Ap hug: Unit 6 Vocab
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Urbanization
Migration of people from rural to urban areas.
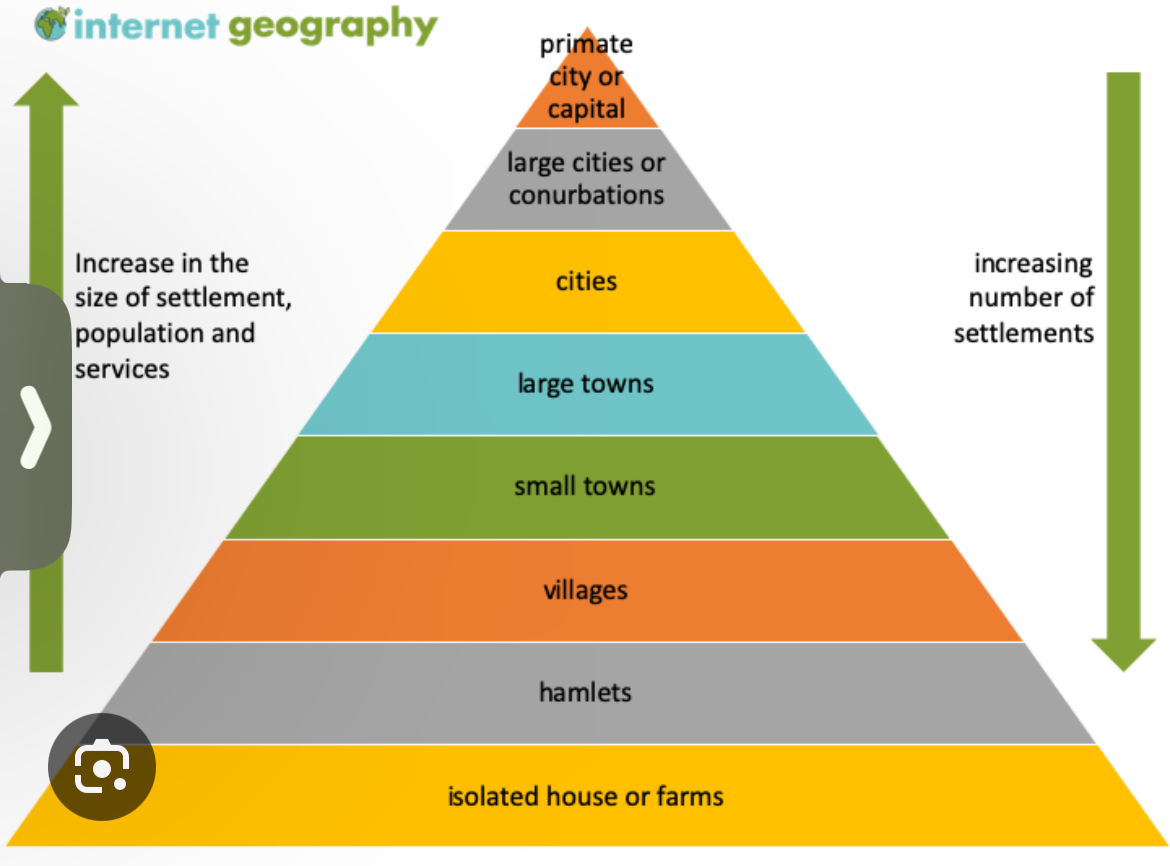
Urban hierarchy
Ranking based on influence of population size
World cities
Cities that exert influence beyond their natural boundaries.
Exmpl: New York, London, Tokyo.
Megacities
City more than 10 million residents.
Exmpl: Tokyo
Metacities
Cities with more than 20 million population.
Exmpl: London
Primate city
The largest city in an urban system is more than twice as large as the next largest city.
Exmpl: Mexico City
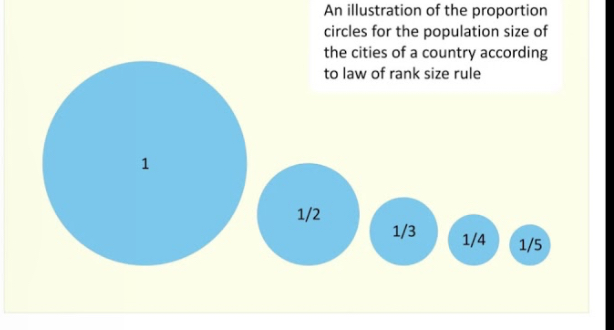
Rank-size rule
Describe one way in which the sizes of cities within a region may develop. Largest city in the region is 1/n the size of THE largest city.)
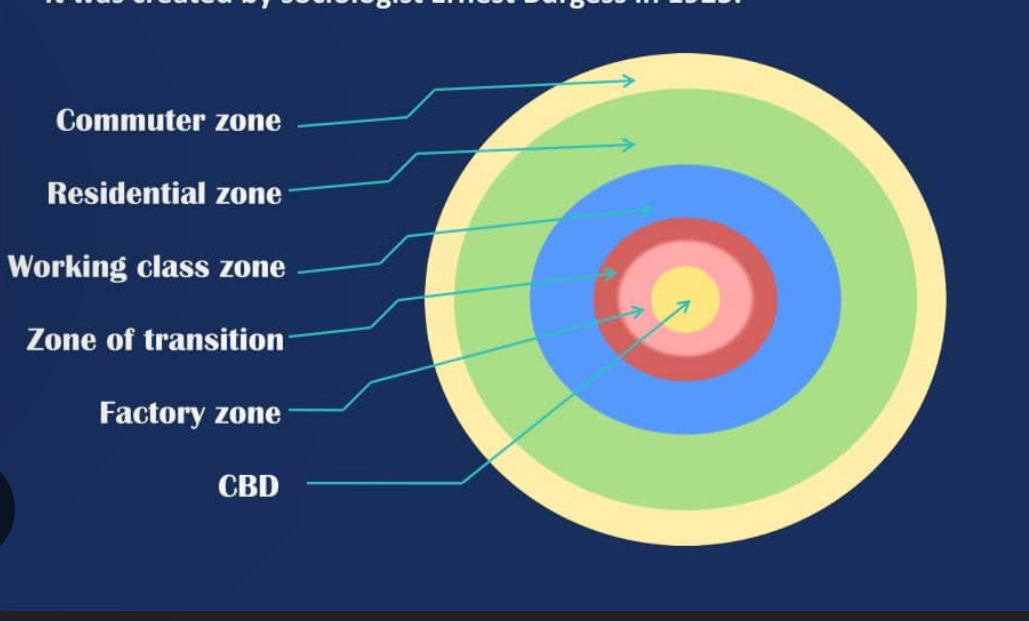
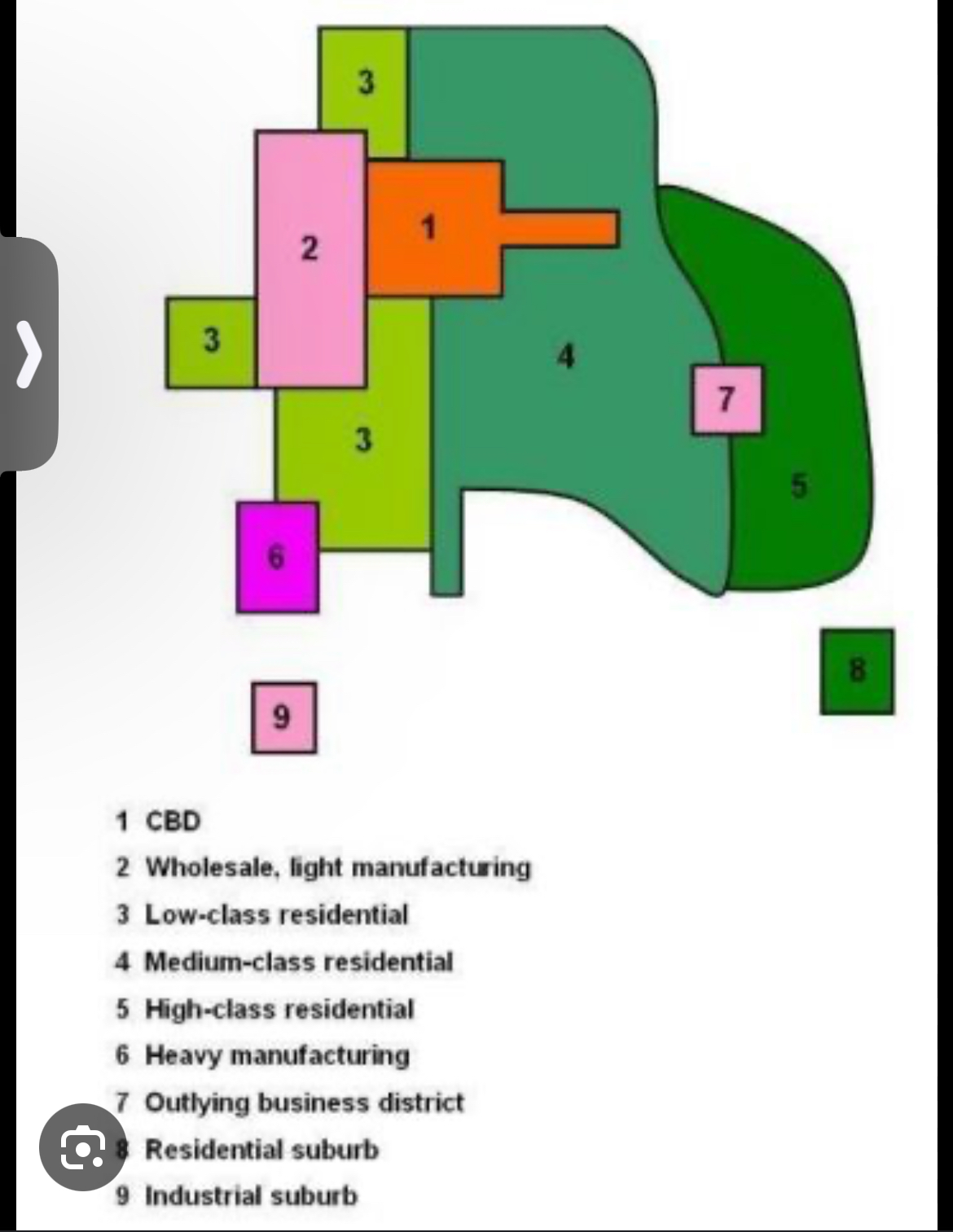
Burgesson concentric zone model
Model shows that a city grows outward from a central area in a series of concentric rings.
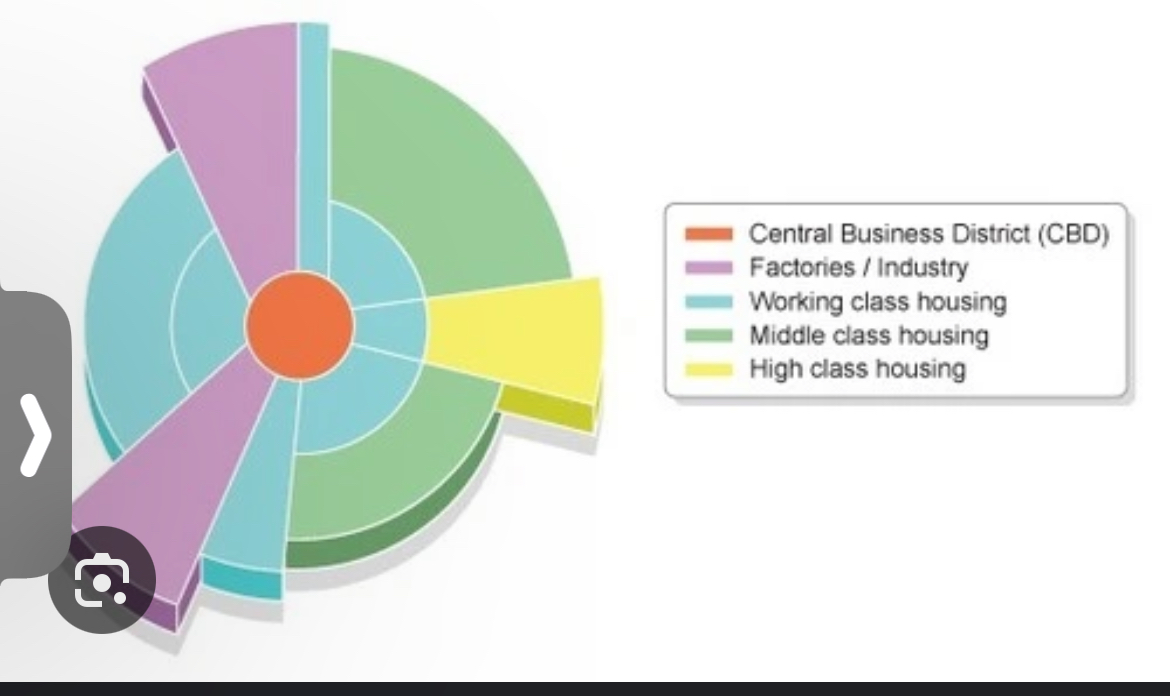
Hoyt sector model
A city develops in a series of sectors. Develops around transportation routes.
Harris-ulmen multiple nuclei model
A city includes a CBD as well as other centers around which activities occurs.
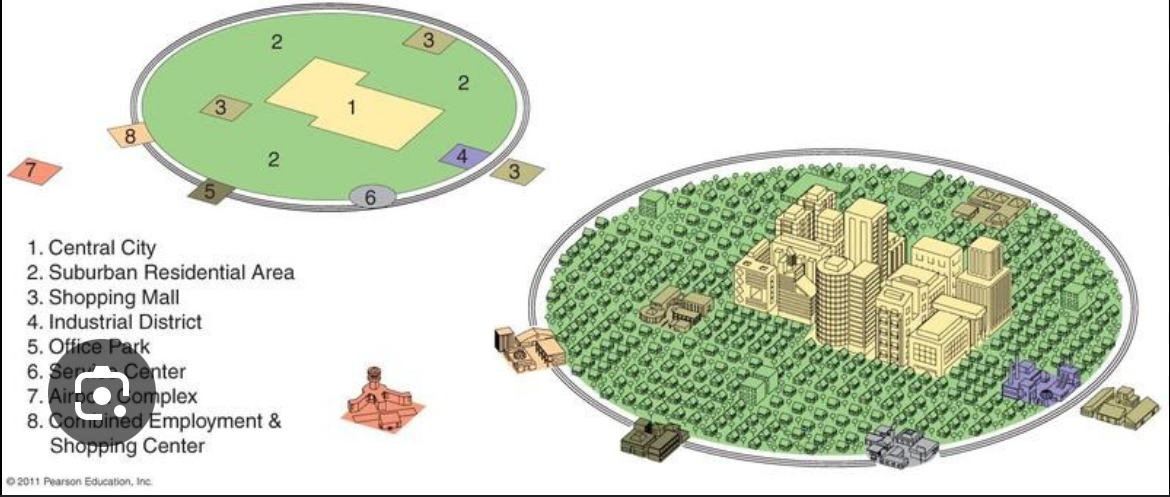
Galactic city model
An urban area consists of an inner city surrounded by large suburban residential and service nodes or nuclei tied together by a beltway or ring road.
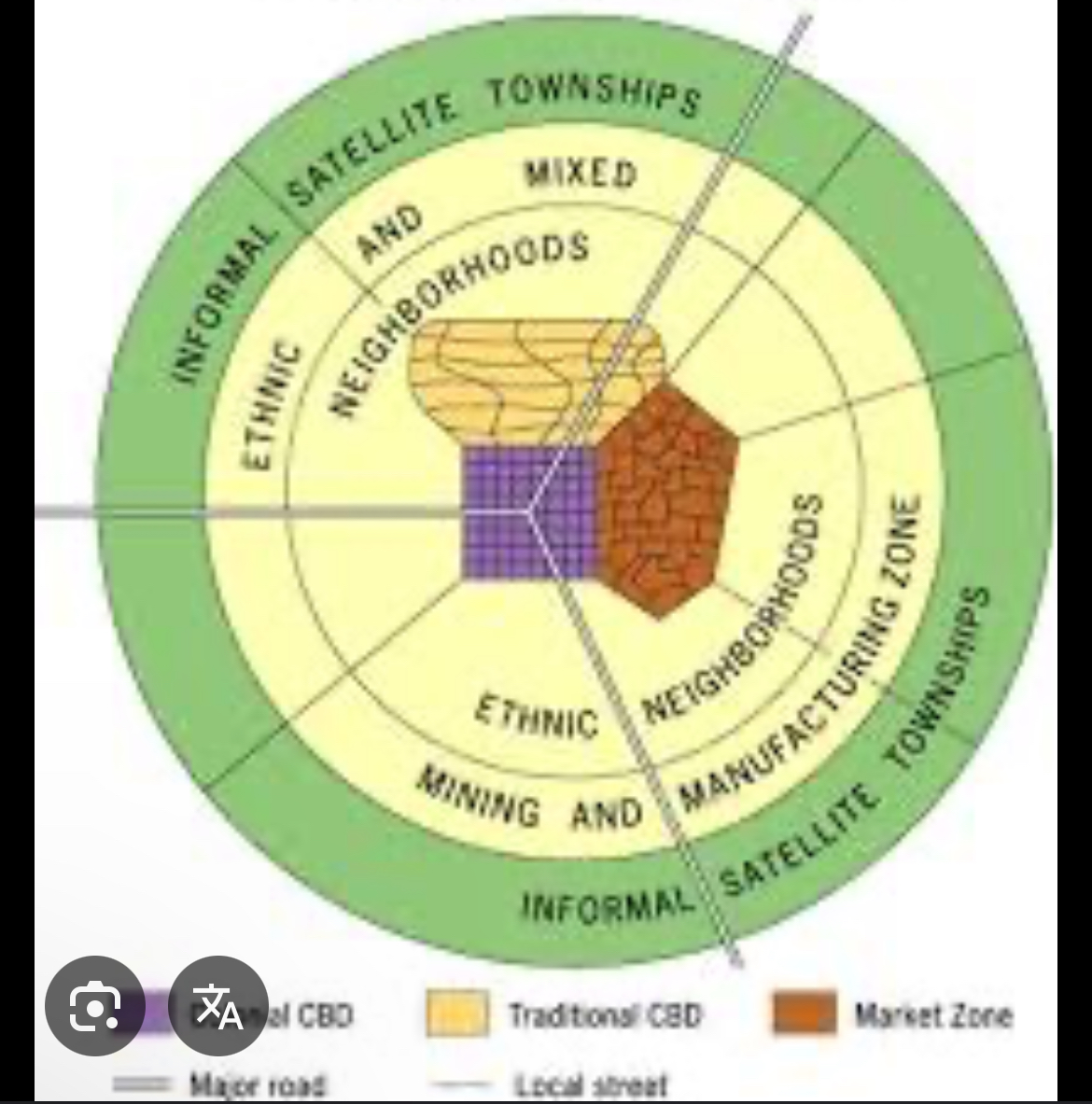
African city model
Explains contemporary patterns within the urban areas in developing countries. Inner rings have higher income people bc near businesses/consumer services and public services. Rings are constantly added to periphery for immigrants from rural areas for job opportunities.
Southeast Asian model
Service nodes of squatter settlements and “alien zones” where foreigners live and work.
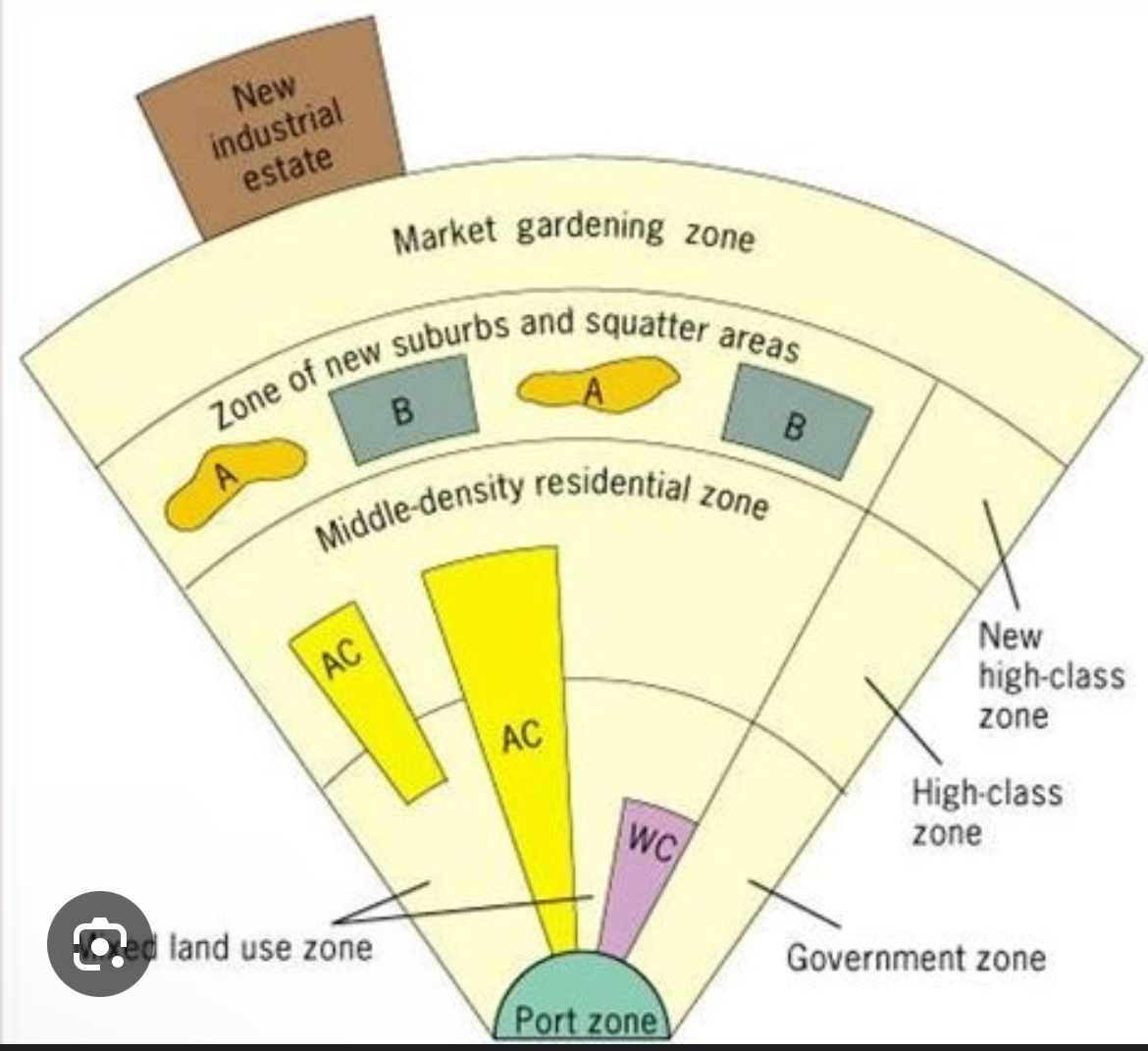
Latin America city model
Wealthy people push out from the center in a well defined elite residential sector.
christallers central place theory
Explain the distribution of cities of different sizes across a region.
Bid rent theory
The farther you are from the market the less the value of land is.
Suburbanization
Process of people moving, usually from cities to residential areas on the outskirts of cities.
Edge cities
Communities located on the outskirts of a larger city within a commercial centers, office space, retail complex, and amenities.
Sprawl
The rapid expansion of the spatial extent of a city which occurs for numerous reasons.
Boom burb
Suburb that has grown rapidly into a large urban sprawl city with more than 100,000 residents.
Exmpl: Pembroke Pines
Exurbs
Community on the outside edge of traditional suburbs, “exurban” (more rural and less connected to the central city core)
Suburban sprawl
The development of suburbs relatively low density and at locations that are not contagious to the existing build up area.
Slow growth cities
Policies to slow the outward spread of urban areas and place limits on building permits to create a denser/compact city.
New urbanisms
Made to put smart growth into action within communities (walkable cities)
Exmpl: more access to transportation, affordable housing, mixed used neighborhoods.
Smart growth
Legislation and regulations to limit suburban growth and preserve farmland.
Urban growth boundaries
A line drawn to define the limits of urban expansion to control urban sprawl and increase efficient land use.
Transportation oriented development
Urban planning approach that focuses on creating compact walkable communities centered around high quality public transportation.
Urban renewal
Redeveloping experienced urban decay to improve infrastructure and increase tax revenues and new residents.
Gentrification
Higher income residents move into lower income neighborhoods and increas property value.
Squatter settlements
Residential area where people have built home on land they do not legally own or have permission to occupy.
Disamenity zones
Areas with a city that lack basic infrastructure, services and opportunities.
Brownfields
Previously developed land that’s been abandoned, carry pollution from industrial use.
Redlining
Discriminatory practice of denying financial services to certain neighborhoods based on race or ethnicity.
Block busting
A real estate practice where they induce panic to sellers in a neighborhood by suggesting that racial/ethnic minorities are moving in and sell them at a lower price.
De facto segregation
Separation of people along racial, ethnic, or socioeconomic lines that is not mandated by law.
Farmland production policies
Minimizes unnecessary and irreversible conversations of farmland to non agricultural uses, ensuring food security and prevention of agricultural land.
Functional fragmentation of government
Challenges that arise when govt power is shared and separated instead of centralized.
Ecological footprint
Number of land and water needed to support population consumption of resources and waste.
Sustainable design initiatives
Urban planning to create cities that are environmentally sound and resilient livable cities.
Urban sustainability
Planning and managing cities to meet the needs of current and features generations without compromising environment or social wellbeing.
Site
Physical characteristics of a place
Situation
A settlements relationship/ position in relation to surroundings.
Decentralization
Distribution of authority, responsibility sesión making power from central authority to regional/local govt.