Chemistry: Measurements Uncertainty, & Sig Figs
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Qualitative observations
descriptions of what you observe
Quantitative observations
• Made by comparing something against a scale
• Include both a number and a scale unit
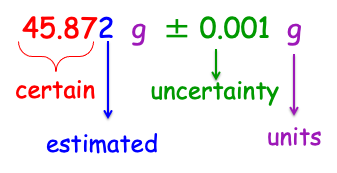
How to Report Measurement
certain value + estimated value ± uncertainty + units
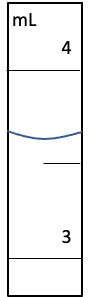
Graduated Cylinder
3.65 mL ± 0.05 mL
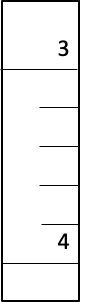
Buret
3.36 mL ± 0.02 mL
Precision
how close the measurements in a series are to each other
Accuracy
how close each measurement is to the actual value
Density
Mass/Volume
0.032
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
B) 2
12.010
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
E) 5
210
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
B) 2
319.3 x 23.566
A) 7524.6238
B) 7524.624
C) 7524.62
D) 7524.6
E) 7525
E) 7525
A) 117
B) 110
C) 120
D) 100
E) 200

4000/34
D) 100
(11.1 - 3.52) x 14.69
A) 111.3502
B) 111.3
C) 111
D) 110
E) 100
E) 100
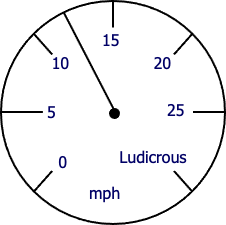
A) 12 mph
B) 12 mph ± 1 mph
C) 12.0 mph ± 0.5 mph
D) 12.00 mph ± 0.05 mph
E.) 12.0 mph ± 1 mph
C) 12.0 mph ± 0.5 mph
9,000,000,655.00 |
Scientific notation
9.000000655 × 106
Normal Notation | Scientific Notation |
0.00000834 |
Scientific Notation
8.34 × 10⁻⁶
Normal Notation | Scientific Notation |
1.21 |
Scientific Notation
1.21 × 10⁰
Normal Notation | Scientific Notation |
14.82 |
Scientific Notation
1.482 × 10¹
Normal Notation | Scientific Notation |
299,800,000. |
Scientific Notation
2.998 × 10⁸
mega (M)
1 X 106
kilo (k)
1 X 103
deci (d)
1 X 10-1
centi (c)
1 X 10-2
milli (m)
1 X 10-3
micro (µ)
1 X 10-6
nano (n)
1 X 10-9
pico (p)
1 X 10-12
Convert 3.8 cm into inches if you know that
1 inch = 2.54 cm
A) 1.496 inches
B) 9.652 inches
C) 9.6 inches
D) 1.5 inches
E) 2 inches
D) 1.5 inches
What is Chemistry?
The study of matter, its properties, the changes that matter undergoes, and the energy associated with these changes.
Law of Conservation of Matter
“Matter can neither be created nor destroyed”
Matter
anything that occupies space and has mass
Element
the simplest type of substance with unique physical and chemical properties
consists of only one type of atom
cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by physical or chemical means
Molecule
structure that consists of two or more atoms that are chemically bound together
behaves as an independent unit
Mixture
group of two or more elements and/or compounds that are physically intermingled (not chemically bonded)
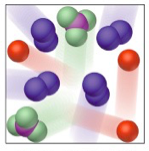
What is this?
Mixture
Physical Changes
changes in the properties of matter that do not effect matter’s composition
Chemical Changes
changes in the properties of matter that change matter’s composition
Solid to Liquid
melting
Liquid to Gas
vaporization
Liquid to Solid
freezing
Gas to Liquid
condensation
Solid to Gas
sublimation
Gas to Solid
deposition
Energy
anything that has the capacity to do work (cause change) or transfer heat
can interact with matter to cause physical and/or chemical changes
has no mass or volume
How do you sense energy?
Motion, Light, and Heat
Scientific Method
Observe —> Analyze —> Hypothesis —> Test —> Explain
Potential Energy
energy due to position of object
Kinetic Energy
energy due to motion of object
Endothermic
“energy in”, energy has to be added to overcome the forces of attraction between the molecules of a substance
Exothermic
“energy out”, heat is released
Endothermic Reactions
Melting, Vaporization, Sublimation
Exothermic Reactions
Condensation, Freezing, Deposition
AMU
Atomic Mass Unit
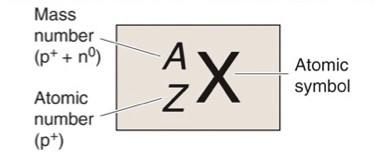
What is X?
Atomic Symbol
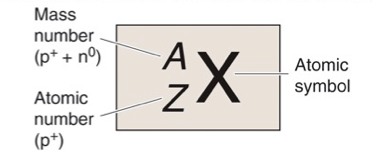
What is A?
Mass Number, Z + N
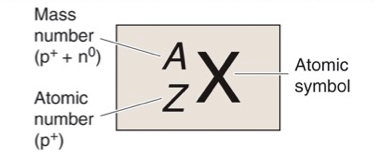
What is Z?
Atomic Number, Number of Protons
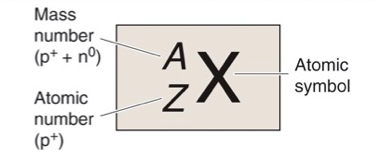
What is N?
Number of Neutrons
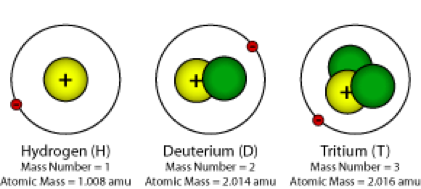
Isotopes
atoms of an element with same number of protons but different number of neutrons, same atomic number, different mass number
Ion
charge atom that has either more or less electrons than protons
Cation
ions with a positive charge; have less electrons than protons
Anion
ions with a negative charge; have more electrons than protons
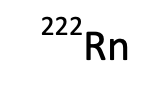
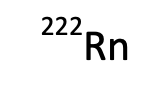
How many protons?
86
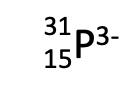
How many neutrons?
16
The elements in the modern periodic table are arranged by….
increasing atomic number (Z) + columns and rows to emphasize periodic properties
The columns are collectively called…
families or groups
The rows are collectively called…
periods
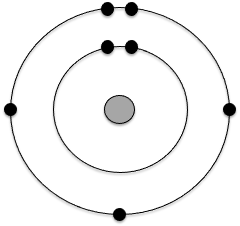
The following is the Bohr model for which atom?
Nitrogen
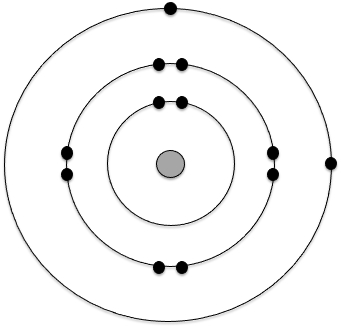
The following is the Bohr model for which atom?
Magnesium
valence electrons
electrons in the outer most shell
Elements with the same number of valence electrons have…
similar reactivity
The noble gases are the most ______________ on the periodic table.
stable (least reactive) elements
Metals tend to lose their own valence electrons, thereby becoming ______
cations
Nonmetals tend to gain extra valence electrons, thereby becoming ______
anions