1 - CARBOHYDRATES
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Glucose, fructose, galactose
Common Sugars
Monosaccharides (3)
Maltose, lactose, sucrose
Common Sugars
Disaccharides (3)
Glucose + Glucose
Common Sugars
Disaccharides
Maltose:
Glucose + Galactose
Common Sugars
Disaccharides
Lactose:
Glucose + Fructose
Common Sugars
Disaccharides
Sucrose:
Starch, glycogen
Common Sugars
Polysaccharides (2)
Starch
Common Sugars
Polysaccharides
Plant-based glucose polymer
Glycogen
Common Sugars
Polysaccharides
Animal-based glucose polymer
Reducing sugars
Common Sugars
Has a free aldehyde or ketone group that can be oxidized
Glucose, fructose, maltose, lactose, galactose
Common Sugars
Examples of reducing sugars (5)
Nonreducing sugars
Common Sugars
Lack a free aldehyde/ketone due to glycosidic bonding
Glucose
Common Sugars
Primary source of energy for humans
Glycogen
Common Sugars
Glucose storage form (liver and muscle)
1.5 to 2
Common Sugars
Glucose level returns to normal _ to _ hours after eating
Glycolysis
Glycogenesis
Lipogenesis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM | ||
↓ Glucose | _ | Glucose → Pyruvate |
_ | Glucose → Glycogen | |
_ | Carbohydrates → Fats | |
Gluconeogenesis
Glycogenolysis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM | ||
↑ Glucose | _ | Noncarbohydrates → Glucose |
_ | Glycogen → Glucose | |
x | Fat → Carbohydrates | |
Embden-Meyerhof pathway (Glycolysis)
Hexose Monophosphate Shunt
Storage (Glycogenesis)
Glucose Metabolism
Once inside a cell, glucose-6-phosphate (phosphorylated glucose) enters into: (3)
Embden-Meyerhof pathway (Glycolysis)
Glucose Metabolism
2 ATP net gain
Hexose Monophosphate Shunt
Glucose Metabolism
NADPH for oxidative damage protection
Storage (Glycogenesis)
Glucose Metabolism
Glycogen
Insulin
Glucose Metabolism Regulation
Only hypoglycemic agent
For glucose uptake into cells
glycolysis, glycogenesis, lipogenesis
Glucose Metabolism Regulation
Insulin
Increases (3)
β-cells
Glucose Metabolism Regulation
Insulin
Synthesized by _ of islets of Langerhans in pancreas
Glucagon
Glucose Metabolism Regulation
Primary hyperglycemic agent
glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis
Glucose Metabolism Regulation
Glucagon
Increases (2)
α-cells
Glucose Metabolism Regulation
Glucagon
Synthesized by _ of islets of Langerhans in pancreas
Somatostatin, GH, Cortisol, Epinephrine, T4
Glucose Metabolism Regulation
Other hyperglycemic agents (5)
Plasma/serum
Whole blood
Specimens for Glucose Measurement (2)
Plasma/serum
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
More preferred
30, 1
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
Plasma/serum
Must be separated within _ minutes/_ hour
11
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
Whole Blood
Glucose ~_% lower than plasma
gray
sodium fluoride
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
Considerations:
Use _-top tubes (_ _) to inhibit glycolysis
citrate
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
Considerations:
Sodium fluoride is now recognized to be ineffective; Less glycolysis was found in tubes w/ _ buffer, separated by gel barrier (Henry’s 24th)
7 mg/dL/hour
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
Considerations:
At RT, glycolysis decreases glucose by _ _ in uncentrifugated blood
2 mg/dL/hr
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
Considerations:
During refrigeration, glucose is metabolized by _ _
2 mg/dL/decade
4 mg/dL/decade
8-13 mg/dL/decade
Specimens for Glucose Measurement
Considerations:
Glucose increases with age:
Fasting: _
Postprandial: _
OGTT: _
Folin Wu
Nelson-Somogyi
Neocuproine
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Copper Reduction (3)
Folin Wu
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Copper Reduction
Copper + phosphomolybdate → Phosphomolybdenum blue
Nelson-Somogyi
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Copper Reduction
Copper + arsenomolybdate → Arsenomolybdenum blue
Neocuproine
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Copper Reduction
Copper + Neocuproine → _____________________________
Hagedorn-Jensen
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Ferric Reduction (1)
Hagedorn-Jensen
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Ferric Reduction
Yellow ferricyanide → Colorless (Inverse colorimetry)
O-toluidine (Dubowski)
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Condensation (1)
O-toluidine (Dubowski)
Glucose Measurement Methods
Obsolete Methods
Condensation
End result of a green Schiff’s base
Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase (GOD-POD)
Hexokinase
Glucose Measurement Methods
Enzymatic Methods (2)
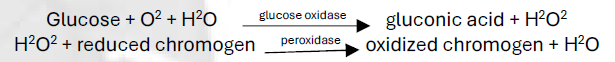
Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase
Glucose Measurement Methods
Enzymatic Methods
Highly specific for glucose
polarographic
Trinder reaction
Glucose Measurement Methods
Enzymatic Methods
Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase
Measures either oxygen consumption (_) or H2O2 (_ _)
decreased
increase
Glucose Measurement Methods
Enzymatic Methods
Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase
Prone to interferences with uric acid, bilirubin, ascorbic acid (all causing false _ results), and bleach (causes false _)
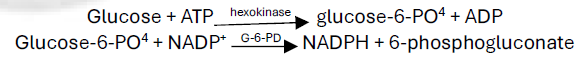
Hexokinase
Glucose Measurement Methods
Enzymatic Methods
Reference Method
Gross hemolysis
bilirubin
Glucose Measurement Methods
Enzymatic Methods
Hexokinase
Highly specific, minimal interference (_ _ and extremely elevated _ may cause a false decrease)
340
Glucose Measurement Methods
Enzymatic Methods
Hexokinase
Measures NADPH formation at _ nm
>100 mg/dL
>140 mg/dL
Hyperglycemia: glucose _ (fasting) or _ (non-fasting)
Insulin
Hyperglycemia
Key Regulator
Hormonal imbalance, especially involving insulin
Hyperglycemia
Cause
insulin
Hyperglycemia
Diabetes Mellitus
Group of disorders characterized by:
Chronic hyperglycemia due to _ defects (secretion, action, or both)
>180 mg/dL
Hyperglycemia
Diabetes Mellitus
Group of disorders characterized by:
Glucosuria when plasma glucose _
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Hyperglycemia
Diabetes Mellitus
Group of disorders characterized by:
_ _ (More common in type 1)
Nonketotic Hyperglycemic State
Hyperglycemia
Diabetes Mellitus
Group of disorders characterized by:
_ _ _ (More common in Type 2)
β-cell destruction
Insulin resistance
TYPE 1 VS TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS | ||
Type 1 | Type 2 | |
Cause | _ | _ |
Childhood/Teens
Advancing age
TYPE 1 VS TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS | ||
Type 1 | Type 2 | |
Onset | _ | _ |
5-10%
90-95%
TYPE 1 VS TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS | ||
Type 1 | Type 2 | |
Incidence | _ | _ |
Genetic, viral
Genetic, lifestyle, obesity
TYPE 1 VS TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS | ||
Type 1 | Type 2 | |
Risk factors | _ | _ |
Develop abruptly
Develop gradually
TYPE 1 VS TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS | ||
Type 1 | Type 2 | |
Symptoms | _ | _ |
Insulin absolute
Oral agents
TYPE 1 VS TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS | ||
Type 1 | Type 2 | |
Treatment | _ | _ |
Type 1.5 DM / Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA)
Other Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Presence of GAD antibodies, like Type 1
Adult onset (usually >30 years), like type 2
Insulin dependence progresses more slowly than classic Type 1
Type 3c DM / Pancreatogenic Diabetes
Other Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Insulin & glucagon loss secondary to pancreatic disease or surgery
Common causes: Pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, cystic fibrosis
No autoantibodies present
Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
Other Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Monogenic: caused by a single gene mutation
Onset before 25 years old but not neonatal
No autoantibodies present, asymptomatic, requires genetic testing
Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus (NDM)
Other Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Also monogenic: Occurs within the first 6 months of life
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM): in 2nd or 3rd trimester
Other Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Maternal risks: Later development of type 2 DM
Neonatal risks: Hypoglycemia, respiratory issues, macrosomia
Level 1 (<70 mg/dL)
Hypoglycemia
Classifications:
Glucose alert value
Level 2 (<54 mg/dL)
Hypoglycemia
Classifications:
Clinically significant hypoglycemia
Level 3
Hypoglycemia
Classifications:
Severe hypoglycemia with cognitive impairment
Postabsorptive (Fasting)
Hypoglycemia
Types:
Seen in insulinomas (pancreatic β-cell tumors)
Postprandial (Reactive)
Hypoglycemia
Types:
Occurs within 4 hours after eating
Alimentary
Hypoglycemia
Types:
Triggered by rapid gastric emptying (after GI surgery)
Drug-induced
Hypoglycemia
Types:
Diabetics taking insulin or insulin secretagogues
Alcohol-induced
Hypoglycemia
Types:
Usually occurs after binge drinking without food
Non-β Cell Tumor
Hypoglycemia
Types:
Paraneoplastic IGF-II ("big IGF-II") production
Von Gierke Disease (Type I Glycogen Storage Disease)
Hypoglycemia
Genetic Defects Causing Hypoglycemia
Most common congenital form of GSD
Deficiency: ________________________
Von Gierke Disease (Type I Glycogen Storage Disease)
Hypoglycemia
Genetic Defects Causing Hypoglycemia
With ↑ lactate, alanine, lipids, uric acid
Diagnosis: Liver biopsy via glycogen stain (PAS)
Pompe Disease (Type II Glycogen Storage Disease)
Hypoglycemia
Genetic Defects Causing Hypoglycemia
Deficiency: Lysosomal acid alpha glucosidase
Hallmark: Muscle weakness
Galactosemia
Hypoglycemia
Genetic Defects Causing Hypoglycemia
Deficiency: Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (most common)
Mechanism: Glycogenolysis inhibition
Galactosemia
Hypoglycemia
Genetic Defects Causing Hypoglycemia
With hyperbilirubinemia and galactose in blood/urine
Diagnosis: Erythrocyte enzyme activity
Fructose Intolerance
Hypoglycemia
Genetic Defects Causing Hypoglycemia
Deficiency: _______________________________
Triggers: Fructose ingestion → nausea, vomiting, hypoglycemia
≥126 mg/dL
≥200 mg/dL
≥200 mg/dL + symptoms
≥6.5%
Hypoglycemia
<50 mg/dL
glucose
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA | |
Type 1 and 2 DM | Hypoglycemia (Whipple’s Triad) |
|
|
70-99
≤140
<5.7%
CATEGORIES OF GLUCOSE LEVELS | |||
FBS | 2-hr PP & OGTT | HbA1c | |
Normal GT | _ mg/dL | _ mg/dL | _ |
100-125
140-199
5.7-6.4%
CATEGORIES OF GLUCOSE LEVELS | |||
FBS | 2-hr PP & OGTT | HbA1c | |
Impaired GT | _ mg/dL | _ mg/dL | _ |
≥126
≥200
≥6.5%
CATEGORIES OF GLUCOSE LEVELS | |||
FBS | 2-hr PP & OGTT | HbA1c | |
Provisional | _ mg/dL | _ mg/dL | _ |
0.0555
To convert mg/dL to mmol/L (glucose only) multiply the mg/dL value with _
Random Blood Sugar
Glucose Biomarkers
Requested during insulin shock and hyperglycemic ketonic coma
Collected anytime
Fasting Blood Sugar
Glucose Biomarkers
A measure of overall glucose homeostasis
8-10 hours (not over 16 hours) fasting required
Self-monitoring (POCT glucometers)
Glucose Biomarkers
If type 1 DM: 3-4x a day
If type 2 DM: Frequently individualized (unknown)
Oral Glucose Tolerance & 2-Hour Postprandial Glucose
Glucose Biomarkers
Measures the response of the body (glucose metabolism)
2-hour postprandial glucose
Glucose Biomarkers
Oral Glucose Tolerance & 2-Hour Postprandial Glucose
2 hours after a full meal (monitoring)
OGTT
Glucose Biomarkers
Oral Glucose Tolerance & 2-Hour Postprandial Glucose
after intaking a glucose load (especially in GDM diagnosis)
OGTT
Glucose Biomarkers
Oral Glucose Tolerance & 2-Hour Postprandial Glucose
after intaking a glucose load (especially in GDM diagnosis)
One Step (1 intake)
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test for GDM
1. Patient undergoes fasting
2. Patient’s blood is drawn
3. Patient intakes glucose load
4. 1hr after intake, blood drawn
5. 2hrs after intake, blood drawn
Two Step (2 intakes)
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test for GDM
1. Patient intakes glucose load
2. 1hr after intake, blood drawn
3. If glucose, ≥140 mg/dL, undergo
fasting, and come back tomorrow
4. Patient’s blood drawn next day
5. Patient intakes ____________
6. 1hr after intake, blood drawn
7. 2hrs after intake, blood drawn
8. 3hrs after intake, blood drawn
≥92
≥180
≥153
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test for GDM
One Step (1 intake)
Diagnostic if AT LEAST 1 was met:
Fasting: _ mg/dL
1h after intake: _ mg/dL
2h after intake: _ mg/dL
≥95
≥180
≥155
≥140
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test for GDM
Two Step (2 intakes)
Diagnostic if AT LEAST 2 were met:
Fasting: _ mg/dL
1h after intake: _ mg/dL
2h after intake: _ mg/dL
3h after intake: _ mg/dL