Skin and nervous system exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:43 PM on 4/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
1
New cards
4 functions of skin
Sensory Organ, Protection, Regulates Body Temp, Vitamin D absorption
2
New cards
How is skin a sensory organ?
neuroreceptors (e.g. pain, touch)
3
New cards
How does skin provide protection?
barrier (water proof, blocks microbes
4
New cards
How does skin regulate body temp?
body heat to surface (radiation, sweating)
5
New cards
What is skin’s role with Vitamin D
it absorbs (UVB) essential for bones and immune system
6
New cards
What are the 3 layers of the skin?
Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis
7
New cards
Epidermis
Outermost layer of skin
8
New cards
What kind of cells is the epidermis made of?
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
9
New cards
What are Keratinocytes?
They produce keratin
10
New cards
What is keratin?
the fibrous protein that makes the epidermis a tough protective layer
11
New cards
Langerhans cells
Langerhans cells are members of the *dendritic cell* family. Their main role is to alert other components of the adaptive immune system to the presence of pathogens and other infectious agents on the skin.
12
New cards
What are cornified epidermis cells?
the upper layer composed of mostly dead, differentiated cells (stratum corneum) with a lot of keratin which helps the skin maintain some protection against water loss and bacteria. Prevents skin from sloughing off
13
New cards
Melanocytes
Melanin pigment (dark brown-black), protects DNA. Freckles, Albinism, Vitiligo
14
New cards
Nails
strengthen & protect finger tips when grasping, used for scratching
15
New cards
Mucous Epithelium
same as skin but w/o cornified layer, hair, sweat glands. Moisture and mucus prevent desiccation.
16
New cards
where are Mucous Epithelium cells found
Conjunctiva, Vagina, Mouth-Pharynx-Oesophagus
17
New cards
Dermis
Middle layer of skin
18
New cards
The dermis layer contains _____________
Sweat Glands, Hair follicles, Neuroreceptors, Capillary beds (heat control)
19
New cards
dermal papillae
Found in the upper layers of the dermis, they create your fingerprint pattern for grip
20
New cards
What is the purpose of hair?
protects bony ridges, sense of touch
21
New cards
Arrector Pili
a smooth muscle attached to hair follicles that causes "goose bumps" to appear on the skin when contracted
22
New cards
What do sweat glands do?
They secrete sweat, located in the dermal layer of the skin. This helps regulate body temperature
23
New cards
Eccrine glands
glands that produce sweat; found over most of the body. whole body, #palms, soles, axilla (armpit)
24
New cards
Apocrine glands
produce sweat (puberty) axilla, pubic area, areola. Sexual (?)
25
New cards
Sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
26
New cards
Hypodermis
connecting the dermis layer of your skin to your muscles and bones, and contains fat to insulate your body and protect your body from harm
27
New cards
Symptoms of aging skin
skin thinner (feel cold), less elastic, drier/itching, wounds easily, skin cancers more common (probably due to sun burns or exposure to toxic agents earlier in life.)
28
New cards
FRICTION causes
calluses, corns
29
New cards
WOUNDS cause
scars, keloids
30
New cards
First Degree burn
Epidermis only. Inflammation only (redness and pain)
31
New cards
Second Degree burn
Dermis. Inflammation + blisters
32
New cards
Third Degree burn
Hypodermis and deeper. Skin charred, painless
33
New cards
WART
virus
34
New cards
MELANOMA
melanocyte cancer
35
New cards
ALOPECIA
hair loss
36
New cards
NEVUS
mole
37
New cards
URTICARIA
hives/ rashes
38
New cards
PRURITIS
itching
39
New cards
DECUBITUS ULCERS
bed sores
40
New cards
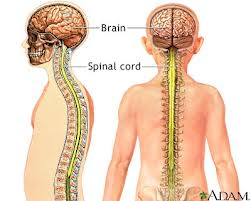
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and Spinal Cord
41
New cards
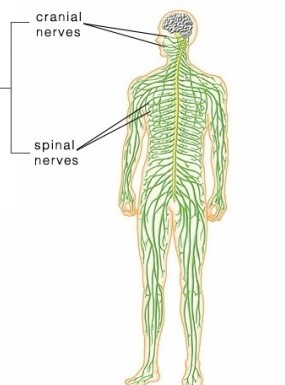
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Cranial and Spinal Nerves branching out from cns
42
New cards
Sensory Division
picks up stimuli, returns info to CNS through afferent nerves
43
New cards
Motor Division
sends directions from your brain to your muscles and glands
44
New cards
Somatic Nervous System (SMS):
part of PNS, controls skeletal muscles movement
45
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
part of PNS. to viscera, smooth Mm, glands, etc. keeps your heart beating, lungs breathing, and stomach churning
46
New cards
sympathetic system
part of ANS (of PNS). controls “fight-or-flight” responses. In other words, this system prepares the body for strenuous physical activity.
47
New cards
parasympathetic system
part of ANS (of PNS). a set of nerves that helps the body return to a normal resting state
48
New cards
Neuroglia \[CNS\]
cells that support and protect neurons
49
New cards
Astrocytes
connective tissue of CNS. form blood brain barrier by anchoring neurons to blood supply
50
New cards
What is the role of the blood brain barrier
shields the brain from toxic substances in the blood, supplies brain tissues with nutrients, and filters harmful compounds from the brain back to the bloodstream.
51
New cards
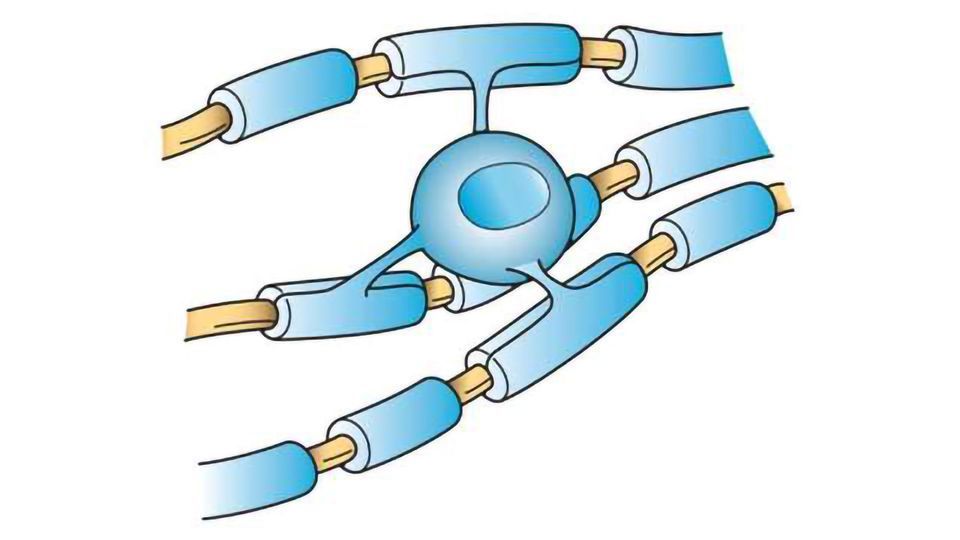
Oligodendrocytes
form myelin sheaths of axons in CNS. Insulates-protects-heals. can connect to Many Axons or places on Axon
52
New cards
Microglia
Act as phagocytes in CNS, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system
53
New cards
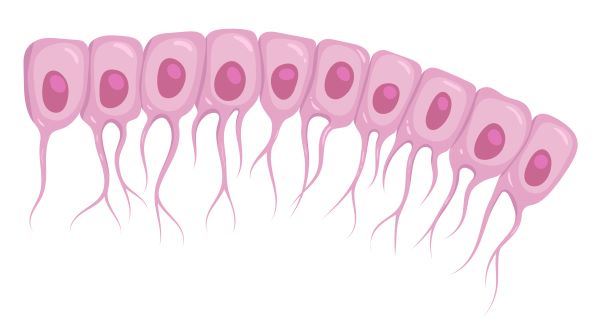
Ependyma
membrane lining the central canal of the spinal cord and the ventricles of the brain. Move Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) in chambers and passages inside CNS; ciliated
54
New cards
Gliomas
Brain tumors that grow rapidly and are highly malignant; blood-brain barrier decreases effectiveness of chemotherapy; treatment consists of radiation or surgery
55
New cards
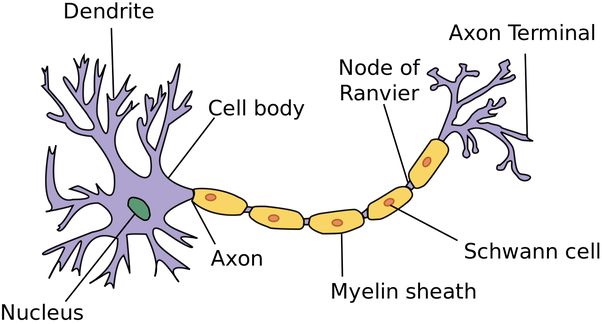
Neurons \[CNS & PNS\]
Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information.
56
New cards
Cell Body of neurons
Contains nucleus, unmyelinated, Nissl Bodies (Rough ER with colour)
57
New cards
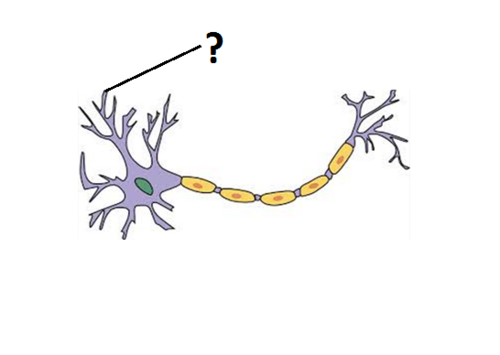
Dendrites
Fibre(s) attached to cell body of neurons, bring info to cell body
58
New cards
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
59
New cards
Axon Hillock
trigger zone of neuron; the conical projection that connects the cell body to the axon
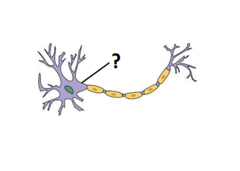
60
New cards
Neurofilaments
Fine thread-like structures that form a matrix in the cytoplasm; they provide support/strength for the cell membrane and maintain the shape of the neuron.
61
New cards
Collateral Branches
side branches of axons allow single neuron to communicate with several other cells
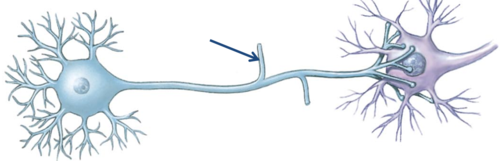
62
New cards
Axon Terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored, Synaptic Bulbs
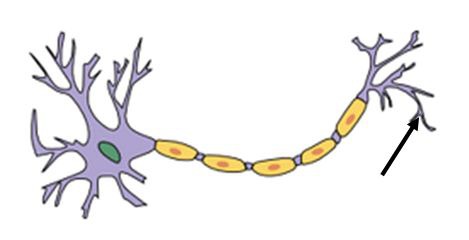
63
New cards
Synapse
Approximation of one axon with the cell body or dendrite of another neuron; gap. Neurotransmitters are released and cross thru fluid gap to receptors on target neuron
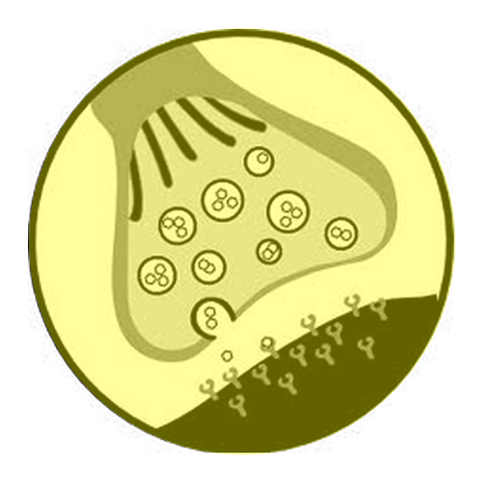
64
New cards
Neurogenesis
creation of new neurons in the adult brain. There’s no mitotic apparatus, hence no mitosis, death. However, new neurons can replace
65
New cards
Unipolar Neurons
sensory. have a short single process leaving the cell body. afferent neurons
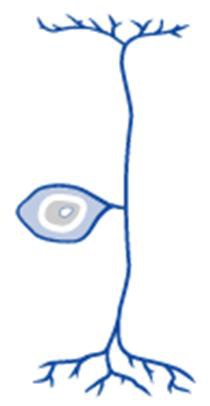
66
New cards
Bipolar Neurons
special senses. A neuron that has only two projections (one axon/one dendrite) from the cell body. found in retina of eye
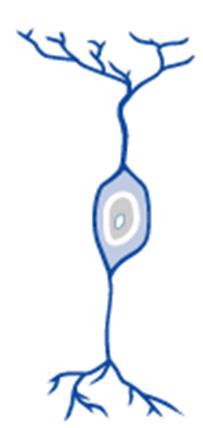
67
New cards
Multipolar
motor. single axon with many dendrites. most common neurons and vary greatly in shape.
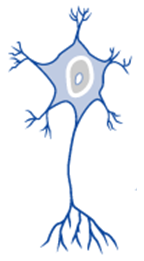
68
New cards
Schwann Cells \[PNS\]
Similar to Oligodendrites by wrapping axons w/myelin, but 1 Schwann to 1 Axon (1:1); Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin.
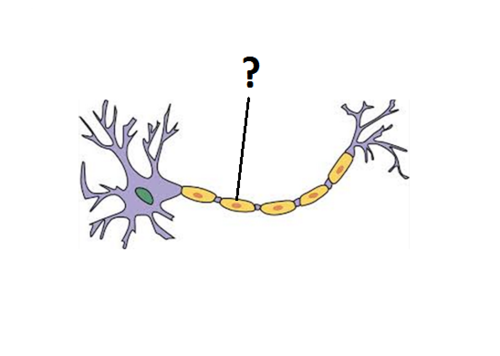
69
New cards
Myelin Sheaths
Lipid electrically insulates axon, protects and heals.
70
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps between Schwann cells (and Oligodentrites); not insulated. Electrical impulses in both PNS and CNS leap from node to node down axon. Hence, heavily \n myelinated nerves (e.g. joint information) carry impulses much faster than unmyelinated \n nerves (e.g. Pain, Touch).
71
New cards
Grey Matter
The portions of the central nervous system that are abundant in cell bodies of neurons rather than axons. Unmyelinated. While the grey matter is mainly located on the surface of the brain. The spinal cord is arranged in the opposite way, with grey matter found deep inside its core
72
New cards
grey matter nucleus
clusters of cell bodies inside the CNS for common function
73
New cards
Nerve and Muscle tissue are excitatory meaning ____
a voltage is created across their membranes
74
New cards
What is the role of the Na+/K+ Pump
Active transporter that moves three Na+ out of a cell and two K+ into the cell against their respective concentration gradients.
75
New cards
What does it mean for a neuron to be polarized?
Disequilibrium of these electrolytes (Na+/K+) across membrane. Creates a Membrane Potential (voltage); An axon membrane at rest where the inside of the cell is negative compared with the outside of the cell
76
New cards
Membrane Potential
\- The voltage across a cell's plasma membrane.
\- maintained by sodium-potassium pump and leak channels
\- maintained by sodium-potassium pump and leak channels
77
New cards
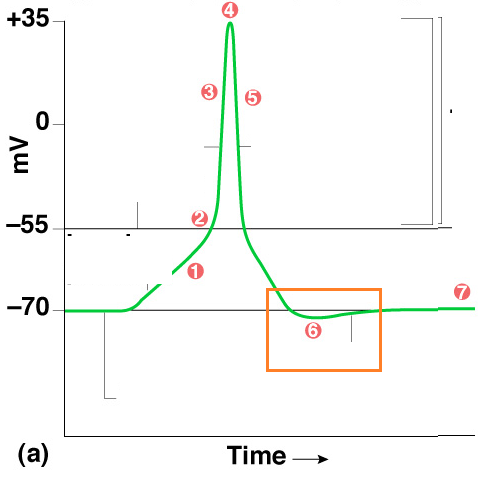
Resting Membrane Potential:
\-70 mv
78
New cards
Threshold Potential:
\-55 mv, once this is reached Na+/K+ gates open
79
New cards
Action Potential:
\+30 mv, a wave of electricity sweeping down axon from Na+/K+ gate to gate like ring of fire
80
New cards
Depolarization
Describes nerve firing, i.e. creating Action Potential; The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.
81
New cards
At what rate do cells depolarize?
Nerve depolarises rapidly = Nerve fires = like electrical spark.
82
New cards
Na+/K+ gates open when
threshold is crossed
83
New cards
What causes the polarised membrane to “depolarise”
Na+ and K+ rushing into and out of \n cell
84
New cards
Hyperpolarizing
increasing the polarity of a neuron, making it less likely to fire
85
New cards
Hypopolarizing
the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential. The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions
86
New cards
Lidocaine
common local anesthetic: Blocks Na/K gates of nerve fibres → no Impulse.
87
New cards
All or None Principle
As with muscle. No impulse will occur until membrane potential reaches threshold. Then, a full action potential is produced—never more or less.
88
New cards
If cell body is damaged_____
the neuron will most likely die and cannot be replaced
89
New cards
If myelin sheath is damaged
the axon *may* die from that point to the terminal
90
New cards
If myelin sheath is damaged in the PNS AND the axon damage is not extensive,
it may repair or even regrow to the terminal (Incredibly slow) because Schwann cells can reproduce and insulate the axon’s healing
91
New cards
If myelin sheath is damaged in the CNS the axon will _______
not heal because Oligodendrites do not reproduce and insulate
92
New cards
Blocking the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
decreased response
93
New cards
Blocking attachment of neurotransmitters to target tissue receptors
decreased response
94
New cards
Blocking removal of neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft.
increased response
95
New cards
Inhibiting neurotransmitter receptors by hyperpolarizing them.
decreased response
96
New cards
Exciting neurotransmitter receptors by hypopolarizing them.
increased response
97
New cards
grey matter
The portions of the central nervous system that are abundant in cell bodies of neurons rather than axons. Unmyelinated.
98
New cards
grey matter Nucleus
clusters of cell bodies inside the CNS for common function
99
New cards
grey matter Ganglion
clusters of cell bodies outside the CNS for common function
100
New cards
White Matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.