COA401_Geology
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
decreases
as pressure increases, melting point
increases
both pressure and temperautre ____ toward the center of the Earth
Lithosphere
hard, birttle part of the upper mantle
→ physical state of rocks change with increasing depth
→ higher temperature override the effect of pressure, causing a tiny portion of the rocks to melt
Asthenosphere
partial melting zone in the lithosphere where rocks flow plastically
→ lower part gradualyl becomes rigid as pressure increases
→ rocks are no logner plastic at 350 km below the Earth Surface
Mesosphere
More rigid zone of the mantle that reaches the top of the core
Hydrosphere
exterior envelope that composes of all free water on earth
97% composed of ocean water
Biosphere
exterior envelope comprising of all living and non living organic matters
→ consists largely of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen compound
→ org matter recycled into the lithosphere
Escarpment
long, steep slopes seperating areas of different heights
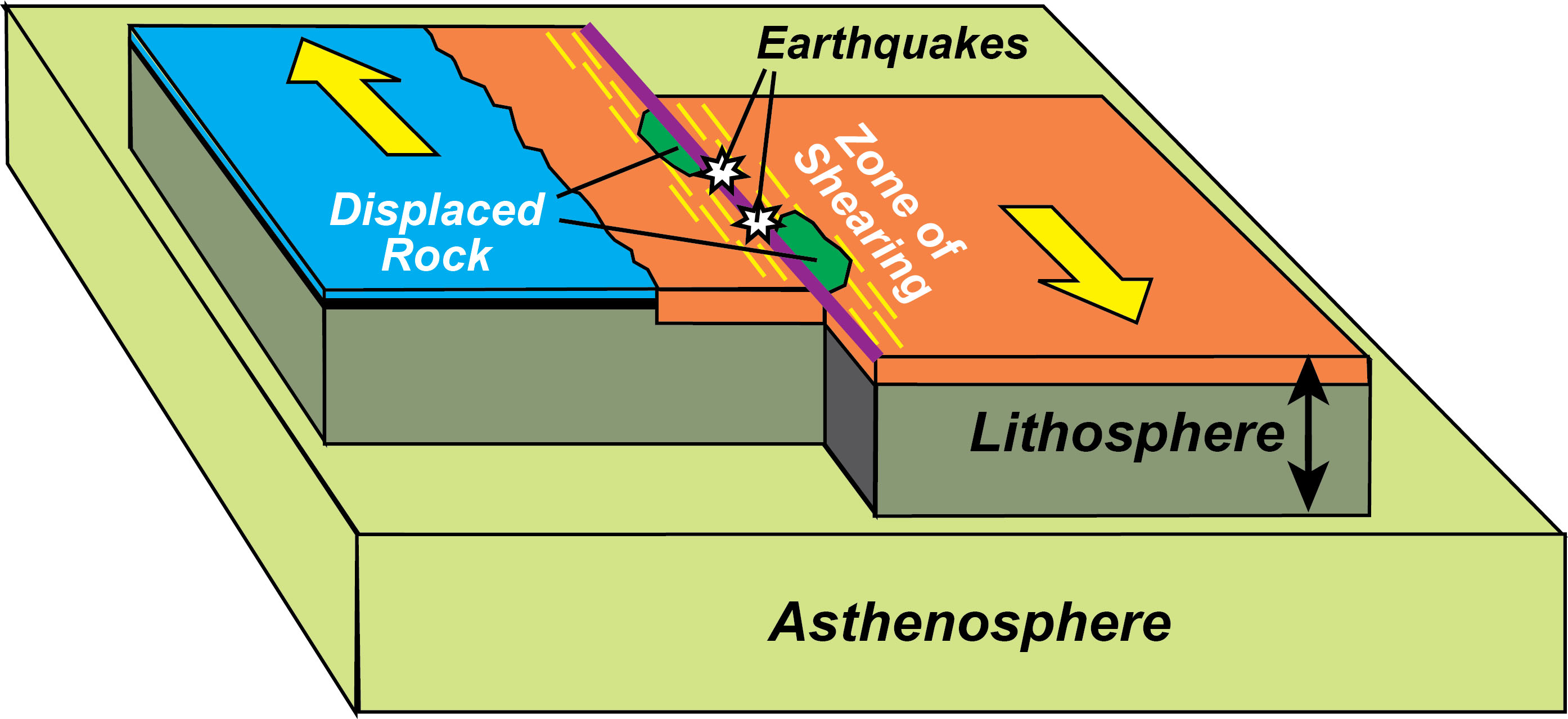
Transform faults
type of tectonic motion where fractured rocks slide past one another, casuing segementations of a geologically active area
creates a zig zag pattern
Fracture zones
inactive arms of transform faults that extend into deep-ocean basins
consit of lienar vallyes and elongated, faulted hills that are orientated at 90 degrees relative to its axis
characterized by escarpment
Contential Slope
Seward shelf breaks, inclined at 4 degrees
base lies at water depths of 2-3 km
consists of mud and sand eroded from the conteint that lies underneath the slope
→ hosts submarine canyons
Submarine Canyons
Deeply inclined land forms that cut into sedimentary depoists
serve as chutes of sedimentary depsoits from contnetial margins to deep ocean basins
Continental shelf
nearly flat plains at the top of the sedimentary wedge beneath the drowned edges of contieints
sliopes seaward at a .5 angle
ends at a shelf break, where the contneital shelf edns on the ocewna side the sea bottom steepns appreciably
shelf break
where the contiental shelf ends on the ocean side, the sea bottom steeps appreciably
occurs at water depths of 130 m
Continental Rise
part of the contiental margins, located at the basin of the continental slopes
ocean bottom flattened to a 1 degree gradient
Can extend more than 500km from the base of the continental slope to water depths approaching 4 km
No great topographic relief, except in areas where submarine canyons extend their channels onto the rise
Underlain by deposits of sediment that are very thick
Derived from the erosion of rock and sediment from nearby landmasses
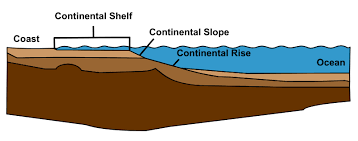
Continental margins
part of the continent that is submerged underwater
sand and mud eroded from continents transported to the shores and accumulated> become shaped into a thick sedimentary wedge along the continental edge
immense deposits of sediments at contential edges comrpise the contnetial margins
composed of: Shelf, shelf break, slope
Abyssal plains
flattest areas of deep ocean basins
regional slope <.5 degrees
drops vertically less than a meter across 1 km of seafloor
composed of land dervied sediments
→ buried irregular volcanic topography of the solid crust of the ocean
→ debris moved from submarine canyons and spilled out to cover the crust of the deep sea
abyssal hills
domes of deep ocean basins, elongated hills of 1,000m
composed of:
volcanic rock
covered in a thin layer of fine grained sediment that has setllted down through the water above
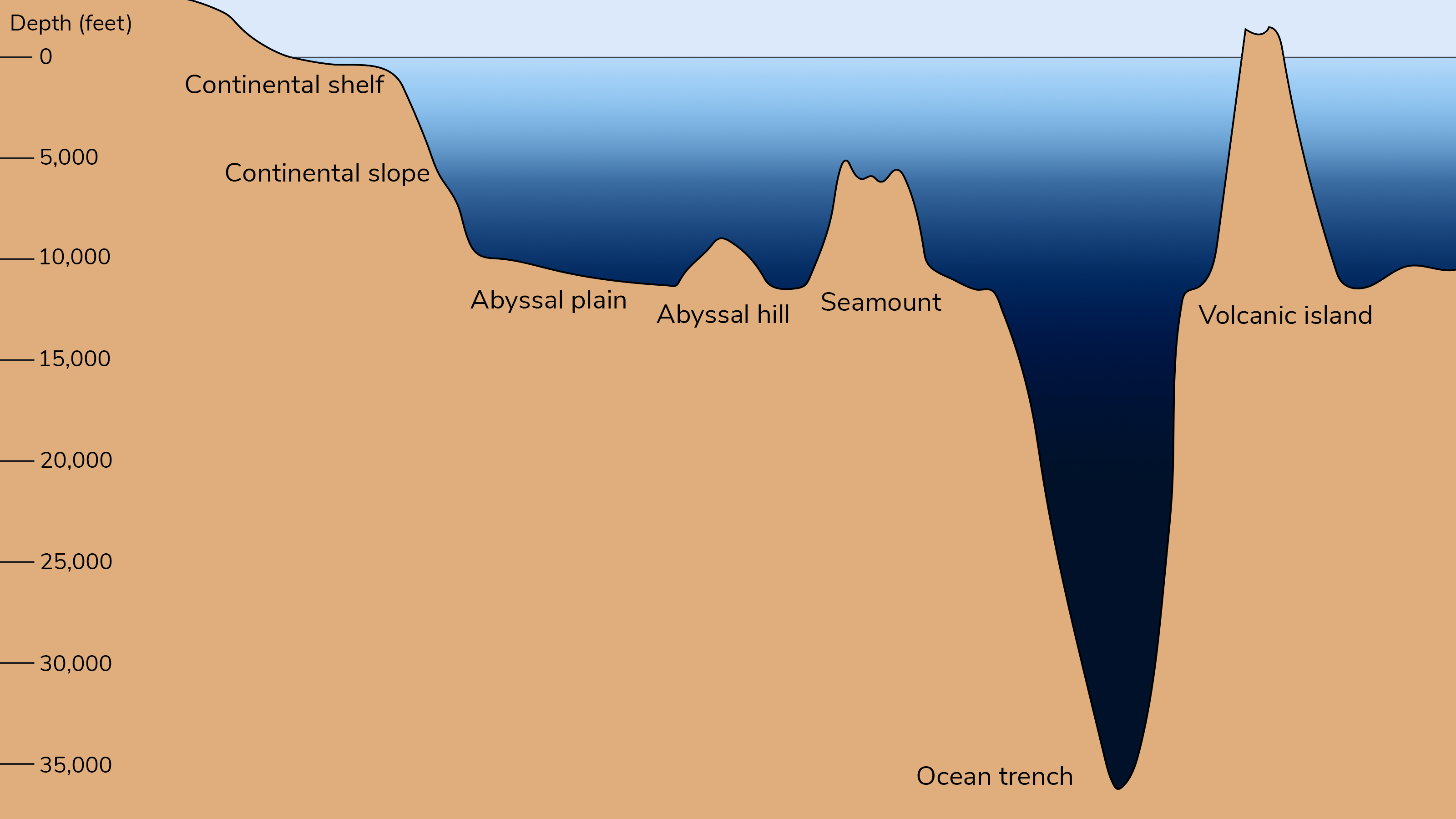
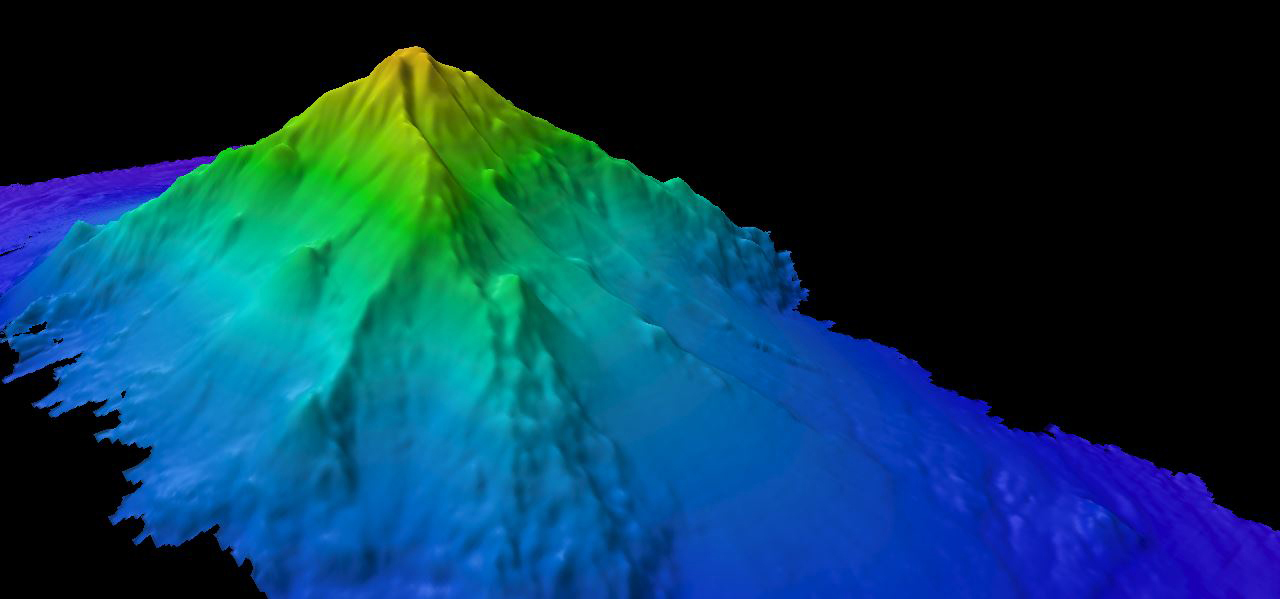
Seamount
part of the deep ocean basin
made of extinict or active volcanos
conical toop and steep sides
Guyots
flattoped sea mounts that were once active volcanos
tops were leveled and flattened by wave erosion
Deep sea trenches
steep, long and narrow depressions basins
can be 3-5km deeper than surrodning ocean floor
deepest regions on earth
close to land, nestled aganist continental margins or chains volcanic islands
associated with active volcanoes and earth quakes
partially filled wit sediment that has been eroded from the nearby landmasses above them
Granite
Contential crust is composed of
Basalt
oceanic crust is primarily composed of
moho
the boundary between the crust and upper mantle
warm, shallow seas
During the age of Pangaea, large portions of the central and western parts of North America were covered by
Mid-ocean ridges
a continuous submarine mountain range that winds its way through all oceans
covers 1/3 of the ocean floor
summit of each ocean ridge is convex or occupied by a rift valley
→ formed by faulting
→ geologically active: characterized by frequent shallow earthquakes
→ show seismicity and volcanism
Submarine canyons
rivers and currents that cut into sedimentary desposits, forming steep V shaped profiles
topographic relief of 2 km
one of the most deeply inclined landforms on Earth
serves as chutes to transfer sediments from contiental margins to deep ocean basins
part of the contiential slope
isostasy
the balance of an object floating upon a floating meidum
→ deep ocean basins and thin and dense, thus do not rise as high above the mantle
thickness, density
Height of the landmass aboe and below the surface of a medium is controlled by____________ and ___________
Alimetry
orbiting satellites use radars to radpily measure the height of the sea surface
→ variations in the height of the ocean reflect the bathymetry below
→ can detect water bound of water over a submarine mountain or volcano
→ can be used to map the ocean’s large scale bathymetric features
Echo-sounding
a sound transmitter mounted on the bottom of the vessel sounds out a sound pulse into the water
→ wave reflects off the ocean floor, where it is recorded by a hydrophone
Side scan sonar
sound directed is sideways to produce a map of the sea bottom traversed by the ship rather than a mere profile of the bottom
valuable for locating sunken ships
seismic reflection
sound pulses reflect on the ocean floor
can ID features within the bottom, revealing the shape and thickness of sediment and rocks beneath the sea floor
uses strong sound pulses and lower frequencies than an echo does
seismic refraction
sound waves bend as they travel through sediment, rock, and waves
reveals: densities, depths, rock thickness
relies on high energies and low frequncies
→ can give the geologic strucutre of crust and mantle
→ most powerful sound pulses
Alfred Wegner
proposes a theory of continental drift based on the fit of contienntal outlines, fossil evidence, geological evidence
100-150 mya
Pangae formed
Mid atlantic ridge
Oceanic ridge algined in the middle of the Atlantic basin
cut by long, linear tranform fauls and fracture zones that divie the ridge axis into many segments, each offset from one another
normal faults
topographic scarps where crustral rocks have broken and dropped past another, creating a valley
occurs along the edges of rift valleys as zones wehre crustal rocks are displaced vertically
→ forms fresh cr
older, distance
baslatic crust becomes increasingly __________ and _____with distance from the ridge line, because of a longer history of spreading and sediment accumulation
Paleomagnetization
occurs as other minearl crystalize, they lock in and trap the alignment of the magnetic grains
grains record the strength and direction of the geomagentic field at the time they crystallized into solid
→ will reflect the polairty of the earth at the time of freeze
Reverse polarity
the periodic switching of Earth’s polarity
has reversed 183 times in the last 83 million years, and at least several hundred times in the past 160 milliom years
magetnic anomaly stripes
reading of the magnetomere that measures either high or lower readings based on the polarity of the earth at the time of magentiization
→ as basalt crust is split at the crest, paris of these are about EQUAL WIDTH, mirror images of eachd other on each side of the flank
1-10cm/yr
rate of sea floor spreading
Tectonism
the deformation of Earth
s crust
Subduction Zones
zone where two plates converge, and one sinks under the other
associated with deep sea trenches and volcanic arcs, deep sea trenches and volcanoes, and mountain belts
→ slab going down generates strong earthqaules as its upper surface slips against the rock above it
→slab melts partially at depths of 100-200kkm
->hot lava rises to the surface and spewed out as volcanic arcs
→ one part of the sea floor plunges below another into the asthenosphere
→ balanced by sea floor spreading (plate growth)
ocean-ocean collisons
type of subduction events where two oceanic plates converge
→ deep sea trenches and volanic arcs
→ aleutian islands
ocean-continent collisons
type of subduction event where a contiental crust and ocean crust converge
→ topography: deep sea trench, volcanoes
→ Andes Mountains
Continent-Continent
type of subduction zone where Continent and continent collison
→ topography: mountain belt
→ no intensity
→ Himalyan Mountains
Thermal Convection
ductile rocks of the asthenosphere begin to rise upward
slow moving currents exert drag on the bottom of the lithosphere plates, setting them in motion
→ drags along the the overlying lithosphere plates away from the crests of ocean ridges
leads dense edges of the lithosphere at subduction zones to pull plate downward, as it sinks to th ehotter astehnosphere
Mantle plume
plume of hot mantle material rises through the lithospehre, spilling out as lava on top of the plate
forming a large volcanic mass
causes the growth of volcanic islands: volcanic plates sticking up past the water surface
Growth of volcanic islands
large volcanic mass at a hot spot are added to a pile, creating a volcanic cone on the ocean floor as the pacific plate drifts over the hot spots> plates stick up past the water surface, can form islands
-> North to North west fomration
→ islands become older and more eorded and lower in elevation as the lithospheric plate drifts north
Embyronic Basin
part of the wilson cycle
spllintering og granite contiental crust, forming long linear rift valleys
fractured by normal faults
motion: uplift
ex: East African rift valley
Juvenile Basin
Occurs when contients are separated into two indepdent masses
baslatic crust forms between them along a young spreading ocean ridge
narrow sea way forms
→ Red Sea
Mature
contiuned sea floor spreading
broad plate ruptures where lithsophere is old and supporting heavy sediment load when large piles of sediment accumlates
→ ocean basin with continental margins
→ Atlantic and Artic Oceans
Declining
Subduction begins where one side of the framented plate overrides the other
elimates much of the sea floor and oceanic ridge
ex: East Pacific Rise
Terminal Stage
when contients on either side of a subduction zone collide, and the last of the sea floor is eliminted
characterized by crust and sedimentary despot uplift
creates a young mountain belt folded and faulted marine sedimentary rocks
→ narrow irregular seas with young mountains
→ ex: Mediterranean Sea
Suturing
plates become sutured tighly togehter throughs edimentary deposition
oceanic crusts are buckled and thrust upward into a mountain range
→ Ex: Himalayan Range
Red Sea
type of juvenille ocean basins that is a result of divergence ebtween african palte and arbian plate
along the center: narrow axial with a expanse of 1000m w/ new baslatic ocean crust forming at the cetner of the sea
→ began to develop 20-30 mya as grantic crust of the plates were stretched until it broke apart a system of normal faults
→ large faults splintered the thick granitic crust into large blocks
→ brine water typically fills the axial trough as a result of flow of groundwater through fractures in underlying rocks
San Andreas fault
example of a transform fault where the sea floor spreading ridge of the Gulf of Califronia with the spreading ridge off of Oregon and washington. Plate motions result in seismic activity
Cascadia Subduction Zone
1,000km long dipping fault from northern Vancouver Island to Cape Mendocino Cali
Separates the Juane de Fuca and NA Plates
New Juan de Fuca plate is created offshore>
Shoved beneath the NA plate (continent)
Benioff Zone
Area of increasingly deeper seismic activity along subduction zomes (45 degrees)
intermeridate and deep earthwuakes ordiante within an incline zone that is tilted away from the deep-sea trench toward volcanic arc
extends to 700km
gravel>sand>mud>colloid
graditation of paricle size (largest to smallest)
Terrigenous sediment
Fine and coarse grains that are produced by the weathering and erosion of rocks on land
Sand or mud
Biogenous sediment
Fine and coarse grains derived from hard parts of organisms
Lime: composed of calcium carbonate
Siliceous: composed of silica
Formed by shells of skeletal debris
Micro and macro algae and organisms
Hydrogenous sediment
Particles precipitated by chemical or biochemical rxns in sw near the seafloor
Volcangeous Sediment
particles ejected from volcanoes
ex: Ash
Cosmogenous sediment
tiny grains that orignate from outer space, mixed into terrigenous and biogenic sediment
particle size distribution
energy conditions at site of deposition
determing factors of sedimentation
high energy conditions
in these conditions, fine grains are contiunally resuspended after momentary settlement.
Constant agitation seperates small grains and transport them into less turbulent water
coarse sand deposited under these condtions
low energy conditions
in these conditions, fine grain sediment settles. Coarse grain are lacking bc weak currents cannot transport them to these sites
mud accumlats here
heterogenous
rapid erosion results in high rate of sedimentation, has this type of depositional form
energy
average particle size is _____ to the energy level present at the time of deposition
homogenous
low rates of sedimentation result in a this type of deposition
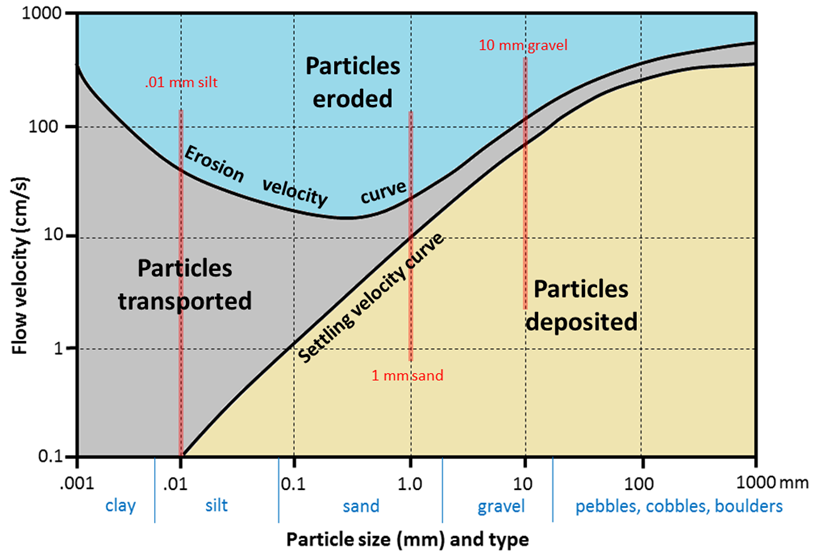
Hjulstrom Diagram
shows the average current velocities necessary for erosion, transportation, and deposition of sediment
→as you go down the graph and decreasing particle size, the average velocity needed for erosion decreases then increases again when it hits clay and slt
systematic decrease
in shelf sedimentation, sediments sort them selves into this order (under normal conditons)
150m
2 mil years ago sea levels dropped _____
relicit sediments
sediments locted on the outershelf that were depsoited during low sea levels, thus are LARGER than expected/ would have been depsoitied in normal conditons
2/3
amount of sedimentation that is made up of relicit sediments
tides, waves, currents, and depth
shelf sedimentation is strongly controlled by
river supplied terrigenous deposits
temp/mid lats sedimentation types
Biogenic sediment, primarily calcium carbonate derived from coral
equator/subtropics sediment
glacial till or ice rafted debris
polar shelves sedimentation
repeated glaciation events
The ‘dominant’ Earth-shaping event of the past million years has been
sediment laden bottom currents
submarine cnayons were deepened during interglacial periods by
passive-type continetal margins
distinict conteintal edge w/ a long history of sedimentation
wedge of sediment deposited between the basalt and granite plates forms> contiental margin is widen and thickened as terrigenous sediment erodes to the shelf
> crust and underlying matnel cool and contract
>weighed down by sediment load, edge of contiennt sinks continually, allowing river sediments to flow in
>NOT tectonically active
deep sedimentation
Accretionary prism
a compressional zone situtated between the deep sea trench and the volcanic arc that widens with the time as sediments are deformed and plastered to its seqared
→ mud is scraped off it as it is subducted
→ material from underwater landlsides are crushed aganist this
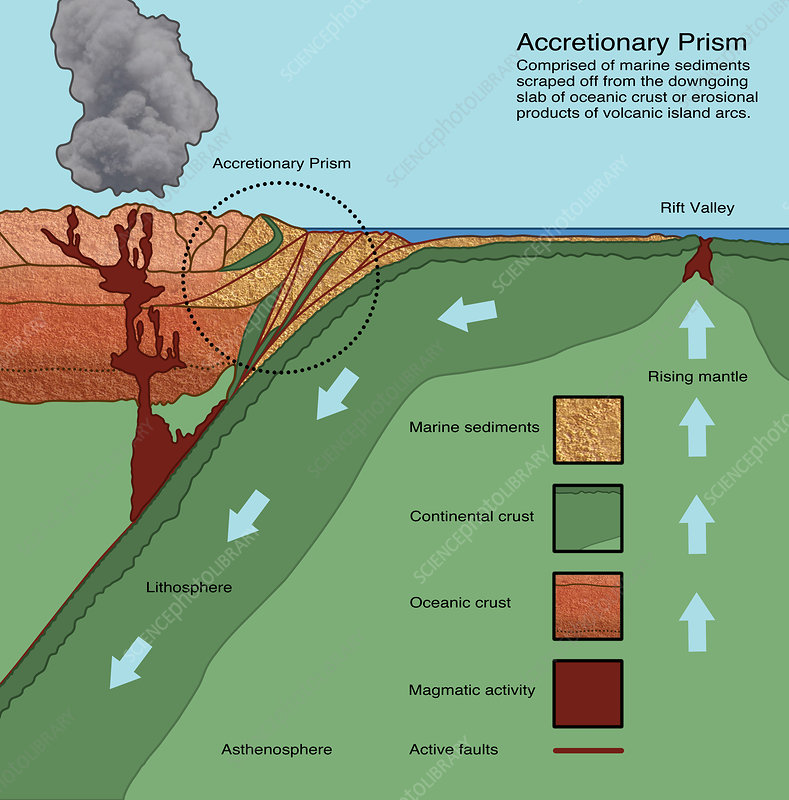
Active-Pacific type margin
Continental margin where compression from subduction squeezes the bed of sediment between colliding plates, folding and faulting the sediment layers
sedimentary layers and basalt scraped off the top of the plate is forced downward
→ continental shelf tends to be narrow and to have an irregular surface
→ near shore fills with sedimetn form volcanic activity, fills any troughs or depression in the rust, and erosion is trying to fill up the lower spots