Unit 3 AP Bio Test, Ap bio college board unit 3
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
What does the chemiosmotic process in chloroplasts involve?
A) establishment of a proton gradient
In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate
B) 2 molecules of ATP are used and 4 molecules of ATP are produced.
In chemiosmotic phosphorylation, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + Pi to ATP?
D) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase
Which statement describes the functioning of photosystem II?
D) The electron vacancies in P680 are filled by electrons derived from water.
The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to
B) act as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water.
During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level?
E) FADH2
Which of the following is likely to lead to an increase in the concentration of ATP in a cell?
B) an increase in a cell's catabolic activity
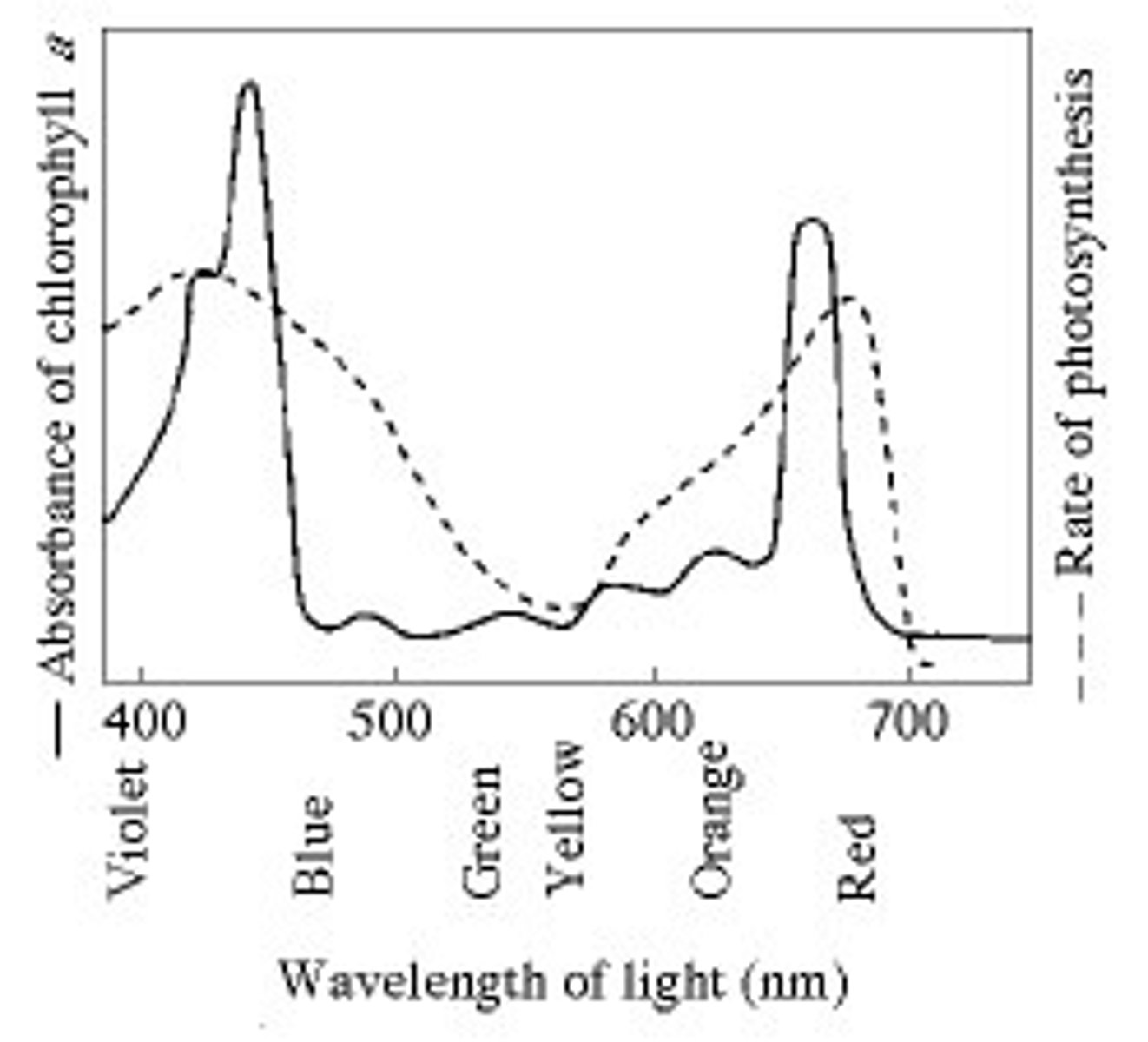
What wavelength of light in the figure is most effective in driving photosynthesis?
A) 420 mm
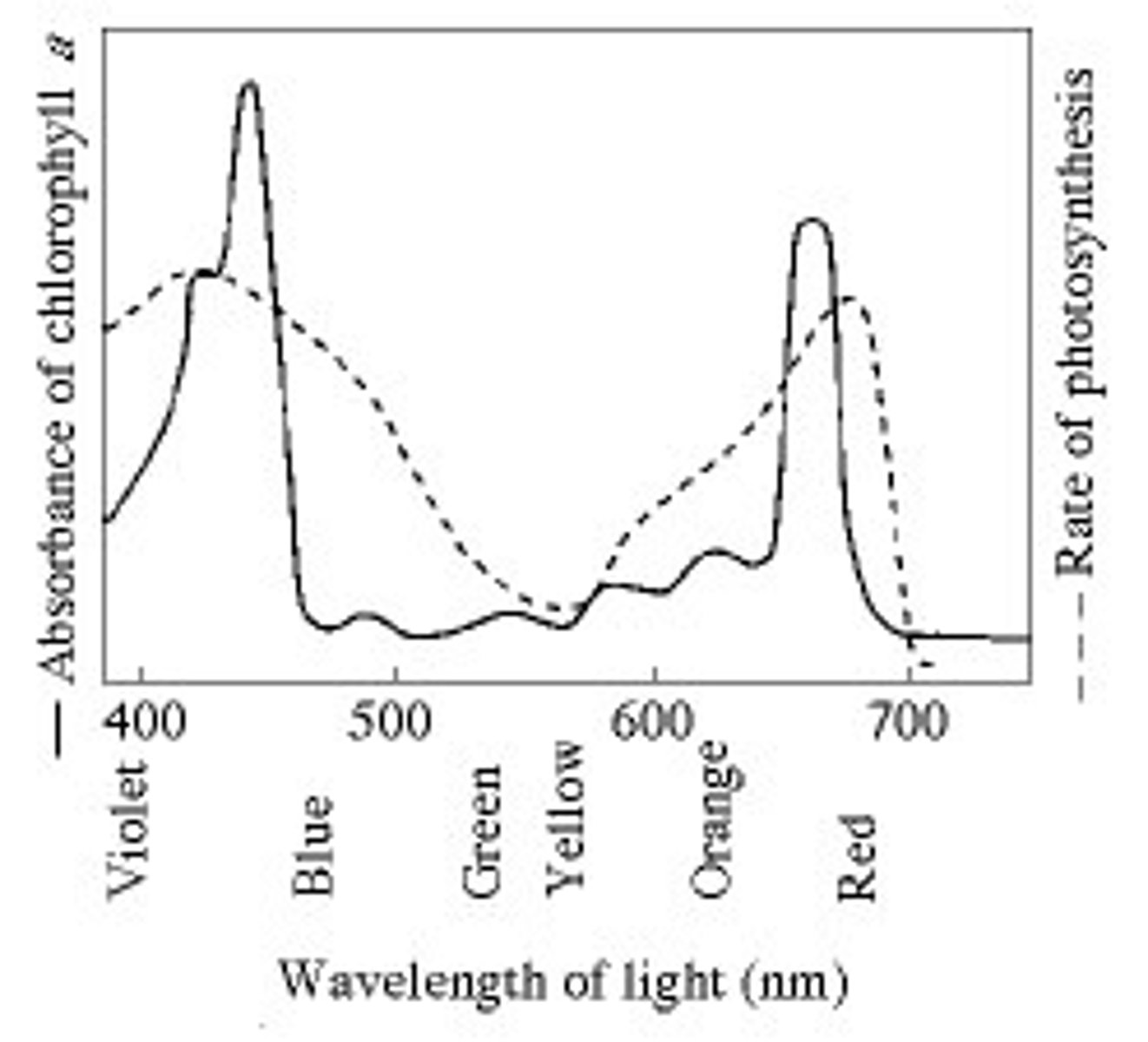
Figure 10.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for
photosynthesis. Why are they different?
D) Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a.
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
B) accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes located?
D) A and C....thylakoid membrane & plasma membrane
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
A) stroma of the chloroplast
Photorespiration lowers the efficiency of photosynthesis by preventing the formation of
B) 3-phosphoglycerate molecules
Which metabolic pathway is common to both cellular respiration and fermentation?
D) glycolysis
Why are C4 plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
B) They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2 .
What are the products of linear photophosphorylation?
C) ATP and NADPH
The ATP made during glycolysis is generated by
A) substrate-level phosphorylation.
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction
B) loses electrons and loses energy.
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
D) a food molecule made up of energy-rich macromolecules
When a molecule of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a hydrogen ion) the molecule becomes
C) reduced.
What is proton-motive force?
B) the transmembrane proton concentration gradient
CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they
fix CO2 into organic acids during the night.
A molecule that is phosphorylated
has an increased chemical reactivity; it is primed to do cellular work
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent?
glycolysis
In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of
ATP, CO2 , and ethanol (ethyl alcohol).
The ATP made during fermentation is generated by which of the following?
substrate-level phosphorylation
As a research scientist, you measure the amount of ATP and NADPH consumed by the Calvin cycle in 1
hour. You find 30,000 molecules of ATP consumed, but only 20,000 molecules of NADPH. Where did
the extra ATP molecules come from?
cyclic electron flow
Where are the molecules of the electron transport chain found in plant cells?
thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Generation of proton gradients across membranes occurs during
both photosynthesis and respiration.
Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
H2O → NADPH → Calvin cycle
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and
respiration?
Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules, while respiration
releases it.
How many carbon atoms are fed into the citric acid cycle as a result of the oxidation of one molecule of
pyruvate?
2
. Synthesis of ATP by the chemiosmotic mechanism occurs during
both photosynthesis and respiration.
Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follow which pathway?
citric acid cycle → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
Reduction of NADP+
occurs during
photosynthesis.
Which of the following normally occurs whether or not oxygen (O2 ) is present?
glycolysis
Which of the following statements describes NAD+
NAD+
is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
When hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the
intermembrane space, the result is the
creation of a proton gradient.
Cellular respiration harvests the most chemical energy from which of the following?
chemiosmotic phosphorylation
In the process of carbon fixation, RuBP attaches a CO2 to produce a 6 carbon molecule, which is then
regeneration of rubisco
In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules?
harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-center chlorophyll
During cellular respiration, acetyl CoA accumulates in which location?
mitochondrial matrix
Approximately how many molecules of ATP are produced from the complete oxidation of two molecules
of glucose (C6H12O6 ) in cellular respiration?
76
P680+
is said to be the strongest biological oxidizing agent. Why?
This molecule results from the transfer of an electron to the primary electron
acceptor of photosystem II and strongly attracts another electron
What is the primary function of the Calvin cycle?
synthesize simple sugars from carbon dioxide
When oxygen is released as a result of photosynthesis, it is a by-product of which of the following?
splitting the water molecules
Assume a thylakoid is somehow punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated
from the stroma. This damage will have the most direct effect on which of the following processes?
the synthesis of ATP
How many reduced dinucleotides would be produced with four turns of the citric acid cycle?
4 FADH2 and 12 NADH
Which of the following intermediary metabolites enters the citric acid cycle and is formed, in part, by the
removal of a carbon (CO2 ) from one molecule of pyruvate?
acetyl CoA
In mitochondria, chemiosmosis translocates protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space,
whereas in chloroplasts, chemiosmosis translocates protons from
the stroma to the thylakoid space
Which of the events listed below occur in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
light is absorbed and funneled to reaction-center chlorophyll a.
Where does glycolysis takes place?
cytosol
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller
ones?
catabolism
The splitting of carbon dioxide to form oxygen gas and carbon compounds occurs during
neither photosynthesis nor respiration
In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis?
NADH and pyruvate
The sugar that results from three "turns" of the Calvin cycle is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
Which of the following is a consequence of this?
The formation of starch in plants involves assembling many G3P molecules, with
or without further rearrangements.
Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located?
mitochondrial inner membrane
Which of the following are directly associated with photosystem I?
receiving electrons from plastocyanin
Which of the following statements best represents the relationships between the light reactions and the
Calvin cycle?
The light reactions provide ATP and NADPH to the Calvin cycle, and the cycle
returns ADP, Pi
, and NADP+
to the light reactions
During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence?
food → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ ions into which location?
mitochondrial intermembrane space
Each time a molecule of glucose (C6H12O6 ) is completely oxidized via aerobic respiration, how many
oxygen molecules (O2 ) are required?
6
Which of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin
cycle?
ATP and NADPH
Which of the following statements about mitochondrial chemiosmosis is NOT true?
Heat energy is required to establish the electron transport chain.
Process in which O2 is released as a by-product of oxidation-reduction reactions
Light dependent reactions of photosynthesis
Process found in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
chemiosmosis
Process in which CO2, is released as a by-product of oxidation-reduction reactions
Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
Process in which carbon from CO2 is incorporated into organic molecules
Calvin Cycle
Process in which sugar is oxidized to pyruvic acid
glycolysis
Which of the following is an important difference between light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH; the light-independent reactions use energy stored in ATP and NADPH.
6CO2 + 12H2O + light energy →
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
If the input water is labeled with a radioactive isotope of oxygen, 18O, then the oxygen gas released as the reaction proceeds is also labeled with 18O. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
During the light reactions of photosynthesis, water is split, removing electrons and protons, and oxygen gas is released.
If the input water is labeled with a radioactive isotope of oxygen, 18O, then the oxygen gas released as the reaction proceeds is also labeled with 18O. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
During the light reactions of photosynthesis, water is split, removing electrons and protons, and oxygen gas is released.
During respiration, most ATP is formed as a direct result of the net movement of
protons down a concentration gradient
A researcher claims that increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels cause increased growth rates in plants.
Which of the following statements best supports the researcher's claim?
Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis, which plants rely on for producing sugars and other organic compounds.
What most likely causes the trends in oxygen concentration shown in the graph above? (Oxygen concentration in the water of the lake graph)
Photosynthesis produces more oxygen than is consumed by respiration during the day
To test the hypothesis that a particular plant synthesizes storage lipids by using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) from photosynthesis, a researcher plans to use radiolabeled precursors to track the molecules through the biosynthetic pathway. Which of the following radiolabeled precursors is most appropriate for the researcher to use?
14C-labeled CO2, because atmospheric carbon is fixed to carbohydrates by photosynthesis
In an experiment, a scientist isolates mitochondria from living cells and suspends them in two different buffered solutions. One solution is maintained at pH 4, while the other solution is maintained at pH 9. The scientist finds that mitochondria in the solution at pH 4 continue to produce ATP but those in the pH 9 solution do not.
The results of the experiment can be used as evidence in support of which of the following scientific claims about mitochondrial activity?
ATP production in mitochondria requires a hydrogen ion gradient that favors movement of protons into the mitochondrial matrix.
Additional observations were made on day 21, and no yellow-leaved seedlings were found alive in either dish. This is most likely because
yellow-leaved seedlings were unable to convert light energy to chemical energy.
According to the results of this experiment, germination of tobacco seeds during the first week is
increased by exposure to light
According to the data, the mice at 10oC demonstrated greater oxygen consumption per gram of tissue than did the mice at 25oC. This is most likely explained by which of the following statements?
the mice at 10oC had a higher rate of ATP production than the mice at 25oC
During aerobic cellular respiration, oxygen gas is consumed at the same rate as carbon dioxide gas is produced. In order to provide accurate volumetric measurements of oxygen gas consumption, the experimental setup should include which of the following?
A substance that removes carbon dioxide gas
Coenzyme that transfers electrons from the Krebs cycle to the mitochondrial electron-transport chain at a lower energy level than that of electrons entering at the beginning of the chain
FADH2
An intermediate electron acceptor for oxidations that occur in both glycolysis and in Krebs cycle reactions
NAD+
The O2 released during photosynthesis comes from
H2O
The figures can best assist in answering which of the following questions?
Do electron transport chains create a gradient so that ATP synthase can generate ATP molecules?
A scientist claims that Elysia chlorotica, a species of sea slug, is capable of photosynthesis.
Which of the following observations provides the best evidence to support the claim?
Elysia chlorotica grows when exposed to light in the absence of other food sources.
In chloroplasts, ATP is synthesized from ADP plus inorganic phosphate (Pi) in a reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase molecules that are embedded in the thylakoid membrane.
Which of the following statements provides evidence to support the claim that no ATP will be synthesized in the absence of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane?
No ATP is synthesized when channel proteins that allow the free passage of protons are inserted into the thylakoid membrane.
Which of the following is most likely to result if oxygen is added to the tissue culture?
For each glucose molecule consumed, more ATP will be formed.
Which of the following would most adversely affect the validity of this experiment?
Large variation in metabolic rates between individuals of a species
Which of the following hypotheses is best supported by the results of this experiment?
metabolic rate per gram of tissue is higher in smaller mammals.
Which metabolic process is common to both aerobic cellular respiration and alcoholic fermentation?
glycolysis
Within the cell, many chemical reactions that, by themselves, require energy input (have a positive free-energy change) can occur because the reactions
may be coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP
Which of the following best describes the function
of the coenzymes NAD+ and FAD in eukaryotic
cellular respiration?
They accept electrons during oxidation-reduction
reactions.
The energy required to run the Calvin cycle reactions of photosynthesis comes from which two substances produced during the light-dependent reactions?
ATP and NADPH
The reactions of glycolysis occur in the
cytosol
The figure above shows an organelle typically found in eukaryotic cells. Which of the following best describes the function of the double membrane system of this organelle?
The inner membrane has specialized proteins that create a hydrogen ion concentration gradient between the intermembrane space and the matrix
Carbohydrate-synthesizing reactions of photosynthesis directly require
products of light reactions
Which of the following questions will best direct an investigation of the mechanism of ATP synthase?
Is the phosphorylation of ADP by ATP synthase dependent on the formation of a proton gradient?
ATP serves as a common energy source for organisms because
its energy can be easily transferred to do cellular work
The carbon 'that makes up organic molecules in plants is derived directly from
carbon fixed in photosynthesis