Gregor Mendel Power point 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Who was Gregor Mendel and when did he live?
1822-1884, a monk/teacher who experimented with pea plants with distinct traits. He tracked these traits through each generation and individually counted everything to understand the genetic ratios.
When was Mendel’s work presented?
1864 but not accepted until 1900s
Important organelles teacher pointed out on eukaryotic cell model
mitochondrion (has some genetic material), ribosomes (makes protein), nucleus, centrioles
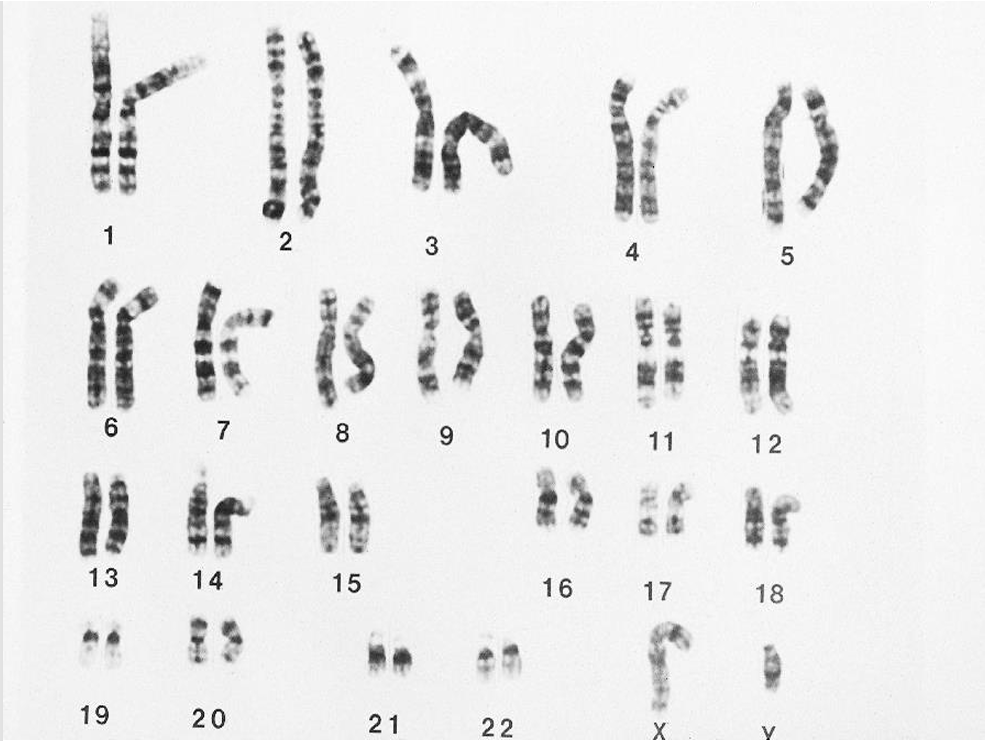
What is this image?
human chromosomes (46 individual, 23 pairs, 1 pair sex chromosomes)
What makes homologous chromosomes? (test question)
they have the same gene sequence and two alleles are present
What does heterozygous mean?
two different genes (Aa)
What does homozygous mean?
two of the same genes (aa)
What is an allele?
a different format of one gene
What is a male chromosome?
y
What is a female chromosome?
x
What is a chromosome?
a threadlike structure made of DNA and proteins that carries genetic information
What does the term “genetics” mean in Greek?
to generate
When and who coined the term “genetics”?
William Bateson in 1905
Who coined the word “gene”?
Johanssen
What is the original Mendelian definition of “gene”?
the inherited unit located on chromosomes that determines a biological characteristic. A unit of function and mutation.
The gene is a substance that satisfies what two essential requirements?
it is inherited between generations in such a way that each descendant has a physical copy of this material (copy and replicate genes)
it provides information to its carriers in respect to structure, function, and other biological attributes
First meiotic prophase (homologous chromosomes in pairs)
genes are parts of chromosomes
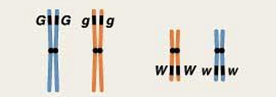
First meiotic anaphase (homologs segregate during meiosis)
each homolog duplicates into two sister chromatids
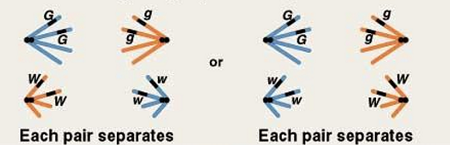
following many meiotic events what happens? (nonhomologous chromosomes assort independently)
gamete (sex cell - sperm and egg) forms
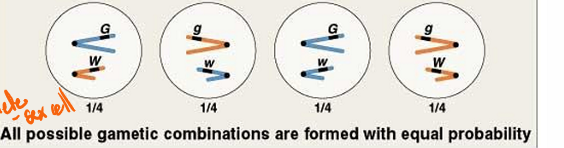
What is the order of the generations we study?
P1 (gamete formation), F1 generation, F1 cross, F2 generation
What is Mendel’s First Law called?
principle of allelic segregation
What is Mendel’s First Law (Principle of Allelic Segregation)?
alleles of each gene segregate (separate) at the time of meiosis (gamete formation), so that half the gametes carry one allele and half carry the other
What are testcrosses used for?
to determine if an individual with a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous dominant
What is Mendel’s Second Law called?
Principle of Independent Assortment
What is Mendel’s Second Law (Principle of Independent Assortment)?
either allele of one gene pair can enter a gamete with either allele of any other gene pair and all possible combinations are produced in equal proportions
What is the phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross?
9:3:3:1