DA: Exam 4 Lecture 1: Biological Products-Proteins - Shaw Dawg
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
natural product that is similar to substances already in the body that can be used for prevention, treatment, cure, or diagnosis of disease or condition
biological product
examples of biological products
A virus,
Therapeutic serum
Toxin, antitoxin
Vaccine
Blood
Blood component or derivative
Allergenic product
protein
Biological products can be made of?
sugar, proteins, nucleic acids,
or
a complex combination of these substances. They can also be living substances such as cells & tissue.
T/F: biological proteins can be living substances
t
Like drugs, biological products are used to either: (3)
-treat or cure diseases and medical conditions,
-prevent diseases
-diagnose diseases
Biological products are used for a wide range of diseases and conditions, including serious and life-threatening conditions such as cancers and rheumatoid arthritis.
what are four examples?
Botox: has both dermatologic and neurologic uses
Herceptin: for a certain type of breast cancer
Vaccines, for example: the Shingles vaccine and the flu vaccines
Enbrel: for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis
what are the uses of botox
dermatologic and neurologic
T/F: Botox kills nerves
t
what is the use of herceptin
certain type of breast cancer
what are the uses for vaccines
shingles and flu vaccine
what is the uses for enbrel
rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis
what are enzymes
proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions
the catalyzation of biochemical reactions by enzymes is dependent upon what
the temperature
Hormone Receptors, Drug Receptors, ion channels are examples of what
proteins
T/F: hormone receptors are mediators
t- carry out hormone function
What three proteins form the intracellular & extracellular scaffolding of cells?
Actins, tubules, & elastin
T/F: without extracellular scaffolding we would have no cells
t- cannot build a cell without it
What transports molecules within a cell or from one organ to another ?
Blood cells, plasma proteins
There are approximately 19,000-20,000 protein-coding genes in the human genome, but due to WHAT TWO THINGS there can be as many as 100,000 functionally distinct proteins formed.
alternative splicing, post-translational modifications
what is described as a library of all human genes leading to DNA
genome
what is the blueprint of making protein
the 4 bases of DNA- A G C T
what action creates mature mRNA and 2% of full starting DNA
alternative splicing
when does post-translated modification take place
after protein is synthesized
what are 4 ways in which post-translational modifications of proteins can be carried out
cleavage, phosphorylation, acylation, glycosylation
process that adds a phosphate group
phosphorylation
process that increases the functionally distinct proteins
glycosylation
what process increases the number of functionally distinct proteins to greater then 100,000
post-translational modification
Aspririn ____ Da
180
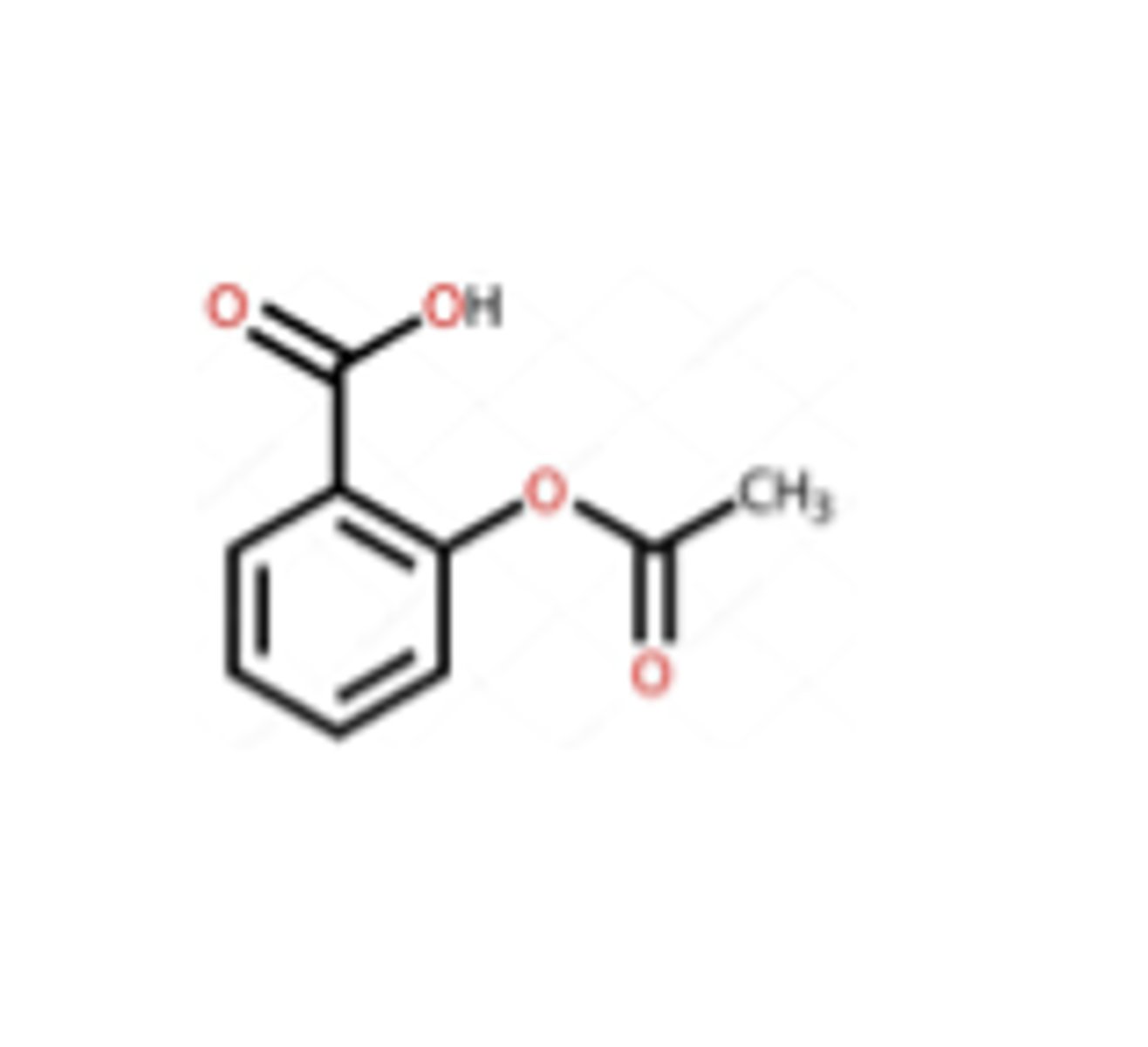
Monoclonal Antibody _______ Da
150,000

is a monoclonal antibody simple or complex
complex
what are the 5 sources of natural products
microbial world
animal sources
marine world
venoms and toxins
plant kingdom
Proteins are so complex because they have to be a specific ________ to function properly. Any change to this structure will change the protein's function.
shape
T/F: Biological products can be obtained from plants, animals, microbes, venoms/toxins, & marine organisms.
T
T/F: One of the disadvantages of biological products is that they will vary from natural source to natural source & within the same natural source. They are also limited when obtained from biological sources.
T
A small number of therapeutic proteins are purified from their native sources. _________ can be obtained from hog & pig pancreas, & __________ can be pooled from human plasma.
Pancreatic enzymes, alpha1-proteinase inhibitor
pancreatic enzymes are obtained from what 2 sources
hog and pig pancreas
alpha1- proteinase inhibitors are obtained from where
human plasma
Most therapeutic proteins are produced by _________ technology & purified from a wide range of organisms such as bacteria, yeast, insect cells, mammalian cells, & transgenic animals & plants.
recombinant DNA
what enables us to produce artificially large quantities of proteins
recombinant DNA technology
production systems for recombinant proteins include 6 things
bacteria, yeast, insect cells, mammalian cells, and transgenic animals and plants
mammalian cell culture takes how long to double
24 hours
avian cell culture takes how long to double
20 minutes
what type of cells are represented in avian cell culture
bird
organism in which genetic material from the DNA of another unrelated organism is artificially introduced
transgenic organism
system in which cells are grown outside of an organism (such as in petri dish)
cell culture
T/F: enzymes can cut a particular part of DNA intended to be multiplied
t
enzymes that cut DNA at very specific sequences
restriction enzymes
T/F: when dealing with recombinant DNA, you are adding the gene you are interested in
t
circular DNA molecule
plasmid
T/F: when a gene is introduced into plasmid, bacteria will start producing the protein
t
When producing recombinant DNA, the unwanted gene is cut out of the plasmid by __________, and the new gene is put in its place by __________.
restriction enzymes, annealing
Fermentor/Bioreactor reproduce what
themselves
T/F: filtration will produce large quantity of needed protein
t
use of heat to recombine DNA
anneal
T/F: Protein production must be processed under tightly controlled conditions throughout the production process to consistently produce safe, pure, & potent products, & to preclude the introduction of environmental contaminants.
T
why must protein production be processed under tightly controlled conditions/controls throughout production (2)
- consistently produce a safe, pure, and potent product
- preclude the introduction of environmental contamination
Biologic products may be susceptible to extreme _______ & _________. They typically need refrigeration, or they may need to be frozen or have added preservatives due to their limited shelf-life.
temperatures, light
T/F: proteins have a limited shelf life
t
Advantages of recombinant proteins include the transcription & translation of an ________ human gene with higher biological activity, a decreased chance of immunologic rejection, & production of proteins that can be produced more effectively, inexpensively, & in limitless quantities.
exact
recombinant proteins have a higher/lower level of biological activity
higher
recombinant proteins have an increased/decreased chance of immunological rejection
decreased
recombinant proteins are produced more/less efficiently and inexpensively
more
Advantages of recombinant proteins include reduction in exposure to animal or human _________, it allows the modification of a protein or selection of a particular gene variant to improve function or specificity, & it allows engineering & production of proteins that provide novel function or activity.
diseases
Recombinant ________ is used to treat T1 & T2 diabetes mellitus
insulin
Insulin was first purified from _______ & _______ pancreases & used to treat T1D, but availability of animal pancreas for insulin production was limited, purification of animal pancreas was very expensive, & some people had immunological reactions to animal insulin.
bovine, porcine
what are the 3 problems with the use of bovine and porcine pancreas for T1D
1. availability of animal pancreas
2. purification of animal pancreas is expensive
3. immunological reactions to animal insulin
________ is used to express human insulin by recombinant DNA technology. It is useful because of its rapid reproduction rate (20 minutes), it is inexpensive, has low immunogenicity, & is free from other animal pancreatic substances.
E. coli
why is the use of E. coli useful in use of express human insulin by recombinant DNA technology
- abundant
- inexpensive
- low immunogenicity
- free from other animal pancreatic substances
when was recombinant insulin approved by the FDA
1982
what does limitaken produce
simple proteins (bacteria)
yeast is simple/complex
complex
The system used for recombinant protein production is based on the cost of production & the modifications required for proper protein function. For example, ________ do not perform glycosylation, so if glycosylation, phosphorylation, or proteolytic cleavage of the protein is required for proper functioning, these organisms cannot be used.
bacteria
does bacteria perform glycosylation reaction
no
what type of system can have processes such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, or proteolytic cleavage
complex- yeast or insect/human cell culture
Protein ________ patterns can have a dramatic effect on the activity, half-life, & immunogenicity of the recombinant protein in the body.
glycosylation
The half-life of native ________, a growth factor important in erythrocyte production, can be increased by increasing the glycosylation of the protein.
erythropoietin
how can erythropoietin be increased
by increasing the glycosylation of the protein
_________ is an erythropoietin analogue that contains 2 additional amino acids that are substrates for N-linked glycosylation reactions. When expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells, the analogue is synthesized with 5 rather than 3 N-linked carbohydrate chains, & this increases the half-life of the substance by 3 times longer than erythropoietin.
Darbepoetin-alpha
T/F: Darbepoetin produces better products of human cells, and leads to an advantage of using this system rather than a different one
t
when darbepoetin-alpha is expressed in chinese hamster ovary cells the analogue is synthesized how
with 5 rather than 3 N-linked carbohydrate chains
darbepoetin alpha being synthesized with 5 rather than 3 N-linked carbohydrate chains increases what, when compared to erythropoietin
half-life of the substance by 3 times longer then erythropoietin
________ (Drugs, Biologics) have low MW & can be organically or chemically synthesized.
Drugs
________ (Drugs, Biologics) have high MW & must be synthesized from cells or organisms, allowing the potential for inherent contamination.
Biologics
________ (Drugs, Biologics) have few critical process steps during production & are well characterized.
Drugs
________ (Drugs, Biologics) have many critical processing steps during production & are less well characterized.
Biologics
________ (Drugs, Biologics) have known structures, are homogeneous, & are usually not immunogenic.
Drugs
________ (Drugs, Biologics) may or may not have known structures, are heterogeneous mixtures that may include variants, & are often immunogenic.
Biologics
T/F: Protein therapeutics have a highly specific & complex set of functions that cannot be mimicked by simple chemical compounds, & they provide less potential for interference with normal biological processes, resulting in a lesser chance of adverse effects.
T
protein therapeutics lead to more/less potential for interference with normal biological processes
less
protein therapeutics lead to less/more chances for adverse effects
less
T/F: protein therapeutics can provide effective replacement treatment for diseases in which a gene is mutated or deleted
t
T/F: protein therapeutics during the clinical development and FDA approval time is slower then that of small molecule drugs
f: faster
T/F: protein therapeutics can address unmet needs for rare diseases
t
are protein therapeutics eligible for orphan drug designation
yes, they can provide priority review by the FDA and extended patent protection terms
T/F: there are no clinically differences between the biological product and the reference product in terms of safety, purity, and potency
t
__________ (Drug, Protein therapeutics) are well tolerated & are less likely to elicit immune responses.
Protein therapeutics
protein therapeutics include what 4 things
1. proteins
2. enzymes
3. antibodies/drug conjugates
4. biological response modifiers
how can biological response modifiers affect protein therapeutics
increasing or decreasing the repsonse
Protein therapeutics can provide effective replacement treatment for diseases in which genes are ________ or _______.
mutated, deleted
Diseases are caused by deficiency or abnormality of a _________, so they can be treated by replacing or replenishing these substances.
protein