Composition of Blood
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
manipulate the composition of blood
-with complete control
-without adverse consequences
functions of the blood
-deliver products
-remove waste
-facilitate signaling
-respond to emergencies
-maintain structural integrity
blood components
-cells
-liquid (serum/plasma)
-serum v. plasma: serum- blood clots in the tube, all coagulation units used up in the clots; plasma- blood does not clot (has coagulation); both liquid component of blood
blood cells
-RBCs
-WBCs- PMNs, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
-platelets
-endothelial cells, HSC, cancer cells (leukemia/solid tumors)
-parasites, bacteria, viruses
RBC
-biconcave disk
-8 microns in diameter
-terminally differentiated
-contains: hemoglobin, lactate dehydrogenase, K+
-does not contain: nucleus, Golgi, mitochondria; lose all organelles as they differentiate
-deliver oxygen
-remove CO2
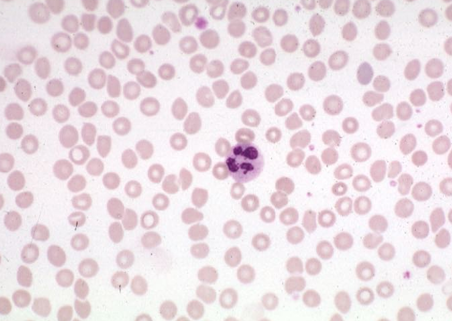
WBC- PMNs
-polymorphonuclear leukocytes/polys/PMNs/neutrophils/segs
-granules- not too blue, not too red; “neutral”
-terminally differentiated
-segmented nucleus
-recruited to sites of inflammation
-phagocytosis, bacterial killing, granule release
WBC- monocytes
-”monos”
-inflammatory monos, patrolling monos, etc.
-circulating form (precursor) of tissue macrophages
-recruited to sites of inflammation
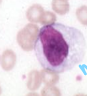
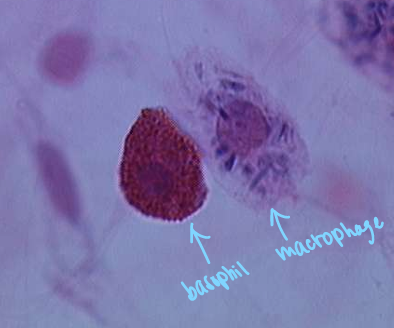
WBC- macrophages
-tissue resident macrophages: fetal development
-”replacement” macrophages: from monos and local proliferation
-lung/peritoneal cavity/spleen/liver/bone marrow: alveolar macrophages/peritoneal/splenic/Kupffer cells/erythroblastic island macrophages
-phagocytosis, bacterial killing, antigen presentation
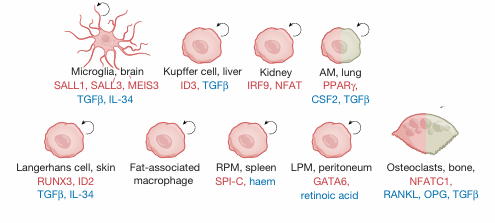
macrophages exist in multiple states of
-activation and/or differentiation
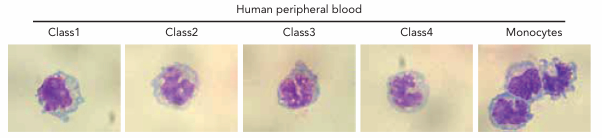
WBC- lymphocytes
-”lymphs”
-acquired immunity
-B cells: antigen presentation, antibody production
-T cells: cytotoxic cells, helper cells, “suppressor” cells
-nucleus round
-chromatin very dark
-nucleus not segmented
-little cytoplasm to see
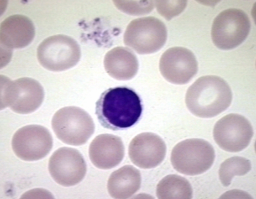
WBC- eosinophils
-”eos”
-terminally differentiated
-contains eosinophilic granules (granulocyte)
-granules contain major basic protein
-recruited to sites of inflammation
-involved in allergy, parasitic infections
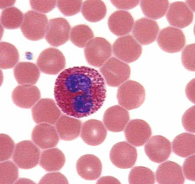
WBC- basophils
-circulating form (precursor?) of tissue mast cells
-terminally differentiated
-contains basophilic granules (granulocytes)
-granules contain histamine, heparin, etc.
-IgE receptors
-involved in allergy
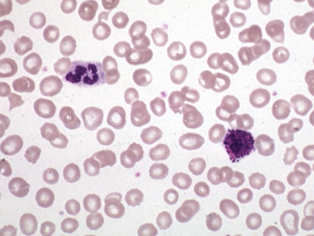
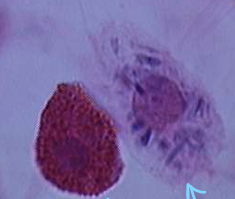
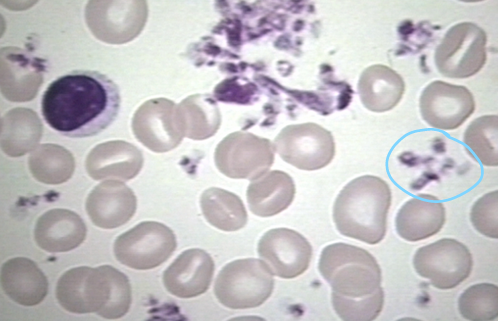
platelets
-derived from megakaryocytes
-terminally differentiated
-contains granules
-does not contain nucleus
-involved in clotting
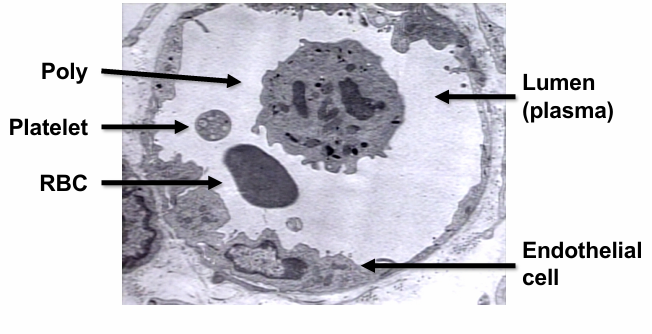
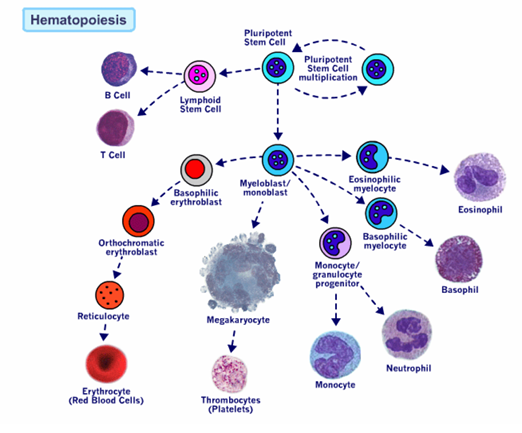
hematopoiesis
liquid (serum/plasma)
-water
-dissolved compounds: small molecules (ions/steroids/lipids/sugars), proteins (carriers/information/structural/defense), exogenous (vitamins/drugs/toxins), “leaked” from cells (PSA, amylase, elastase, troponins)