Physio Lect 28 - Concentration and Dilution of Urine
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
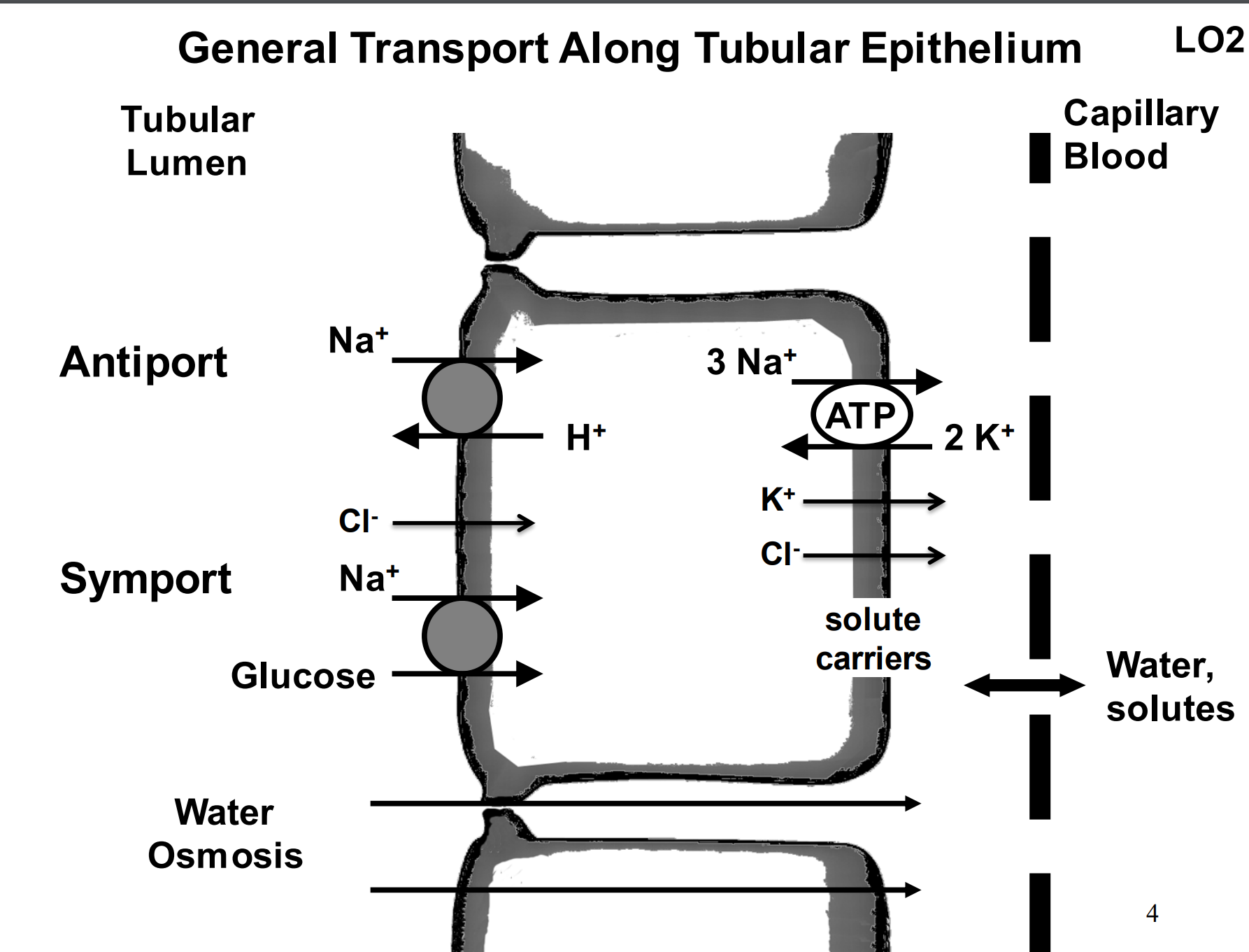
What is happening here?
The sodium potassium pump is creating a gradient to allow the sodium to flow in from the left side of the gradient to the right.
T/F: The major function of the proximal tubule is to reabsorb the majority of filtrate.
T, and for this to happen the epithelial cells must be leaky to permit passage of water.
What are the two ways water is transported?
Transcellular and Paracellular
Define transcellular transportation of water.
Epithelial cells have water channels (Aquaporin 1)
Define Paracellular transportation of water.
Junctions between epithelial cells are permeable to water and some small solutes
How does glucose return?
Sodium glucose transporter 1 and 2 (SGLT1 and SGLT2) - A glucose passes through the epithelium with 2 sodiums, and then freely passes through a channel into the capillary bed.
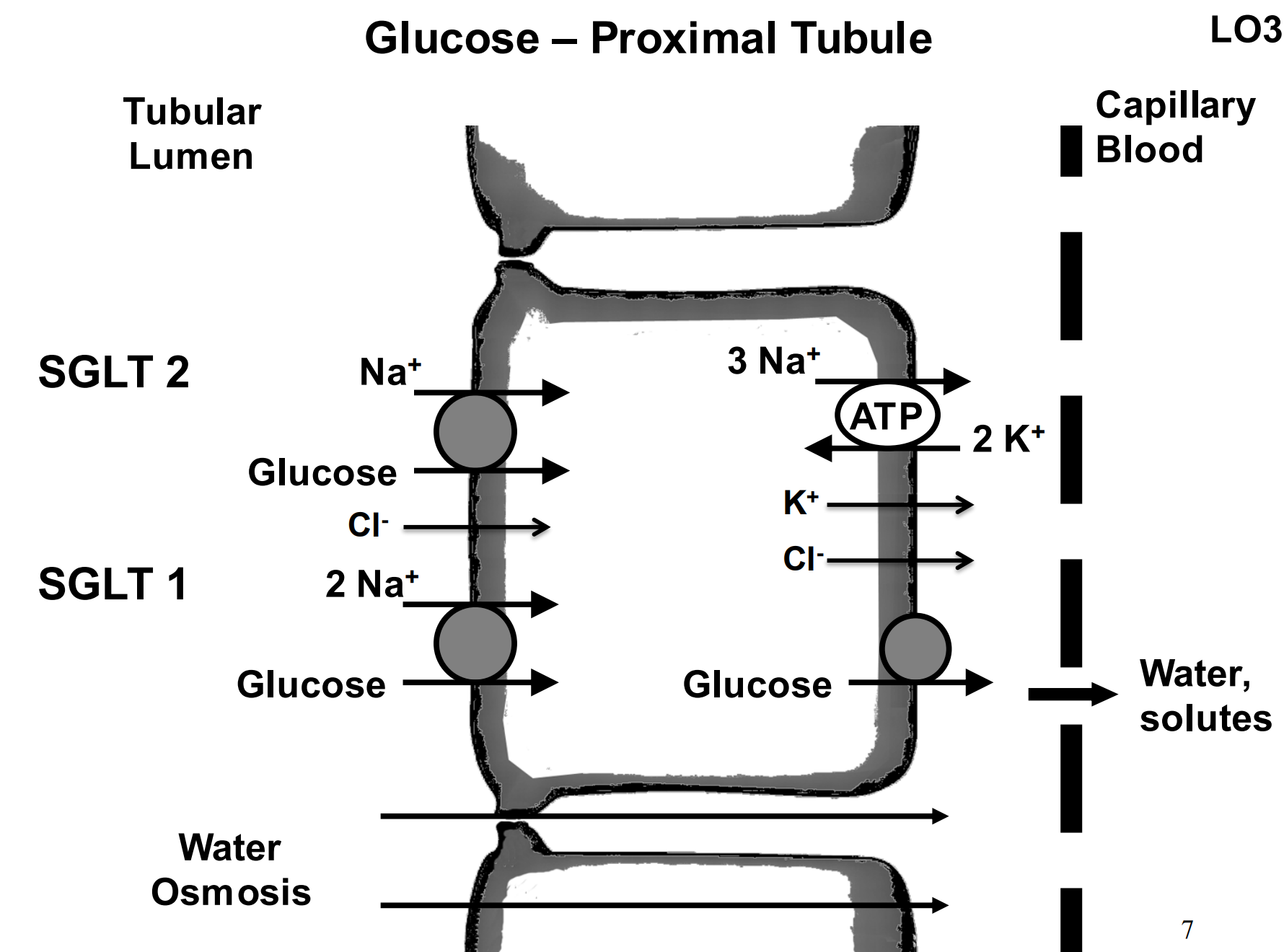
Where does a lot of transcellular transport occur?
Late proximal tubule.
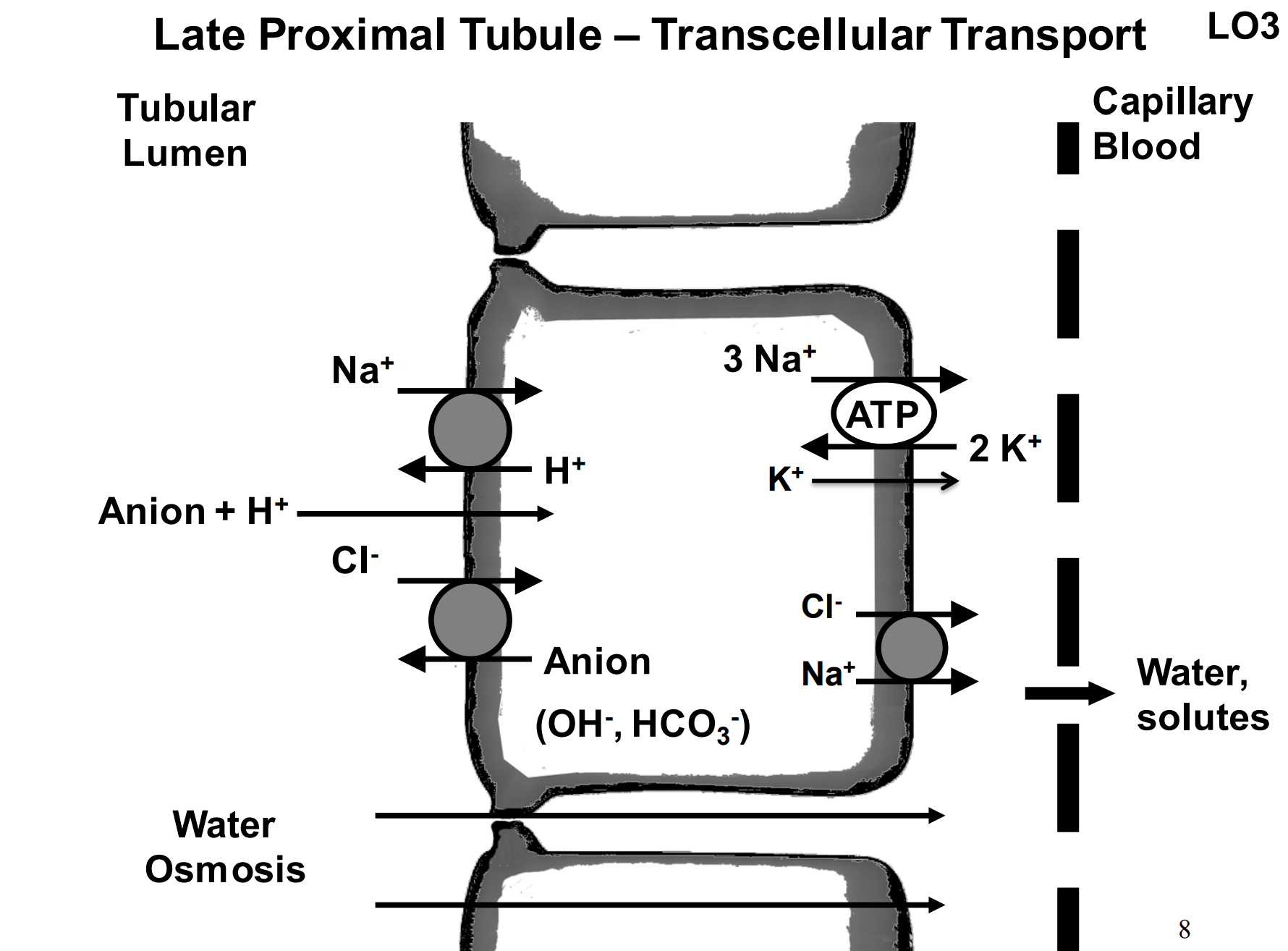
T/F: In the late proximal tubule there is a lot of exchange of ions that regulate pH
T - see in the image what is regulated
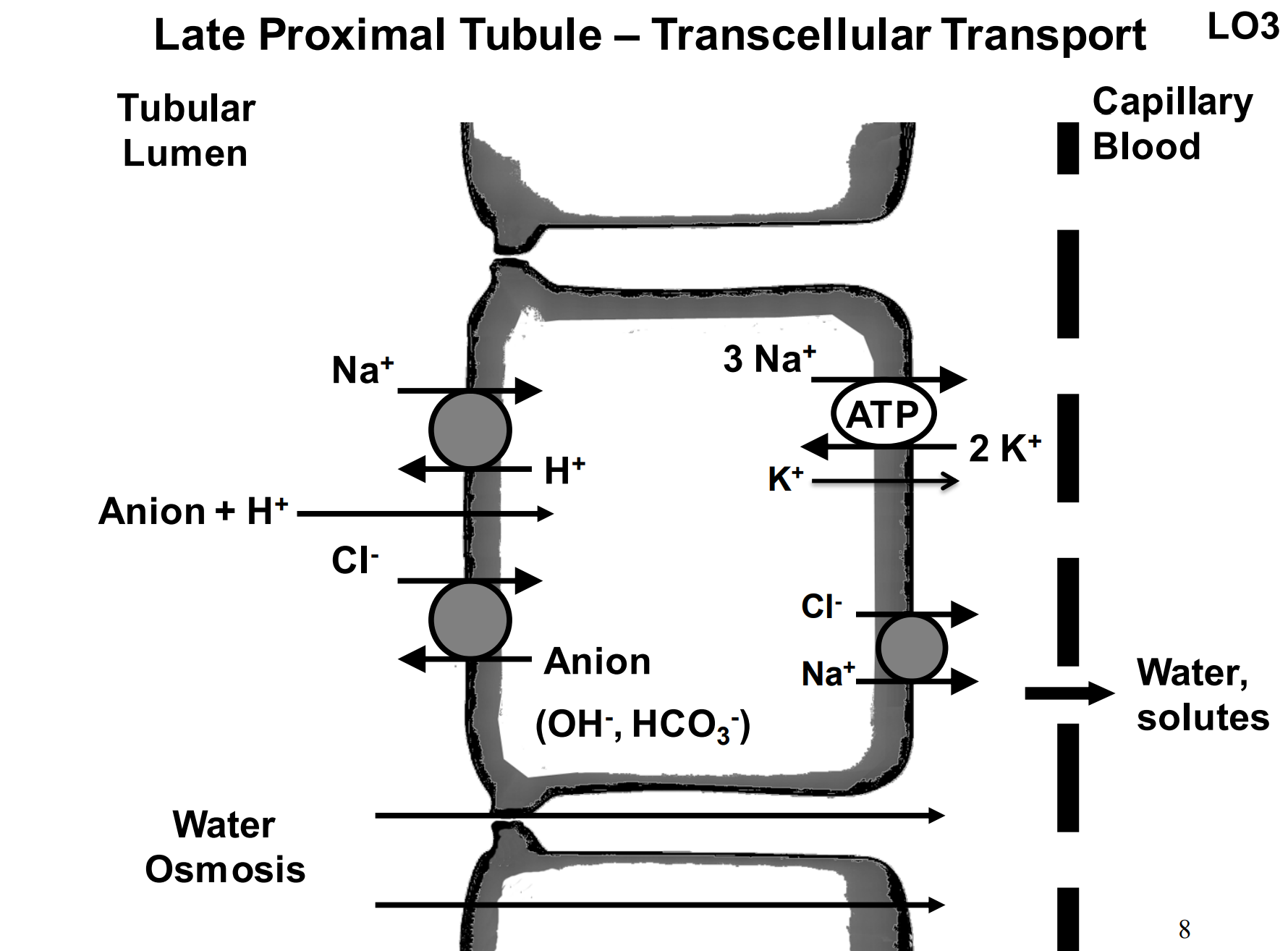
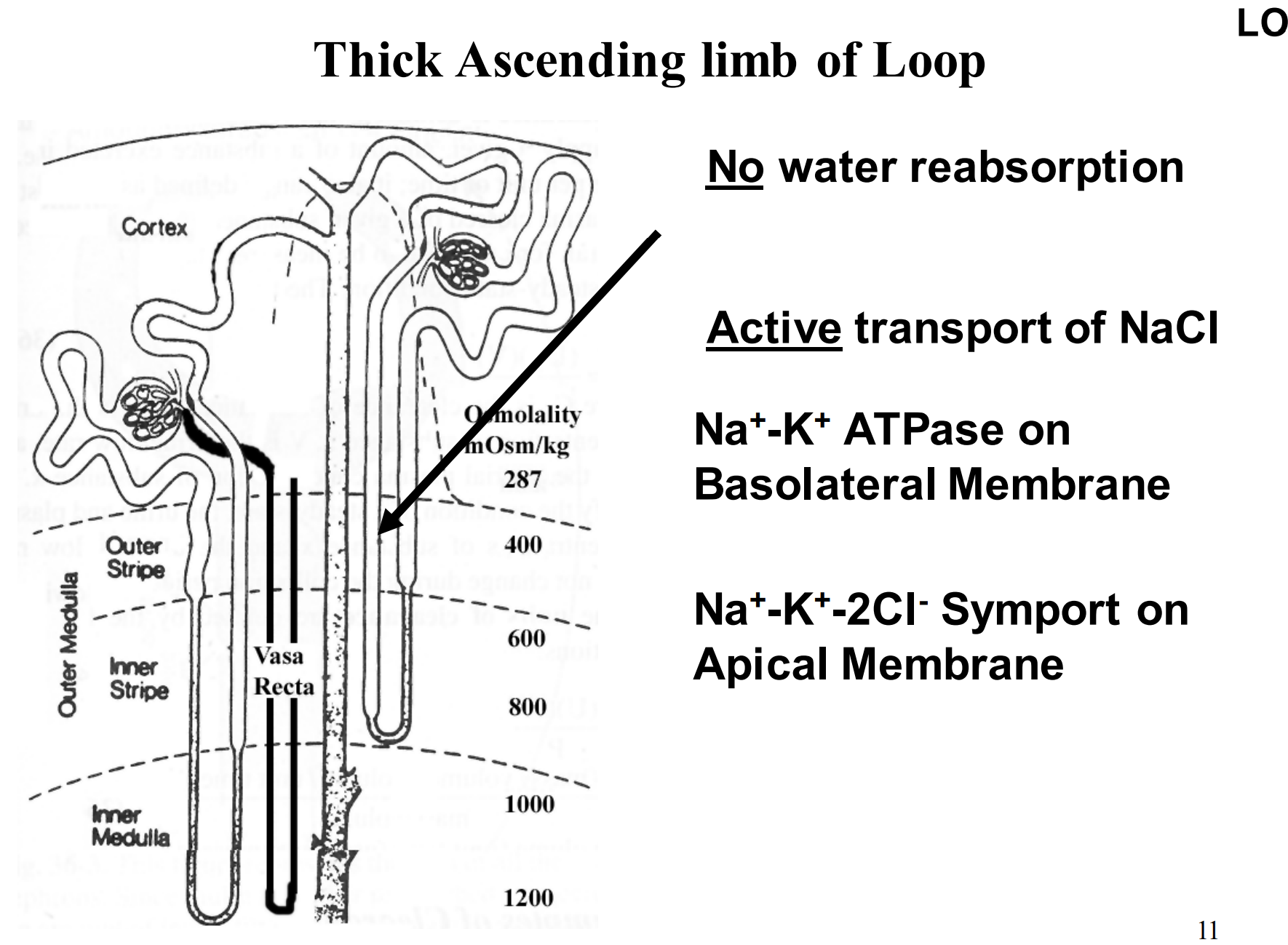
What is the general function of the loop of Henle?
sets up a driving force for water reabsorption along the medullary collecting duct
What is the general function of the distal tubule?
Called the diluting segment and responsible for water excretion
What is the general function of the collecting duct?
Hormonal regulation
What is the descending limb of the loop of Henle responsible for? And the ascending?
Where water reabsorption takes place (from tubules into the blood supply)
Where active transport of NaCl occurs (reabsorbing NaCl)
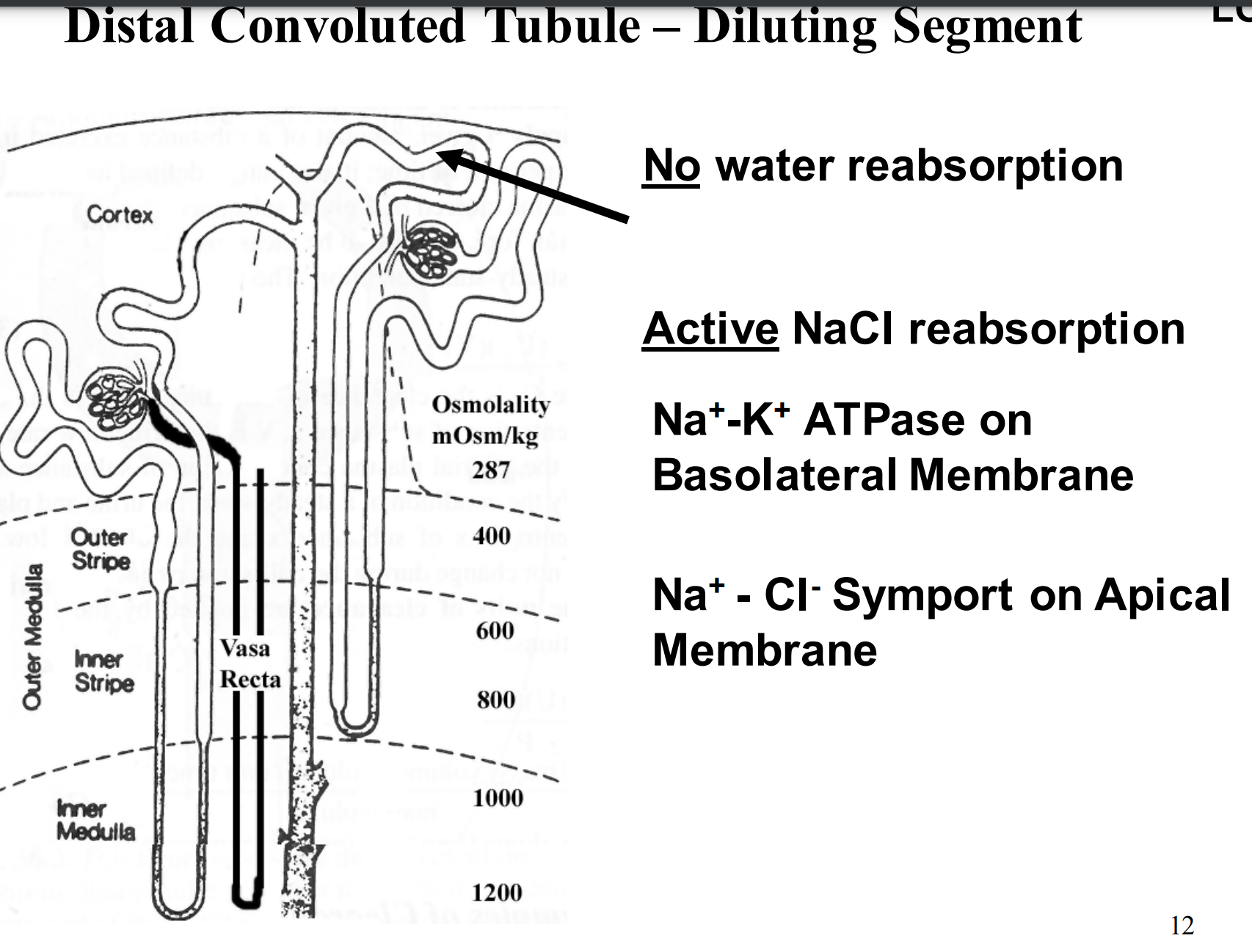
What happens in the diluting segment? (distal tubule)
No water reabsorption
Active NaCl reabsorption
Na+ -K+ ATPase on Basolateral Membrane
Na+ - Cl- Symport on Apical Membrane
What are the two hormones that control the collecting duct?
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) - prevents water excretion
Aldosterone (controls Na+ reabsorption)
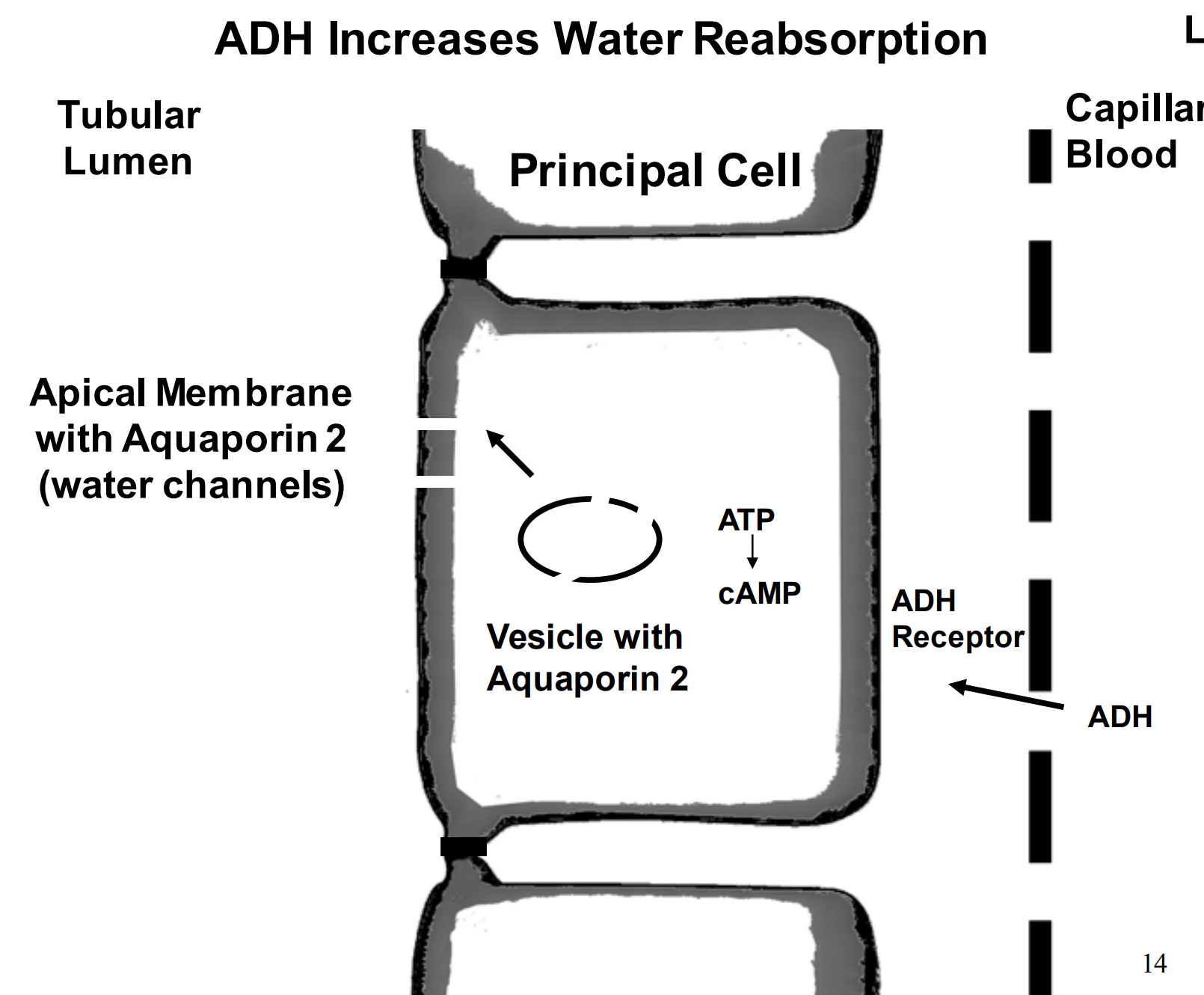
How does ADH increase water reabsorption?
High levels of ADH form aquaporin 2 (channels) and allow the catching and reabsorption of water.
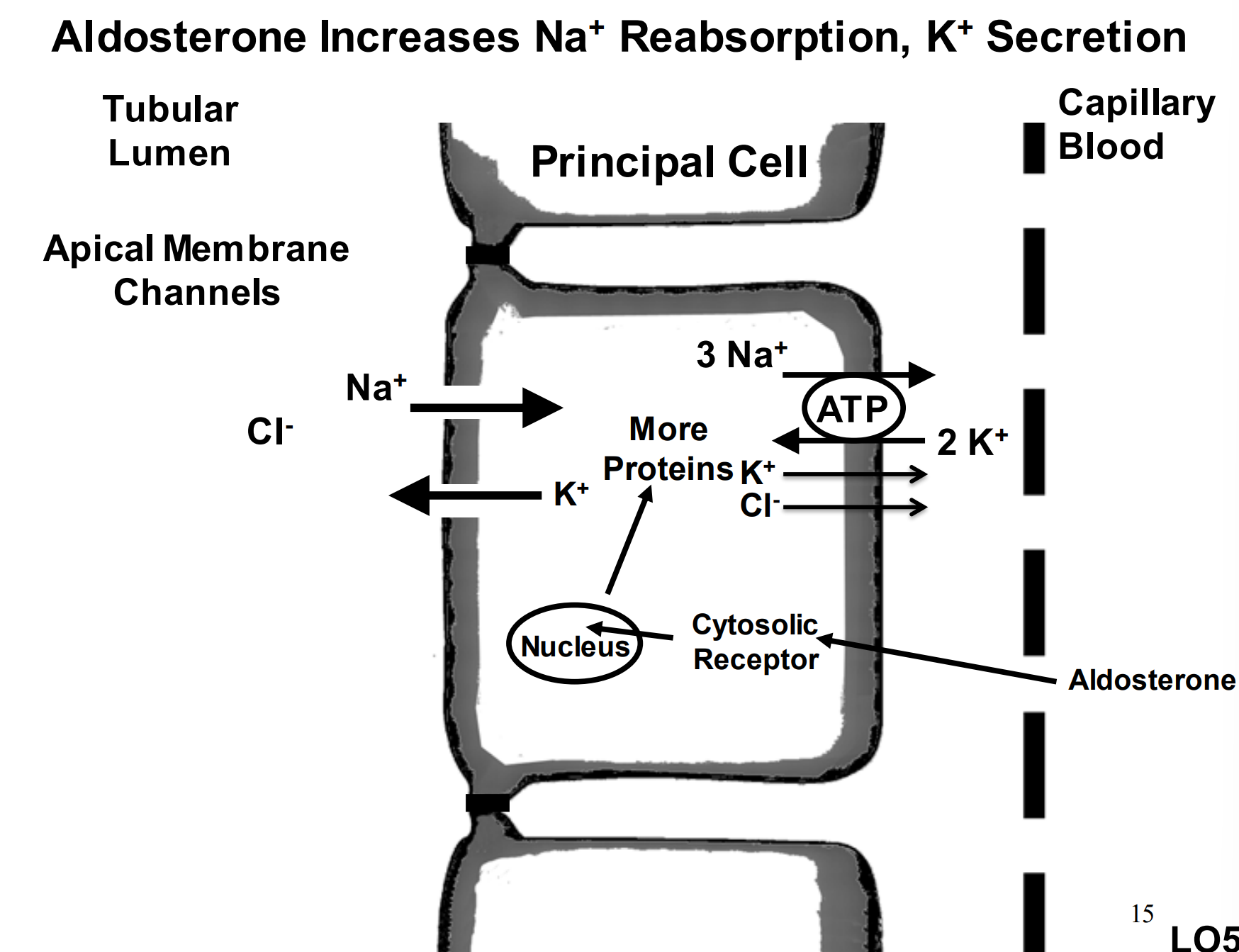
What does increase in aldosterone do?
increase sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion
When do we form a concentrated urine?
When ADH is present, we do this to reabsorb a lot of water back into the bloodstream, the same thing that happens in the distal tubules occurs in the collecting duct.
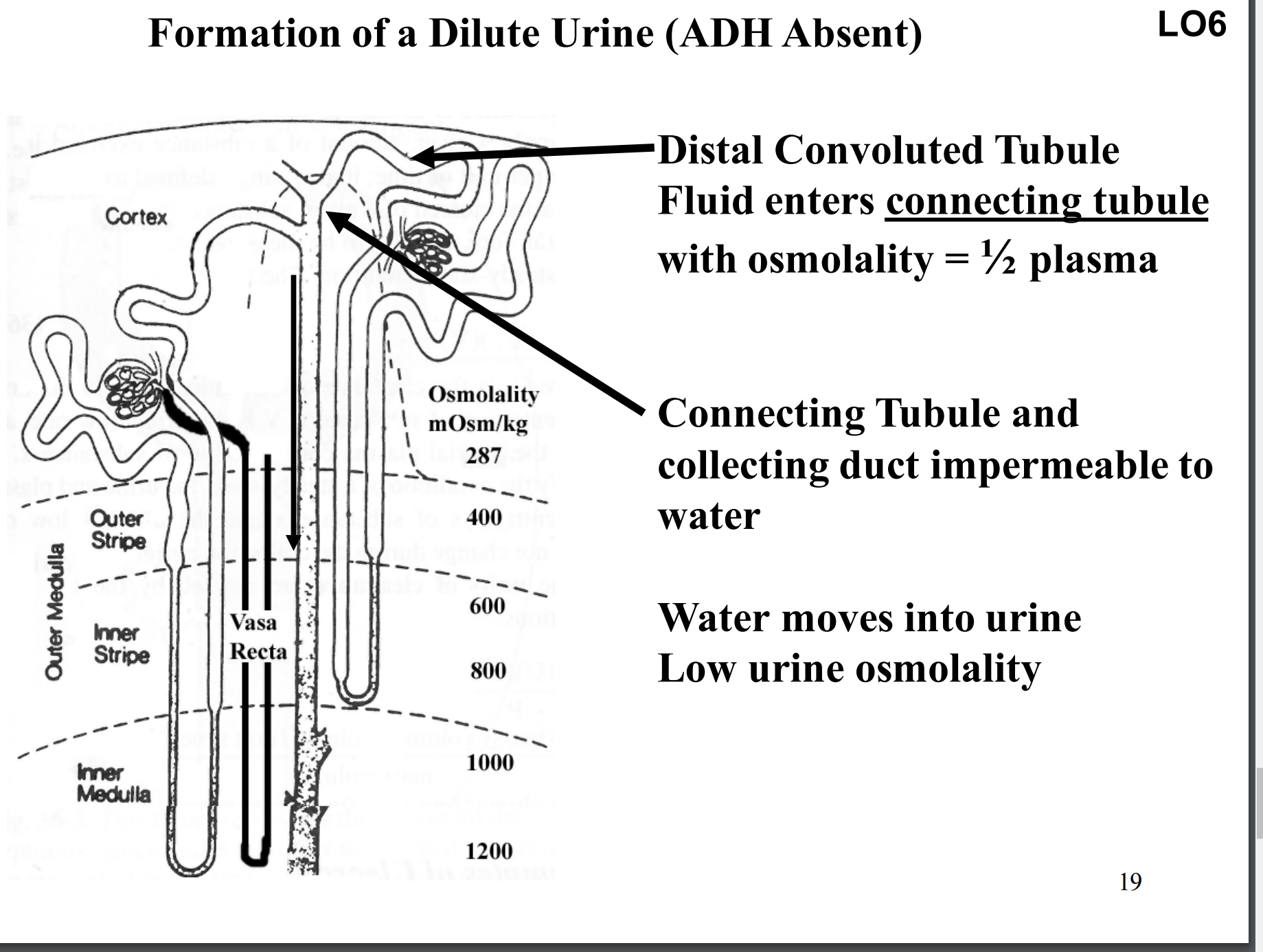
What happens when ADH is not present?
Formation of a dilute urine.
Increase in water excretion rate.
No change in Na+ excretion rate, K+ excretion rate, urea excretion rate, or excretion rates for other solutes (just more water not anything else)
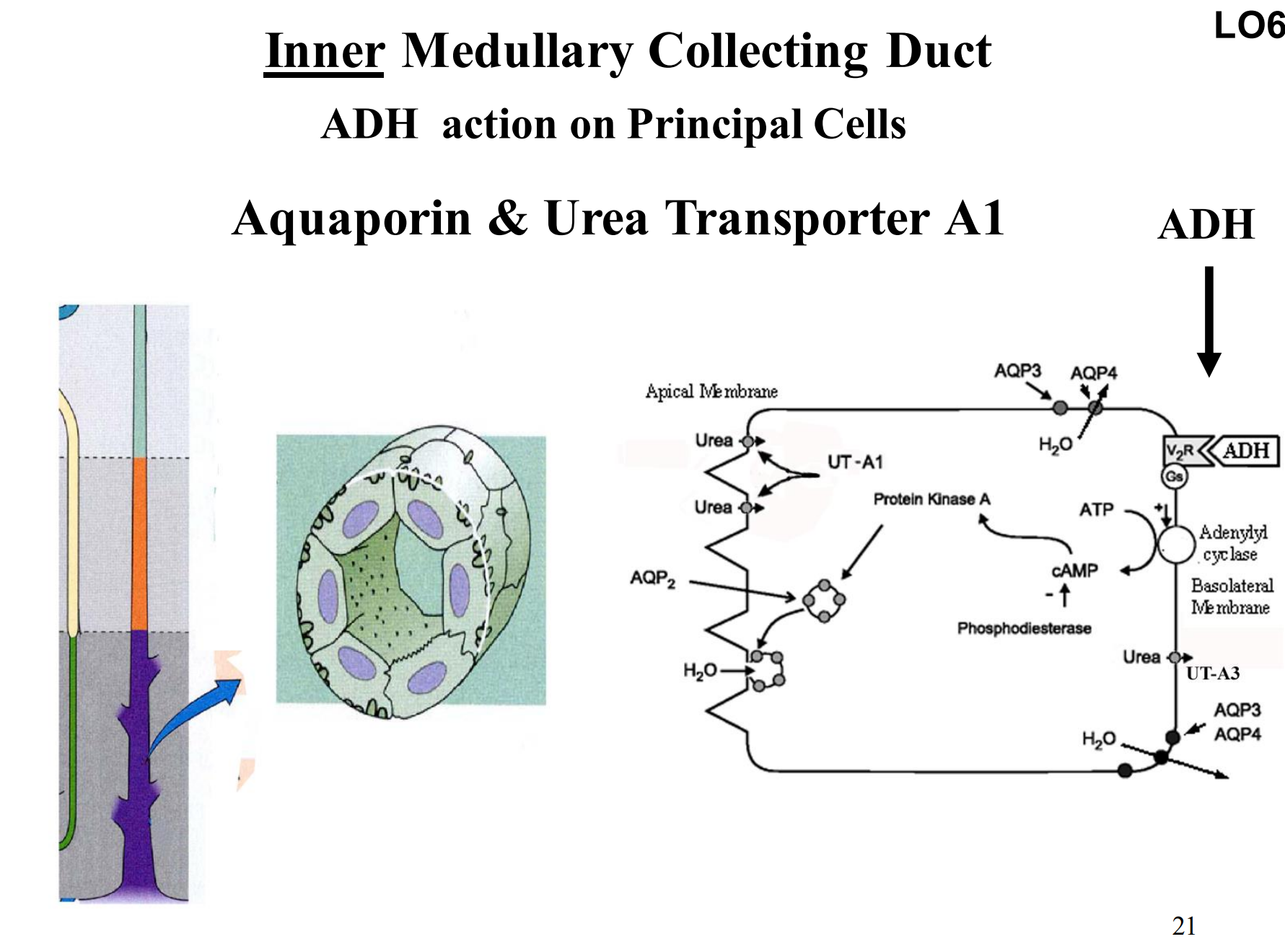
Inner Medullary Collecting Duct
Aquaporin & Urea Transporter A1
Urea transporter in inner medulla prevents urea from acting as an osmotic diuretic and inhibiting water reabsorption
Urea “recycling” from loop to inner medullary collecting duct increases interstitial urea concentration and prevents significant urea reabsorption
