3.1 Biological Molecules
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
Define monomers
the smaller units from which larger units are made
Define polymers
Molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together
Give examples of monomers
Monosaccharides, amino acids and nucleotides
What is the general formula of carbohydrates
Cx(H2O)y
What are monosaccharides (give examples too)
the monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made
- e.g. (glucose, galactose and fructose)
What is the general formula of monosaccharides ?
CnH2nOn
Name some properties of monosaccharides
sweet, small, soluble in water and crystallisable
What is the formula of trioses
C3H6O3
Give examples of trioses and where they are found
- glycerate 3 phosphate (light independent stage of photosynthesis)
- glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (glycolysis)
What is the formula for pentoses
C5H10O5
Give examples of pentoses
- deoxyribose (DNA)
- ribose (RNA and ATP [adenine triphosphate])
What is the formula for hexoses
C6H12O6
Give examples of hexoses and where they are found
- glucose (main respiratory substrate)
- fructose (found in nectar, and fruit to attract animals to eat them)
- galactose (found in milk)
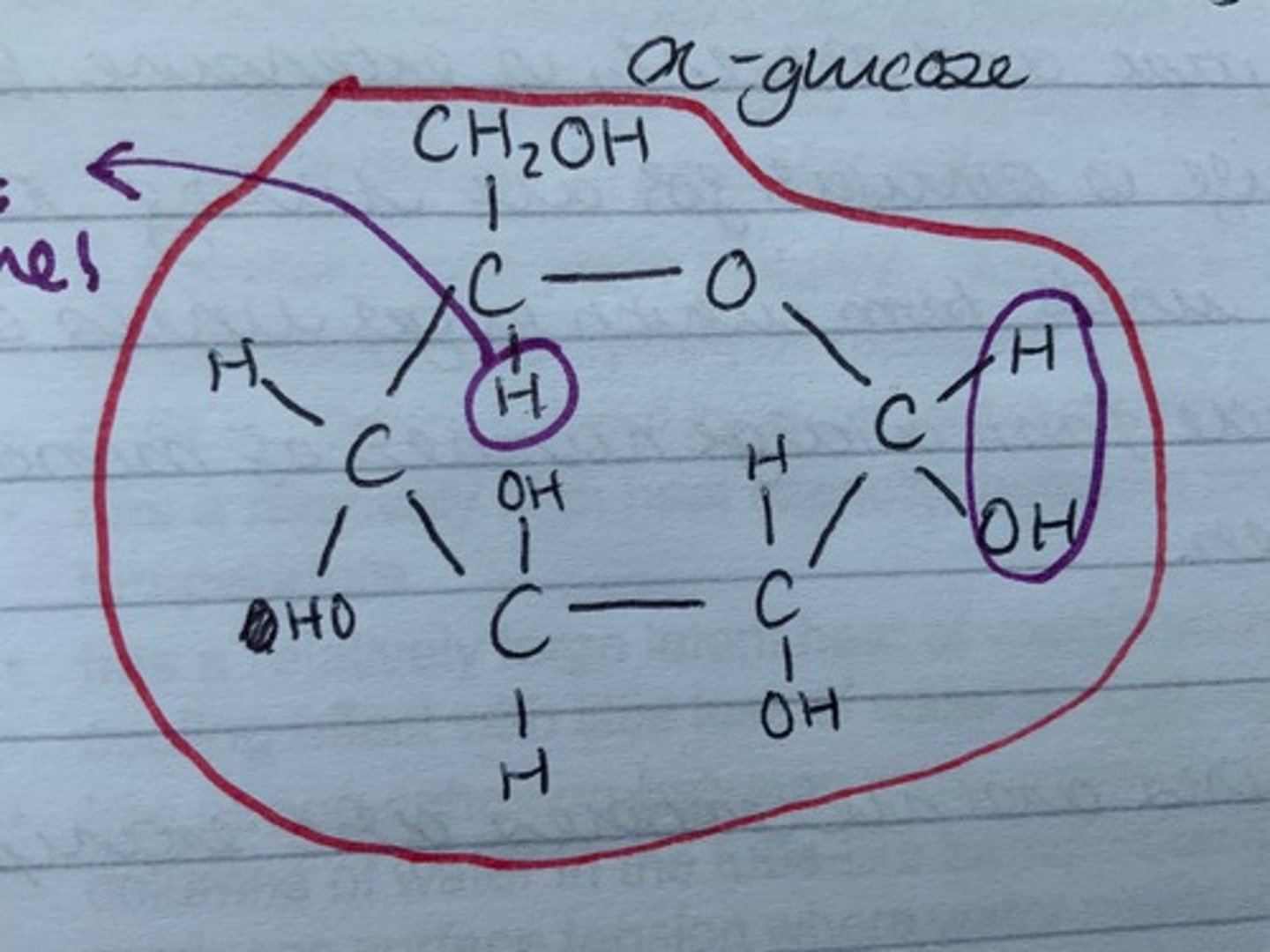
In alpha glucose, is the hydroxide on C1 on the bottom or the top?
bottom
Draw alpha glucose
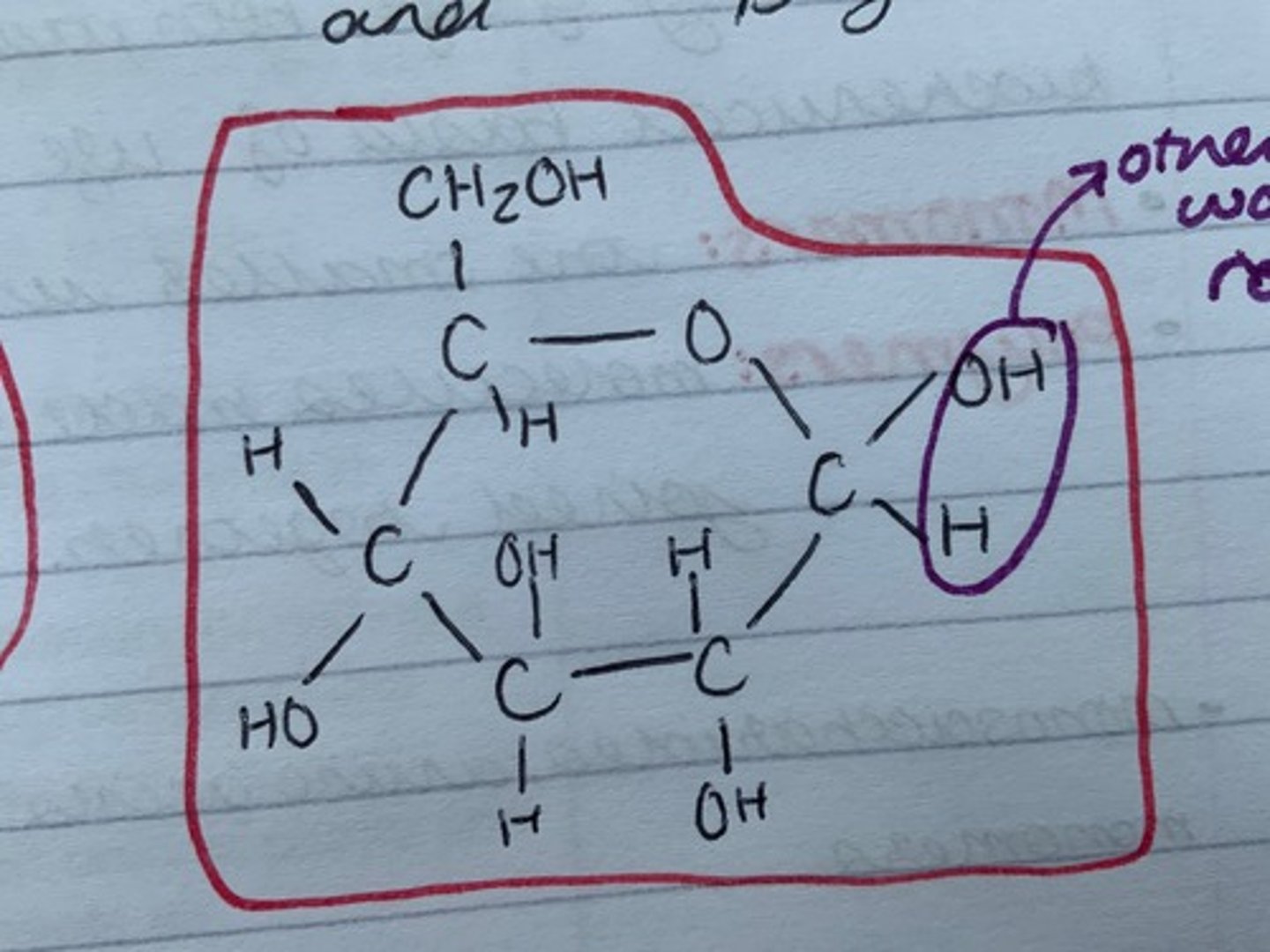
Draw beta glucose
Define condensation reaction
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water.
Define hydrolysis reaction
Breaks the chemical bond between monomers and involves the use of a water molecule.
Name some properties of disaccharides
sweet, soluble in water, and crystallisable
Give an example of a disaccharide, and how it is made
maltose - made from two glucose molecules
Draw maltose
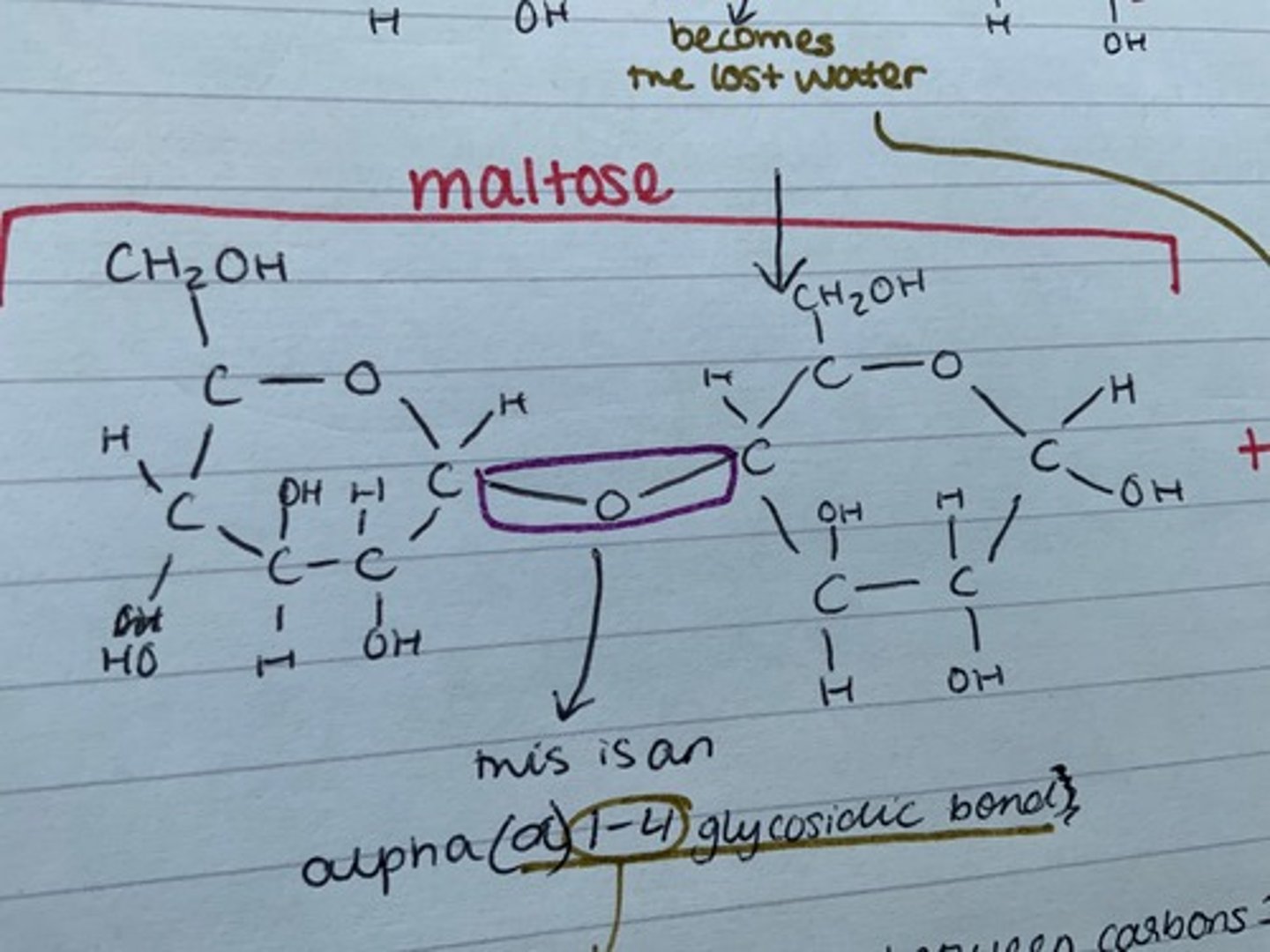
What is the bond joining the two glucose molecules used to make maltose called, and why?
an alpha (a) 1-4 glycosidic bond
this is because it is between carbons 1 and 4
what is the reaction to form maltose?
glucose + glucose -> maltose + water
Describe the test for starch
Add a few drops of iodine solution to 2cm^3 of the sample. It should go yellow-brown to blue-black to show a +ve result
Describe the test for reducing sugars
Add 2cm3 of the sample to a boiling tube and heat in a water bath at 80°C for 5 minutes. It should go blue to a brick red precipitate to show a +ve result.
Describe the test for non-reducing sugars
First test for reducing sugars and obtain a negative result.
1) Add 2cm3 of HCl to the sample and heat in a water bath at 80°C for 5 minutes.
2) Add 2cm3 of NaOH to neutralise
3) Add 2cm3 of Benedict’s solution and heat in a water bath at 80°C for 5 minutes.
4) It should go from blue to brick red to show a positive result
Describe the test for protein
Add 2cm3 biuret solution to 2cm3 of the sample solution. It should go from blue to lilac to show a positive result.
Describe the test for lipids
1. Shake the test substance with 2cm3 ethanol for about a minute
2. Then add 2cm3 distilled water
3. If lipids are present, there will be a change from colourless to see a milky-white suspension
What are polysaccharides? Name some examples.
Polysaccharides are polymers - they are made up of many monosaccharides by multiple condensation reactions.
e.g. Starch, cellulose and glycogen
What is starch? What two polymers does it consist of?
It is the main polysaccharide stored in plants, a polymer of alpha-glucose formed of condensation reactions. It consists of two polymers: amylose and amylopectin.
Describe the structure of amylose.
- a straight, unbranched chain of a-glucose that forms a spiral.
- it forms a helix by hydrogen bonds which holds and forms a complex with iodine when we test for starch
- because of the helix structure, it is very compact so is a very efficient way to store glucose
Describe the structure of amylopectin.
~ Long, unbranched chains of α-glucose
~ Has side branches which allows enzyme to hydrolyse bonds more easily - glucose is released quickly
~ Contain 1-4 glyosidic bonds
~ every 25 glucose molecules, it branches with 1-6 glyosidic bonds
What are the properties of starch?
- insoluble so does not affect the water potential ( osmotically inert)
- helical: it is compact
- large molecule so stays inside cells (cannot easily pass through a partially permeable membrane)
What is glycogen?
main storage polysaccharide in animal cells (muscles and liver)
polymer of a-glucose
Describe the structure of glycogen.
a highly branched molecule of alpha glucose joined by 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds. It has a very similar structure to amylopectin but has many more branches, which are shorter. It is even more compact than amylopectin, too.
What is cellulose?
Polymer of beta glucose. It is a structural polysaccharide in plants.
What are the properties of cellulose? How does it affect the cell wall's permeability?
It has a high tensile strength. The cell wall is fully permeable to water and solutes as the gaps in the layers of fibrils provide permeability. The molecules of the matrix are hydrophilic so the cell wall is continually saturated in water.
Describe the structure of cellulose.
~ Long, unbranched chains of β-glucose
~ The OH groups stick outwards from these chains in all directions which can form hydrogen bonds with neighbouring chains, which are parallel. (different to amylose in starch where the OH groups project inwards)
Why does cellulose have a high tensile strength?
It is strong due to the glycosidic bonds and the hydrogen bonds. 2000 cellulose chains form microfibrils, which are 10-30 nm in diameter. These microfibrils are laid down in different directions parallel to each other. Bundles of microfibrils form fibrils.
What are lipids made from?
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
what is the general formula for the formation of a lipid? What kind of reaction is this?
1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids -> 1 triglyceride + 3 water
this is a condensation reaction
What is the structure of glycerol?
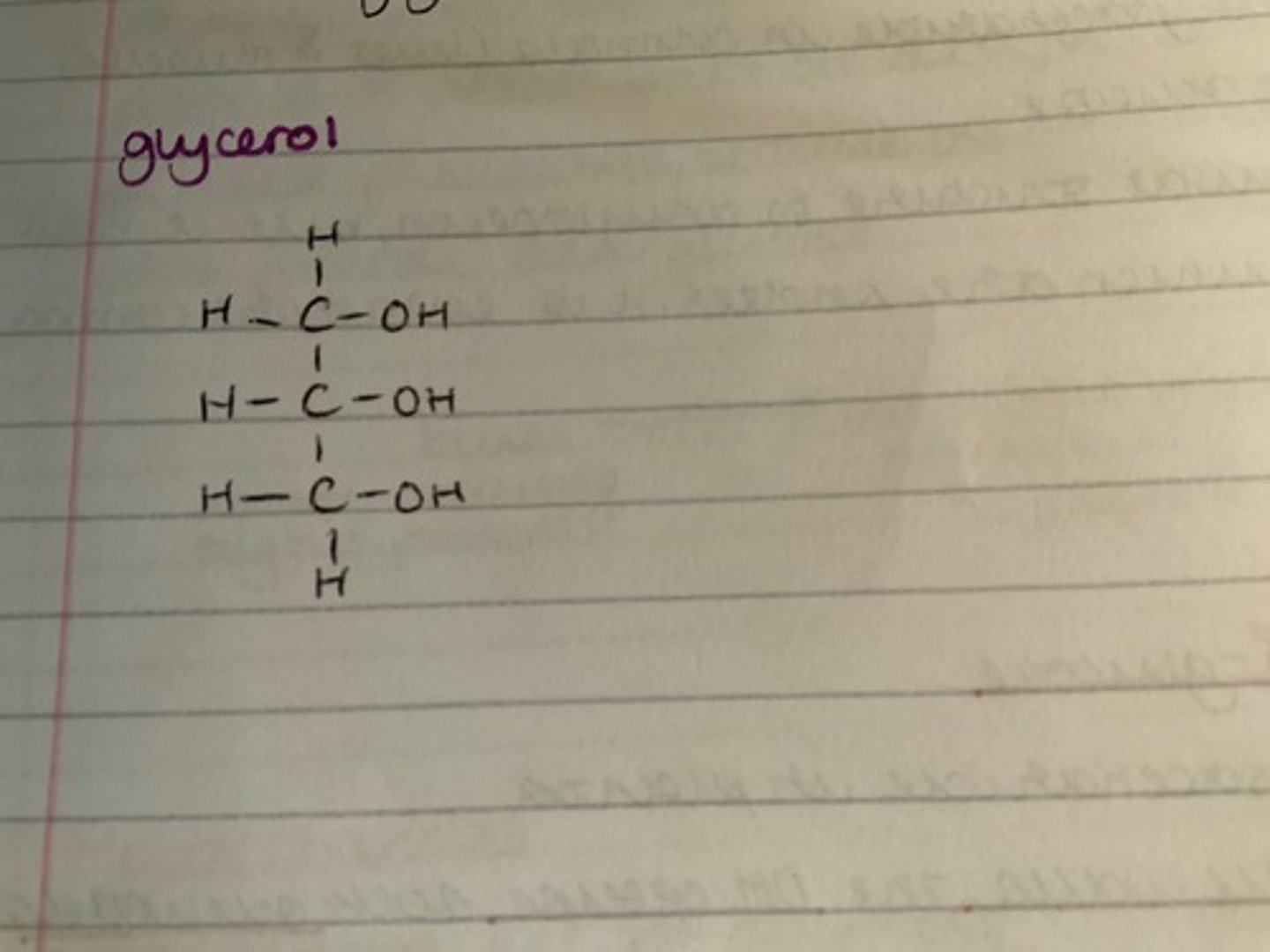
What are the properties of lipids?
- they contain C,H and O
- the proportion of O to C and H is smaller than that in carbs
- insoluble in water
- soluble in organic substances (eg alcohols and acetone)
What are the functions of lipids?
- phospholipids contribute to the flexibility of cell-surface membranes and the transfer of lipid-soluble substances across them
- they are a source of energy, and provide more than twice the energy as the same mass of carbs when oxidised, as well as releasing water
- Waterproofing (hydrophobic). - waxy cuticle in plants/ insects and oily secretion from glands in mammals
- electrical insulators in myelin sheath, thermal insulation when stored under skin in animals
- protects delicate organs, such as the kidneys, which it is often stored around
What are triglycerides?
A Lipid built with 3 fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol molecule.
They all have a carboxylic (- COOH) group with a hydrocarbon chain attatched
What makes a triglyceride mono-unsaturated? Draw a diagram.
This is when there is one C=C double bond.

What makes a triglyceride poly-unsaturated? Draw a diagram.
This is when there is more than one C=C double bond

What makes a triglyceride saturated? Draw a diagram.
This is when there are no C=C double bonds.

Why are triglycerides an excellent source of energy?
they have a high ratio of energy-storing carbon-hydrogen bonds to carbon atoms
Why are triglycerides good storage molecules? Why is this beneficial to animals?
They have low mass to energy ratio making them good storage molecules because much energy can be stored in a small volume. This is beneficial to animals as it reduces the mass the have to carry around.
Why are triglycerides insoluble in water?
They are large, non-polar molecules. This means their storage does not affect osmosis in cells or the water potential of them.
Why do triglycerides release water when oxidised?
they have a high ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms. They therefore provide an important source of water, especially for organisms living in dry deserts.
What are phospholipids?
Similar to lipids, but one fatty acid molecule is replaced by a phosphate molecule.
Describe a different property between phosphate and fatty acid molecules
Phosphate molecules are hydrophilic, whereas fatty acid molecules are hydrophobic
Why are phospholipids said to be polar molecules?
They have a hydrophilic phosphate "head" and a hydrophobic fatty acid "tail".
What happens to phospholipid molecules when placed in water?
They reposition themselves so that their hydrophilic heads are as close to the water as possible, and their hydrophobic tails are as far from the water as possible.
Draw the structure of phospholipids when placed in water.
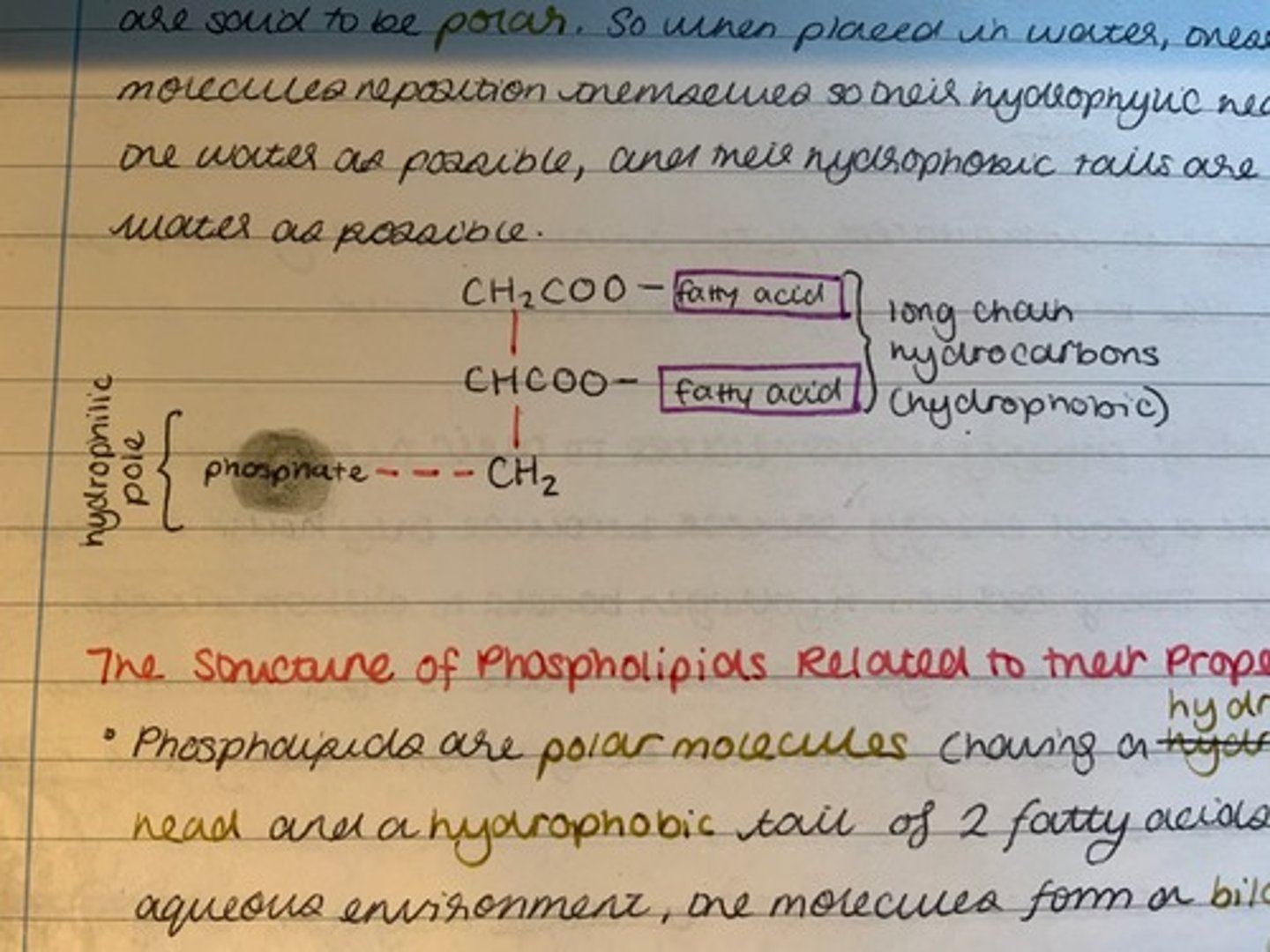
What happens to phospholipids in an aqueous environment?
The molecules, due to their polar properties, form a layer within cell surface membranes, causing a hydrophobic barrier to form between the inside and outside of a cell.
The hydrophilic 'heads' of these molecules help to hold at the surface of the cell surface membrane.
What does the structure of phospholipids help them with?
It helps them to form glycolipids by combining with carbohydrates within the cell surface membrane. These glycolipids are important in cell recognition.
Which elements are in proteins?
C, H and O, N Some also contain S and P.
How many naturally occurring amino acids are there?
about 20
What are proteins?
polymers of amino acids
What are amino acids?
monomers of proteins
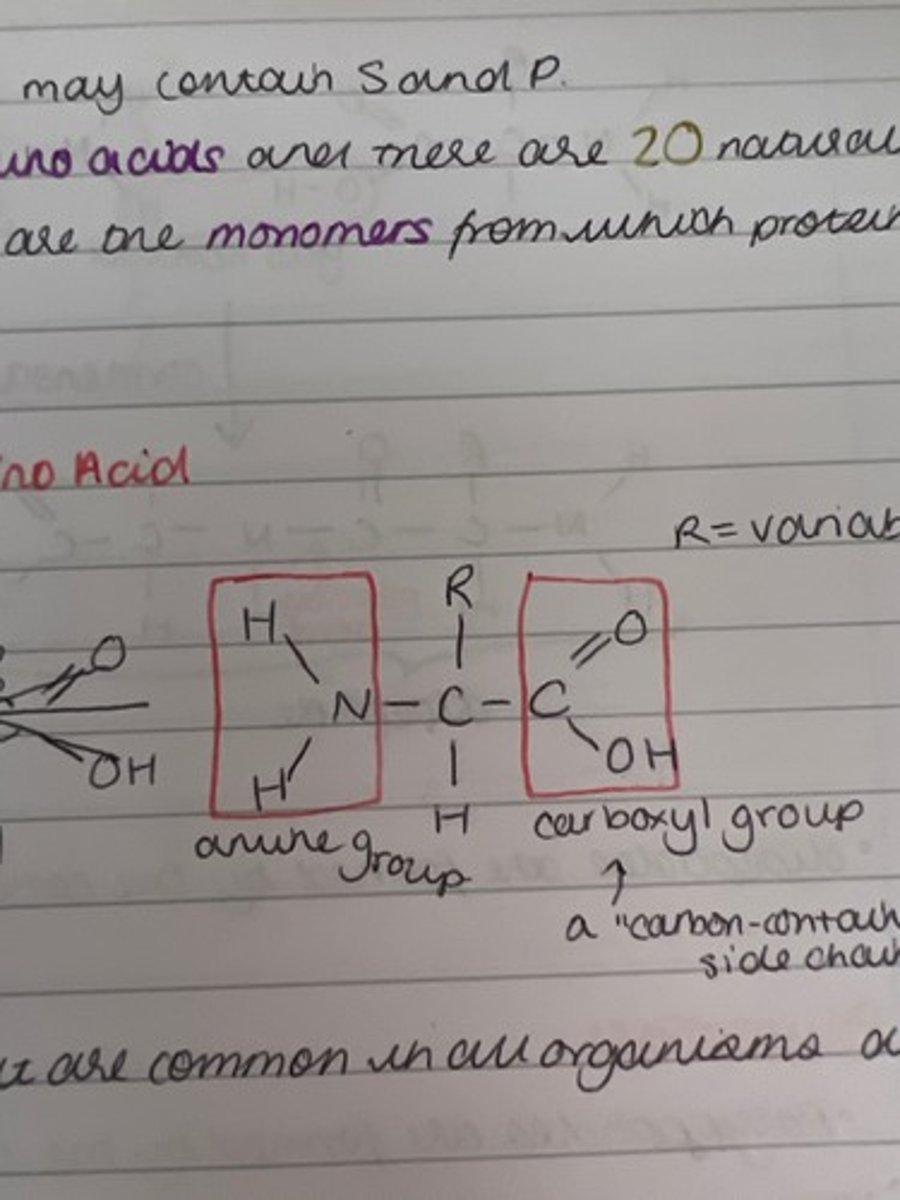
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
carboxyl and amine groups
What is a carboxyl group?
COOH
What is the amine functional group?
H2N
What is the general structure of amino acids?
What is the amino acid when R=H?
glycine
What is the amino acid when R=CH3 ?
alanine
What is the amino acid when R = CH2SH?
cysteine
What does amphoteric mean?
can act as an acid or a base.
amino acids are amphoteric
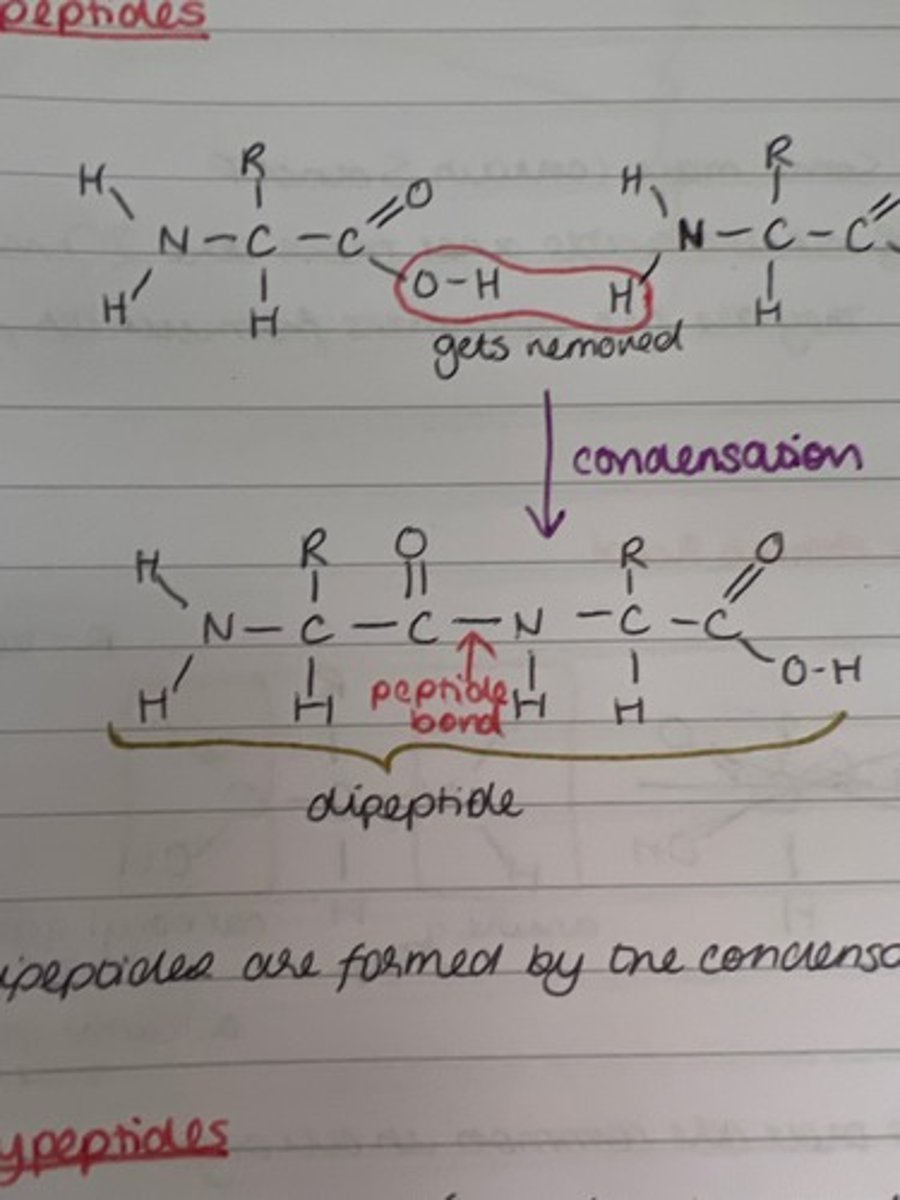
What are dipeptides?
2 amino acids joined together
What bond joins amino acids together?
peptide bonds
What reaction forms dipeptides?
condensation
Draw a dipeptide
What is the sequence of amino acids determined by?
sequence of bases in DNA
What are polypeptides?
Long strands of amino acids. As the chain grows, new amino acids are added onto the amino end. (NH2)
What is the primary structure of a protein?
sequence of amino acids
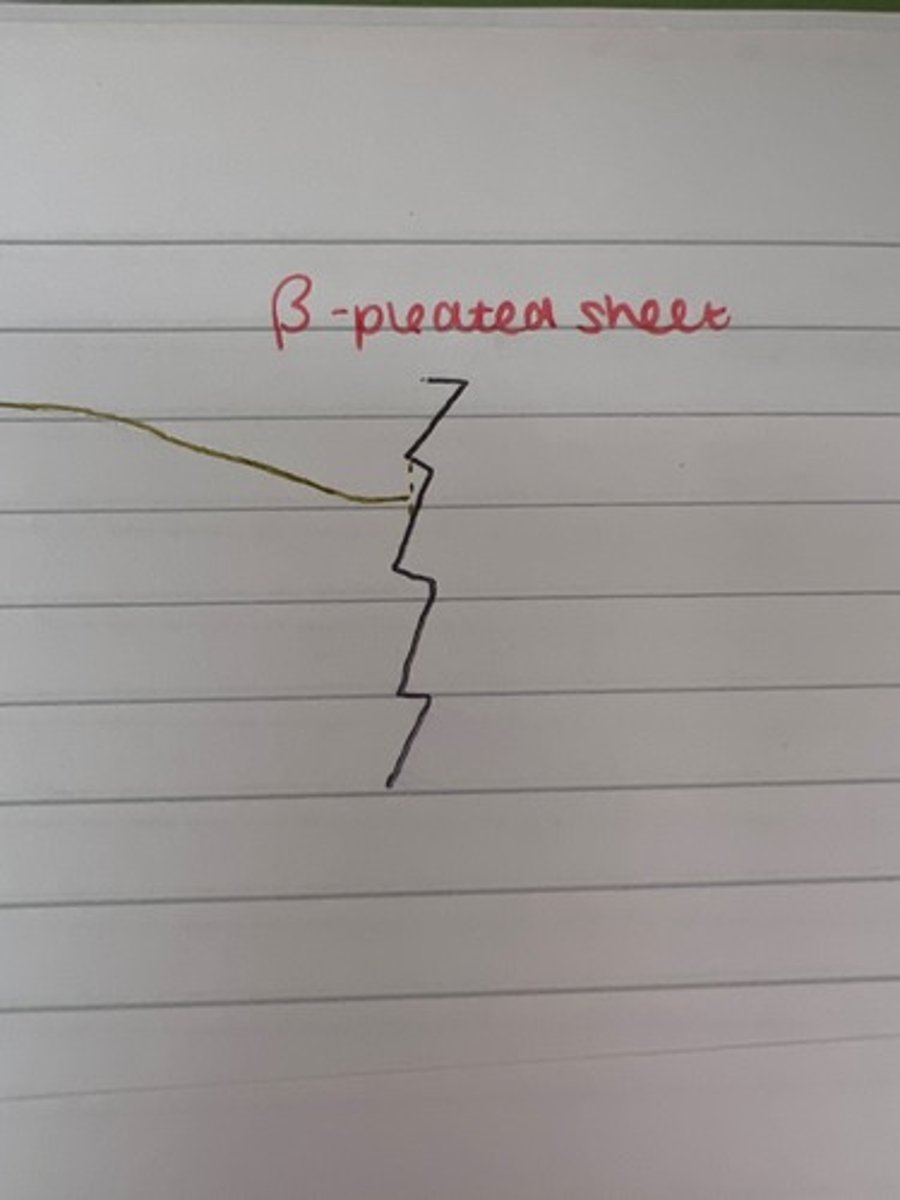
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
How the primary structure folds due to hydrogen bonding creating an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
Draw an alpha helix

Draw a beta pleated sheet

What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The way in which the alpha helix or beta pleated sheet is further cooled or folded due to the arrangement of the amino acids. It consists of one polypeptide chain.
What three bonds are found in the tertiary structure?
Hydrogen, Disulphide bridge, Ionic
What are the main two types of protein?
Globular and Fibrous
Describe globular proteins and their functions.
highly folded, water soluble, spherical
they carry out metabolic functions
Describe fibrous proteins and their functions
They are insoluble, and consist of long, parallel polypeptides with cross-linkages
They have structural functions
Give examples of fibrous proteins
keratin, elastin, collagen
Give examples of globular proteins
antibodies, enzymes, haemoglobin
Why is the quarternary structure? Give examples.
Composed of 2 or more polypeptide chains
insulin has 2 chains
haemoglobin has 4 chains
How do disulfide bridges form?
R group of cysteine contains sulfur, bridge forms between 2 such R groups when opposite each other in the tertiary structure.
draw a disulfide bond
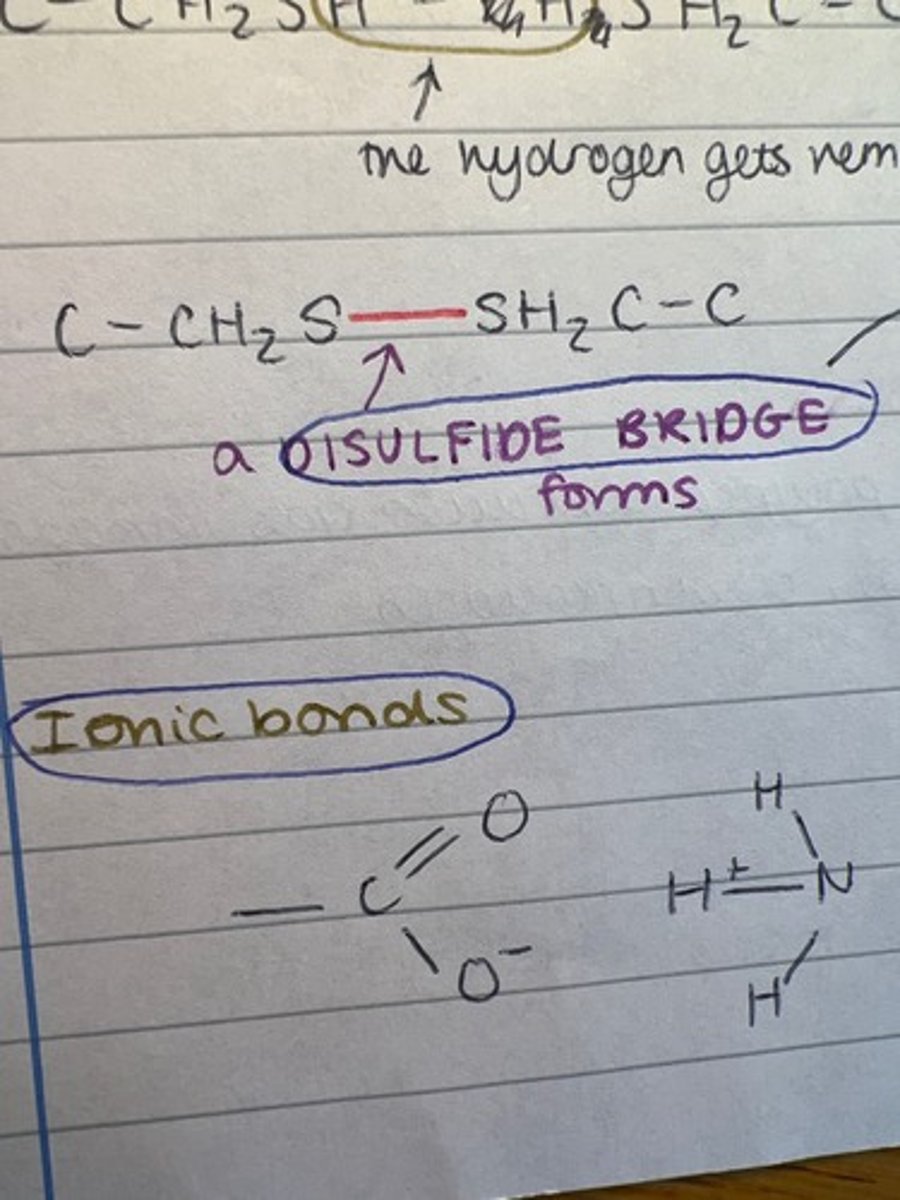
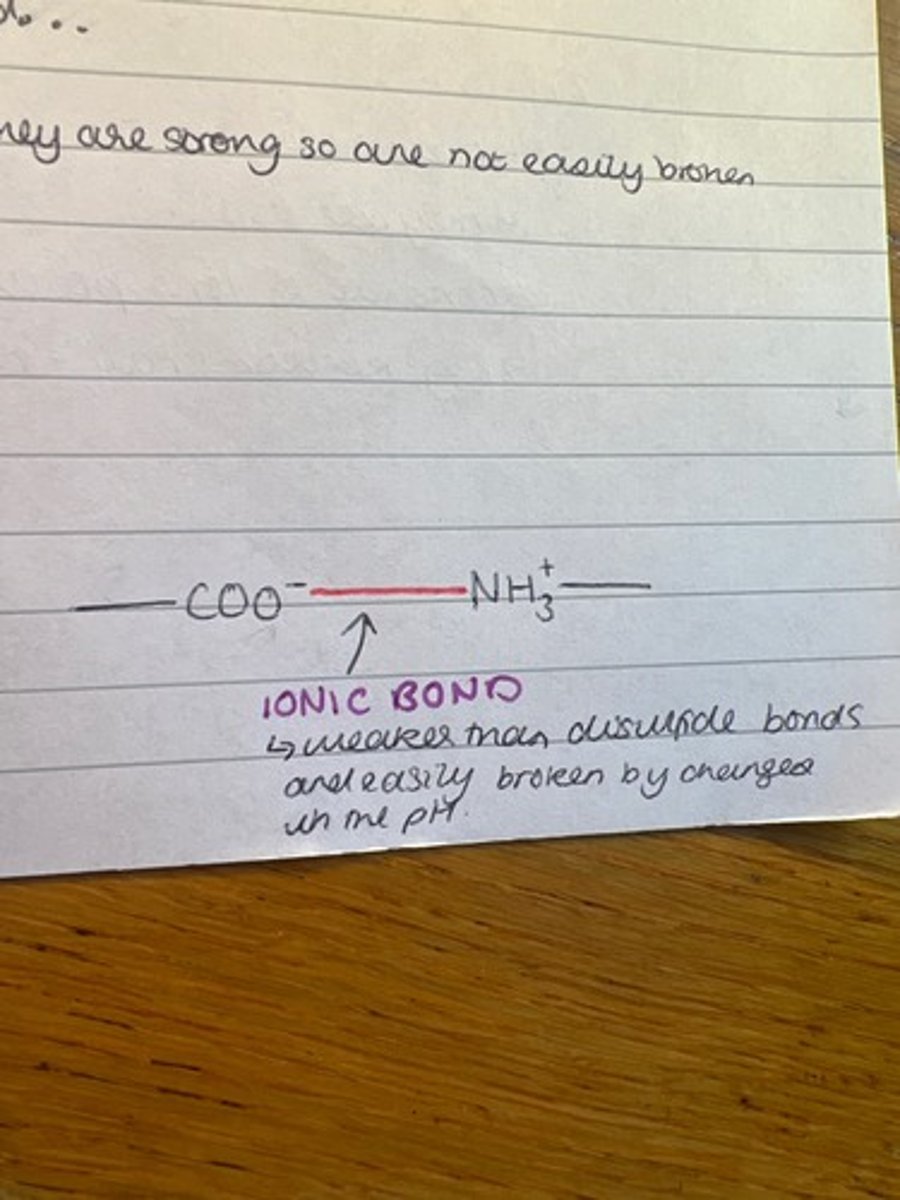
Draw an ionic bond (in tertiary structure)
Describe disulfide bonds
Fairly strong and therefore not easily broken. The strongest bond in the tertiary structure.
Describe ionic bonds (proteins)
Formed between any carboxyl and amino groups that are not involved in forming peptide bonds. Weaker than disulfide as they are easily broken by changes in the pH
Describe hydrogen bonds (proteins)
numerous and easily broken
How do oxygen atoms contribute to the formation of hydrogen bonds?
They are highly electron negative, so attract electrons.
What is chromatography?
An analytical method used to separate the substances in a mixture based on their solubility in a solvent.
Describe the method for chromatography of amino acids.
1) Draw a line of origin in pencil, 2cm from the bottom of the chromatography paper
2) using a fine capillary tube,place a small drop of amino acid on the line of origin and allow to dry. Repeat twice more so a concenerated spot is produced. Label each amino acid used in pencil.
3) Repeat for each amino acid.
4) Make the lantern paper into a cylinder and fix using paper clips
5) Into the fume cupboard, add a small volume of the organic solvent and lower the paper into a chromatography tank, ensuring it doesn't touch the line of origin.
Place lid on the chromatography tank, and allow the solvent to travel up the lantern paper.
6)Mark the solvent front in pencil and allow to dry by hanging in the fume cupboard
What can we use to stain the amino acids on a chromatogram?
Ninhydrin
Why do we need to stain the amino acids on a chromatogram?
Because they are colourless so we can't see them.