Step1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/505
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
506 Terms
1
New cards
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale. What does this mean?
The pH scale is lo(pH = -log([H+]). A difference of 3 pH units corresponds to a 103 = 1000-fold difference in proton concentrations.garithmic (pH = -log([H+]). A difference of 3 pH units corresponds to a 103 = 1000-fold difference in proton concentrations.e pH scale is lo(pH = -log([H+]). A difference of 3 pH units corresponds to a 103 = 1000-fold difference in proton concentrations.garithmic (pH = -log([H+]). A difference of 3 pH units corresponds to a 103 = 1000-fold difference in proton concentrations.
2
New cards
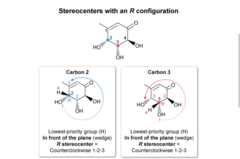
R or S configuration
The highest priority is assigned to the substituent atom with the greatest atomic number (ie, priority is 1). If two substituent atoms are the same, the atomic numbers of the next attached atoms are then considered.
When the lowest-priority group (ie, priority is 4) is pointed behind the plane (dashed), a clockwise arrangement of groups 1, 2, and 3 gives an R configuration whereas a counterclockwise arrangement gives an S configuration. The configurations are reversed when the lowest-priority group is pointed in front of the plane (wedged).( Basically if we lable priorties and they go 1 to 2 to3 to 4 counter clockwise and lowest priorty is dashed its S but if same conditions but lowest priorty is wedge we say R instead if lowest. if clockwise and lowest priorty dashed R if counter lowest dash s)
When the lowest-priority group (ie, priority is 4) is pointed behind the plane (dashed), a clockwise arrangement of groups 1, 2, and 3 gives an R configuration whereas a counterclockwise arrangement gives an S configuration. The configurations are reversed when the lowest-priority group is pointed in front of the plane (wedged).( Basically if we lable priorties and they go 1 to 2 to3 to 4 counter clockwise and lowest priorty is dashed its S but if same conditions but lowest priorty is wedge we say R instead if lowest. if clockwise and lowest priorty dashed R if counter lowest dash s)
3
New cards
sinoatrial node (SA node)
The heart controls its own rhythm through an electrical signal from the sinoatrial node (SA node) above the right atrium. This means that there is no external signal from the brain to tell the heart to beat—the SA node acts as the pacemaker of the heart.
4
New cards
This initial action potential travels to?
This initial action potential travels to both atria, but not the ventricles, causing only the right and left atria to contract.
5
New cards
(AV node), bundle of His, the Purkinje fibers
The atrioventricular node (AV node) then propagates the action potential to the ventricles by sending the signal through the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers, which spread the impulse evenly throughout both ventricles.
6
New cards
cardiac output
the amount of blood pumped through the heart each minute. The equation for cardiac output is as follows:
Cardiac Output = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
Cardiac Output = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
7
New cards
Stereotype threat
refers to the anxiety experienced by an individual who feels judged based on a negative stereotype about a group to which he or she belongs.
8
New cards
dyad
A dyad (relationship between two people) has only one social tie, making dyadic relationships the most intimate (eg, romantic couples, business partners); however, dyads are also less stable than larger groups because if either person leaves, the group ceases to exist.
9
New cards
A triad
A triad (relationship among three people) can have three potential social ties, making triadic relationships more stable but less intimate than dyads. The presence of a cultural liaison increases the number of social ties, resulting in a more stable group
10
New cards
Stereotype boost
Stereotype boost (also known as stereotype lift) occurs when positive stereotypes about social groups cause improved performance.
11
New cards
Confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is a type of cognitive bias (common error in thinking) in which individuals tend to embrace evidence supporting their beliefs, dismiss or ignore evidence refuting their beliefs, and interpret ambiguous evidence as support.
12
New cards
Labeling theory
Labeling theory suggests that when someone is labeled as deviant, the act of being labeled produces further deviance.
13
New cards
Differential association theory
Differential association theory suggests that deviance is learned through interaction.
14
New cards
Conflict theory
Conflict theory suggests that laws are created to serve those in power and maintain their privilege. Individuals engage in deviance as political protest against inequalities. The passage does not suggest recidivism is a conscious choice to act in ways to subvert the current social order.
15
New cards
cognitive dissonance theory
According to cognitive dissonance theory, cognitive dissonance (mental conflict) results from beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors that are contradictory or incompatible. Cognitive dissonance causes a state of discomfort that results in motivation to reduce the conflict by aligning thoughts and/or behaviors.
16
New cards
Symbolic Interactionism
George Herbert Mead, who is most associated with the sociological theory of symbolic interactionism, argued that social (rather than biological) factors influence identity formation. Mead suggested that the experience of "self" emerges through social interaction with others who play important and formative roles in one's life (eg, family).
17
New cards
The two aspects of the self are the "I" and "me," which develop in stages:
Play: Through play (eg, pretending to be a doctor), preschool-age children begin role-taking (ie, understanding the perspectives of others). When children understand themselves as individuals separate from others, the "I" component of the self has developed. Children then begin to imagine how others perceive them, which is the beginning of the development of the "me."
Game: :Me developed here: School-age children become aware of their position/role in relation to others. They begin to see themselves from the perspective of the more abstract generalized other, further developing the "me" to incorporate the values and rules of the society in which they live.
Game: :Me developed here: School-age children become aware of their position/role in relation to others. They begin to see themselves from the perspective of the more abstract generalized other, further developing the "me" to incorporate the values and rules of the society in which they live.
18
New cards
World systems theory
World systems theory is an economic theory of globalization that views the world as a global economy where some countries benefit at the expense of others:
19
New cards
Core nations
Core nations are wealthy with strong, diversified economies and centralized governments. Core nations (eg, United States, Western European countries) take resources from (exploit) poorer countries and lead the global economic market through the export of goods around the world.
20
New cards
Periphery nations
Periphery nations are poor and have weak governments and economies. Periphery nations (eg, Latin American, African countries) rely on the export of their resources (eg, oil, coffee, labor) to wealthier countries, making them dependent on (and exploited by) core nations.
21
New cards
Semi-periphery
Semi-periphery nations (eg, India, Brazil) are between core and periphery nations, with economies that are relatively more diversified than those of periphery nations.
22
New cards
four main tissue types in the human body:
four main tissue types in the human body: epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous tissue.
23
New cards
RNA polymerases
RNA polymerases are responsible for carrying out transcription and must bind DNA at a promoter region for transcription to be initiated.
24
New cards
Transcription factors
Transcription factors are proteins that can bind to DNA near gene promoter regions and either increase transcription (activators) or decrease transcription (repressors).
25
New cards
Ohm's Law for heart flow
Ohm's Law quantifies the relationship between these variables as ΔP = Q x R, where ΔP is the pressure gradient between the arteries and veins, Q is the blood flow defined by the cardiac output, and R is the resistance.This equation gives us some important conclusions, mainly that blood pressure changes with either cardiac output or resistance (and only those!).
26
New cards
Driving force of blood
The driving force in blood flow is the pressure caused by the heart pumping in one direction. Opposing this force is friction, which is caused by the blood cells against the vessel walls, and the technical term is resistance. T
27
New cards
As the blood continues through the circulatory system, the pressure continues to ?
As the blood continues through the circulatory system, the pressure continues to decrease and is close to zero in the veins right before the heart. Overall, this pressure can be modeled in the figure below.
28
New cards
When none of the subunits are bound to oxygen, the hemoglobin assumes what is known as a___ conformation
The way each hemoglobin is structured, the four subunits do not bind oxygen independently. When none of the subunits are bound to oxygen, the hemoglobin assumes what is known as a tense conformation. This tense conformation has a low affinity for oxygen.
29
New cards
When the first subunit binds oxygen, however, the conformation changes to a_____ state. Because of this, hemoglobin is said to bind oxygen in a_____ fashion.
When the first subunit binds oxygen, however, the conformation changes to a relaxed state, which has a higher affinity for oxygen. Because of this, hemoglobin is said to bind oxygen in a cooperative fashion(sigmoidal shape).
30
New cards
Certain conditions within the body help stabilize the tense configuration (remember, no oxygen is bound in this configuration
These factors are decreased pH, increased partial pressure of carbon dioxide, and increased temperature. Together, the ability of these factors to stabilize the tense conformation is known as the Bohr effect.By decreasing the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen, a low pH or an increased PCO2 leads to more oxygen being released from the blood
31
New cards
The tendency of hemoglobin to bind oxygen can be quantified using
% sat = (# of bound O2 molecules) / (# of binding sites) x 100%
32
New cards
Right shift
Factors which result in shifting of the oxygen-dissociation curve to the right include increased concentration of pCO2, acidosis, raised temperature and high concentrations of 2,3 diphosphoglycerate (2,3 DPG). These factors, in effect, cause the Hb to give up oxygen more readily.
33
New cards
Left Shift
high blood pH (breathing off CO2 - an acid)
low temperature (ambient temperature usually lower than that of the lungs)
reduced PCO2 (ventilation)
decreased 2,3-DPG and the presence of fetal Hgb
low temperature (ambient temperature usually lower than that of the lungs)
reduced PCO2 (ventilation)
decreased 2,3-DPG and the presence of fetal Hgb
34
New cards
Mechanism that slows. down the heart
The mechanism through which this occurs is the vagus nerve releasing acetylcholine near the SA node to inhibit depolarization and binding to receptors. The constant inhibition level is known as the vagal tone, and it changes based on the needs of the body.(parasympathetic)
35
New cards
Co2 transport in blood
There are three main ways in which carbon dioxide is transported from the tissues to the lungs. The first way is in the form of carbonic acid(H2CO3). An enzyme called carbonic anhydrase facilitates this process, and it forms a water-soluble molecule that can easily be dissolved in the blood. The second mechanism that accounts for about a fifth of carbon dioxide transport is that the carbon dioxide simply sticks to the hemoglobin. It doesn't bind at the oxygen-binding sites, but it does bind to various other sites on the protein. The third, and most insignificant method, is by dissolving directly into the blood. Carbon dioxide is more water-soluble than oxygen, so a small portion can be transported directly in the plasma.
36
New cards
Increasing the heart rate
This works through a series of nerves that innervate the heart and norepinephrine to stimulate muscle contraction. Additionally, epinephrine secreted from the adrenal medulla stimulates muscle in the heart. Together, both of these increase the heart rate as well as the force of contraction.
37
New cards
_______ in the heart. These receptors measure blood pressure and send signals to the central nervous
baroreceptors in the heart. These receptors measure blood pressure and send signals to the central nervous system when the pressure is too high. The CNS then sends signals to the heart to correct this via an increased vagal tone or decreased sympathetic signaling.
38
New cards
Transcription factors
Transcription factors are proteins that can bind to DNA near gene promoter regions and either increase transcription (activators) or decrease transcription (repressors).Activators facilitate RNA polymerase binding to the promoter, and repressors inhibit binding.
39
New cards
Replication vs. Transcription
Replication is the duplication of two-strands of DNA. Transcription (ran polymerase) is the formation of single, identical RNA from the two-stranded DNA. The two strands are separated and then each strand's complementary DNA sequence is recreated by an enzyme called DNA polymerase.
40
New cards
Heterochromatin
Heterochromatin consists of DNA that is tightly coiled around histone proteins.DNA in heterochromatin is not readily accessible to RNA polymerase and so cannot be readily transcribed.
41
New cards
Euchromatin
Euchromatin forms when histones are modified, often by acetylation of lysine residues. The added acetyl group neutralizes the positive charge on the histone, reducing interactions between histones and DNA. The reduced interactions yield a more open form that is more accessible to RNA polymerase, allowing euchromatin to be more readily transcribed.
42
New cards
Alternate splicing
Alternate splicing produces multiple protein products from the same gene, not multiple similar genes.
43
New cards
Conjugation
Conjugation: The bacteria uses a sex pilus, which is a long, thin, hollow tube used to connect one bacteria to another. The genetic material will travel through this tube from the donor to a recipient. In order to have a sex pilus, the bacteria needs something called the "fertility factor", which is just the plasmid that codes for the sex pilus.
44
New cards
Transduction
Transduction: The bacteria is infected by a virus (bacteriophage) carrying DNA. The viral DNA will combine w/ the bacteria's genetic material.
45
New cards
Transformation
The bacteria will pick up random foreign DNA from the environment and mix it into its own DNA. If the bacteria takes in a fragment of DNA, it will be incorporated into its own original DNA. If it takes up a plasmid, it'll just hold onto the plasmid w/o mixing it into its original DNA.
46
New cards
Reflex arcs begin with the stimulation of a?
Reflex arcs begin with the stimulation of a sensory neuron, which leads to an electrical impulse that travels toward the spine along a sensory nerve. This impulse enters the spine via the dorsal root ganglia and can be transmitted in one of two ways:
Directly to the effector neuron (ie, a monosynaptic reflex arc), or
Indirectly through an interneuron that interfaces with the effector neuron (ie, a polysynaptic reflex arc)
Directly to the effector neuron (ie, a monosynaptic reflex arc), or
Indirectly through an interneuron that interfaces with the effector neuron (ie, a polysynaptic reflex arc)
47
New cards
Afferent
Afferent information approaches the central nervous system [CNS]
48
New cards
effector
effector (target) organ generates the desired response to the stimulus.
49
New cards
Pathway for food
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
50
New cards
right hemisphere
The right hemisphere is crucial for processing visuospatial patterns.In addition to visuospatial processing, the right hemisphere is important for artistic and musical abilities, visualization, and emotion.
touch movement of left side
touch movement of left side
51
New cards
left hemisphere
the left hemisphere is important for language ability, including speaking, writing, and comprehension. The left hemisphere is also superior at analytical reasoning skills and logic, which are used in mathematics and science. touch movement of right side
52
New cards
The chiral amino acids produced by living organisms are almost exclusively?
The chiral amino acids produced by living organisms are almost exclusively L-amino acids.
53
New cards
chiral amino acids are designated a? depending on ?
The chiral amino acids are designated as L- or D-amino acids, depending on the orientation of the substituents around the α-carbon
54
New cards
L-amino acids
Most proteinogenic L-amino acids have an S-absolute configuration at the α-carbon. However, L-cysteine has an R-configuration at the alpha carbon
55
New cards
Reducing sugar vs non reducing
sugars can be classified as reducing if they contain a free anomeric carbon that can be oxidized, and as nonreducing when this carbon is linked to another molecule.(If the anomeric carbon has on -OH attached to it, it is considered a reducing sugar. If it doesn't, it's considered a nonreducing. At least, that's the way I think of it. Hope it helps)
56
New cards
anomeric carbon in ring form
When the ring forms, one of the substitutent OH groups attacks the carbonyl carbon. So, one easy way to identify the anomeric carbon in a circular sugar is to look at which carbon is bound two two separate oxygens.
57
New cards
anomeric cabon when In straight configuration
So, the anomeric carbon is the carbon containing the carbonyl functional group when in straight chain form.
58
New cards
In the backbone of these strands, adjacent ribose sugars are joined by phosphodiester bonds at the 5′ and 3′ carbons. Each nucleotide contains a nitrogenous base bound to a sugar through a covalent bond known as a glycosidic bond.
59
New cards
Protein secondary structure consists primarily of ?
Protein secondary structure consists primarily of α-helices and β-strands
60
New cards
Two amino acids are known to disrupt α-helices?
Two amino acids are known to disrupt α-helices: glycine and proline. Neither of these amino acids is likely to be found within an α-helix.
61
New cards
Tertiary structure is primarily stabilized by what type of bonds?
Tertiary structure is primarily stabilized by noncovalent interactions between side chains
62
New cards
primary protein structure
Primary structure consists of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are between the alpha-carboxyl of one amino acid, and the alpha-amine of the next amino acid.
63
New cards
secondary protein structure
The secondary structure arises from the hydrogen bonds formed between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. The hydrogen bonds form between the partially negative oxygen atom and the partially positive nitrogen atom.
64
New cards
A ternary complex is?
A ternary complex is a group of three molecules bound together, generally with at least one of the molecules being a protein. Ternary complexes may form by either of two mechanisms: ordered, in which the ligands must bind in a specific sequence, or random, in which the order of binding does not matter.
65
New cards
Native PAGE
Native PAGE takes place in a polyacrylamide gel in the absence of any detergents or reducing agents. These gels preserve the native structure of the protein, allowing for analysis of interactions with other molecules.
66
New cards
SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE is PAGE performed in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), a detergent that causes the protein to denature (ie, unfold) and coats it with negative charge. This version of electrophoresis separates proteins on the basis of mass only. This approach is useful for analyzing changes in protein molecular weight as a result of post-translational modifications, or for simply visualizing the different protein sizes present in a mixture. Reducing agents (eg, dithiothreitol) may be added to SDS-PAGE experiments to break any disulfide bonds that are present.
67
New cards
Neuroleptic treatments for schizophrenia effect ?
Schizophrenia is often treated with neuroleptic (conventional, typical, or first-generation) or atypical (second-generation) antipsychotic medication; both are generally effective in reducing positive symptoms. However, neuroleptics may exacerbate (worsen) negative symptoms through sedation or cognitive dulling, and they carry the risk of movement (eg, tremors) and other side effects.
68
New cards
prejudice
prejudice (negative or positive ideas/beliefs about a specific group),
69
New cards
discrimination
discrimination involves actions that negatively impact specific groups.
70
New cards
Phosphorylation can occur at various residues, but by far the most common are ?
Phosphorylation can occur at various residues, but by far the most common are serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues, each of which contains a hydroxyl group in its side chain. (OH group)
71
New cards
If a protease is used what is the effect on SDS-page
SDS page goes off size. More degradable so well see a dec in visibility compared to non treated
72
New cards
The interactionist theory
The interactionist theory proposes that language acquisition is the result of both biological (eg, normal brain development) and environmental/social factors, particularly the interaction that occurs between children and their caregivers.
73
New cards
nativist perspective
human brain has an innate
capacity for acquiring language (language acquisition
device), possibly during a critical period of
time after birth; and that children are born with a
universal sense of grammar (Noam Chomsky).
capacity for acquiring language (language acquisition
device), possibly during a critical period of
time after birth; and that children are born with a
universal sense of grammar (Noam Chomsky).
74
New cards
learning perspective
learned through oterm-78perant conditioning(Operant conditioning relies on a fairly simple premise: Actions that are followed by reinforcement will be strengthened and more likely to occur) language imitation and practice
75
New cards
Immigration vs. Emigration
Immigration is the relocation of individuals into an area, whereas emigration is relocation out of an area
76
New cards
Push vs. Pull Factors
Push factors (eg, unemployment, war) in the country of origin drive emigration, whereas pull factors (eg, job opportunities) in the receiving country attract people to immigrate.
77
New cards
Social capital
Social capital refers to a person's networks of people that can be converted into economic gain.
78
New cards
Social mobility? higher Social capital causes?
Social mobility refers to the movement of individuals, groups, or families between or within status categories in society (eg, from middle class to upper class). Social mobility can be horizontal or vertical and is related to a multitude of other factors, such as education, job loss, marriage, and institutionalized discrimination.
79
New cards
actor-observer bias
The actor-observer bias is an attributional bias that describes the tendency to attribute one's own actions to externalfactors but the actions of others to internal factors.
80
New cards
fundamental attribution error
The fundamental attribution error, an attributional bias, is the tendency to blame others' behavior on internal (eg, "they are lazy") instead of external factors.
81
New cards
Self-serving bias
Self-serving bias is an attributional bias that occurs when individuals credit their successes to internal factors but blame their failures on external factors.Self-serving bias is an attributional bias that occurs when individuals credit their successes to internal factors but blame their failures on external factors.
82
New cards
AUG codon
start codon (methionine)
83
New cards
Cathode vs Anode Cation vs Anion
Cathode is the negatively charged end, and anode is the positively charged end. Cations are positively charged, and anions are negatively charged. Thus, positive charged species (cations) will go towards the cathodes (negatively charged end), and vice versa. Because DNA is negatively charged, it will flow towards the anodes
84
New cards
non polar amino acids
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Proline
85
New cards
Alophatic amino acids
basically means carbons and hydrogens but not aromatic. Glycine Proline Alaine Valine leucine Methionone isoleucine
86
New cards
Proline
Pro, P
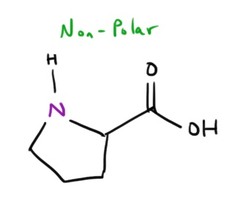
87
New cards
What are the common phosphorlaed amino acids
Serine, Tyrosine, Theronine because of OH- group
88
New cards
Phosporlating an amino acids changes the charge to ?
Neg charged after. If near another negative charge amino acid it would repeal each other causing a change in confirmation structure hence how phosphorylation is able to activated or deactivate a protein by changing conformation shape
89
New cards
What are the effects of replacing an amino acid that can be phosphorated with a amino acid that's neg charged?
Protein is always active. negative charged replacement amino acid mimics the phosporlated amino acid
90
New cards
Epimers
Epimers are a type of diastereomer that differ in spatial orientation at only one stereocenter.
91
New cards
Stereoisomers
Stereoisomers are compounds with the same molecular formula and atom connectivity but the bonds are oriented differently in space. Stereoisomers have one or more stereocenters, also known as chiral centers, which consist of an atom bonded to four different substituents.
92
New cards
Diastereomers
Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomer where at least one (but not all) of the stereocenters differ in orientation.
93
New cards
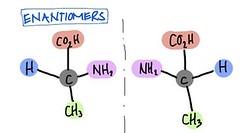
Enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
94
New cards
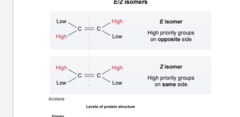
E/Z
E= highest priority functional groups on opposite sides
Z= highest priority functional group on same side
Z= highest priority functional group on same side
95
New cards
SN2 reaction
An SN2 reaction is a concerted substitution reaction. A nucleophile attacks an electrophile on the opposite side of the leaving group (ie, the nucleophile does a backside attack), and if the electrophilic center is a chiral center, the stereochemistry of the chiral center is inverted.
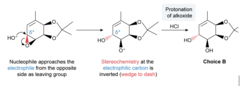
96
New cards
specific roation
calculated from observed rotation and experimental parameters. Specific rotation [α] describes the direction (+ or −) and magnitude (degrees) a chiral molecule rotates plane-polarized light. A clockwise rotation is classified as positive (+) and a counterclockwise rotation is negative (−)
Enantiomers have specific rotations of equal magnitude but opposite directions. If the molecules were enantiomers, they would either have specific rotations of +40° and −40° or +25° and −25°.
Enantiomers have specific rotations of equal magnitude but opposite directions. If the molecules were enantiomers, they would either have specific rotations of +40° and −40° or +25° and −25°.
![calculated from observed rotation and experimental parameters. Specific rotation [α] describes the direction (+ or −) and magnitude (degrees) a chiral molecule rotates plane-polarized light. A clockwise rotation is classified as positive (+) and a counterclockwise rotation is negative (−)
Enantiomers have specific rotations of equal magnitude but opposite directions. If the molecules were enantiomers, they would either have specific rotations of +40° and −40° or +25° and −25°.](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b8fce24708514eaf9ac8c3dd0f08079f.jpg)
97
New cards
TLC Chromatography
-"Polar is Slower" because tlc is coated with polar compound. So non polar will migrate faster in solvent
-Separation of mixtures using a Mobile and Stationary Phase
-Separation of mixtures using a Mobile and Stationary Phase
98
New cards
Rf value equation for TLC
Rf = distance travelled by substance / distance travelled by solvent
99
New cards
Nucleophile
Nucleophiles are atoms on a molecule that donate electrons (usually two at a time) to a target molecule to form a bond. Generally, atoms are nucleophiles, or nucleophilic, if they have a large electron density that results from full or partial negative charge. This means that atoms such as oxygen, fluorine, and chlorine are excellent nucleophiles.
-Hence the ability to donate electrons increases with the increase in the number of electrons. Therefore, as the species become more and more electron rich, the nucleophilicity increases.
-Hence the ability to donate electrons increases with the increase in the number of electrons. Therefore, as the species become more and more electron rich, the nucleophilicity increases.
100
New cards
Electrophile
electron pair acceptor. ATTRACTED TO ELECTRONS AND HAS A PARTIAL POSTIVE CHARGE. Your typical electrophiles will have good leaving groups like halides or sulfonate ester groups. They may also have polarizable C=O bonds like in aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids derivatives.