Pathophysiology CARDIO EXAM
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
Give the “equation” of cardiac output:
stroke volume x heart rate
2
New cards
What is the normal range of cardiac output in a healthy adult?
6-7L/min
3
New cards
What is a normal heart rate?
60-80 bpm
4
New cards
What is a normal stroke volume?
100ml
5
New cards
What does stroke volume mean?
Volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle during systole
6
New cards
What is ejection fraction?
The percentage of the blood in the ventricle ejected at each systole
7
New cards
What is a normal ejection fraction?
65%
8
New cards
What is preload?
The force which stretches the cardiac cavity
9
New cards
Fill in the gap: Stroke volume increases as ……. augments
Preload
10
New cards
What is Afterload?
The amount of resistance the heart must pump against when ejecting blood
11
New cards
Is contractility dependent or independent on preload and afterload?
Independent
12
New cards
What is contractility?
The ability of the heart to eject a stroke volume
13
New cards
list the 4 factors that affect cardiac output:
1\.Preload
2\.Afterload
3\.Intrinsic contractility
4\.Extrinisic regulation (e.g hormones)
2\.Afterload
3\.Intrinsic contractility
4\.Extrinisic regulation (e.g hormones)
14
New cards
List 3 non-invasive ways to assess the heart:
1\.ECG
2\.MRI
3\.Electrocardiograph
2\.MRI
3\.Electrocardiograph
15
New cards
What is the Langerdoff technique?
Use of an animal heart in the lab to study the effect of various things on cardiac output.
We can also record intraventricular pressure
We can also record intraventricular pressure
16
New cards
Give the 4 main causes of death in heart failure:
1\.Cardiac output decrease
2\.Pulmonary edema
3\.Ventricular fibrillation
4\.Myocardial rupture
2\.Pulmonary edema
3\.Ventricular fibrillation
4\.Myocardial rupture
17
New cards
What is an arrythmia?
Condition where the heart rate is abnormal. Too fast, too slow or irregular
18
New cards
Heart rate is too slow in….
Bradycardia
19
New cards
Heart rate is too fast in…
tachycardia
20
New cards
List the 4 types of arrythmias according to origin of the problem:
1\.Atrial arrythmia
2\.Junctional (nodal) arrythmia
3\.Heart blocks
4\.Ventricular arrythmias
2\.Junctional (nodal) arrythmia
3\.Heart blocks
4\.Ventricular arrythmias
21
New cards
Atrial extrasystoles and atrial fibrillation are which type of arrythmia?
Atrial Arrythmia
22
New cards
Heart blocks can be broken down into three types, which ones?
1\.first-degree atrioventricular block
2\.second-degree atrioventricular block
3\.third-degree atrioventricular block
2\.second-degree atrioventricular block
3\.third-degree atrioventricular block
23
New cards
How do we see a first-degree atrioventricular block from an ECG?
PR interval is longer than normal
24
New cards
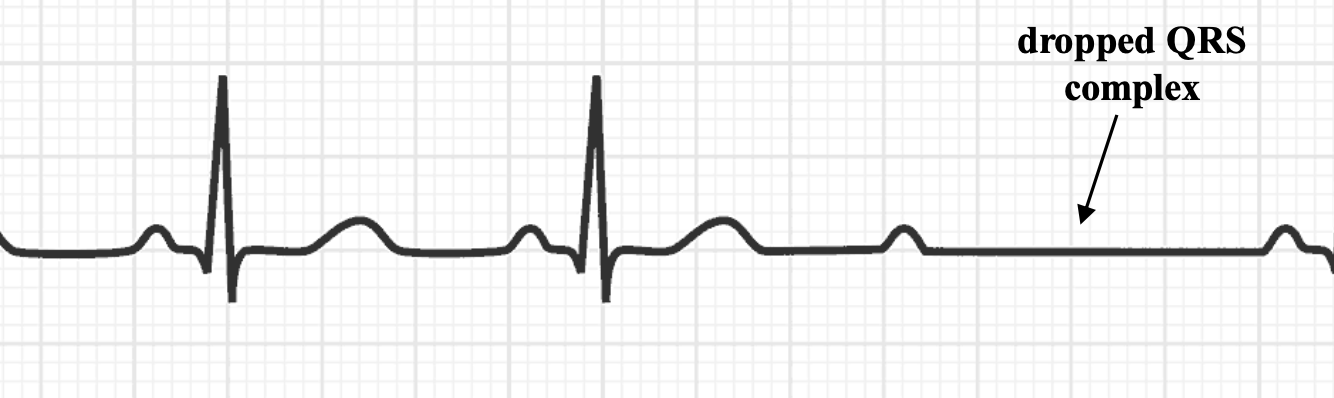
How do we see a second-degree atrioventricular block from an ECG?
Constant PR interval with intermittently dropped QRS complexes.
25
New cards
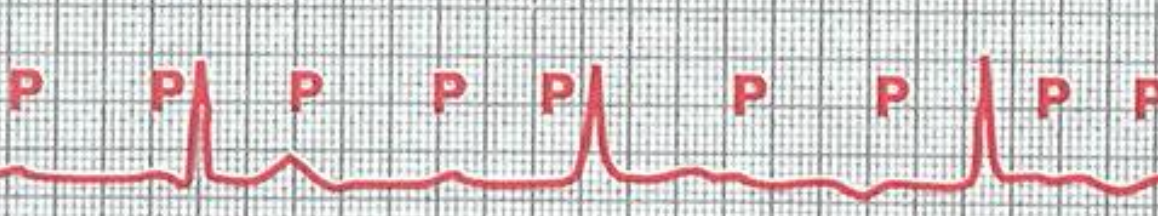
How do we see a third-degree atrioventricular block from an ECG?
A complete loss of electrical communication between the atria and the ventricles (Super abnormal ECG)
26
New cards
List a few examples of ventricular arrythmias:
1\.Premature ventricular contractions (extrasystoles)
2\.Ventricular fibrillation \n
2\.Ventricular fibrillation \n
27
New cards
Arterial hypertension induces …….. ventricle hypertrophy
Left
28
New cards
What 4 pathophysiological changes observed in Arterial hypertension?
1\.Coronary blood flow changes
2\. Arrhythmogenic substrate
3\.Diastolic dysfunction
4\.Systolic dysfunction
2\. Arrhythmogenic substrate
3\.Diastolic dysfunction
4\.Systolic dysfunction
29
New cards
What is pulmonary arterial hypertension characterized by?
A mean pulmonary arterial pressure greater than 25 mm Hg at rest
30
New cards
Describe athlerosclerosis:
progressive thickening and hardening of the walls of medium-sized and large arteries as a result of fat deposits.
31
New cards
What is a myocardial ischaemia?
When blood flow to the heart is decreaesed and oxygen supplies are low.
32
New cards
Describe the cellular disturbances produced by ischaemia:
1\.Inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation
2\.Acceleration of glycolysis and glycogenolysis \n 3.Hyperproduction of lactate and intracellular acidosis. \n 4.ADP breakdown
5\.Calcium overload (irreversible)
6\.Lesions of cell membrane (irreversible)
7\.Cell osmolarity (irreversible)
8\.Cell death (irreversible)
2\.Acceleration of glycolysis and glycogenolysis \n 3.Hyperproduction of lactate and intracellular acidosis. \n 4.ADP breakdown
5\.Calcium overload (irreversible)
6\.Lesions of cell membrane (irreversible)
7\.Cell osmolarity (irreversible)
8\.Cell death (irreversible)
33
New cards
What are some drugs to give to someone under Acute myocardial infarction?
Analgesics (pain)
Anticoagulants
Thrombolytics
Vasodilators
Beta blockers (nervous system hyperactivation)
Sedatives (stress)
Anticoagulants
Thrombolytics
Vasodilators
Beta blockers (nervous system hyperactivation)
Sedatives (stress)
34
New cards
What are Cardiomyopathies?
Diseases of the myocardium associated with mechanical and/or electrical dysfunction
35
New cards
Give a definition for heart failure
syndrome when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs.
\
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome in which heart disease reduces cardiac output, increases venous pressure (hemodynamic abnormality), and is accompanied by molecular abnormalities that cause progressive deterioration of the failing heart and premature myocardial cell death
\
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome in which heart disease reduces cardiac output, increases venous pressure (hemodynamic abnormality), and is accompanied by molecular abnormalities that cause progressive deterioration of the failing heart and premature myocardial cell death
36
New cards
Give a few characteristics of systolic failure
\-ventricular dilatation
\-diminished ejection fraction
\-LV end-diastolic volume (or pressure) may increase as the stroke volume (or CO) decreases
\-diminished ejection fraction
\-LV end-diastolic volume (or pressure) may increase as the stroke volume (or CO) decreases
37
New cards
Give a few characteristics of diastolic failure
\-ejection fraction is normal (>50%) or supranormal
\-end-diastolic ventricular pressure is increased
\-myocardial contractility is normal or hyperdynamic
\-end-diastolic ventricular pressure is increased
\-myocardial contractility is normal or hyperdynamic
38
New cards
what is myocardial remodelling characterized by?
hypertrophy and heart failure
39
New cards
What two factors can you target in high blood pressure?
1. Cardiac output (Qc)
2. Vascular resistance (PVR)
\
40
New cards
Which target should we act on to target Caridac output?
Beta-1 adrenergic receptor
41
New cards
Which target should we act on to target PVR?
alpha-1 adrenergic receptor
42
New cards
alpha-adrenergic receptors have higher affinity for which neurotransmitter?
Noradrenaline
43
New cards
Beta-adrenergic receptrors have higher affinity for which neurotransmitter?
It has an equal affinity for both noradrenlaine and adrelanine
44
New cards
To vasoconstrict, do we prescribe a alpha-adrenergic agonist or antagonist?
Agonist
45
New cards
To vasocontrict, do we prescribe a beta-adrenergic agonist or antagonist?
Antagonist
46
New cards
Why do we use Beta-1 antagonists and not beta-2 antagonist when a patient has high blood pressure?
Beta-2 antagonists are not specific on the heart, they will also target the blood vessels which can further constrict. Beta-1 antagonists only act on the heart and the liver so we do not get unwanted effects.
47
New cards
Name 4 targets of the RAAS system:
1. AT receptor
2. ACE
3. Renin
4. The mineralocorticoid receptor
48
New cards
What is the type of calcium channels in the heart called?
L-type channels
49
New cards
What is the effect of an inhibitor of Cav1.2?
Vasodilation, chronotropic, ionotropic
50
New cards
Complete the sentence: To target heart failure we can either decrease the ……… needs or increase the ……… supply
OXYGEN
51
New cards
How can we increase oxygen supply to the myocardium?
Decrease heart rate to increase coronary perfusion
52
New cards
How can we decrease oxygen needs of the myocardium?
1\.decrease heart rate
2\.decrease contractility
3\.decrease wall tension
2\.decrease contractility
3\.decrease wall tension
53
New cards
Name a type of drug used to increase the oxygen supply:
beta-blockers
54
New cards
Name a type of drug that can be used to decrease the oxygen needs:
ACE inhibitors, MR antagonists
55
New cards
PVR= ?

56
New cards
What is the effect of an increased radius of the vessel?
vasodilation
57
New cards
Which actin-binding protein is missing in smooth muscle cells?
Troponin
58
New cards
Calcium binds to what?
Calmodulin
59
New cards
What happens when calcium binds to MLCK?
myosin phosphorylation →CONTRACTION
60
New cards
What binds to MLCP to cause vasodilation?
cGMP
61
New cards
Name a method used to study arterial tone ex vivo?
Myography
62
New cards
What can you study in myography?
Effect of vasoconstricting and vasodilating drugs by measuring the resistance of the
63
New cards
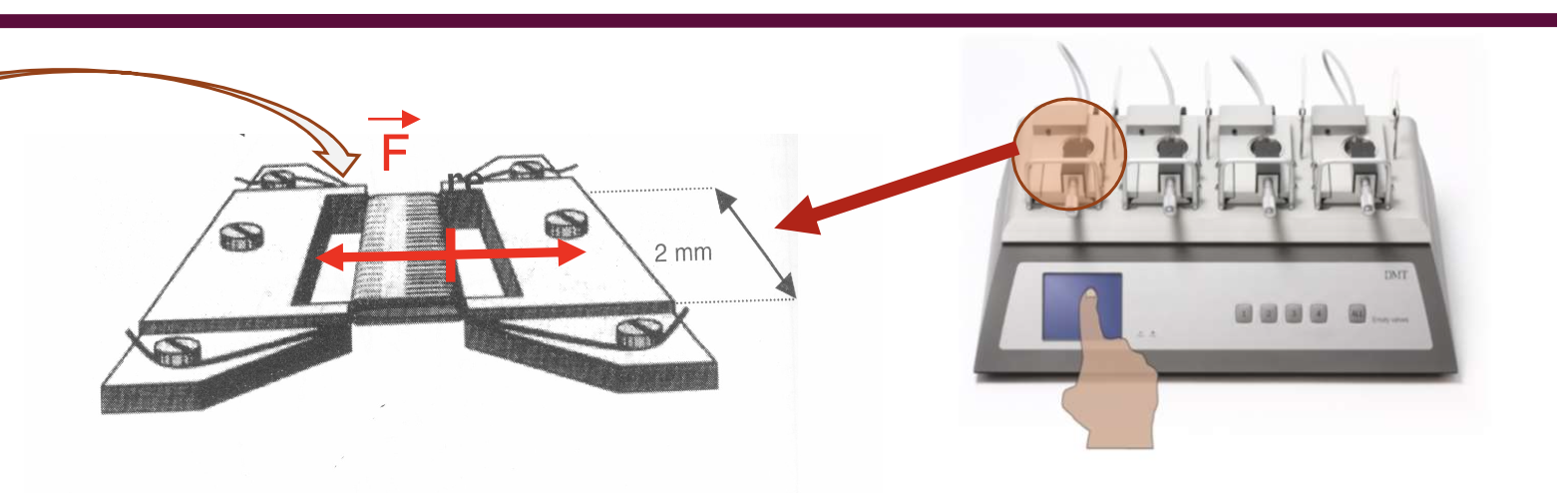
what does the myograph look like?
Like that.
64
New cards
What is the effect of PDE inhibitors on the smooth muscle cell? why?
Vasodilation because there is an accumulation of CAMP which inhibits MLCK.
65
New cards
Write the 3 cardinal features of endothelial quiescence
1\.anti-inflammatory
2\.anti-thrombotic
3\.semi-permeable
2\.anti-thrombotic
3\.semi-permeable
66
New cards
Write the 3 cardinal features of endothelial activation (abnormal state)
1\.Pro-inflammatory
2\.Pro-thrombotic
3\.Not semi-permeable
2\.Pro-thrombotic
3\.Not semi-permeable
67
New cards
Name a molecule that is responsible for disruption of endothelial junctions in an activated state ofthe endothelium
histamine
68
New cards
What is expressed on the endothelial during activation?
P and E selectins
69
New cards
During rolling, what do the cells circulating bind to ?
P and E selectins
70
New cards
During firm-adhesion, what is expressed by the endothelial cells?
ICAM-1 and VCAM-1
71
New cards
What are the 3 main steps of leukocyte recruitment from the endothelium?
rolling→firm adhesion→diapedesis
72
New cards
Explain how endothelial activation can trigger platelet accumulation:
VWF→Tissue Factor→thrombin→fibrin
73
New cards
What molecules are released from the weibel palade bodies?
VWF, P-selectin,Ang-2,endothelin-1
74
New cards
What is the slow and fast step of endothelial activation?
Rapid=exocytosis of weibel-palade bodies
Fast=Gene expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM1
Fast=Gene expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM1
75
New cards
What receptor is involved in the maintenance of a quiescent endothelium?
TIE2 receptor
76
New cards
How does the TIE2 receptor contribute to maintening a quiescent endothelium?
Ang-1 binds to TIE2 in order to keep the endothelial in a quiet state
77
New cards
What happens if Ang-2 binds to TIE2?
It will activate the endothelium
78
New cards
What is KLF2?
A transcription factor
79
New cards
What class of drug targets KLF2?
Statins
80
New cards
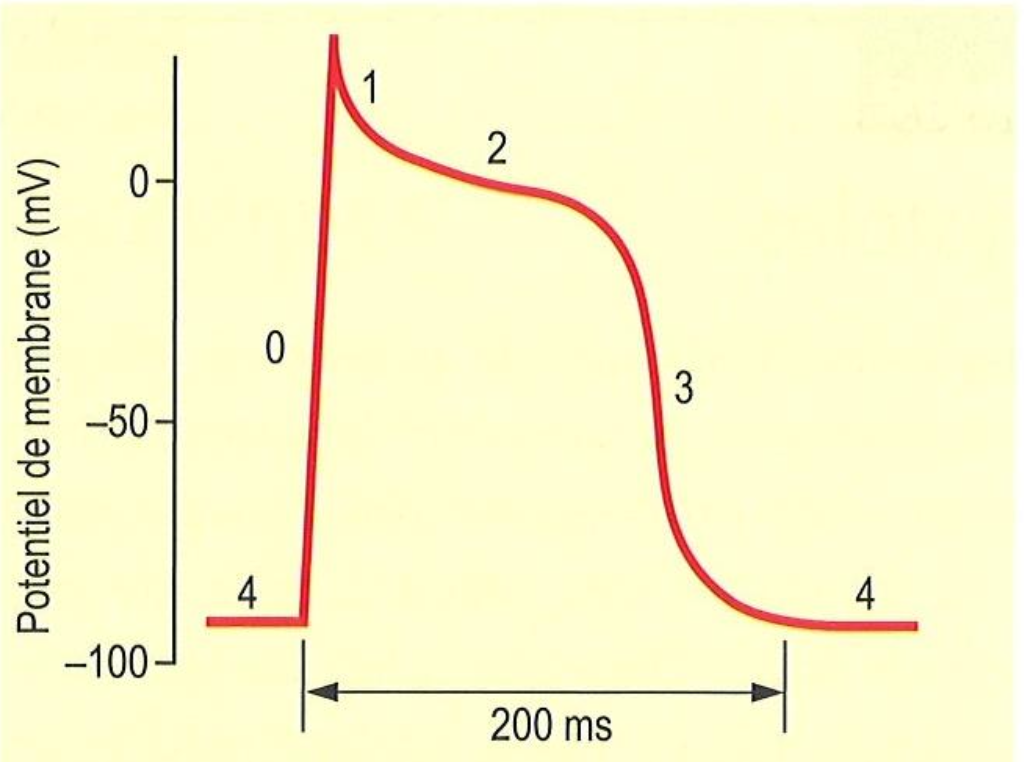
In terms of channel activity, what happens at 0
Na+ influx for depolarization
81
New cards
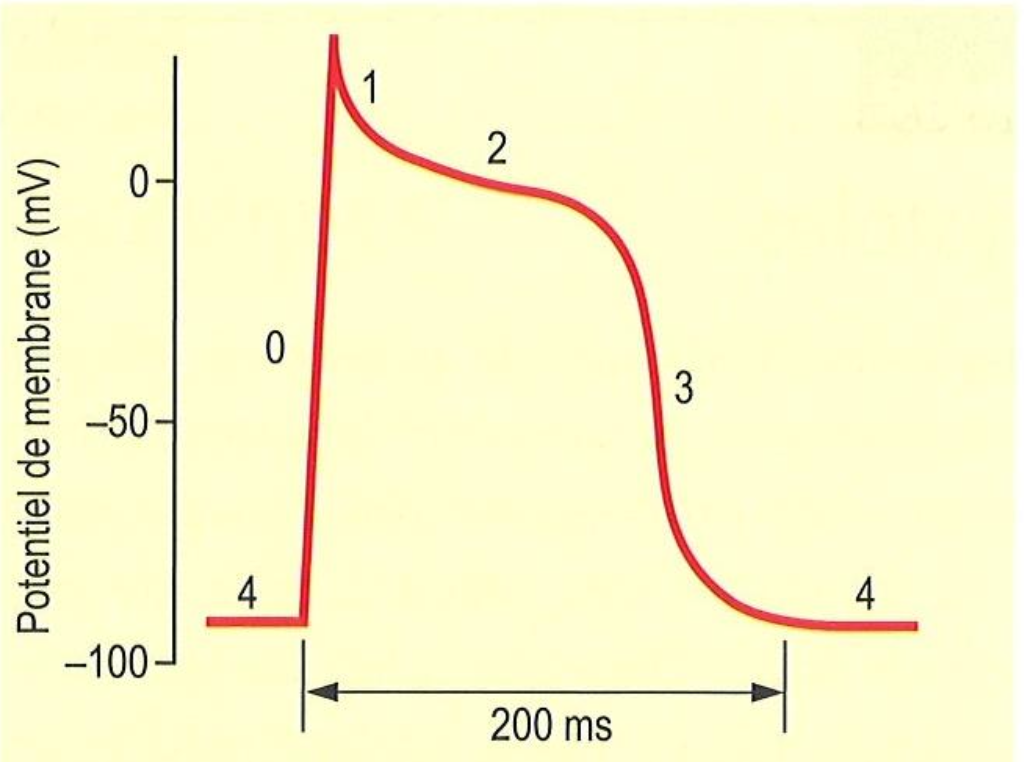
In terms of channel activity, what happens at 1
L-type open for calcium slow influx
82
New cards
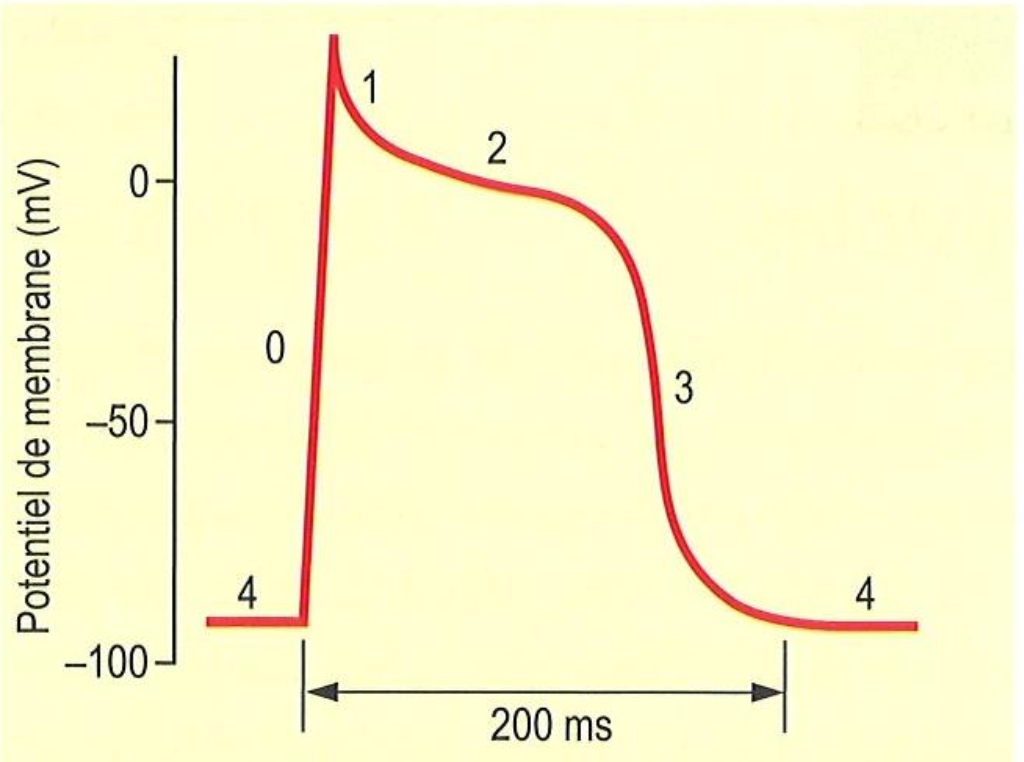
In terms of channel activity, what happens at 2
K+ opening and Na+ closing→early repolarization
83
New cards
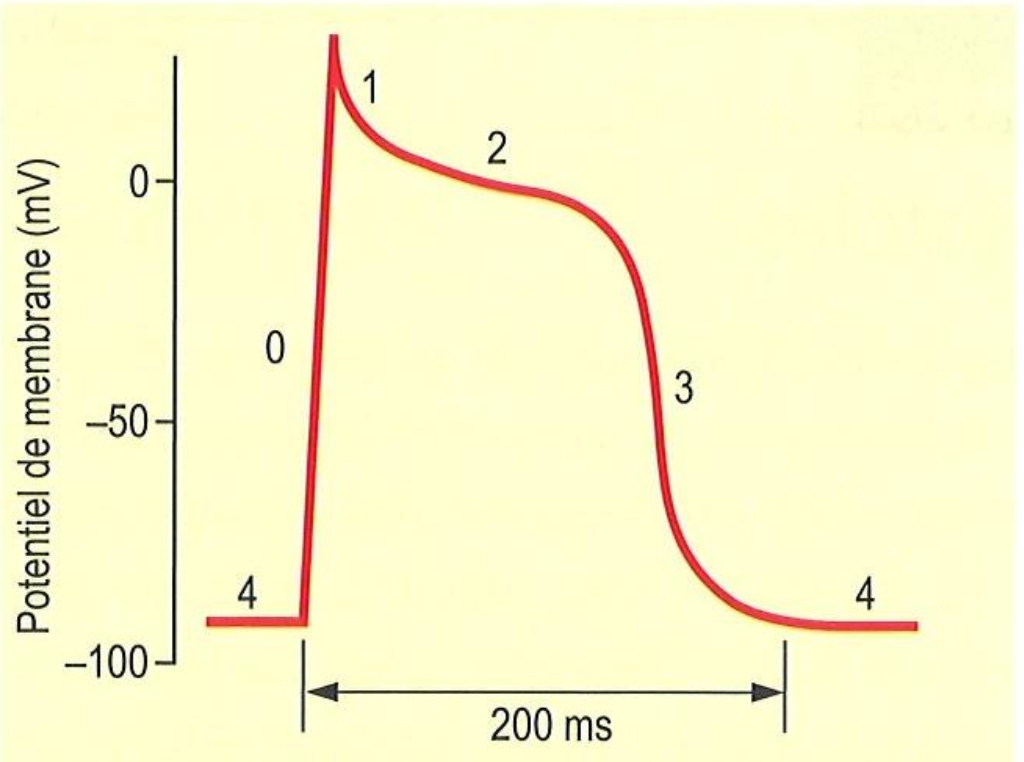
In terms of channel activity, what happens at 3
L-type Ca2+ closes slowly and K+ remains open
84
New cards
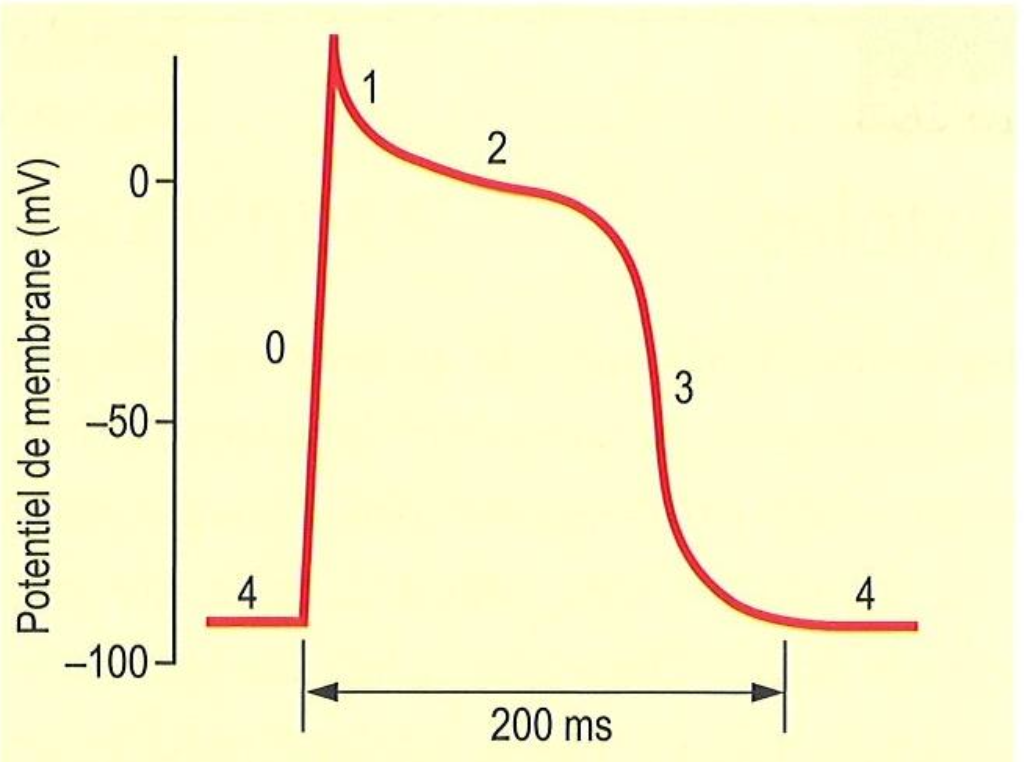
In terms of channel activity, what happens at 4
Cell depolarizes Na+
85
New cards
What does the patch clamp allow us to do?
allows to electrically isolate a fragment of membrane or an entire cell in order to apply a current (current clamp) or a potential (voltage clamp) to it and record the response
86
New cards
What is the funny current?
Current from pacemaker cells from the SA node, it is spontaneous
87
New cards
Cell signalling can be divided in three different stages, list them:
Reception→Transduction→Response
88
New cards
What kind of receptions are there?
Mechanical forces and Ligands
89
New cards
Site two second-messengers of GPCRs
cAMP and cGMP
90
New cards
What happens when adenylate cyclase is activated?
ATP is converted to cAMP→increase in concentration of PKA→activation of EPAC
91
New cards
Name a modulator of cAMP?
PDE
92
New cards
What happens when guanylate cyclase is activated?
GTP is converted to cGMP
93
New cards
What are the 5 steps of ECC?
1\.Depolarization
2\.Ca2+ influx
3\.Calcium-induced calcium release
4\.Contraction
5\.Relaxation
2\.Ca2+ influx
3\.Calcium-induced calcium release
4\.Contraction
5\.Relaxation
94
New cards
In ECC, where are the L-type calcium channels found?
In the T-tubules
95
New cards
Explain depolarization in ECC
Action potential leads to depolarization though opening of the Na/K pumps
96
New cards
Explain how calcium first enters the cell
The depolarization will trigger opening of L-type calcium channels located on the T-tubules. Leading to calcium influx
97
New cards
What is calcium-induced calcium release?
When the calcium enters the cells, it will trigger the phosphorylation of RyR (ryanodine receptor), which is on the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ryr will open to release even more calcium into the cytoplasm.
98
New cards
How does contraction happen once the calcium is in the cytoplasm?
The calcium will bind to calmodulin, which will bind to MLCK to trigger the phosphorylation of myosin filaments. Leading to contraction as it interacts with the actin filament during cross-bridge.
99
New cards
How does relaxation occur after contraction?
Relaxation occurs when Ca is removed from the cytosol either back across the cell via NCX or back into the SR via the SR Ca-pump (SERCA).
100
New cards
What does Ryr stand for?
Ryanodine receptor