c3 - elements compounds and mixtures
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is relative atomic mass
the mass of an atom compared to the mass of 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom
what is an empirical formula
the simplest whole-number ratio the atoms of each element in a compound
what is a pure substance
a substance that consists of only one element or compound
what is an alloy
a mixture of a metal with one or more other elements
how do the melting points of a pure and impure substance differ
the melting point of a pure substance is a single temperature
if the substance is impure the melting point is less than that of the pure substance AND it often melts over a range of temperatures
the greater the range of melting points, the less pure a substance is likely to be
how do you determine a melting point without losing accuracy
heat a substance and measure the temperature when it melts
heat the substance slowly so the whole sample’s temperature increases at the same time
stir the substance as it melts to ensure the entire sample is at the same temperature
what is a:
solution
solute
solvent
solution - the product formed when a substance dissolves in another
solute - the substance that dissolves
solvent - the liquid the substance dissolves in
what does dissolve mean
when the solute particles separate and are completely mixed with the particles of the solvent
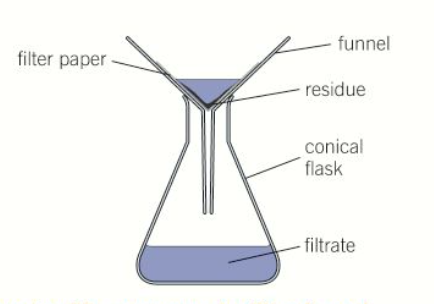
what is filtration
a method used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid
what is the residue and the filtrate
residue - the insoluble solid that is filtered out
filtrate - the liquid that passes through the filter
draw a diagram of filtration
how does crystallisation work
if you heat a solution slowly the solvent evaporates and the solute forms crystals
what is a saturated solution
a solution where no more solute can be dissolved at that temperature
describe a crystallisation practical (4)
evaporate the solvent till its a saturated solution
slowly heat it till crystals form
pat the crystals dry and put them in a warm oven to evaporate any remaining solvent
draw a diagram of a fractional distillation experiment
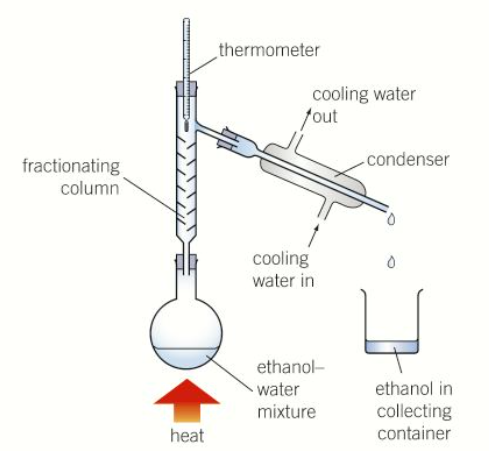
why is a fractionating column used
as it has a larger surface area so the vapours can continually condense easier
how do you calculate rf value
rf = distance travelled by substance / distance travelled by solvent
what are the two phases in gas, paper, and thin layer chromatography
stationary - silica / alumina powder in the metal column, silica / alumina powder spread on a glass / plastic plate, absorbent paper
mobile - unreactive carrier gas, solvent in liquid state
what does gas chromatography do
separates the components of a mixture and measures their amounts
how do gas chromatography (4)
the sampel turn into the gas state when it’s injected into the column
the carrier gas pushes the sample through the column
3.different components take different times to travel through the column depending on how strongly the bond to the stationary phase
4.a detector sends a signal to a computer that makes a chromatogram as each component leaves the column
what are 3 advantages to thin-layer chromatography
it is quicker
it is more sensitive so a smaller sample can be used
there is a larger range of stationary phases and solvents to choose from
how do you separate insoluble and soluble substances
dissolve then filter
how do you separate a solute dissolved in a solvent
crystallise to get the solute then simple distillation to get the solvent
how do you separate two or more substances in the liquid state
fractional distillation
how do you seperate coloured soluble substances
paper or thin-layer chromatography
how do metal and non-metal physical properties compare (6)
metal non-metal
shiny dull
malleable brittle
high melting point low melting point
solid at room temp solid / gas at room temp
ductile non-ductile
conductors insulators
what is the difference between metal and non-metal oxides
metal oxides dissolve in water to form alkaline solutions while non-metal oxides form acidic solutions
what are the chemical properties of metals and non-metals
metals lose electrons to form positive ions while non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions
metals don’t react with each other but non-metals react and produce compounds
how is the periodic table arranged
in order of increasing atomic number
rows are called periods and columns are called groups
what are ions
a charged particle formed when an atom loses or gains electrons
how do ionic compounds form
when a metal and non-metal bond and electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal
what is a giant ionic lattice
a structure where oppositely charged ions are held in place with ionic bonds in the solid state
what is a covalent bond
a bond formed when two non-metals share electrons to achieve a full outer shell
what are simple molecules
a molecule that only contains a few atoms