Lecture 3 - Time Value of Money: Valuing Shares (using Dividends)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Three forms of organisation
Sole trader
Partnership
Company/corporation
Characteristics of the Corporation (3 important ways the Corporation differs from other forms of business organisation (e.g., sole traders, partnerships))
Ownership is usually widely dispersed.
Shareholders have no right to be involved in the daily running of the corporation.
Shareholders have limited or no liability for the liabilities incurred by the corporation.
Separation of Ownership and Control
The concept where individuals that own shares of a company are not involved in the daily running of the corporation.
What liabilities do shareholders have for debts incurred by the corporation?
Shareholders will either have no liability or limited liability for the liabilities incurred by the corporation.
Rights of Shareholders
The right to vote on how the corporation will be controlled.
A claim to a fraction of the cash flows remaining in the corporation after all other claims have been deducted (i.e., in the form of dividends).
Sell their stocks when they so choose.
What are the Two Main Types of Shares
Ordinary shares (“common” shares)
Preference shares
Ordinary shares (“common” shares)
An equity security issued by a corporation that gives its holder the right to vote and the right to any (variable) dividend declared by the board of directors. However, ordinary shareholders rank last in the event of liquidation.
Preference shares
An equity security issued by a corporation that is given priority over ordinary shares for (fixed) dividends and in the event of liquidation. However, these shares generally have no voting rights attached to them.
What are the 2 types of gains shareholders receive from owning shares?
Dividends
Capital Gains
Theoretical Value of Share
Value = Present Value of Future Cash Flows
3-step approach to asset valuation
Identify all the cash flows generated by the asset as well as when they occur.
Find the present value of each cash flow that was identified in Step 1.
Sum the present values of all cash flows calculated in Step 2.
2 simplifying assumptions when calculating the theoretical value
The stock (and therefore the company it gives ownership in) has infinite life.
Every market participant is in agreement about the dividend payments that are to be made by the company in the future.
Present Value of Dividends Formula
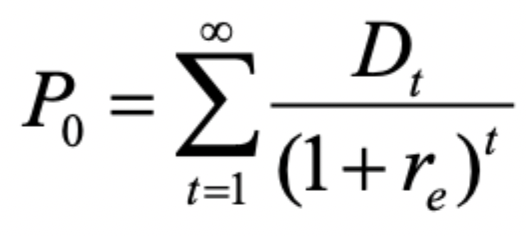
Constant Dividends
Future dividends are constant, meaning Dt = D for all values of t.
Constant Dividends Formula
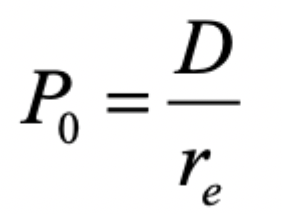
Dividends with Constant Growth
Dividends paid to shareholders will grow indefinitely at a constant rate of g% per period.
Dividends with Constant Growth Formula
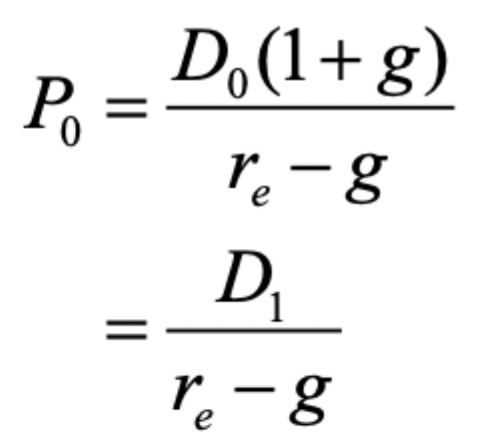
Code
The unique ASX identifier code (e.g., the ASX code for A2 Milk is A2M).
Company
The Company’s full name.
Price
The last sale price for the stock (on the most recent trading day).
Change (level and percentage)
The move in the last sale price from the second most recent trading day’s close to the most recent trading day’s close, in dollars and in % (green shows increases, red shows decreases).
52 Week High and Low
The highest and lowest traded price for the stock during the last year and give some indication of the variability of the stock.