Chapter 2 Observation and Magnification
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Observation and Magnification
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
faceted
facets are cut and polished as a number of flat faces on the surface of the gemstone
most transparent material (coloured and non-coloured gemstones)
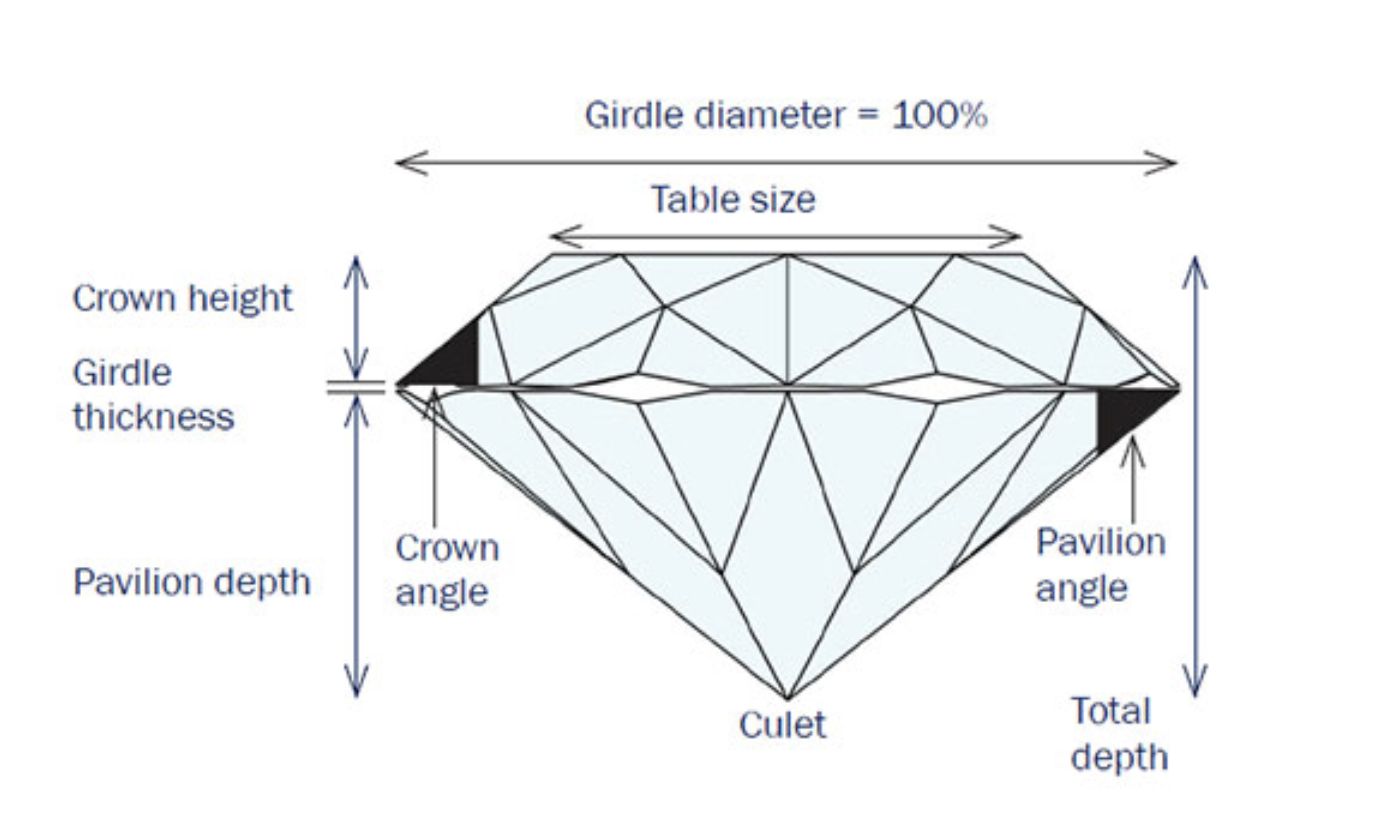
name the diamonds top, bottom etc.
top = table crown girdle etc

cabochon
Consist of a domed and polished top surface with a flat, unpolished back.
The outline is round or oval
it flatters the appearance of dark stones or those lacking in transparency
lustre
Lustre relates to the quality and quantity of light reflected from the surface of a material.
It can be described as shiny, dull, or glassy, influencing the appearance of gemstones.
results from a combination of factors, including the chemical and structural nature of the material AND quality of polish
non-faceted stones can be
cabochons, carvings, beads, cameos (on top of a stone)
Optical effect
Chatoyancy
Asterism
Iridenscence
Fire
What is chatoyancy also called?
Cat's eye effect
What is chatoyancy?
The effect is due to reflection of light from regularly orientated inclusions or channels within the gem
which gems can have chatoyancy
Chrysoberyl
Rose quartz
Tourmaline
What is asterism
star effect;
at the surface of certain gems
when they are cut as cabochons
the effect is due to the reflection of light from regularly oriented inclusions or channels within the gem.
The plane of inclusions is parallel to the base.
What is asterism?
An optical effect caused by light reflecting off two or more sets of parallel needle
WHEN cut as a cabochon
which gems can have asterism
ruby
sapphire
garnet
quartz
when cut as a cabochon!
iridescence
play of colour = colour effect
(in greek iris = rainbow)
what is iridescence
The colour effect is seen when light travels through or is reflected or refracted by the surface of very thin layers or cracks in a material, creating a spectrum of colours.
Certain colours in the reflected light interfere and cancel out to leave residual colours
which gems can have iridescence
Opal
some feldspar
Labradorite
Fire
flashes of colour
what is fire
Fire is seen when a transparent faceted gemstone is rotated under a lamp or in sunlight
describe the amount of perceived dispersion in a facetted gem material
which gems can have fire
strongest seen with faceted gems which are pale/colourless = diamond or synthetic moissanite
three types of illumination
bright-field
dark-field
top illumination
Top illumination
illumination from above or obliquely (schuin)
Observation use:
= Observe features on the surface of Opaque/nearly opaque materials
= Observe features within transparent /translucent gemstones
= HELP with detecting differences in lustre on composite or treated stones
bright-field illumination
illumination from directly below
Observation-use:
= transparent + translucent gem material
= certain features on/inside transparent materials
= Not the best for a good examination of the stone
dark-field illumination
illuminated from the sides
not directly from below
Observation use:
Transparent gems - particularly their internal features
what contributes to the beauty of a gem
shape or style of cut
Colour
transparency
Lustre
optical effects
different terms of lustre
@Mettalic:
polished silver and gold
pyrite and hematite
@Adamantine:
diamond
@sub-adamantine
zircon and demantoid garnet
@Bright-vitreous
ruby and sapphire
even to or even brighter than polished glass
@vitrious
the lustre is seen from ordinary windows and bottle glass
It is seen in many rough and polished gems, including emerald, agate and tourmaline.
Dull, earthy, resinous, silky, pearly and waxy other words to describe lustre
Transparency
Transparent: you can see through
Translucent; disrupts the passage of light. some light will pass through
Opaque: allow no light to pass through (hematite, malachite, rhodochrosite)
Internal features can be
@ solid, liquid or gas inclusions:
single mnonophase inclusions
two-phase inclusions
three-phase inclusions
@ zones or crystal growth or other structural features, including colour zones and layers of inclusions.
@inclusions in characteristic shapes such as hollow growth tubes and needle-shaped crystals
@ healed fractures (fingerprints)
twin-plane revealing change in the direction of crystal structure
internal fissures, celavage and stress cracks
evidence of treatment in gems f.x dying, drilling holes, facture filling (ruby, sapphire, emerald)
weight of gems
1 ct = 0.2 gram
5 ct = 1.0 gram
what means achromatic
no colour fringes (randen/franjes)
what means aplanatic
no distortion (vervorming)
Fluorescent table lamp
used for transparent to translucent stones
those lamps with white light tubes; diamond grading
effects as asterism and chatoyancy best seen under a single spotlight