
What percent of released thyroid hormone is T4 vs T3?
90% = T4
10% = T3
Metabolic activity is determined by the _____ amount of T3 and T4 hormones
free
Thyroid stimulation and it’s secretion of hormones is controlled by a _________ feedback mechanism
Negative
What hormone causes the thyroid to create and secrete T3 and T4 hormones?
TSH- thyroid stimulating hormone
Describe the negative feedback mechanism regulating the thyroid.
hypothalamus releases TRH (Thyrotropin releasing hormone) or TRF (thyrotropin releasing factor)
Pituitary gland releases TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
TSH causes thyroid to make and secrete T3 and T4 hormones
The hypothalamus releases ____ and ___ hormones, stimulating the pituitary gland to secrete TSH
TRH - thyrotropin releasing hormone
TRF - thyrotropin releasing factor
________ circulating hormone (T3, T4) will signal the pituitary gland to decrease the amount of TSH it is producing
Increased
________ circulating hormone (T3, T4) will cause the pituitary gland to increase the amount of TSH it is producing
Decreased,
A patients bloodwork showed elevated TSH. Does this patient have hypo or hyper-thyroidism?
hypothyroidism
A patients bloodwork showed decreased TSH. Does this patient have hypo or hyper-thyroidism?
hyperthyroidism
Hormone production problems are caused by what condition?
hyper and hypothyroidism
Mechanical issues (ex. trouble swallowing or hoarseness) are typically caused by
swollen gland
Nodules or lumps in the thyroid could be caused by:
cancerous lumps or leison
What can cause hypothyroidism?
Iodine deficiency or excess
inherited enzyme deficiiency
post ablation
end stage toxic
Mets
thyroiditis
pituitary or hypothalamus dysfunction
What causes primary hypothyroidism?
failure of thyroid gland to synthesize and release thyroid hormones
What causes secondary hypothyroidism?
TSH is deficient
can be either congenital or from tumor in pituitary
In patients w/ hypothyroidism, ___ will be elevated, and ___ will be low
TSH will be elevated
T4 willl be low
In patients w/ hyperthyroidism, ____ will be low, and _____ will be elevated
TSH will be low
T4 will be elevated
What are some causes of hyperthyroidism?
Grave’s disease
Solitary nodule
Multinodular goiter (MNG)
Thyroiditis
What are some symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
(unofficially: think about Gary)
Elevated metabolic rate
Excessive perspiration
Rapid, Irregular heartbeat
Nervousness
Weight loss
Exophthalmos: protrusion of the eyeballs caused by edematous tissue behind the eyes
What are some symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Low metabolic rate
Always cold
Constipation
Dry skin
Weight gain
Puffy face
Hair loss
What is Myxedema?
Swelling of the body or face that often accompanies hypothyroidism.
What does thyroid storm mean?
Sudden release of large amounts of thyroid hoormones
What is Exophthalmos?
bulging of eyes that often accompanies hyperthyroidism
What does Goiter mean?
swelling of the thyroid gland
What is Cretinism?
infantile hypothyroidism - shows stunted growth, thickened facial features, abnormal bone development and delay in mental development
How is hyperthyroidism treated?
Surgical resection
radioactive iodine treatment
anti-thyroid medications
beta blockers (only treats symptoms)
How is hypothyroidism treated?
hormone replacement medications
What signs/symptoms of Benign thyroid nodules?
family history of Hashimotos thyroiditis or benign thyroid nodule or goiter
symptoms of hyper or hypothyroidism
pain or tenderness associated w/ a nodule
Soft, smooth, mobile nodule
simple cyst on ultrasound
What is the palatable difference between a benign thyroid nodule and a malignant nodule?
Benign - soft, smooth, mobile nodule
Malignant - firm, irregular, and fixed nodule
What are some signs and symptoms of malignant thyroid nodules?
common in ages < 20 or age >70
new onset of swallowing difficulties or hoarseness
history of external neck irradiation during childhood
firm, irregular and fixed nodule
presence of cervical lymphadenopathy (swollen hard lymph nodes in the neck)
previous history of thyroid cancer
nodule that is "cold" on scan
solid or complex on ultrasound
What are the indications for a thyroid WB scan?
pre-ablation
post-treatment
routine follow up
What is the ½ life, energy and emission of I-131?
8.1 days
364keV
Gamma and Beta
What is the ½ life, energy and emission of I-123?
13hrs
159keV
Gamma
What is the ½ life, energy and emission of Tc-99m?
6hrs
140keV
gamma
What is the energy of I-131?
364keV
What is the energy of I-123?
159keV
What is the ½ life of I-131?
8.1 days
What is the ½ life of I-123?
13hrs
What is the mechanism of uptake of I-131 or I-123?
Organified by the thyroid - bound to thyroglobulin
What is the mechanism of uptake of Tc-99m pertechnetate?
active transport - trapped in follicle
What are the contraindications for a thyroid study?
Meds that have not been stopped
What pt. history should be acquired prior to a thyroid scan?
Family history of cancer/thyroid disease
Taking any thyroid medication or anything that contains iodine
Neck swelling or lumps
Weight changes / comfort or discomfort with base temperature
Recent Xrays, taking vitamins
Lab work
What restrictions/patient prep should be followed prior to a thyroid NM study?
low iodine diet
anti-thyroid medications
hormone replacements
What is the dose of I-123 for a thyroid uptake scan?
200-300 µCi I-123
What is the dose of I-131 for a thyroid uptake?
5-10µCi I-131
When can you obtain counts for a thyroid uptake scan? When are counts most commonly obtained?
@ 2, 4, 6, 24, or 48 hrs
most commonly obtained @ 24 hrs
How do you calculate the % of radioactive iodine uptake?
% Uptake =
[(net neck counts - net thigh counts)x 100]
(net standard counts - background counts) (decay factor)
Calculate the uptake of this patient @ 4hrs:
4 hour uptake: 4 hour decay factor= 0.810
Capsule 734,915 cpm
Bkgd 103 cpm
Thyroid 29,760 cpm
Thigh 683 cpm
29,760 cpm – 683cpm
%uptake= ----------------------------------------------- x 100 = 4.8%
(734,915 cpm – 103cpm)(0.810)
What is a normal radioactive iodine uptake values @ 4-6 hrs?
5-20%
What is a normal radioactive iodine uptake values @ 24 hrs?
7-35%
< __ uptake of radioactive iodine @ 24hrs would indicate Hypothyroidism
<7%
> __ uptake of radioactive iodine @ 24hrs would indicate hyperthyroidism
>35%
What uptake value range would indicate hypothyroidism?
< 7%
What uptake value range would indicate hyperthyroidism?
> 35%
What tracers can we use for a thyroid scan?
I-123
Tc-99m pertechnetate
What is the Tc-99m pertechnetate dose for a thyroid scan?
2-10 mCi Tc-99m pertechnetate
Imaging for a thyroid scan using Tc-99m would begin ____ post inj
15-30 min
When would imaging for a thyroid scan using Tc-99m Pertechnetate begin?
15-30min post inj
How is Tc-99m Pertechnetate given for a thyroid scan?
Via IV
What is the dose for I-123 for a thyroid scan? How is it given?
200-500 µCi
Via IV
When are images taken for a thyroid scan using I-123?
4hrs
18-24hrs delay
Images using I-123 for a thyroid scan can be acquired @ ___ and ___ hrs post administration
4hrs
18-24hr delay
What views are acquired for a thyroid scan using I-123 or Tc-99m Pertechnetate?
Anterior
Anterior with marker
RAO
LAO
What type of collimator is used for a thyroid scan using I-123 or Tc-99m pertechnetate?
pinhole
What are the imaging acquisition time parameters for a thyroid scan using Tc-99m?
100,000-200,000 count image or 5-min
What are the imaging acquisition time parameters for a thyroid scan using I-123?
50,000-100,000 counts or 10min
What does normal uptake on a thyroid scan look like?
Euthyroid / homogenous uptake
Lt typically smaller than rt plus pyramidal lobe
Location – inferior thyroid cartilage and superior to supra sternal notch
Uptake = or > salivary gland
What is the energy peak of Co-57?
122keV
Uptake was 10.15%. Is this scan normal or abnormal
normal
How would Plummers – autonomous multinodular goiter, appear on a Thyroid scan?
hot or cold solitary or multiple
If a patient w/ the clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism but no visualization of the thyroid on the scan, what could this be a sign of?
thyroiditis
How would thyroiditis present on a thyroid scan?
non visualization of the thyroid, but clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism
How would graves disease present on a thyroid scan?
enlarged, high uptake
How would Hashimotos thyroiditis present on a thyroid scan?
enlarged, mottled
How would thyroid cancer present on a thyroid scan?
solitary nodules - typically cold, sometimes hot
What types of artifacts may appear on a thyroid scan?
Iodine contaminants I-123
Tc99mO4- less accurate, lower uptake high background
Metal on neck
Improper collimator for isotope
Markers being placed incorrectly
Patient movement
What types of variations can we use when performing a thyroid scan? What are the reasons for these?
Perchlorate wash-out - test for problems w/ organifcation
i.e. Hashimotos or congenital enzyme deficiencies
TSH and TRH stimulation tests
T3 – triodothyronine (cytomel) suppression test to diagnose hyperthyroidism
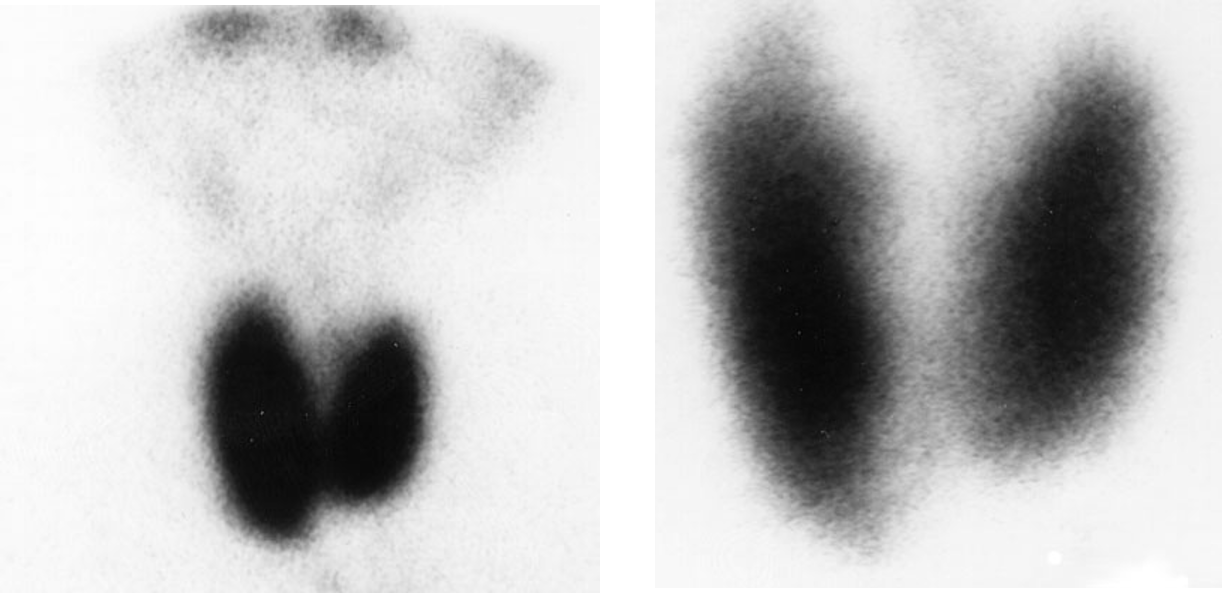
The 24hr calculated uptake was 73%. What is your impression of this scan?
hyperthyroidism - Graves disease
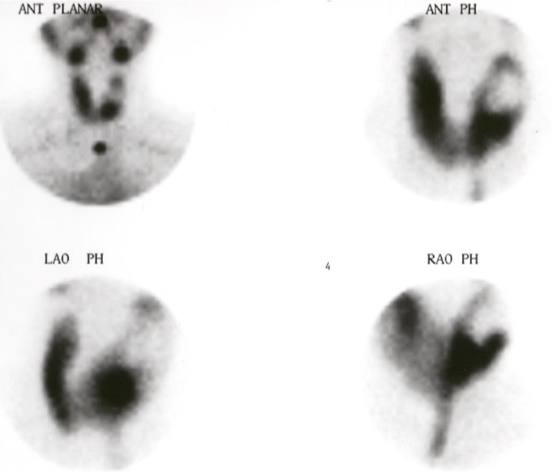
What is your impression of this scan?
cold nodule
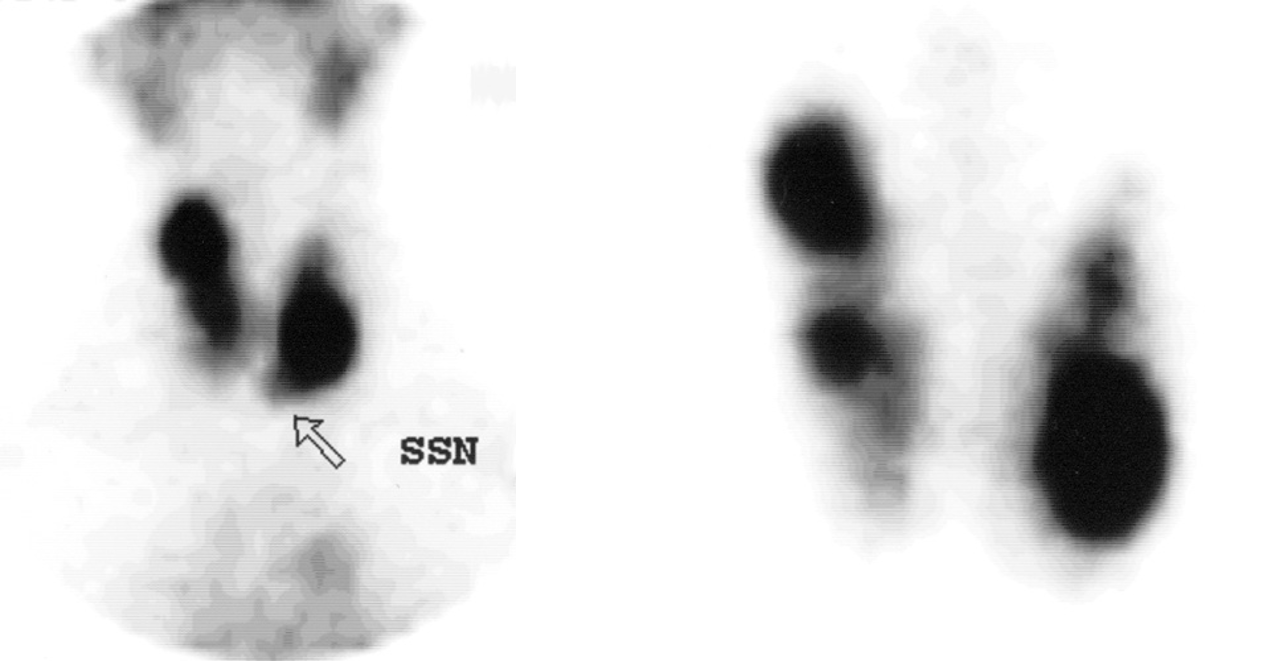
Pt. is a 61 year-old female with suppressed (low) TSH, and a diffusely enlarged thyroid. What is your impression of this scan?
Toxic Multinodular Goiter
Why should you obtain lateral views for a thyroid scan for pediatric patients?
bc thyroid originates sublingual-ly
What are the 2 types of thyroid cancer?
Papillary
Follicular
What is the most common type of thyroid cancer? Papillary or Follicular
papillary
Why do we use high doses of I-131 to treat cancer, compared to a relatively low dose for treating hyperthyroidism?
Bc we are trying to treat relatively small amounts of thyroid tissue
when treating hyperthyroidism, relatively larger target
want to minimize target to non-target radiation exposure
For a thyroid uptake scan:
does the patient typically have a thyroid
what radiopharms can we use
and what images are we acquiring
yes - although can be part of i-131 pretreatment scan, in which case there is no thyroid
I-123 or I-131
n/a - acquiring counts not images
For a thyroid scan:
does the patient typically have a thyroid
what radiopharms can we use
and what images are we acquiring
yes - although can be part of i-131 pretreatment scan, in which case there is no thyroid
I-123 or Tc-99m O4
Ant
Ant w/ marker
obliquee