Acids, Bases, and Redox Reactions Overview
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
Acid
Substance releasing H+ ions in solution.

Hydrogen Ion
Proton, H+, released by acids in water.
Strong Acid
Completely dissociates in aqueous solution.

Weak Acid
Partially dissociates, releasing few H+ ions.
Hydrochloric Acid
Strong acid, formula HCl, fully dissociates.
Ethanoic Acid
Weak acid, formula CH3COOH, partially dissociates.
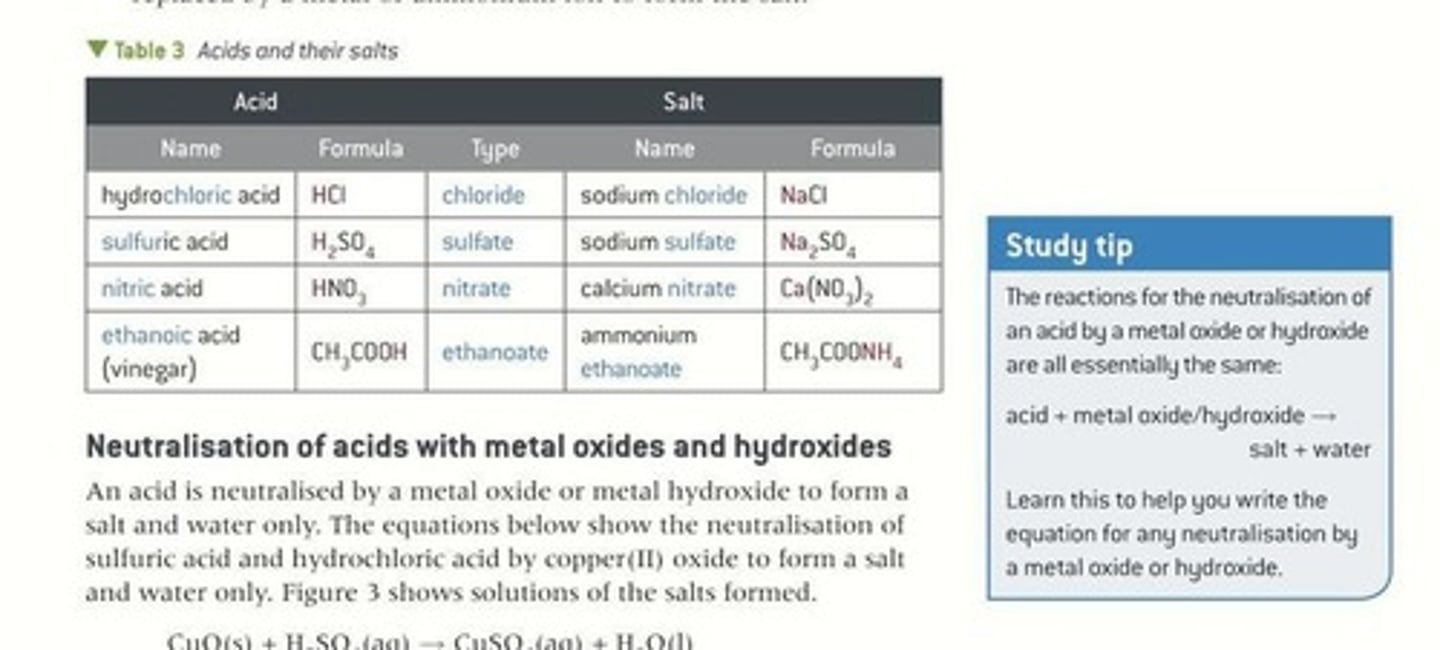
Neutralisation
Reaction of acid with base to form salt.
Base
Substance that neutralises an acid.
Alkali
Base dissolving in water, releasing OH- ions.
Sodium Hydroxide
Alkali, formula NaOH, releases OH- in water.
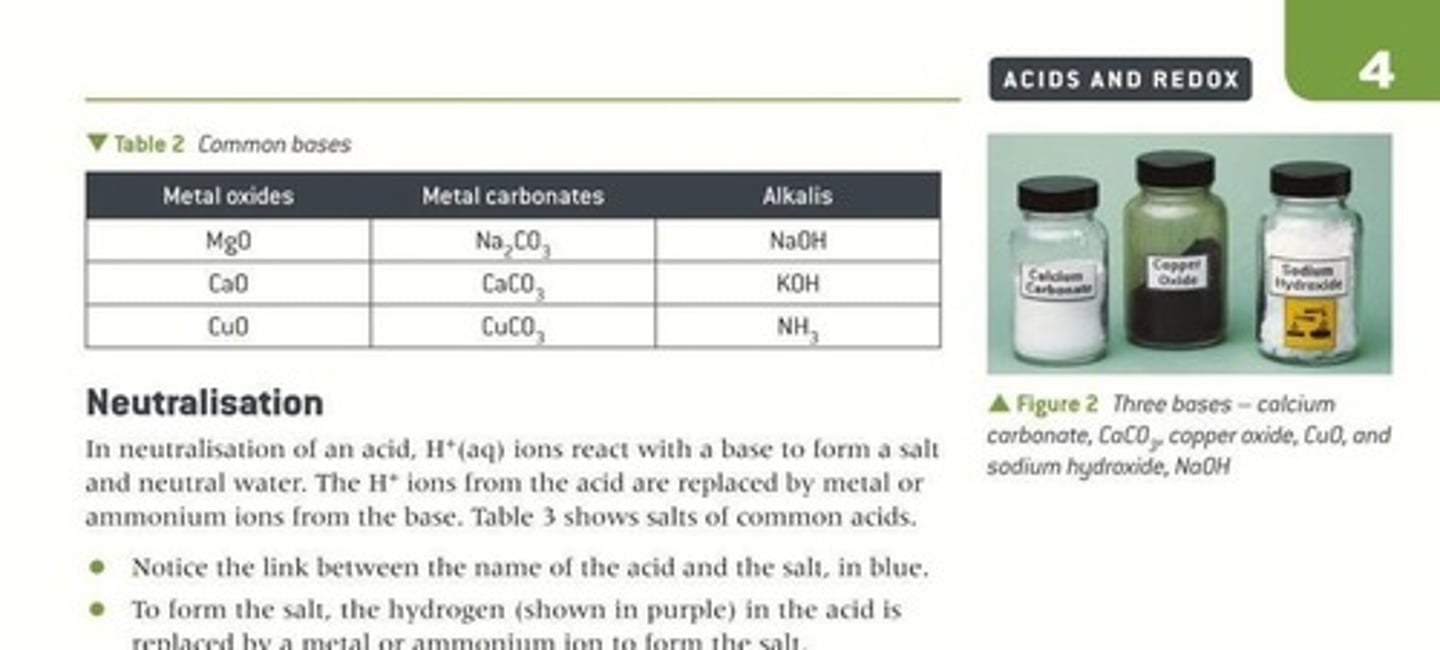
Metal Oxide
Base that reacts with acids to form salts.
Metal Hydroxide
Base that releases hydroxide ions in solution.
Salt
Product formed from neutralisation of acid and base.
Hydrogen Replacement
H+ from acid replaced by metal/ammonium ion.
Sulfuric Acid
Strong acid, formula H2SO4, fully dissociates.

Nitric Acid
Strong acid, formula HNO3, fully dissociates.
Calcium Carbonate
Base, formula CaCO3, neutralises acids.

Copper(II) Oxide
Base, reacts with acids to form salts.
Neutral Water
Water produced in acid-base neutralisation.
Equilibrium Sign
Indicates incomplete reaction in weak acid dissociation.
Common Bases
Includes metal oxides, hydroxides, and carbonates.
Acid-Salt Link
Salt name derived from the corresponding acid.
Neutralisation Equation
Acid + Base → Salt + Water.
Neutralisation
Reaction forming salt and water from acid and alkali.
Ionic Equation
Simplified representation of ionic reactions.
Copper(II) Sulfate
Blue salt formed from sulfuric acid and copper.

Copper(II) Chloride
Green salt formed from hydrochloric acid and copper.
Metal Carbonates
React with acids to produce salt, water, and CO2.
Sulfuric Acid
Strong acid that partially dissociates in water.
Dissociation
Process of breaking down into ions in solution.
Hydrogen Ion (H+)
Positively charged ion from acid dissociation.
Weak Acid
Partially dissociates in solution, like HSO4-.
Strong Acid
Completely dissociates in solution, like HCl.
Acid Salt
Salt formed by partial neutralisation of a weak acid.
Baking Powder
Contains organic acid and bicarbonate for baking.
Titration
Technique to measure solution volumes for reactions.

Standard Solution
Solution with known concentration for titrations.
Concentration
Amount of solute in a given volume of solution.
Quality Control
Ensuring purity of substances for safety.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Gas produced during carbonate neutralisation reactions.
Ethanoic Acid
Weak acid used in vinegar, reacts with bases.
Nitric Acid
Strong acid used in various chemical reactions.
Phosphoric Acid
Acid with three dissociable hydrogen atoms.
Complete Neutralisation
All acid reacts with base to form salt.
Partial Neutralisation
Only some acid reacts with base, forming acid salt.
Hydrochloric Acid
Strong acid commonly used in titrations.
Pharmaceutical purity
High purity level is essential for drug safety.
Standard solution
A solution with a known concentration.
Volumetric flask
Used to prepare standard solutions accurately.

Graduation line
Mark indicating the precise volume in flasks.
Meniscus
Curved surface of a liquid in a container.
Titration
Process of determining concentration via reaction.
Acid-base titration
Titration involving an acid and a base.
Pipette
Device for measuring and transferring liquids.
Burette
Instrument for delivering variable volumes of liquid.

Titre
Volume of solution added during titration.
Initial burette reading
Starting volume measurement before titration begins.
Final burette reading
Volume measurement after titration is complete.
Indicator
Substance that changes color at endpoint.

Conical flask
Container used to mix solutions during titration.
Trial titration
Initial titration to estimate the titre volume.
Concordant titres
Titration results agreeing within 0.10 cm³.
Tolerances of volumetric flasks
Precision limits for flask volume measurements.

Rinsing
Process of cleaning flasks to ensure accuracy.
Dilute solution
Solution with a lower concentration than intended.
Mixing solutions
Inverting flask ensures uniform distribution of solute.
Air bubbles in burette
Can cause errors in titration volume measurement.
Accurate weighing
Essential for preparing standard solutions correctly.
Adding distilled water
Final step to reach the graduation line.
Concordant titres
Two titres agreeing within 0.10 cm³.
Burette reading
Volume measurement from a burette in cm³.
Pipette
Device for measuring and transferring liquid volumes.
Mean titre
Average of concordant titration results.
Titration
Process of adding a solution to determine concentration.
Meniscus
Curved surface of liquid in a container.
Air bubble effect
Causes inaccurate volume measurement in pipette.
Top meniscus reading
Incorrect method leading to volume overestimation.
Bottom meniscus reading
Correct method for accurate burette measurement.
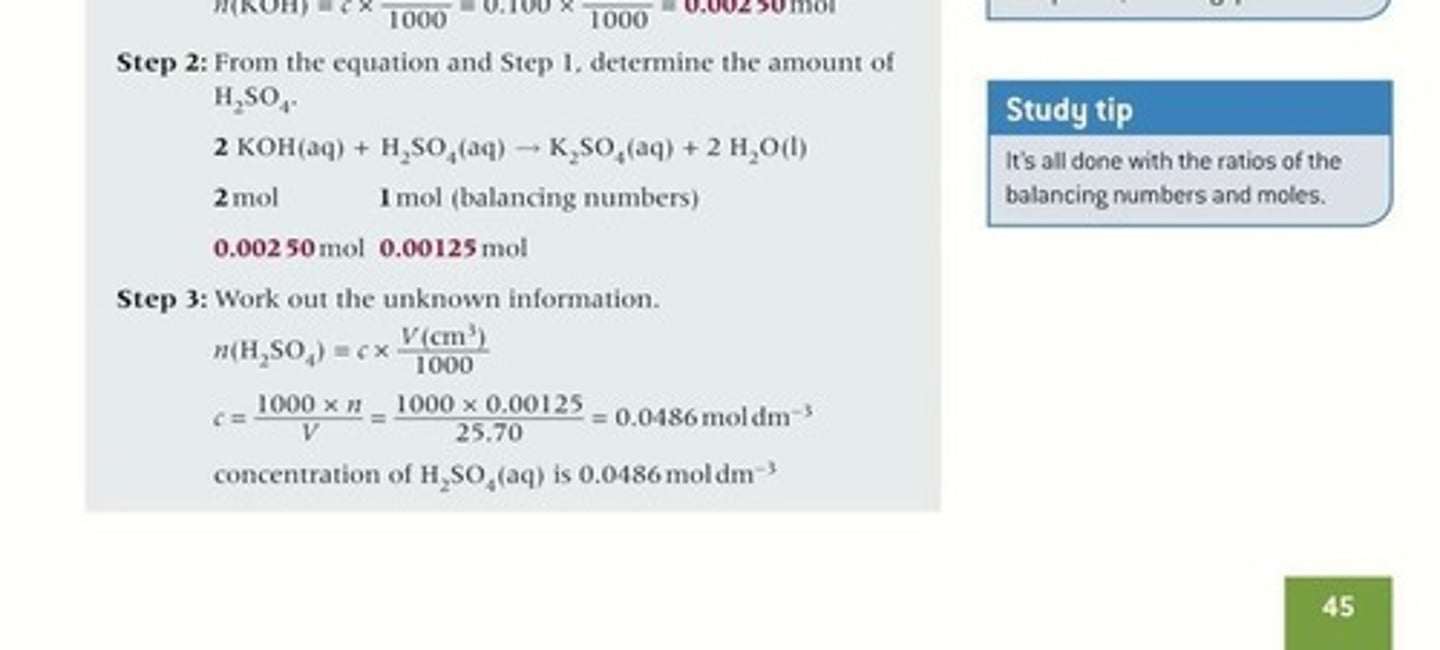
Titration calculation steps
Procedure to find unknown solution concentrations.

Concentration (c)
Amount of solute per volume of solution.
Reacting volume (V)
Volume of solution involved in a reaction.
Mole calculation
Determining amount of substance in moles.
Balanced equation
Chemical equation showing reactants and products ratios.
KOH(aq)
Potassium hydroxide solution used in titration.
H₂SO₄(aq)
Sulfuric acid solution used in titration.
Unknown concentration
Concentration of a substance to be determined.
Volumetric flask
Glassware for precise liquid volume preparation.
Hydrochloric acid
Strong acid used in titration experiments.
Mass of XCO₃
Weight of unknown carbonate measured in grams.

Titration results analysis
Interpreting data to identify unknown substances.
Final burette reading
Volume measurement after titration completion.

Initial burette reading
Volume measurement before titration begins.
Mean Titre V
Average volume used in titration experiments.

Concentration of HCl
Measured in mol/dm³, indicates strength of acid.
n(HCl)
Moles of hydrochloric acid calculated from volume.
X,C0,
Unknown carbonate reacting in titration.
Balancing Numbers
Coefficients indicating mole ratios in reactions.
Scaling Factor
Ratio used to adjust volumes in calculations.
Molar Mass
Mass of one mole of a substance.
Unknown Acid HA
Acid whose properties are to be determined.