Free trade and Protectionism
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Free trade
Absence of goverment intervetion of any kind in international trade, so that trade takes palce without restrictions between individuals, firms or goverments of different countries.
Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
Trade agreement to expand the market for goods and services among the participant countries.
Advantages of free trade
Greater efficency in production and productivity
Lower price for consumers
Greater choice for consumers
Increased competition
Acces to larger markets
More efficient resource allocation
Protectionism
Economic policy that seeks to protect a country's production and jobs by imposing restrictions, limitations or tariffs on goods or services from abroad (imports), making them more expensive to make them less competitive with domestic products.
Advantages of Protectionism
Protection of new infant industries
Protecting domestic employment
National security and strategic reasons
Avoid over-specialization
Prevent dumping
Health and environmental standards
Protect industries from cheap labor
Raise goverment revenue
Correct balance of payments
Disadvantages of Protectionism
Missalocation of resources
Higher cost of production
Reduced efficency
Higher consumer prices
Less choice
Reduced export competitivines
Retaliation, potentialy leading to trade war
Types of protectionism
Tarifs
Quotas
Subsidies
Administrative barriers
Nationalist campaigns
Tariffs
Import tax that increases the price of imported products
Most common form of protectionism.
Purpose:
Protection of domestic firms
Increase goverment revenue
Winners:
Domestic producers
Domestic employment
Goverment (tariff revenue)
Losers:
Domestic consumers
Foreign producers
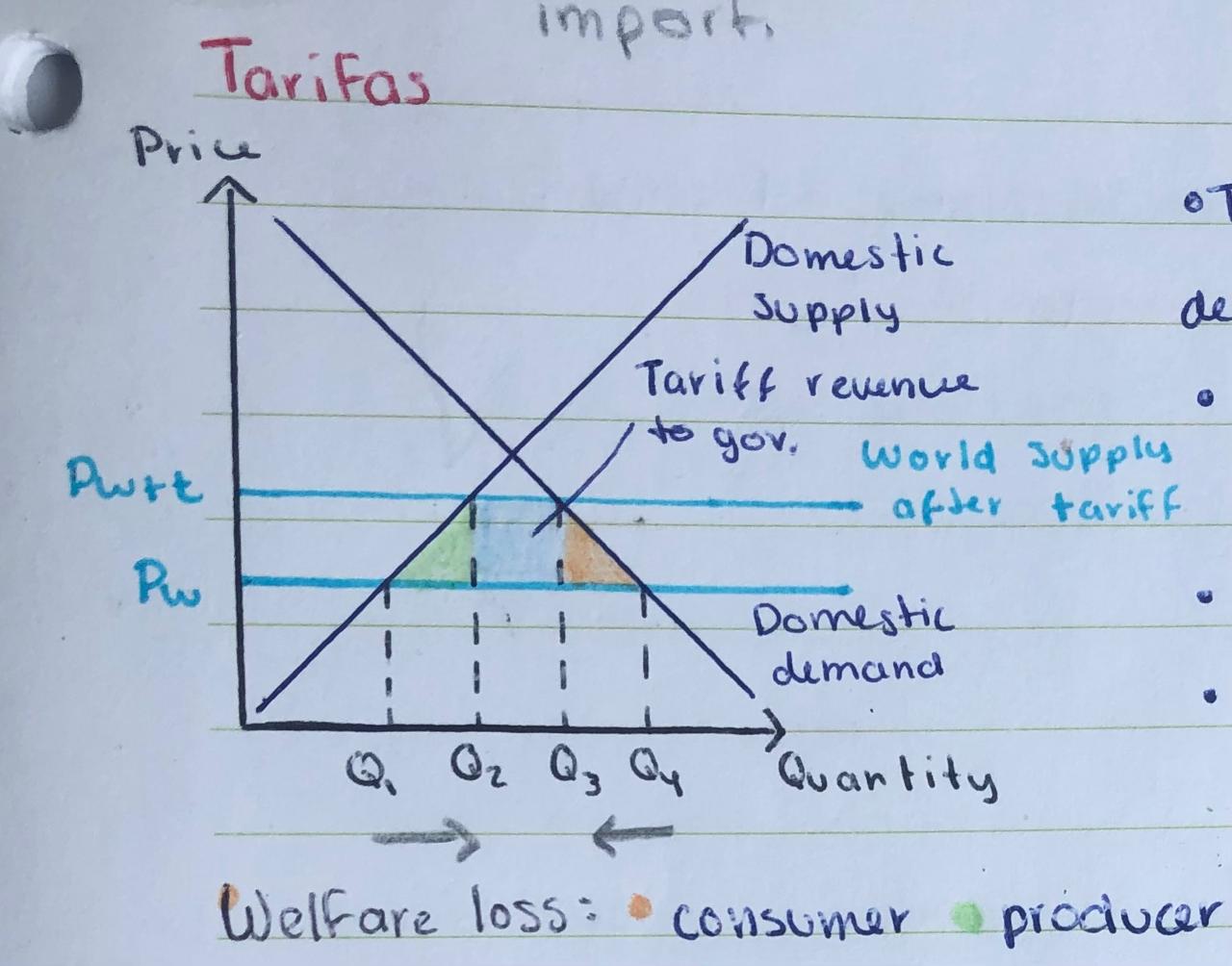
Tariffs diagram
Price of the products increases from Pw → Pwt
Quantity of imported products demanded reduced: Q4 → Q3
Quantity of national market products increases: Q1 → Q2
Actual import sales: Q2 - Q3
Subsidies
Aid from the government to stimulate a good. It is used to protect domestic production from imports.
Subsidy allows producers to increase their production since its cost of production are low.
Winners:
Local producers
This gain does not affect the consumers.
Affected:
Foreign producers
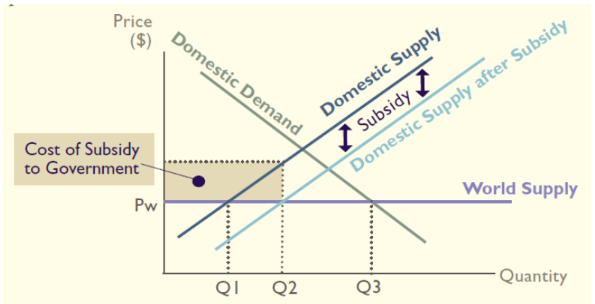
Subsidies diagram
With world price at Pw, producer can sell more from Q1 → Q2
Q2 - Q3 is fullfilled by imports
Quotas
Non-tariff barrier.
Quantitative restriction to trade through which a limit is set on the total amount of imports of a good allowed into the country for a given period of time.
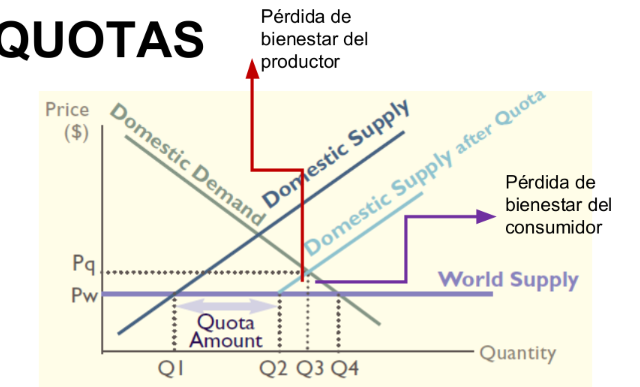
Quotas diagram
The consumers will only be able to buy imported products from Q1 - Q2
In Q2 the national supply has a shift to the right → national prices increase
Q3: National consumers can sell their products at Pq (consumers lose)
Product supply decreases from Q4 → Q3. Foreign producers can charge up to Pq to compensate the loss.
Non-tariff barriers
Mechanism that allows the application
of restrictions to international trade.
Main Non-tariff barriers
Licenses
Sanctions
Embargos
Licenses
This mechanism allows only certain companies to import certain commercial goods. The rest of the goods destined for trade are restricted in the rest of the country.
Sanctions
Increase bureaucracy to make international trade more difficult.
Impose new administrative measures.
Minimum price of import.
Standardization of products.
Sanitary and safety rules.
Embargos
Actions taken by any country to prohibit another country from trading with any type of service or good determined.