AP Psychology Unit 1: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Heredity
The passing of traits from parents to offspring.
Nature
The influence of genetics on behavior.
Nurture
The influence of the environment on behavior.
Genetic predisposition
A genetic tendency to develop certain traits or disorders.
Evolutionary perspective
A perspective focusing on how evolution shapes behavior.
Natural selection
The process by which traits that enhance survival are passed on.
Eugenics
The scientifically erroneous and immoral theory of “racial improvement” and “planned breeding,” which gained popularity during the early 20th century.
Twin studies
Studies comparing similarities between identical and fraternal twins.
Family studies
Studies comparing similarities among family members.
Adoption studies
Studies comparing adopted children to their biological and adoptive families.
Central nervous system
The part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral nervous system
The part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord.
Autonomic nervous system
The part of the peripheral nervous system controlling involuntary actions.
Sympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that activates fight-or-flight responses.
Parasympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body.
Somatic nervous system
The part of the peripheral nervous system controlling voluntary movements.
Neurons
Specialized cells transmitting electrical and chemical signals.
Glial cells
Supportive cells assisting neurons.
Reflex arc
The neural pathway consisting of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron that transmits signals quickly to produce an automatic response.
Sensory neurons
Neurons transmitting sensory information to the brain.
Motor neurons
Neurons transmitting signals from the brain to muscles.
Interneurons
Neurons communicating between sensory and motor neurons.
Neural transmission
The process of transmitting a neural signal.
Action potential
The brief electrical charge that travels down the axon of a neuron, triggering the release of neurotransmitters at the synapse.
All-or-nothing principle
The principle that a neuron fires fully or not at all.
Depolarization
The change in a neuron's charge that initiates an action potential.
Refractory period
The period when a neuron cannot fire after an action potential.
Resting potential
The stable, negative charge of an inactive neuron.
Reuptake
The reabsorption of neurotransmitters by a neuron.
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger an action potential.
Multiple sclerosis
A disease damaging the myelin sheath around neurons.
Myasthenia gravis
A disorder causing muscle weakness due to damaged nerve receptors.
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that increase the likelihood of a neuron firing.
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that decrease the likelihood of a neuron firing.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter involved in movement, motivation, and reward.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter regulating mood, appetite, and sleep.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in alertness and arousal.
Glutamate
The main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain.
GABA
The main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Endorphins
Neurotransmitters that reduce pain and enhance pleasure.
Substance p
A neurotransmitter involved in pain perception.
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter involved in muscle action and memory.
Hormones
Chemical messengers released by glands.
Adrenaline
A hormone that increases heart rate and energy.
Leptin
A hormone regulating appetite and energy balance.
Ghrelin
A hormone stimulating hunger.
Melatonin
A hormone regulating sleep-wake cycles.
Oxytocin
A hormone associated with bonding and social behavior.
Psychoactive drugs
Drugs affecting the brain and behavior.
Agonists
Substances that enhance the action of a neurotransmitter.
Antagonists
Substances that block the action of a neurotransmitter.
Reuptake inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit the reabsorption of neurotransmitters.
Stimulants
Drugs that increase central nervous system activity.
Caffeine
A stimulant found in coffee and tea.
Cocaine
A powerful stimulant derived from coca leaves.
Depressants
Drugs that decrease central nervous system activity.
Alcohol
A depressant commonly consumed in beverages.
Hallucinogens
Drugs causing hallucinations and altered perceptions.
Marijuana
A psychoactive drug derived from the cannabis plant.
Opioids
Drugs derived from opium that relieve pain.
Heroin
A potent opioid causing euphoria and addiction.
Tolerance
The need for increasing amounts of a substance to achieve the same effect.
Addiction
A compulsive craving for and use of a substance.
Withdrawal
Symptoms experienced when stopping a substance.
Brain stem
The lower part of the brain connecting to the spinal cord.
Medulla
The part of the brain controlling vital functions like breathing.
Reticular activating system
A network controlling arousal and attention.
Reward center
A brain region involved in processing rewards.
Cerebellum
The part of the brain involved in coordination and balance.
Cerebral cortex
The outer layer of the brain involved in complex functions.
Limbic system
A group of brain structures involved in emotion and memory.
Thalamus
The brain's relay station for sensory information.
Hypothalamus
A brain region regulating homeostasis and basic drives.
Pituitary gland
A gland controlling growth and other endocrine glands.
Hippocampus
A brain structure involved in forming new memories.
Amygdala
A brain region involved in processing emotions.
Corpus callosum
A bundle of fibers connecting the brain's two hemispheres.
Occipital lobes
The lobes at the back of the brain involved in vision.
Temporal lobes
The lobes on the sides of the brain involved in hearing and memory.
Parietal lobes
The lobes at the top of the brain involved in sensory processing.
Association areas
Regions of the brain involved in integrating information.
Somatosensory cortex
A brain area processing touch and body position.
Frontal lobes
The lobes at the front of the brain involved in decision-making and movement.
Linguistic processing
The process of understanding and producing language.
Higher-order thinking
Complex mental activities such as thinking, reasoning, and planning.
Executive functioning
Processes involved in managing and regulating behavior.
Prefrontal cortex
The front part of the frontal lobes involved in planning and decision-making.
Motor cortex
A brain region controlling voluntary movements.
Split brain research
Research on the functions of the brain's hemispheres.
Hemispheric specialization
The specialization of the brain's hemispheres for different functions.
Broca's area
A brain area involved in speech production.
Wernicke's area
A brain area involved in language comprehension.
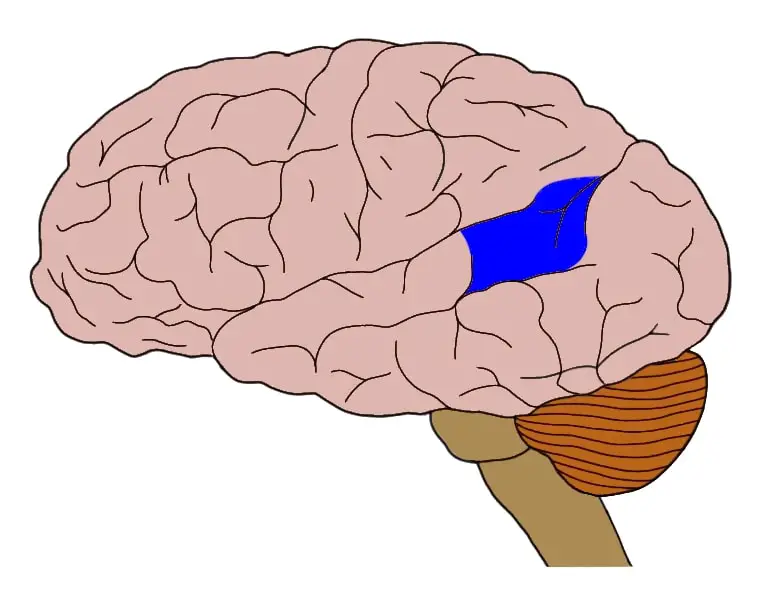
Aphasia (Broca's and Wernicke's)
Language disorders due to damage in specific brain areas.
Contralateral hemispheric organization
The organization where each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body.
Plasticity
The brain's ability to change and adapt.
EEG
A technique for recording electrical activity in the brain.
fMRI
A brain imaging technique showing brain activity.
Lesioning
The removal or destruction of brain tissue.
Consciousness
The state of being awake and aware.
Circadian rhythm (sleep/wake cycle)
The body's natural 24-hour cycle.