Chemistry: Units 3-4
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Periods
The rows across the periodic table
There are ____ periods.
7
Periods have the increase in ______ heading right.
protons
Groups
The columns up and down the periodic table
There are ______ groups.
18
Groups have all the same what?
Amount of valence electrons
Metals have a ____ charge.
+
Non-metals have a _____ charge.
-
10 Periodic Families
Alkali metals
Alkali earth
Transition
Post-transition
Halogens
Noble gases
Metalloids
Lanthanides
Actinides
Reactive non-metals
It takes ______ of years for a star to expand before _______.
millions, exploding
Different colors of stars means what?
The star changes its size and resources it has (they implode when they stop burning)
Mostly metals on periodic table = mostly ________ = most of _______.
solids, table
The phases of elements are based upon “_____ _______.”
room temperature
Room temperature
25 C, 77 F
The formation of Earth was due to ______.
stars
Stars
Balls of hydrogen that under pressure and high temperature they collide with each other forming helium and elements up to iron
Nuclear Fusion
When stars collide with each other and form helium and elements up to iron when under pressure and high temperature
Supernovae
A giant explosion of the stars when they die and what elements past iron were formed through
Alkali metals
They have 1 valence electron = highly reactive (explosive)
Alkali earth
These are the 2nd most reactive metals because they have 2 valence electrons (aren't as explosive, but still highly reactive)
Reactive Non-Metals
Make negative charges and have very low melting points except for carbon
Transition metals
Mostly used to build tools, structures, and items
Post-transition
Charges of +3 with the others further to the right having +2 or +4 charges
They are after and have larger melting points than transition metals
So soft, used in high tech items (aluminum foil)
Metalloids
These can act as nonmetals or metals (makes them unique)
Can form both anions and cations
Lanthanides
Shiny white metals with varying properties
Actinides
Extremely radioactive metals
Very short-lived and unstable
Halogens
The most reactive nonmetals because they have 7 valence electrons
Common react with the alkali and alkaline earth metals
Noble gases
Doesn’t react with other elements because they have perfect octet of valence electrons (nonreactive)
Symbol
A combination of letters to tell us what element we are talking about
Subscripts
The numbers of the bottom right of the symbols that tell us how much what element makes up a compound
Coefficients
Tell us how many compounds of elements there are
2C>6H>12O>6 symbols?
C, H, O
2C>6H>12O>6 subscript?
6, 12, 6
2C>6H>12O>6 coefficient?
2
Bonding
When there is an attraction between two molecules that makes them connect or stay together
Ioic bonds
When atoms connect to each other due to differences in charge
NaCl
Since Cl-1, NaCl gets +1 from Na
Polyatomic ions
When sometimes things bond to each other but still carry a charge. These are found in Table G.
Process for naming ionic compounds for regular ionic bonds
Name the Cation (positive atom) as it I called on the periodic table
Name the anion (negative atom) as it is called on the periodic table with the end of -ide
Process for naming ionic compounds for polyatomic bonds
Use the the same naming conventions as regular ionic bonds, but just use the polyatomic ion’s name
Chemical equation
A mathematical way to show when things are built up or broken down in chemistry
Reactants
Things that go into the chemical equation
Products
Things that go at the end of a chemical equation
Law of conservation of mass
Matter is not created or destroyed it is just converted into different atoms
Balancing equations
The process of matter sure there’s an equal amount on both sides by adjusting coefficients
Potassium Oxide reacts with Copper (I) Chloride to yield Potassium Chloride and Copper (I) Oxide
K>2O + 2CuCl —> 2KCl + Cu>2O
Synthesis reaction
A reaction when two simple elements combine to build a compound
Decomposition reaction
A reaction when a singular compound is broken into its basic elements
Single replacement reaction
One where a compound and an element swap spots with similar ions
Double replacement reaction
Always 2 compounds combine together and swap ions from each compound
Top 5 common elements for percent abundance
Hydrogen
Helium
Oxygen
Carbon
Neon
Hydrogen percent abundance
74%
Helium percent abundance
24%
Oxygen percent abundance
1% (ab)
Neon percent abundance
0.13% (ab)
The drop off for percent abundance is ______.
steep
Large elements are not common because why?
They are unstable due to too many protons close together that repel each other
Nuclear Decay
When an element is too large and unstable and it breaks into smaller more stable elements (too many protons)
Atomic radius
The radius of an atom or width from center to edge
Atomic radius based on what 2 things?
The amount of protons and electrons
The effective nuclear charge
Effective nuclear charge
The amount of positive pull from the protons in the nucleus of an atom
Is Na+ able to pull electrons well?
No (+1 valence electrons and doesn’t have high effective nuclear charge)
Ionization energy
The energy required to remove an electron
What does ionization energy depend on?
How close the atom is to the octet
How high the effective nuclear charge is
Electronegativity
The tendency for an atom to hold onto electrons more strongly than other atoms
Protons and electrons work like ______ that hold onto each other.
magnets
Higher _____ _____ ______ means more pull.
effective nuclear charge
Effective nuclear charge =
number of valence electrons
Na +1 is how strong the _____ is (valence _______).
pull, electrons
For atoms, it’s ______ energy to keep electrons, and less energy to give them _______.
more, away
Atoms want to be at _____ so if they are close to ____, they are willing to part with their electrons and become positive.
8,0
Other atoms may be close to _____ and not want to give up their _____, so it takes more _____ to steal them.
8, electrons, energy
High ionization energy = high _______.
electronegativty
K has 1 valence electrons and has an effective nuclear charge of ______.
+1
Electronegativity has the same trend as ionization energy why?
Because if an atom is more electronegative, it grabs electrons more and doesn’t want to lose them (ionization)
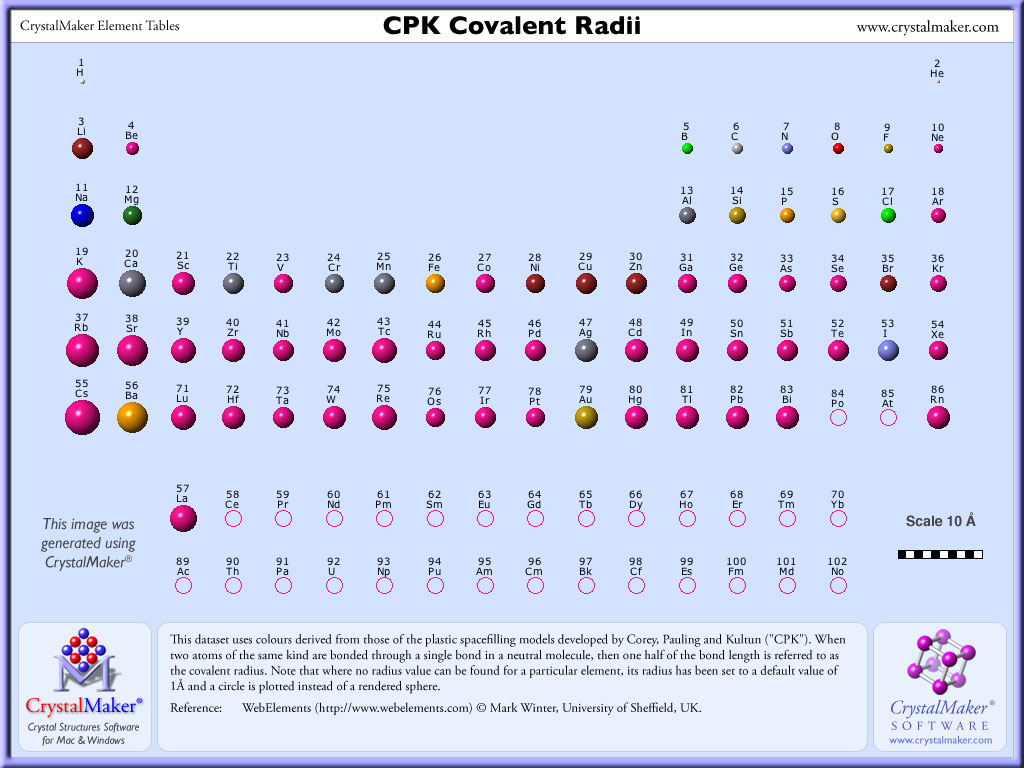
What’s the rule with radii?
The more up and right, the smaller the radius, and the more left and down, the smaller the radius (decreases as you go up and right)
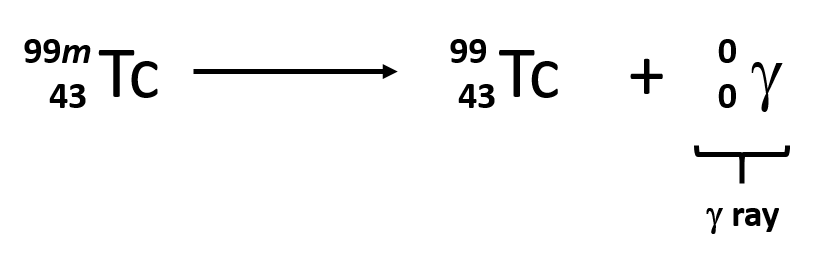
Gamma decay
Same but add energy symbol
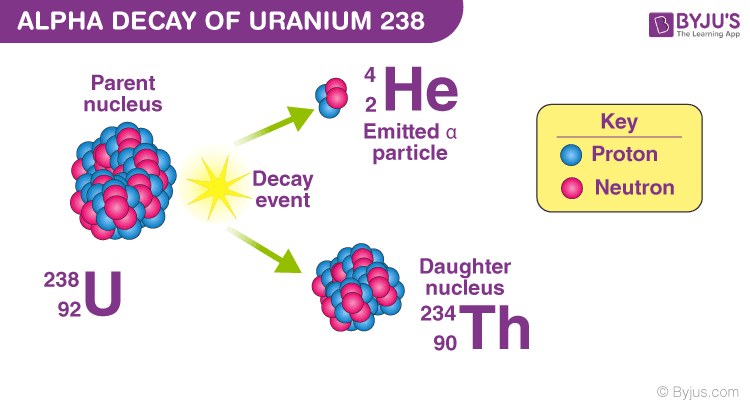
Alpha decay
-4/2 (He)
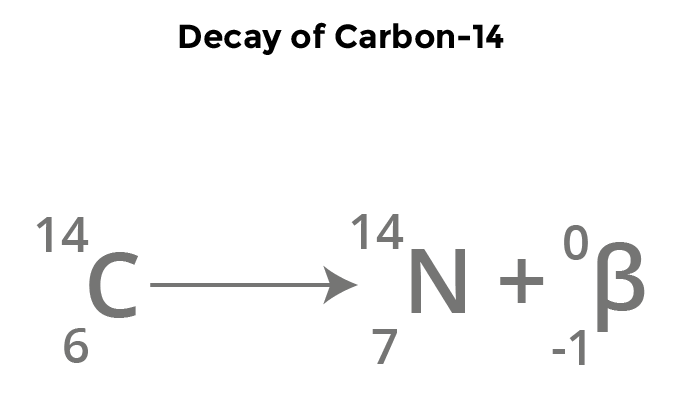
Beta decay
0/+1
Metals are known for their
Conductivity
Malleability
Ductility (plastic deformation)
Lustrous
React with Copper (II) Chloride
Non-metals are best know fortheir
Non-conductivity
Not lustrous
Brittle
Do not react with Copper (II) Chloride
Metalloids are a combination of both sets of properties
Bonding
The attraction between two or more elements
Balancing
Stating how many elements or compounds are needed to complete a chemical reaction