Life 102 (Exam 2- Cellular respiration & Photosynthesis)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Cellular Respiration (Purpose)
Breaks down food (Glucose) to generate ATP for use by the cell.
Glycolysis: Step 1 Of cellular respiration
Location: Cytosol
Input: Glucose
Output: 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
No oxygen Required.
Pyruvate Oxidation: Step 2
Location: Mitochondria
Input: 2 pyruvate
Output: 2 Acetyl CoA, 2 Co2, 2 NADH
Requires Oxygen - INDIRECTLY
Citric Acid Cycle: Step 3
Location: Mitochondria
Input: 2 Acetyl CoA
Output: 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH, 4 Co2
Requires O2 - INDIRECTLY
Electron Transport Chain: Step 4
Location : Inner Mitochondria; Membrane
Input: O2 Electron from NADH & FADH2
Output: ATP, H2O
Requires Oxygen DIRECTLY
Chemiosmosis- Cellular Respiration
Purpose: Formation of ATP
Location: Inner Mitochondrial membrane
Chemiosmosis
The movement of hydrogen ions down their concentration gradient across a semi- permeable membrane (Through ATP synthase)
Oxidation phosphorylation
The production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in mitochondrial.
- hydrogen ions gradient is formed by the electron transport chain is used by ATP synthase to form ATP
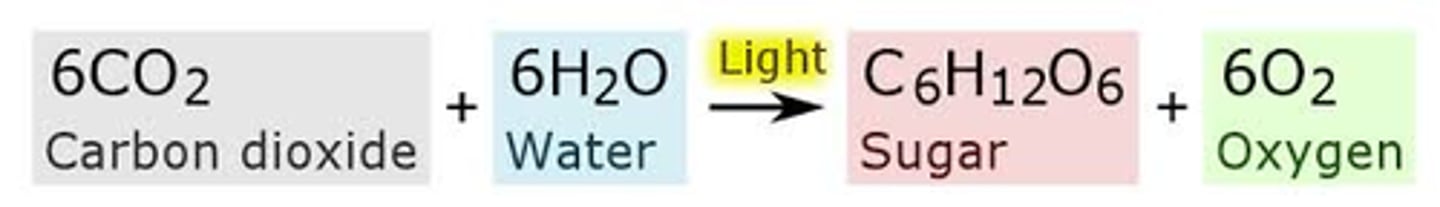
Photosynthesis (Purpose)
to utilize energy from the sun to generate sugars for use by the plant cell
Light- Dependent : Step 1 Photosynthesis
Location: Thylakoid membrane
Inputs: H2O, light energy
Outputs: ATP, NADPH, O2
Light- Independent: Step 2
Calvin cycle: Dark reaction
Location: Stroma
Inputs: Co2, ATP, NADPH
Output: Sugar
Carbon Fixation
fixing carbon into an organic molecule such as monosaccharide
Chemiosmosis- Photosynthesis
Location: Thylakoid membrane
Purpose : To use the movement of H+ down their gradient through ATP Synthase to generate ATP for use by the Calvin Cycle
Gibs free energy
Energy available to do work
Spontaneous: Negative
Non-spontaneous: Positive
Delta G
Free energy to change a reaction.
-Determines whether it's spontaneous or non - spontaneous
Activation Energy
The energy required to start any chemical reaction.
-Enzymes lower activation energy
- Enzymes do not change Delta G
Why does Chemiosmosis occur?
There is a difference in the concentration of H+ ions on either side of membrane.
Pigments- Photosynthesis
- Pigment absorb light energy
- Color is determined by the light they do not absorb.
- In plants chlorophyll A & B do not absorb green light .
- Chlorophyll A & B absorb red-orange & blue - violent wavelengths. Green light is reflected.
- Carotenoids do not absorb yellow light, so they yellow.
Thermodynamics Definition
Study of energy on a system
1st Law
_ The energy of the universe is constant
-Can not be destroyed or created
- Can transferred/ transformed
2nd Law
States that energy transformation increased disorder (Entropy)
Catabolic ( Cellular respiration )
Breaking down molecules.
Anabolic (Photosynthesis)
Building up molecules.
Tonicity
Comparison (Inside/outside a cell) across a membrane between 2 solutes
Hypertonic
A solution of higher concentration than a cell
Hypotonic
A solution of lower concentration than a cell
Isotonic
A solution of equal concentration than a cell
Osmosis- Direction, effects of gradients
* Selectively Permeable
* Passive transport
* Movement Of water
- From high to low water concentration
- From low to high solute concentration
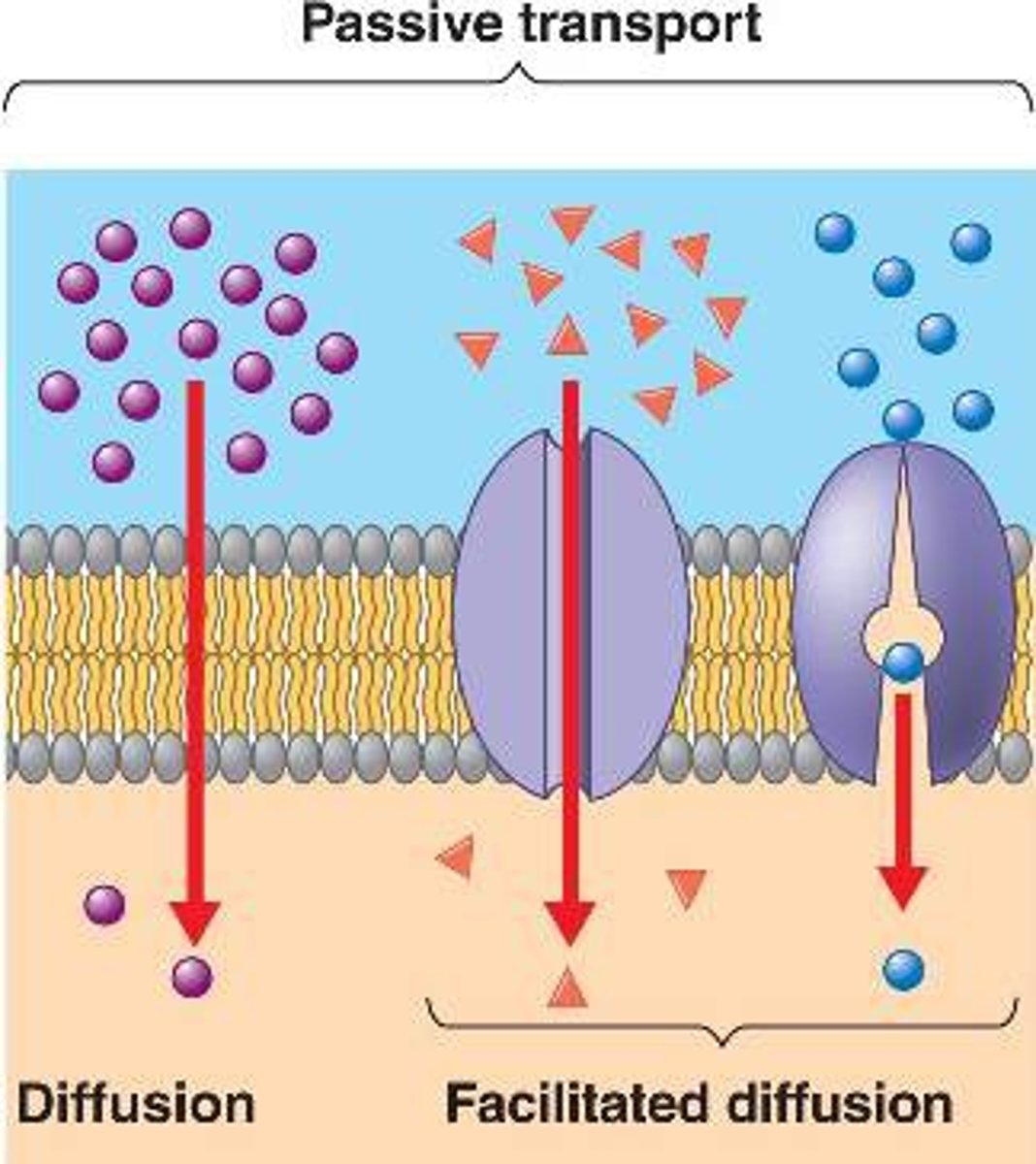
Active Transport
Movement of molecule against the concentration gradient
- Requires Cellular energy
Passive transport
Molecules, like water that are able to freely pass through the membrane without the cell using any energy use
Oxidation
- Oxidation always accompanies reduction
- is a chemical process in which a substance:
Loses electrons,
Gains oxygen, or
Loses hydrogen.
reduction
Redox Reaction: is a chemical involving both reduction and oxidation.
-Results in changes in the oxidation numbers of atoms included in the reaction
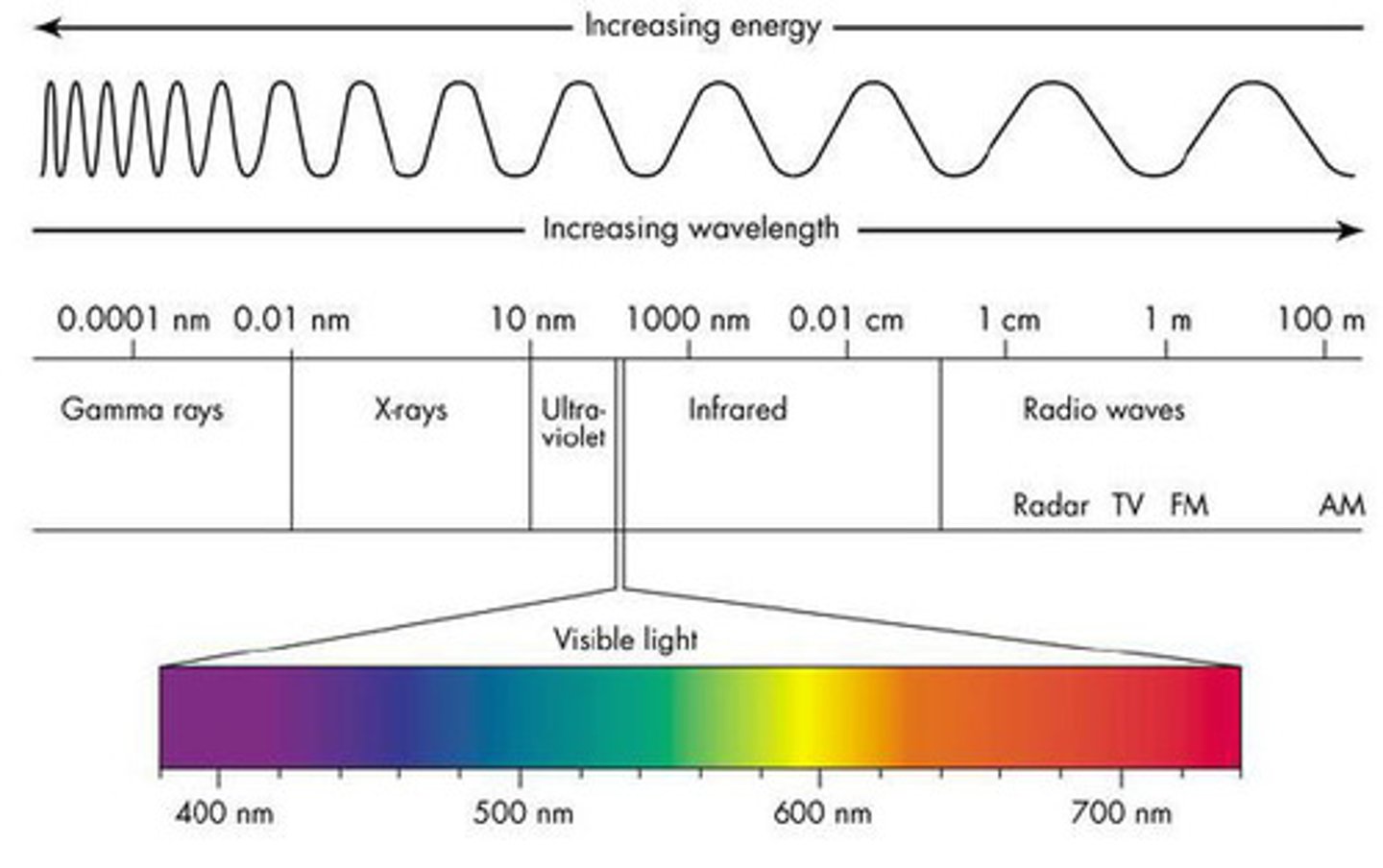
Light energy to- Wavelength
- Electromagnetic Radiation
- Given off by electrons in an object; moves in the waves .
- Spectrum: different frequencies & wavelengths.
- Long wavelength: Low frequency- low energy
- Short wavelength- High frequency- high energy.
Potential energy
Condensation- Water gain or loss
* Condensation refers to a type of chemical reaction where two molecules are joined together with the loss of a water molecule.
* Water Loss (Anabolic)
Hydrolysis - Water gain or loss
* Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where a larger molecule is broken down into smaller parts by adding water.
* Water Gain (Catabolic)
Describe enzyme- function, inhibition,
Enzymes Job: Help reaction to occur, Lowering activation energy.
Inhibitors= to regulate pathways/inhibits reaction:
-Competitive: Bind to active site, same as substrate
- Non-competitive (Allosteric) : Bind to other site, not active site.
Photosynthesis photo-systems
* Photosystems are protein-pigment complexes found in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. They are key players in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
* Photosystem II (PSII)
- First in the sequence, even though it's "II"
- Absorbs light best at P680 nm wavelength
- Splits water (H₂O) to replace lost electrons
- This releases O₂ gas and protons (H⁺)
- Electrons go down the electron transport chain
- Energy from this pumps H⁺ into the thylakoid, making a gradient for ATP production via ATP synthase
Input: Light + H₂O
Output: O₂ + ATP
* Photosystem I (PSI)
-Absorbs light best at P700 nm
-Receives electrons from PSII
-Light excites electrons again
-Passes them to NADP⁺, reducing it to NADPH
Input: Light + electrons from PSII
Output: NADPH
Phosphorylation- ADP/ATP
= Adding a phosphate group
Ex: to ADP to become ATP
ADP: 2 phosphate
ATP: 3 phosphate
Endothermic
- En - enter
- Heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings
Exothermic
Ex- Exits
- Heat energy is released into the surroundings
OIL RIG
- Oxidation is loss of electrons
- Reduction is gain of electrons
Phosphorylation - Substrate lvl
Enzyme transfers phosphate from substrate to ADP to make ATP
oxidative phosphorylation
- Electrons from the reduced cofactors NADH & FADH2 are passed to proteins in the respiratory chain
Calvin Cycle
Light independent- Dark RxN
* Co2 enters through stomata
- Diffuses into stroma
* Uses energy from light reactions
- ATP & NADPH
Cellular Respiration- Equation

Photosynthesis- equation
Properties of phospholipids
* Molecules that have both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-fearing) parts.
* The head is hydrophilic (attracted to water).
* The tails are hydrophobic (repel water).
* Bilayer: Self-assembled double layer → forms cell membranes
* Fluidity: Membrane is flexible; affected by tail type, cholesterol, and temperature
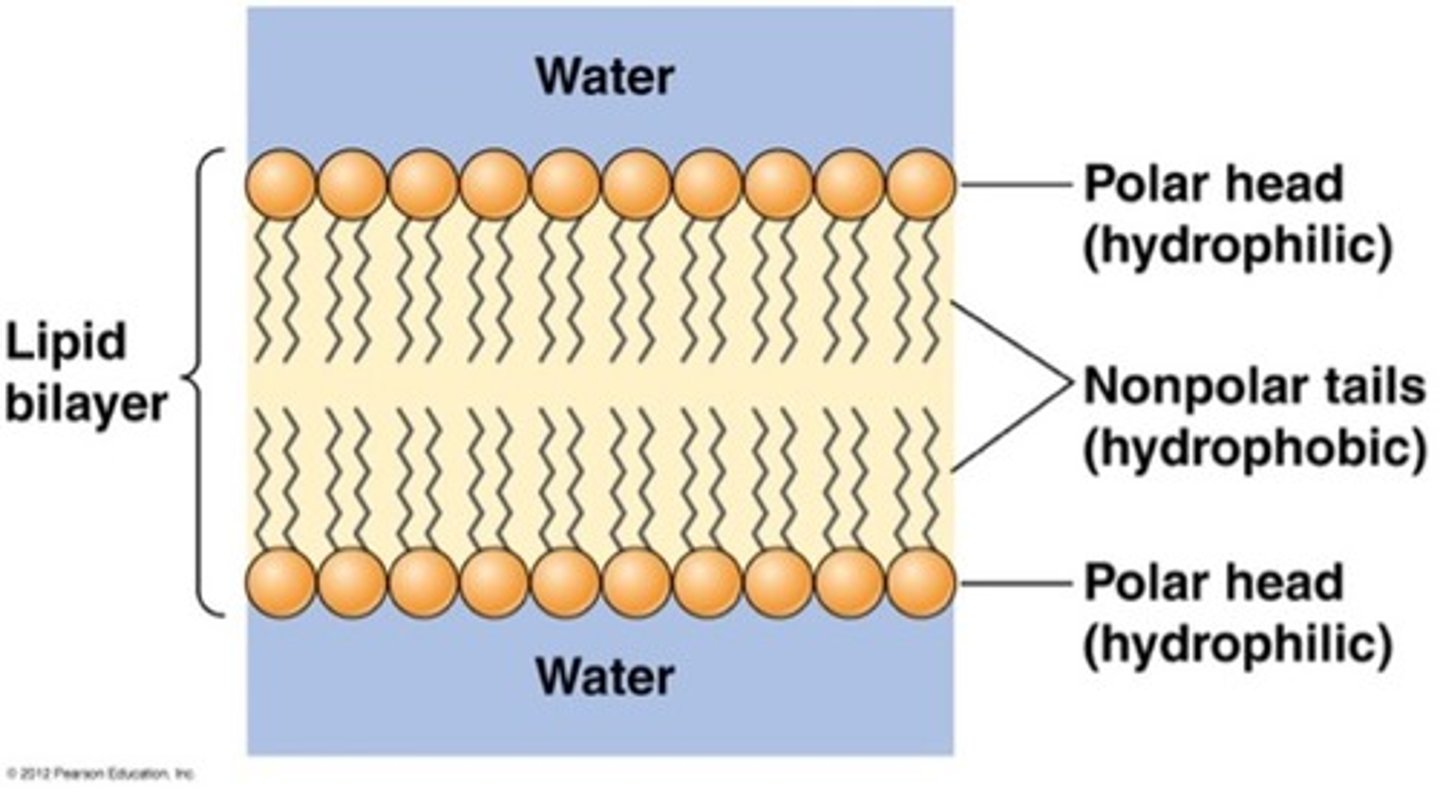
Why is a membrane required for chemiomosis?
A membrane is required to create a gradient
Reactants & Products for cellular Respiration
Reactants : O2 + Glucose
Products: H2O + Co2 + ATP
What happens to water in the light- dependent reaction?
It splits into electron, o2 , H+
What provides the energy for the light- dependent reactions?
The sun provides light-energy
What is the CO2 used for in the light - independent reactions
CO2 is fixed into sugars in the Calvin Cycle
Why do plants use both photosynthesis and CR
Plants use cellular respiration to provide energy in the form of ATP of cellular processes & photosynthesis to create sugars for use by the plant.
Endergonic
A chemical reaction that absorbs energy
Exergonic
Chemical reactions that release energy
What happens when there's no oxygen in Pyruvate oxidation
Fermentation occurs and produces NADH +
Electron Transport Chain - equation
E- + H+ + O2 = H2O