Unit 3: Cognition
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Cognition
The mental processes involved in acquiring, processing, and storing knowledge, including perception, memory, reasoning, thought, problem solving, and intelligence
Perception
way in which we make sense of sensory information from our environment
Bottom-Up Processing
relies on analyzing what is externally available to our senses, and is based on what we take in through our senses
Top-Down Processing
relies on analyzing what is internally available to our senses, and is based on knowledge we already have in our brain
Internal Factors that our brain uses to filter our perceptions:
Perceptual Set and Schema
Perceptual Set
mental predisposition to perceive stimuli in a particular way (based on previous experiences, expectations, beliefs, and context)
Schema
a cognitive framework that helps organize and interpret information by providing a structure for understanding new experiences based on prior knowledge. (based on our current knowledge, beliefs, and expectations)
External Factors that affect our perceptions:
culture, experiences and social context
Selective Attention
the process of focusing on a specific object or event in the environment while ignoring other stimuli. It influences how we perceive and respond to information.
Cocktail Party Effect
a phenomenon wherein individuals can focus on a single conversation in a noisy environment, such as a party, while filtering out other background noise.
Inattention Blindness
a cognitive phenomenon where an individual fails to notice an unexpected stimulus in plain sight when focused on a different task.
Change Blindness
failure to notice changes to stimuli in the environment around you due to a lack of attention or distraction from other tasks.
Stroop Effect
ability to OR inability to (due to interference) respond to one stimuli while… being presented a second at the same time and trying to ignore it!
McGurk Effect
interaction between hearing and vision causes interference leading to the perception of a third sound
Gestalt Principles
a set of laws that explain how humans naturally organize visual elements into groups or unified wholes. These include closure, figure-ground, proximity, and similarity

Closure
the tendency to perceive incomplete shapes as complete by filling in gaps.
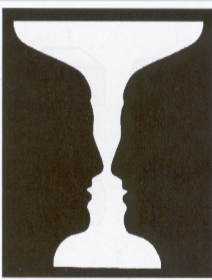
Figure-Ground
the principle that allows us to distinguish an object (the figure) from its background (the ground) in visual perception.

Proximity
tendency to perceive objects near one another as one

Depth Perception
the ability to perceive the world in three dimensions and judge distances between objects.
Binocular Cues
visual cues to depth or distance that require the use of both eyes (2 or 3-dimensional objects)

Monocular Cues
give the illusion of depth on flat 2-dimentional surfaces (seen with use of one eye alone)
Convergence
merging of retinal images by the brain that occurs when eyes turn inward
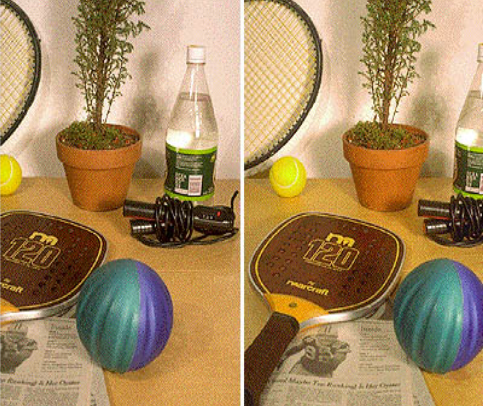

Retinal Disparity
difference between images projected onto the retina based on distance between eyes on your face (use to judge distance)

Relative Clarity
objects that appear sharp, clear, & detailed are perceived as closer

Relative Size
distance is based on comparison of size between objects

Texture Gradient
A visual cue where objects that are closer appear more detailed and textured, while those farther away appear smoother and less defined.

Interposition
when objects block one another, the object that is partially covered to appear more distant

Linear Perspective
objects closer to the point where two lines converge are perceived as being at a greater distance

Visual Perception Constancy
the tendency to perceive objects as unchanging despite changes in sensory input, such as size, shape, and color.
Concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, or people, allowing for easier understanding and categorization of the world.
Prototypes
mental images or best examples of a category that help in classifying and recognizing new instances.
Assimilation
taking in new information but not changing our schema
Accommodation
taking in new information & changing the schema to include new info
Algorithm
a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem or reaching a goal that guarantees a correct solution.
Heuristic
a mental shortcut that allows for problem-solving or decision-making, often focusing on practical solutions over guaranteed outcomes.
Representative Heuristic
a cognitive bias that involves making judgments about the probability of an event based on how similar it is to a prior expectation, leading to potential misclassifications.
Availability Heuristic
decisions based on information already in your mind that comes to mind first
Trail and Error
a problem-solving method that involves trying different solutions until finding one that works.
Executive Function
the mental processes that help manage thoughts, actions, and emotions to achieve goals.
Mental Sets
the tendency to approach problems in a particular way, often based on past experiences.
Fixation
the inability to see a problem from a new perspective, often hindering problem-solving.
Functional Fixedness
the cognitive bias that limits a person to using an object only in the way it is traditionally used, preventing creative problem-solving.
Framing
the way information is presented or framed, which can significantly influence decision-making and judgment.
Priming
the process by which exposure to one stimulus influences a response to a subsequent stimulus, often without conscious guidance.
Gambler’s Fallacy
the belief that past random events can influence the outcomes of future random events, such as assuming a losing streak in gambling will be followed by a win.
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
the tendency to continue an endeavor once an investment in money, effort, or time has been made, due to the fear of wasting that investment.
Creativity
a way of thinking that generates novel thoughts and divergent thinking
Divergent Thinking
thought process used to generate creative ideas by exploring many possible solutions. It contrasts with convergent thinking, which focuses on finding a single, correct answer.
Convergent Thinking
cognitive process that involves bringing together information and ideas to find the best solution or answer to a problem. It emphasizes logical reasoning and relies on prior knowledge.
Memory
the cognitive process of encoding, storing, and retrieving information. It is essential for learning and influences our ability to recall past experiences.
Explicit Memory
the type of memory that involves conscious effort recalling of facts and events
Semantic Memory
a subtype of explicit memory that involves the storage and recall of facts, concepts, and general knowledge about the world.
Episodic Memory
a subtype of explicit memory that involves the storage and recall of personal experiences and specific events in time.
Implicit Memory
skills that were learned that don’t require conscious effort for recall
Procedural Memory
a type of implicit memory that involves the performance of tasks and skills, such as riding a bike or playing an instrument, without conscious awareness.
Prospective Memory
a type of memory that involves the ability to remember to perform intended actions in the future, such as remembering to take medication or attend appointments.
Eidetic Memory
the ability to recall images, sounds, or objects in memory with high precision after only a few instances of exposure, often referred to as "photographic memory."
Long-Term Potentiation
a long-lasting strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity, believed to be a mechanism underlying learning and memory.
Stress Hormones
hormone that is triggered by heightened emotions which create stronger memories
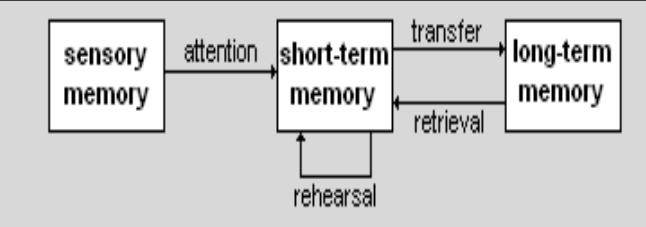
Multi-Store Model
of memory that proposes three distinct stages: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory, explaining how information is processed and stored.
Sensory Memory
the initial stage of memory that holds brief sensory impressions of stimuli, lasting only a few seconds.
Iconic Memory
a type of sensory memory that retains visual information for a very brief period, typically less than a second.
Echoic Memory
a type of sensory memory that retains auditory information for several seconds, allowing the processing of sounds after they occur.
Short-Term Memory
the stage of memory that temporarily holds a limited amount of information for about 20 to 30 seconds, facilitating immediate recall and cognitive processing.
Long-Term Memory
the stage of memory that stores information for extended periods, potentially a lifetime, and includes both declarative and non-declarative memory types.
Encoding
putting information into the brain
Storage
retaining the information
Retrieval
getting information out of the brain
Working Memory Model
type of short-term memory that stores information temporarily during the completion of cognitive tasks (comprehension, problem solving, reasoning, learning). Includes the central executive, phonological loop, and visuospatial sketchpad
Central Executive
component of the Working Memory Model that controls attention and coordinates information from the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad.
Phonological Loop
component that processes verbal and auditory information, allowing for temporary storage and rehearsal of sounds.
Visuospatial Sketchpad
component that processes visual and spatial information, enabling the temporary storage and manipulation of images and spatial awareness.
Levels of Processing Model
theory that suggests memory retention depends on the depth of processing, ranging from shallow (surface features) to deep (meaningful connections).
Structural
what it looks like
Phonemic
what is sounds like
Semantic
what it means
Effortful Processing
the encoding of information that requires attention and conscious effort. focus on meaning by relating new info to other info
Shallow Processing
the encoding of information based on its surface features, such as sound or appearance, rather than its meaning. no conscious effort
Mnemonic Devices
strategies that link or associates new information to information already encoded
Method of Loci
a mnemonic technique that involves visualizing a familiar place and associating items to be remembered with specific locations within it.
Word Associations
a technique that connects new words to existing knowledge or related concepts to aid memory retention.
Chunking
a memory strategy that involves grouping information into larger, manageable units to enhance retention and recall.
Imagery
the use of mental pictures or visual representations to enhance the encoding and retrieval of information in memory.
Serial Position Effect
a cognitive phenomenon where people remember the first and last items in a list better than the middle items.
Primacy Effect
the tendency to better remember items at the beginning of a list.
Recency Effect
the tendency to better remember items at the end of a list.
Spacing Effect
the phenomenon in which information is more easily retained when study sessions are spaced out over time rather than crammed.
Distributed Practice
A learning strategy that involves breaking up information into smaller, more manageable parts and studying them over time to enhance retention.
Massed Practice
A learning strategy that involves cramming all study or practice into a single session, leading to poorer long-term retention compared to spaced practice.
Rehearsal
the cognitive process of repeatedly practicing or retrieving information to enhance memory retention and recall.
Elaborative Rehearsal
a memorization technique that involves linking new information to existing knowledge through meaningful connections and associations, enhancing understanding and retention.
Maintenance Rehearsal
a memorization technique that involves the repetition of information without attempting to make meaningful connections, primarily to keep the information active in short-term memory.
Autobiographical Memory
a type of long-term memory that involves recollection of personal experiences and specific events in one's life, including contextual details such as time and place.
Recall
the process of retrieving information from memory, often involving the reconstruction of past experiences or learned material without direct cues.
Recognition
a memory process that involves identifying previously learned information from a set of options, such as multiple-choice questions.
Testing Effect
the enhanced ability to remember information when it has been tested through practice or retrieval, as opposed to simply studying the material.
Metacognition
the awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes, including regulation of cognitive activities in learning.
Context Dependent Memory
better memory retrieval when physically being back in the place where you made (encoded) a memory
Mood-Congruent Memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current mood, leading to easier retrieval of memories matching that emotional state.
State-Dependent Memory
is the phenomenon where memory retrieval is enhanced when an individual is in the same physiological or psychological state as when the memory was formed.