PSYC330: Alcohol (Ethanol)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
History
Strong association with human society
Fermentation is said to have developed in parallel with civilization
Speculation that human alcohol use is linked evolutionarily to a preference for fermenting fruit
The presence of ethanol signals fruit is ripe but not yet rotten
The earliest records of distilled spirits appeared in China ~1000BC
Alchemists were captivated by the invisible “spirit”
Remedy for almost all diseases
Whiskey is derived from usquebaugh
Gaelic for “water of life”
Became a major ingredient of many tonics and Elixirs
Alcohol- Types
Methyl (wood alcohol)
Produced synthetically
Antifreeze, fuel
Ethy (grain alcohol)
Produced by fermentation
The one people drink
Isopropyl (rubbing alcohol)
Fermentation
Organic material with sugar content
Yeast (from the air) consumes the sugar
1 molecule of sugar consumed -> 2 molecules of alcohol + 2 molecules of carbon dioxide
Distillation
A fermented beverage is heated to a vapor, which is then cooled
What is the purpose of this?
Become more concentrated!
Consumption changes across history
The average American drinker:
1800s
4-5 standard drinks per day
Currently
3-4 standard drinks per week
US Alcohol Use (2022 NSDUH)
The highest consumption is in the college-age group
48.7% (12 and older) drank in the last month
21.7% binge drink (4-5 more drinks on an occasion) in the past month
5.7% engaged in heavy drinking (5 or more drinks on an occasion on 5 or more occasions per month) in the past month
Male and female drinking rates are converging- lifetime drinking in 12+: males (79.7%), females (77.3%)
The number of binge drinking days increases with age during adolescence
Alcohol Content of Various Beverages
Beverage | % Alcohol | Proof (proof is double what the percentage of alcohol is) |
Beer (*depends on the type of beer) | 4-6 | 8-12 |
Wine | 7-15 | 14-30 |
Spirits (hard liquors) | 40-95 | 80-190 |
Alcohol Beverage Equivalents: Standard Drink Sizes
12 oz beer = 8-9oz of malt liquor = 5oz of table wine
Broad Scope
Economic burden >$200B / year
Medical and social impacts
100,000 deaths/year
15.1 million (1:20) meet criteria for alcohol use disorder (2015)
Diagnosis and treatment are often delayed until the disease is advanced
Complicated by social and health issues -> difficult to treat
Among the “diseases: with genetic and environmental influence
Stigmas and moral failures impede the recognition and treatment of alcohol problems
ADMET(T)
Large amounts are required for physiological effects
Consumption is more like a food than a drug
Serving size is about 14g in a typical better, glass of wine, or shot
consumed/ dosage in grams qualities
Absorption
Oral route of administration
Most common method
Inhalation
AWOL (alcohol without liquid)
Vaportini
Higher blood alcohol levels (BALs)
Banned in most states
Powdered Alcohol
Approved in 2016
Banned in 31 states
Why haven’t these other methods taken off?
They are harder to control the amount being consumed
Simple small molecule
Soluble in water and lipids
Neural particle- diffuses easily through membranes
Rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream
Stomach (slower) and small intestine (faster)
Distributes into the total body water
What about food in the stomach
It will slow down ethanol absorption -> lower BAL
Distribution
Weight
Gender
The muscle/fat ratio is greater for men
Age
Distributed throughout the body
~90% reaches blood -> crosses Blood Brain Barrier
Blood Alcohol Level/Concentration (BAL/BAC)
Concentration of alcohol in blood
Metric measurements and percent
BAL expressed in mg of alcohol per 100 milliliters (deciliter)
Ex: 80mg/dL -> .08g/100mL ->.08%
Legal limit is .08% (80mg/dL, ~17mM)
A standard drink contains ~30mg/dL
Alcohol Metabolism in the Liver
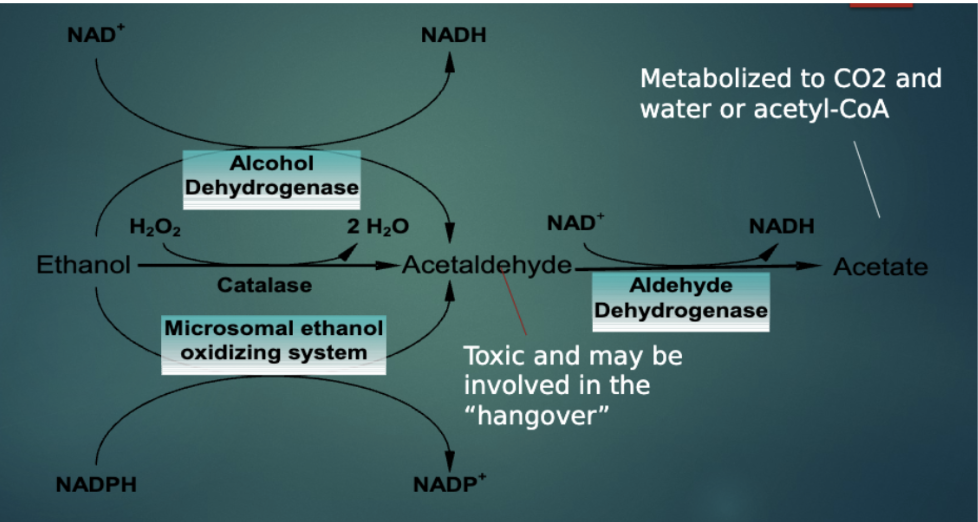
Metabolism
Liver metabolizes majority of ethanol
Fatty acids build up in liver
Leads to cell death
Alcoholic fatty liver -> alcoholic hepatitis -> cirrhosis -> liver failure
Some breakdown in stomachs
Males > females
Excretion
~2-8% unchanged through lungs
Breathalyzers useful for determining BAL
90-95% oxidized slowly (kidney)
Alcohol increases urination
Ingestion of liquid
Suppression of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Pharmacodynamics- “Dirty Drug”
“Dirty” drug
It has many specific effects
Can affect all cells in the body
An impact all systems in the body in specific ways
Alcohol has a lot of very specific effects on binding sites and neurotransmitter receptors
Pharmacodynamics: Positive reinforcement reward system
GABA interneurons synthesize and release GABA on the dopamine cell body, inhibits dopamine release so there isn’t too much firing at once
Opioid Peptides regulates the GABA interneurons
Alcohol has three specific effects in this system
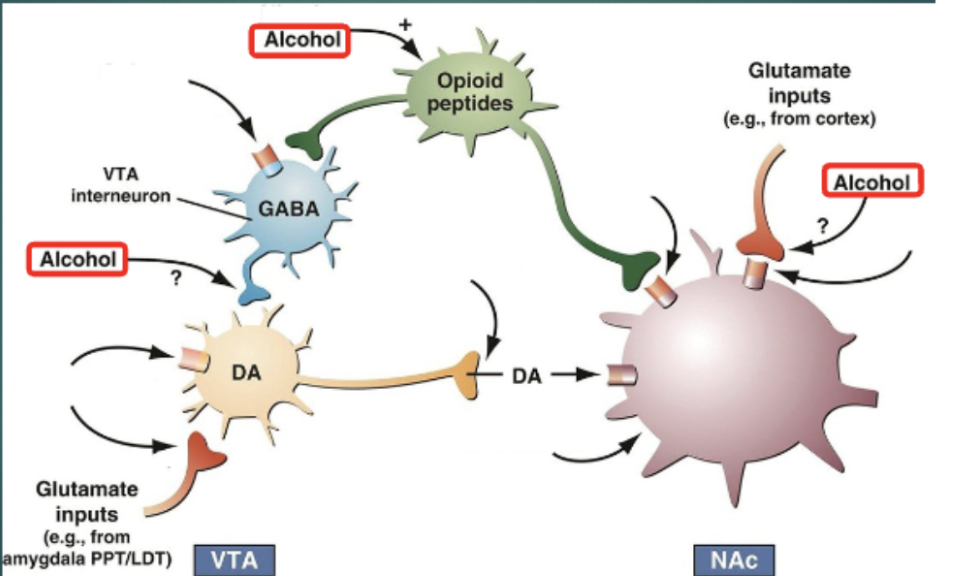
Mechanism of Action
Our bodies and nervous system works to balance things to keep us at baseline
Alcohol has a specific effect on GABA and glutamate system
Acute effects
Alcohol enhances the GABA inhibitory system
More inhibition of the GABA system
Decreases excitation of the Glutamate system
Inhibiting the currents through glutamate (excitatory receptors)
Shifts the homeostasis in one direction and it makes it confused and less likely to release action potentials
Disturbs fine balance between excitatory and inhibitory influences
Results in anxiolytics, amnesia, ataxia, and sedation
Number of putative sites of action have been identified
Likely produces its effects by simultaneously altering function of numerous proteins that affect neuronal activity
Examples of Additional Sites of Action
Ligand-gated ions channels
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Serotonin (5-HY3) receptors
Multiple metabotropic receipts
Dopamine receptors
Opioid receptors
Voltage-gated channels
Calcium channels
Sodium channels
Behavioral effects
Acute Intoxication (Non-Tolerant Individuals )
BAC g/dL | Clinical effect |
0.05-0.1 (11-22mM) | Subjective high “buzz”, anxiolytics, sedation |
0.1-0.2 (22-44mM) | Motor impairment, slurred speech, blackout |
0.2-0.3 (44-66 mM) | Emesis (vomiting), stupor (near unconsciousness) |
0.3-0.4 (44-88mM) | Coma |
>0.5 (110mM) | Respiratory depression, death |
*this is just average, in chronic alcohol users, 0.4 g/dL will not be lethal
Peripheral Effects
Dilates Blood Vessels
Decreases body temp
Increases effect of other depressant drug