Year10 - Medical Science
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
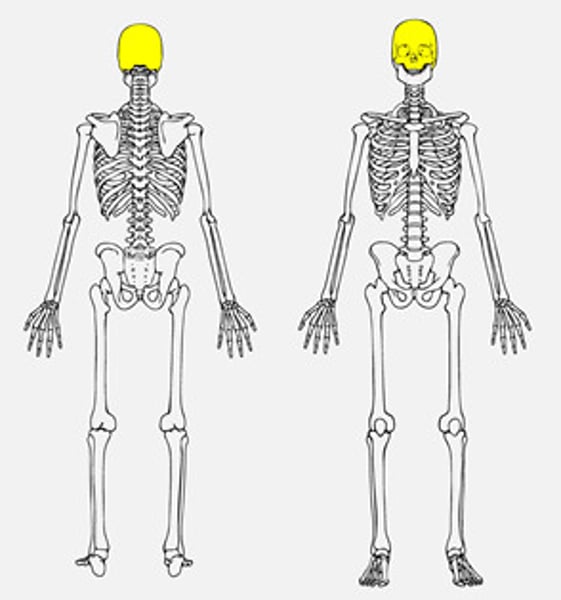
Cranium
the portion of the skull that encloses the brain
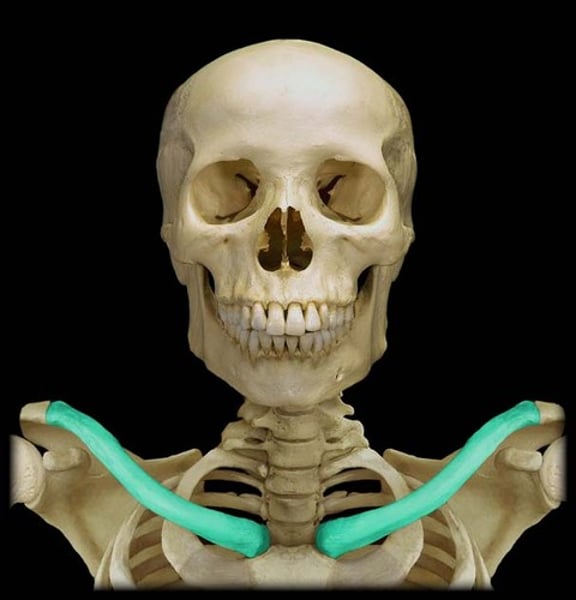
clavicle
collar bone
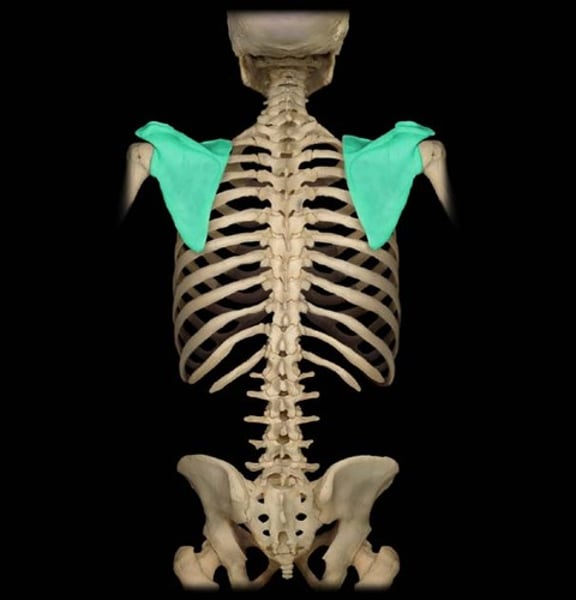
Scapula
shoulder blade
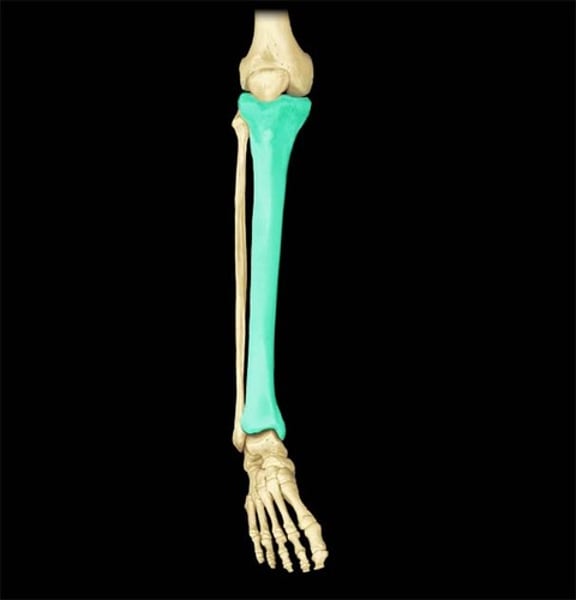
Tibia
shin bone
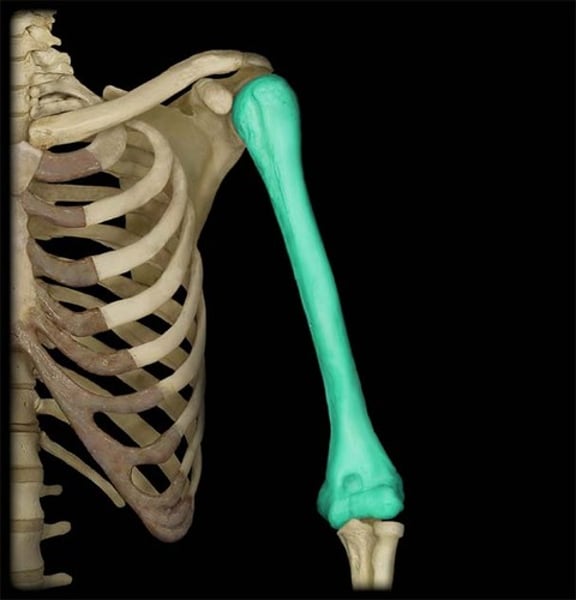
Humerus
upper arm bone
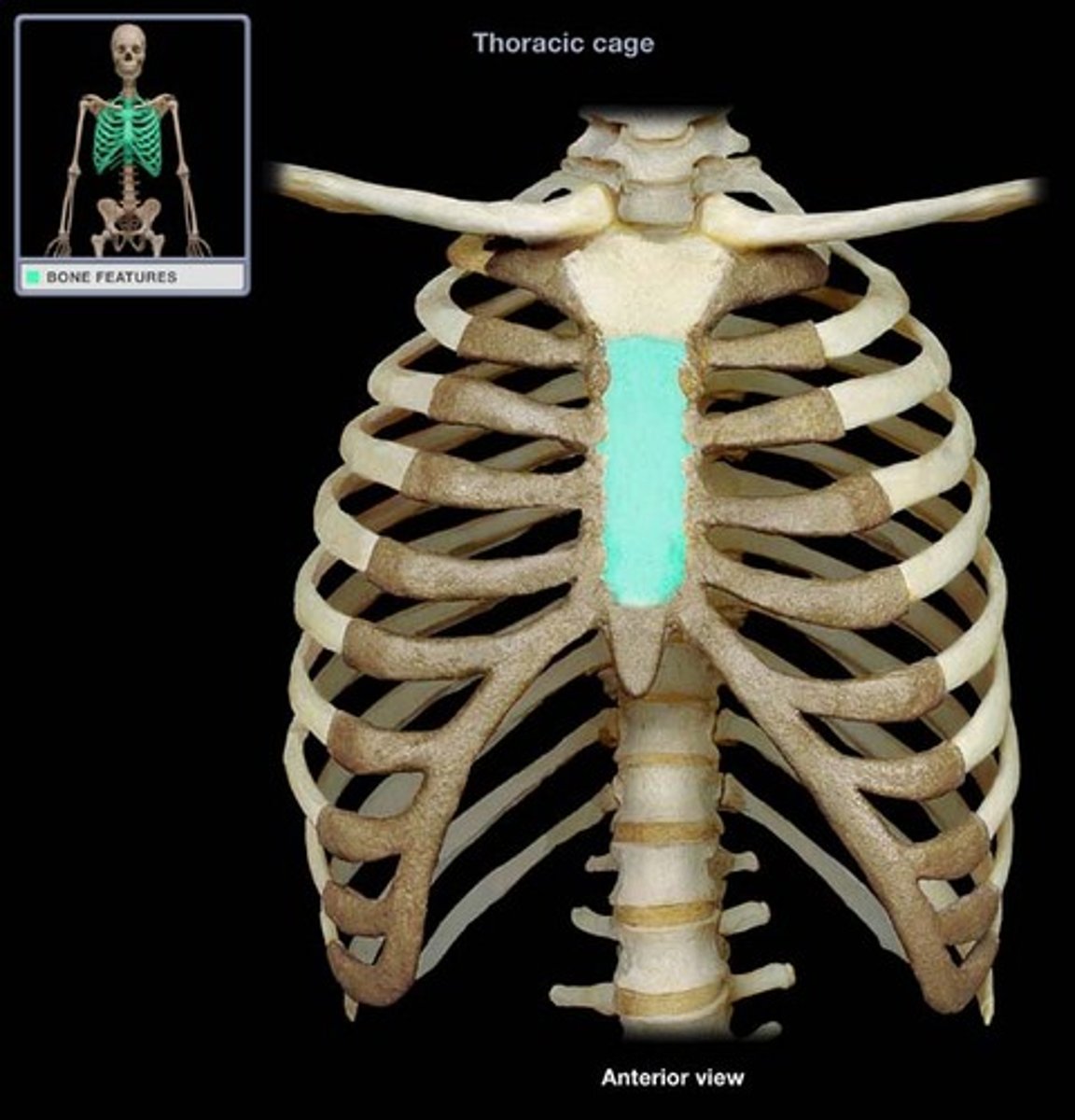
Sternum
breastbone
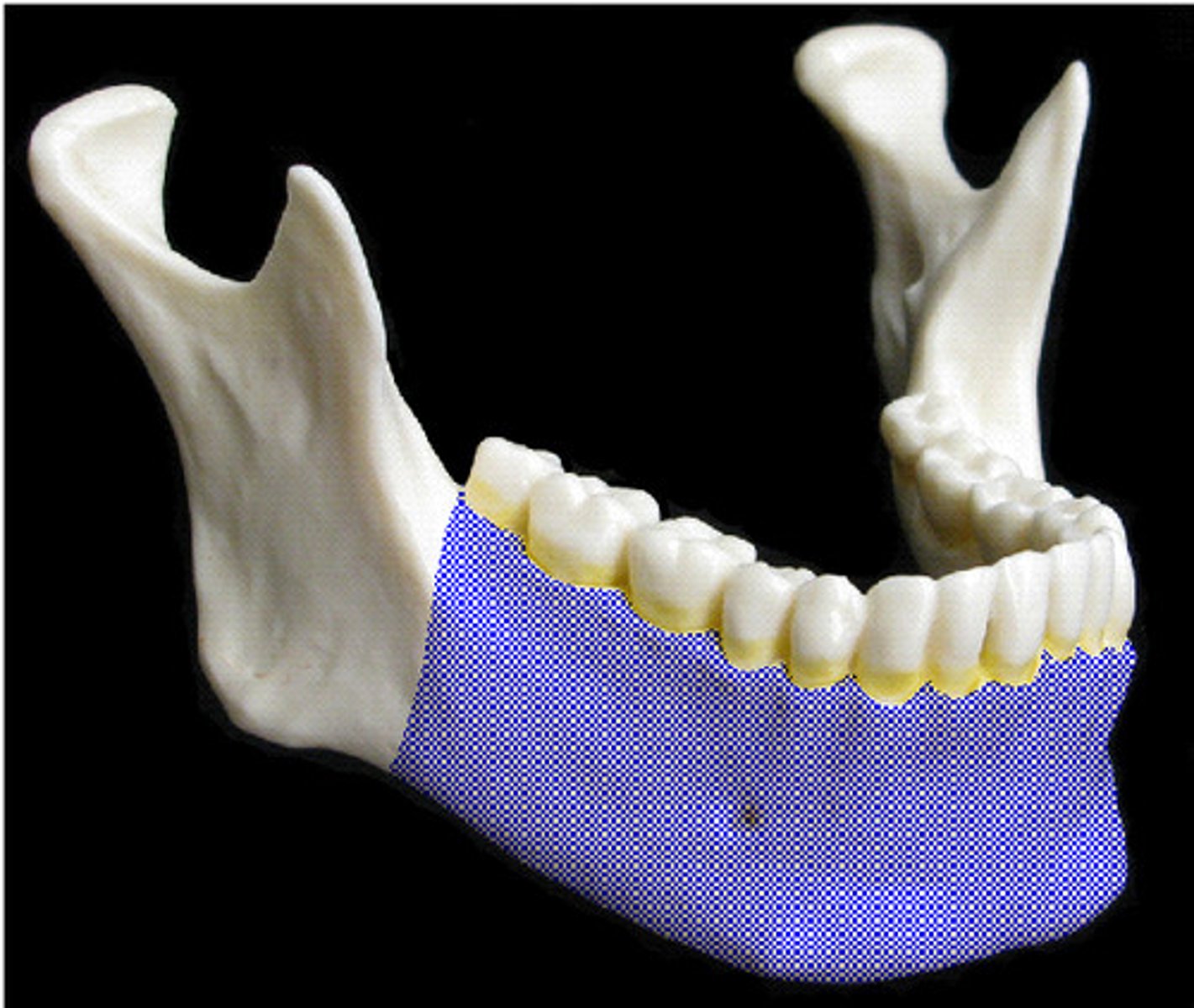
Mandible
lower jaw bone
Quadriceps
a muscle group consisting of four muscles that is located along the front of the thigh
Synovial fluid
The small amount of liquid within a joint used as lubrication.
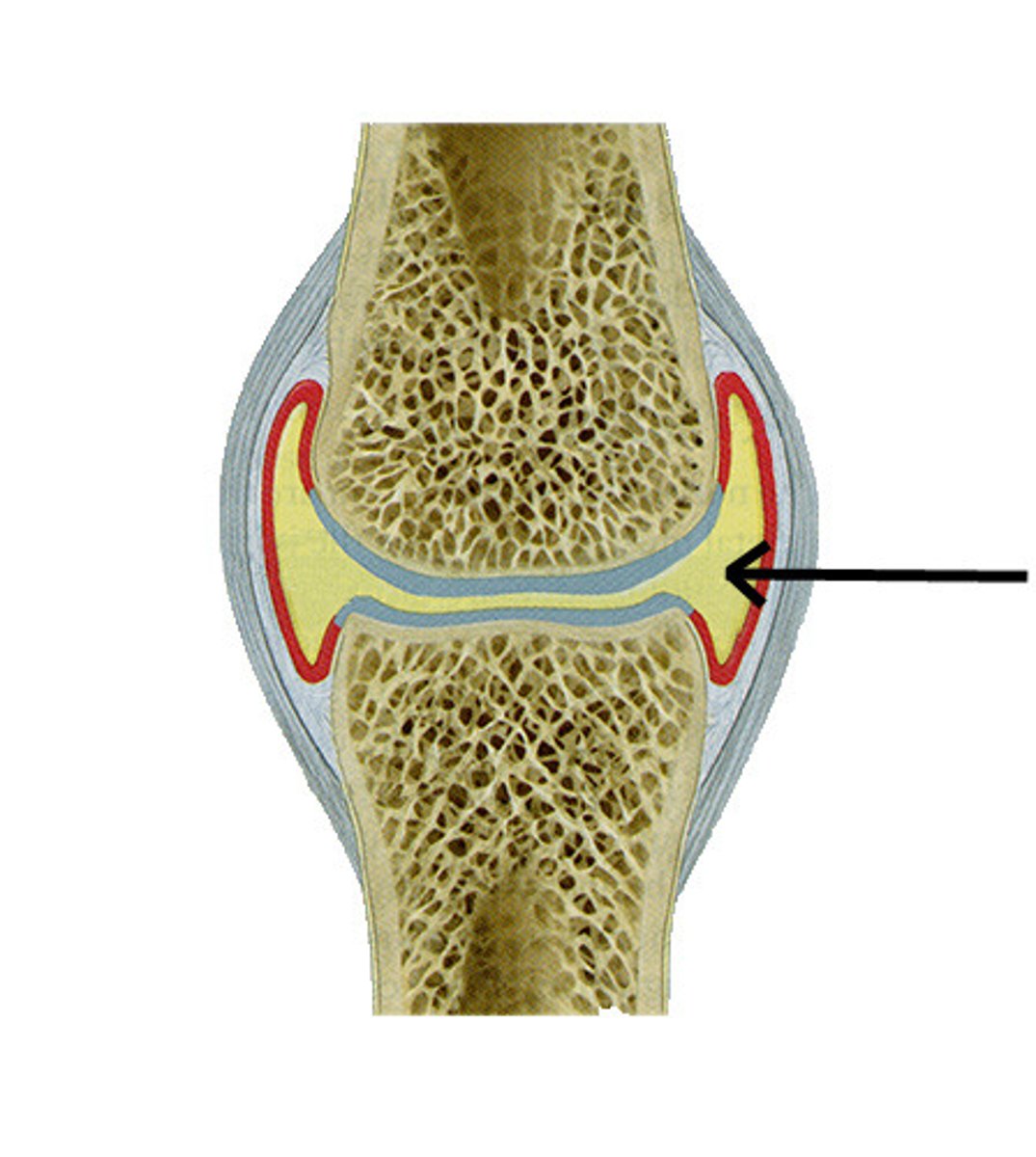
Cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together.
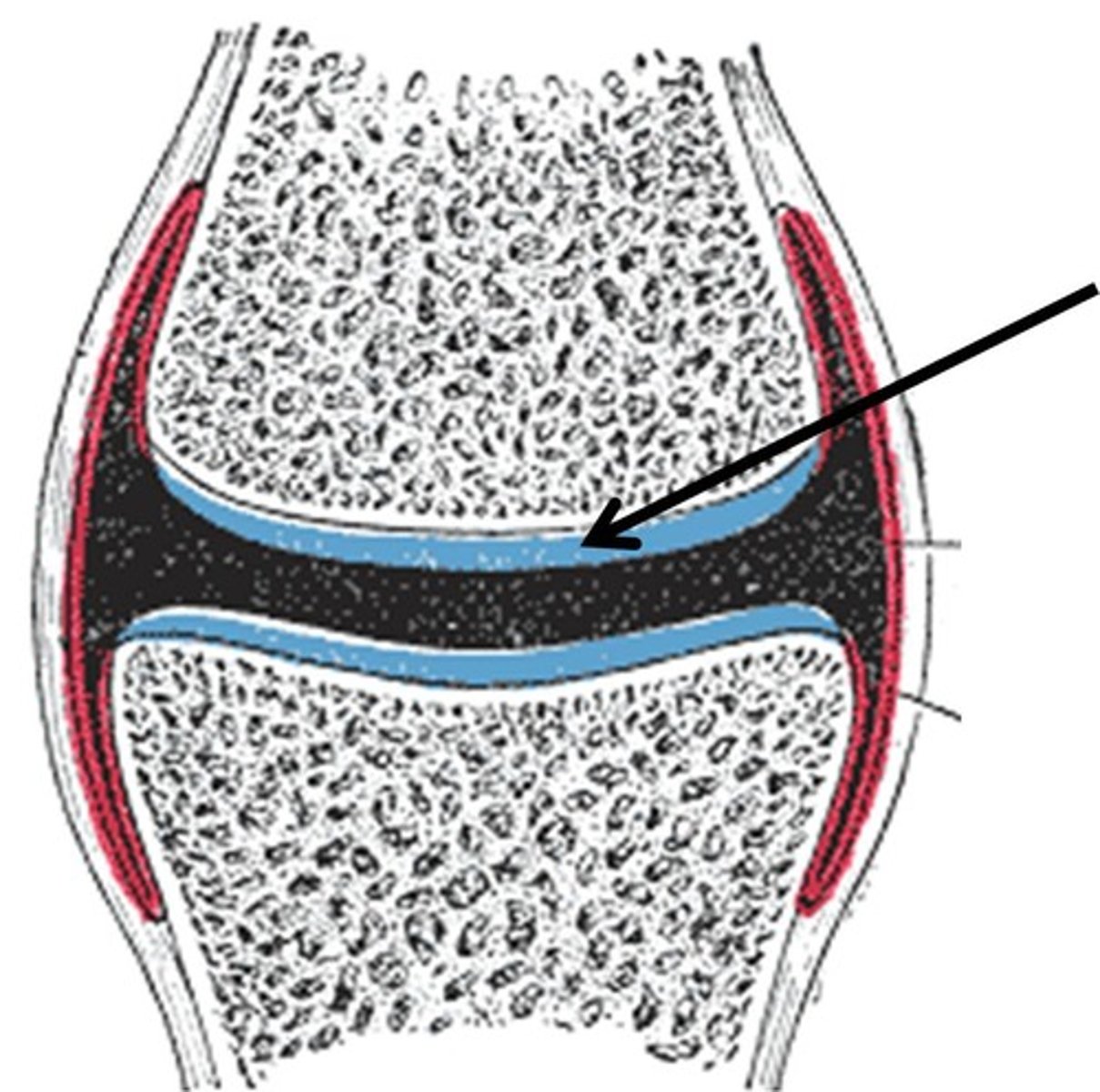
synovial membrane function
lines the capsule and secretes synovial fluid
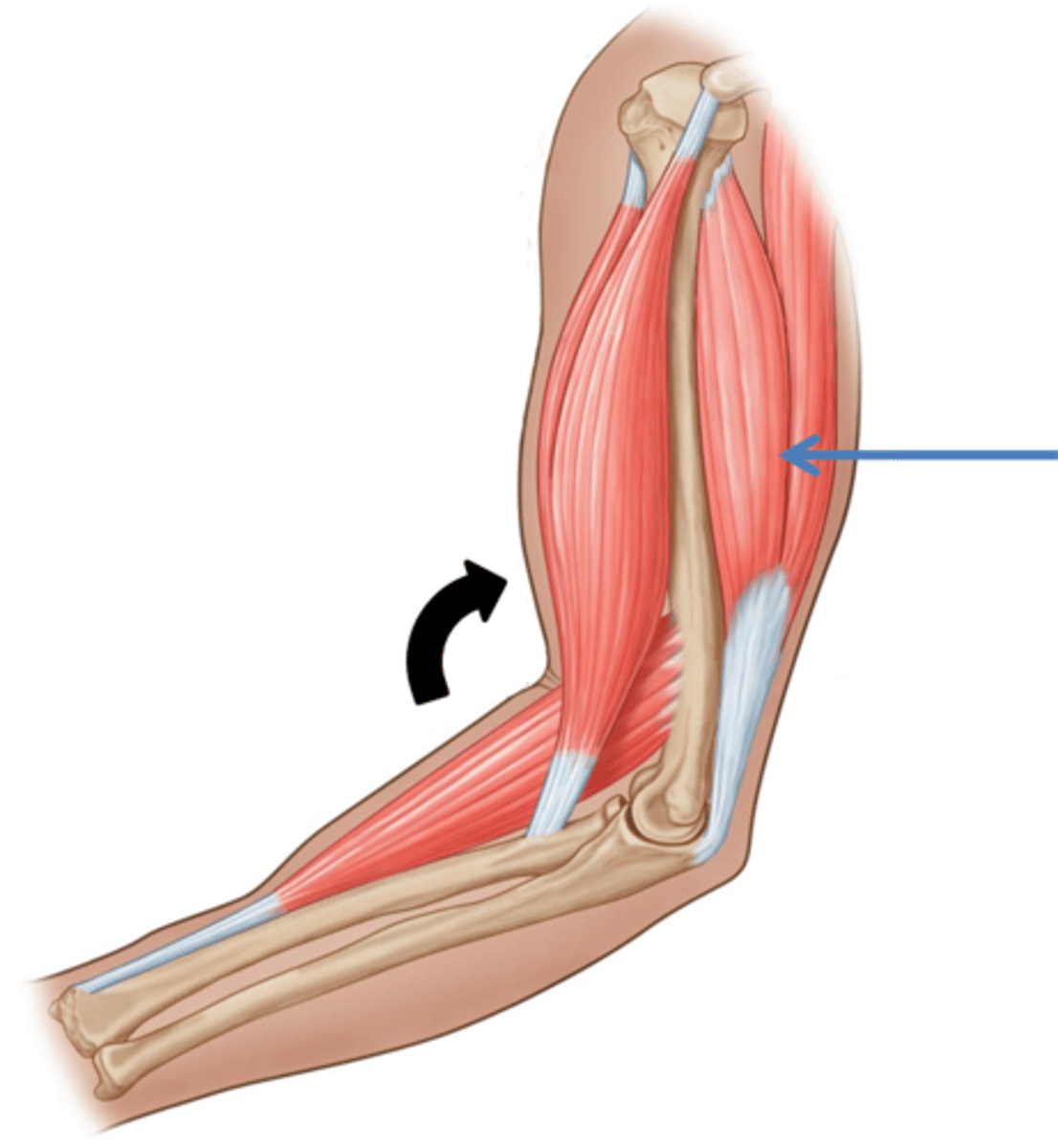
Antagonistic muscles
muscle pairs arranged to work against each other to move a joint
Blood composition
plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
Blood circulation
Movement of blood throughout the body
Red blood cells
carry oxygen
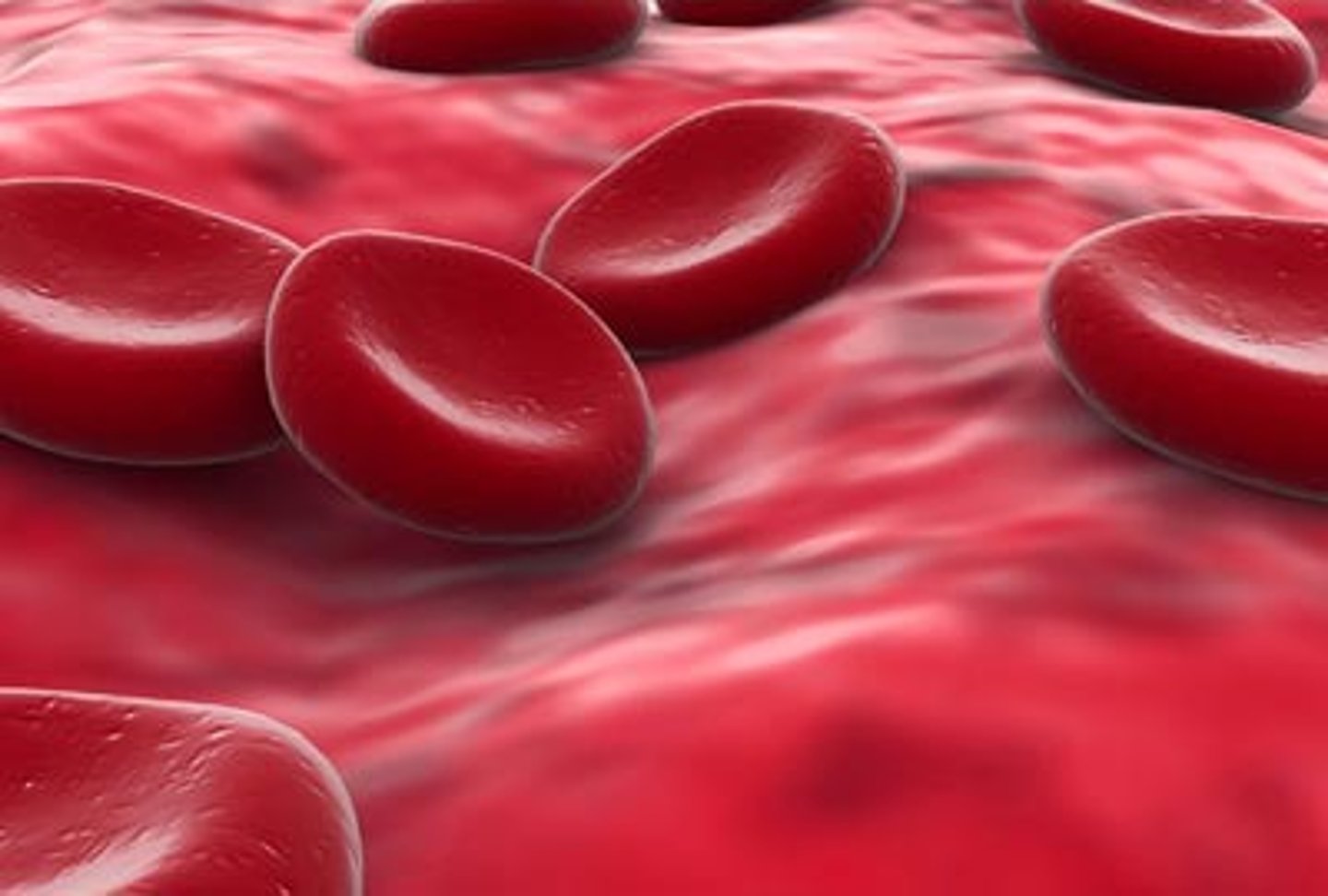
White blood cells
Fight infection and at as a defense system
Platelets
Clot blood when you get a cut
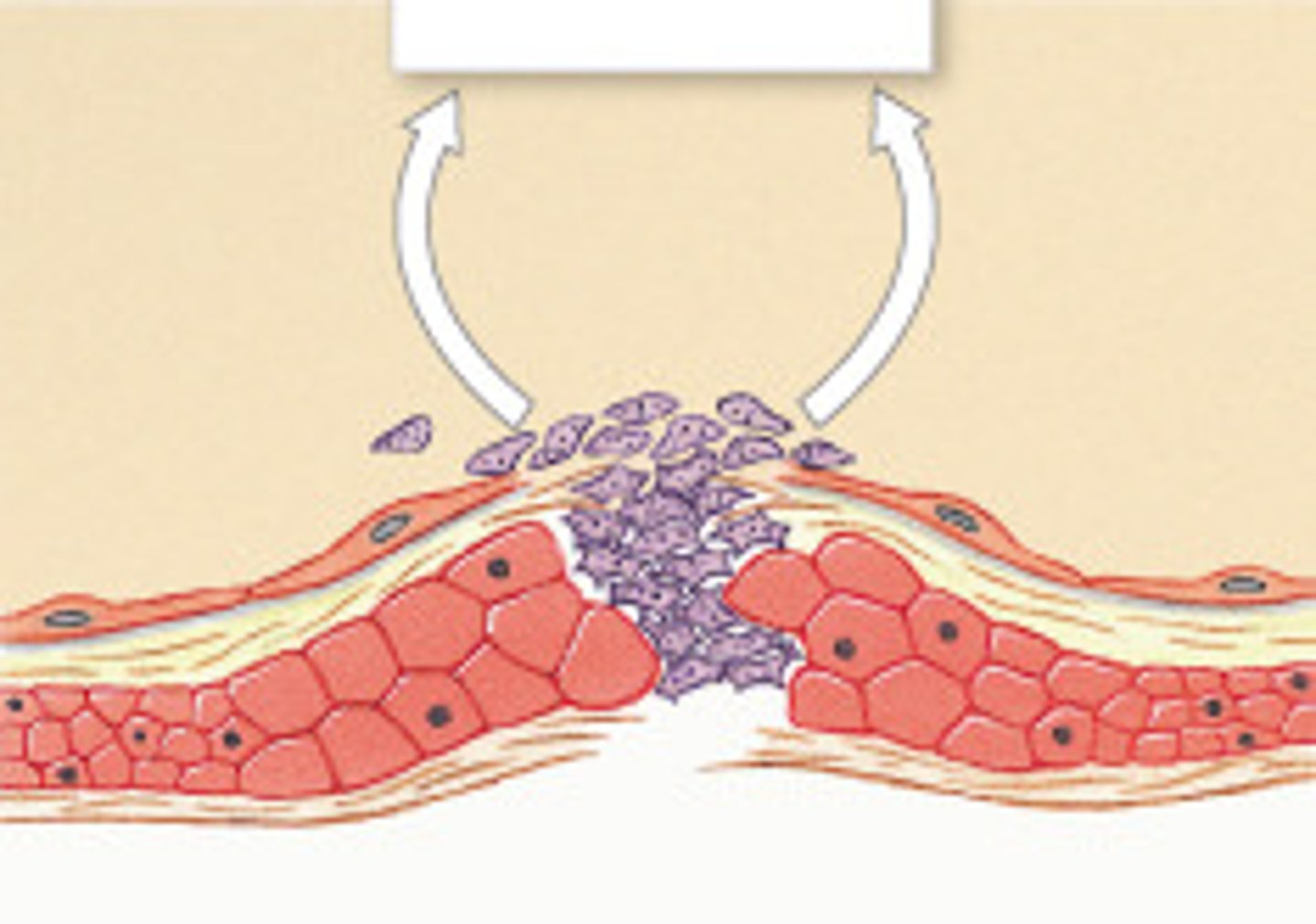
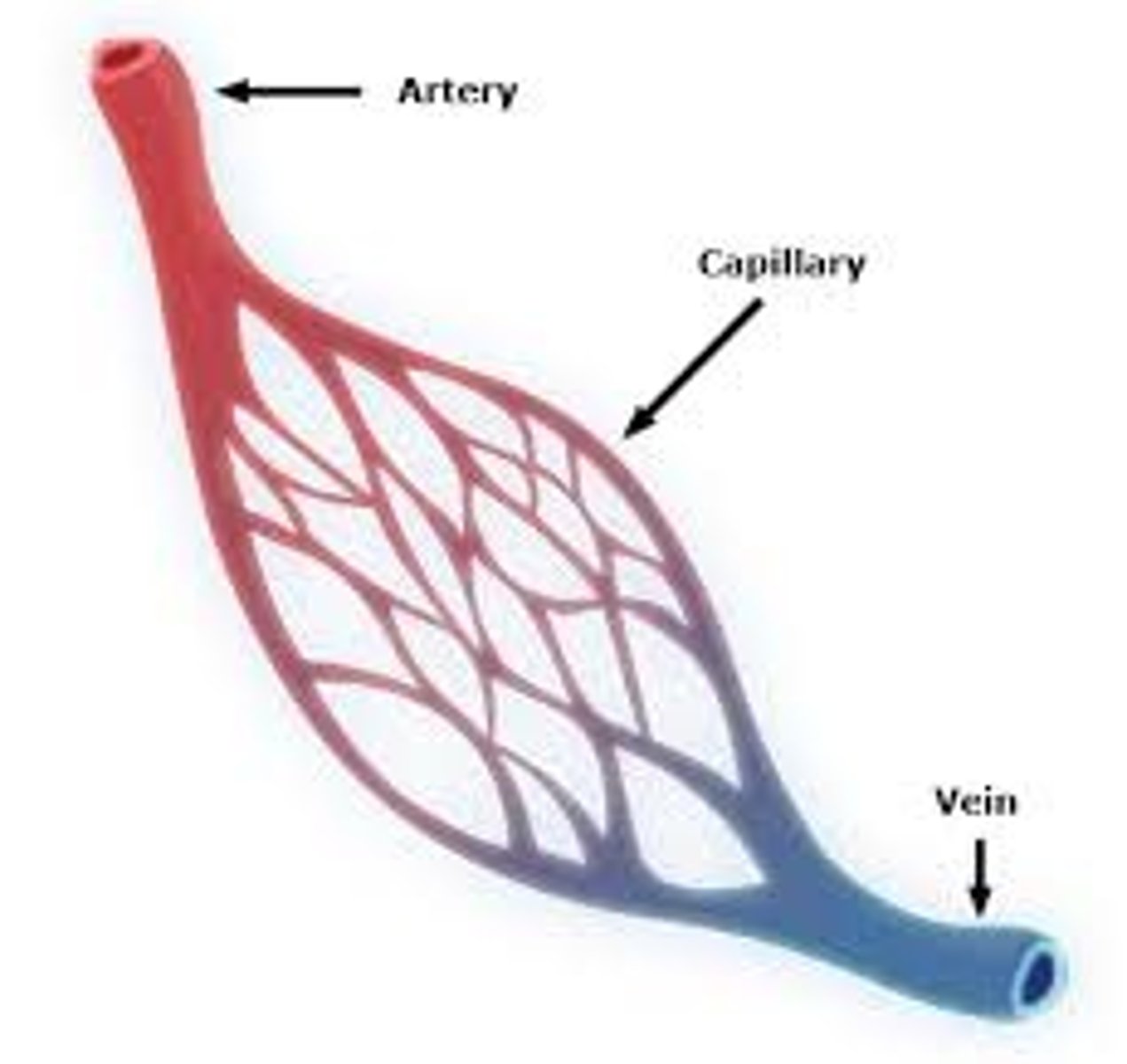
Veins
carry deoxygenated blood to the heart
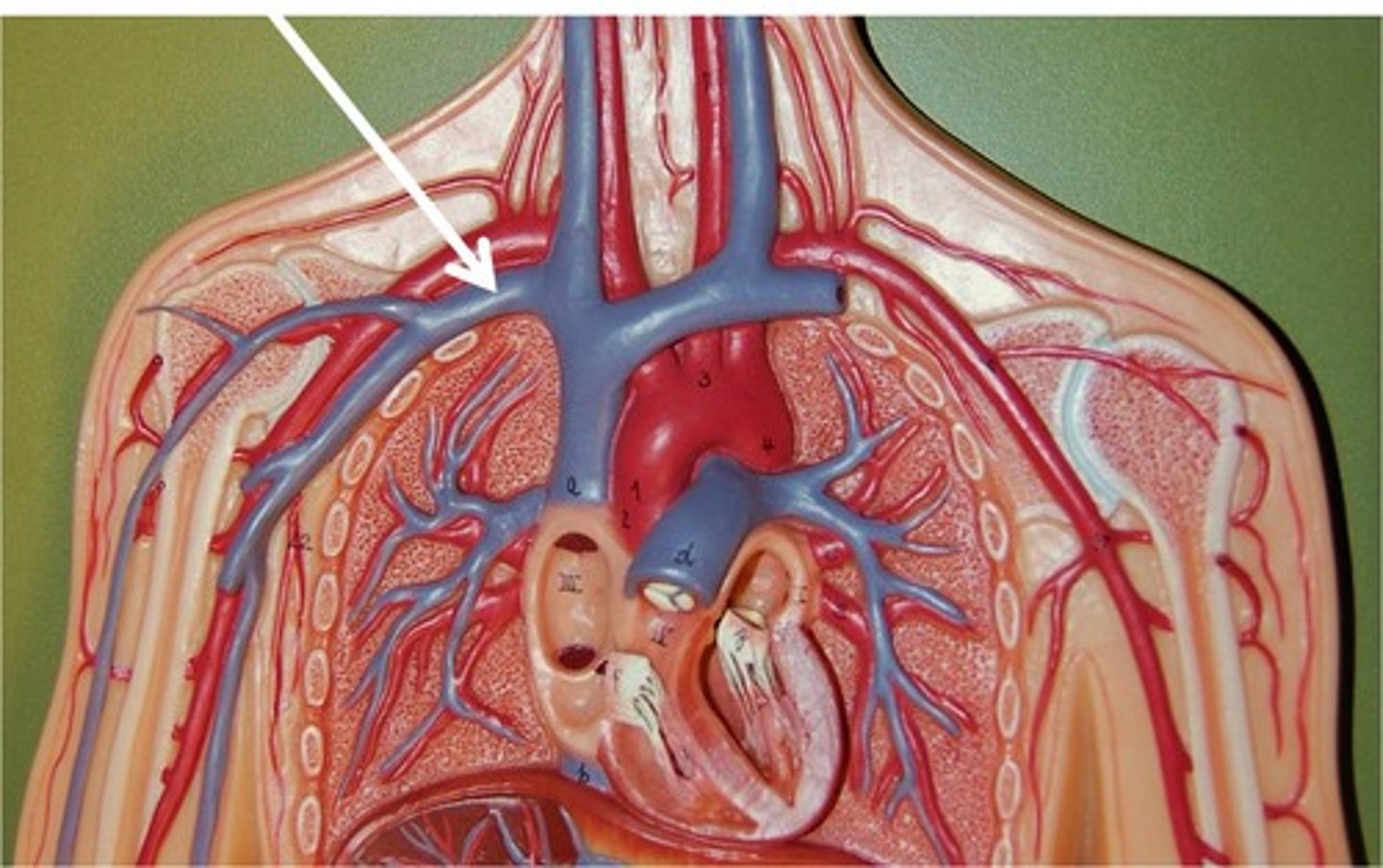
Arteries
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
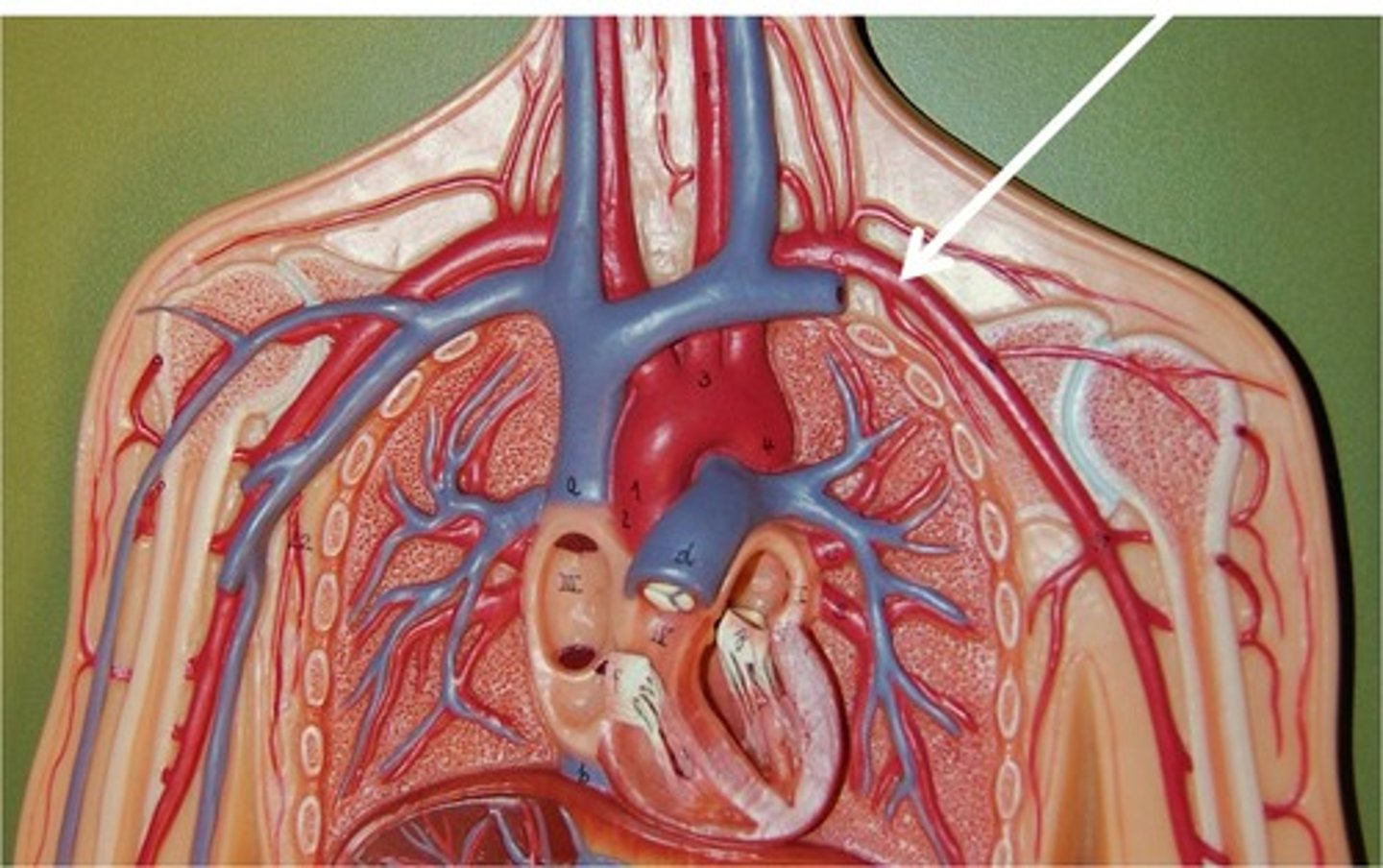
Capillaries
Microscopic vessels through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
Lungs
Main organs of the respiratory system
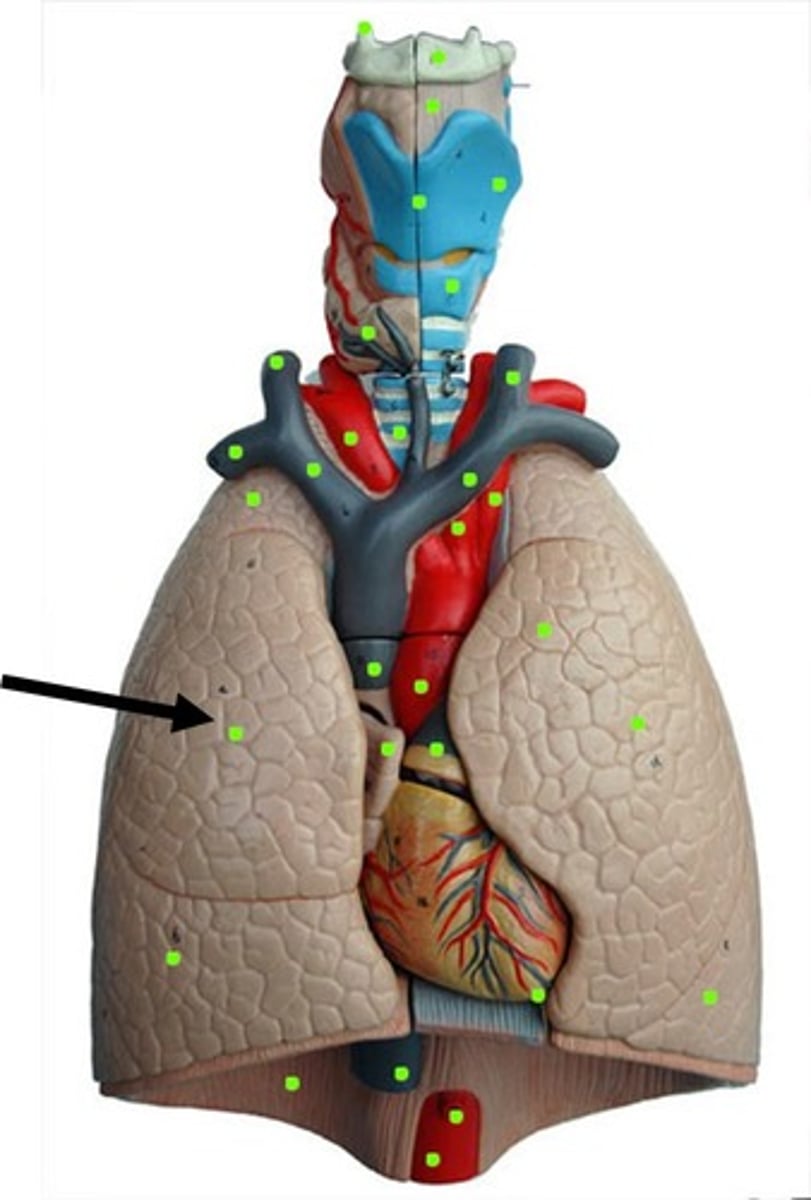
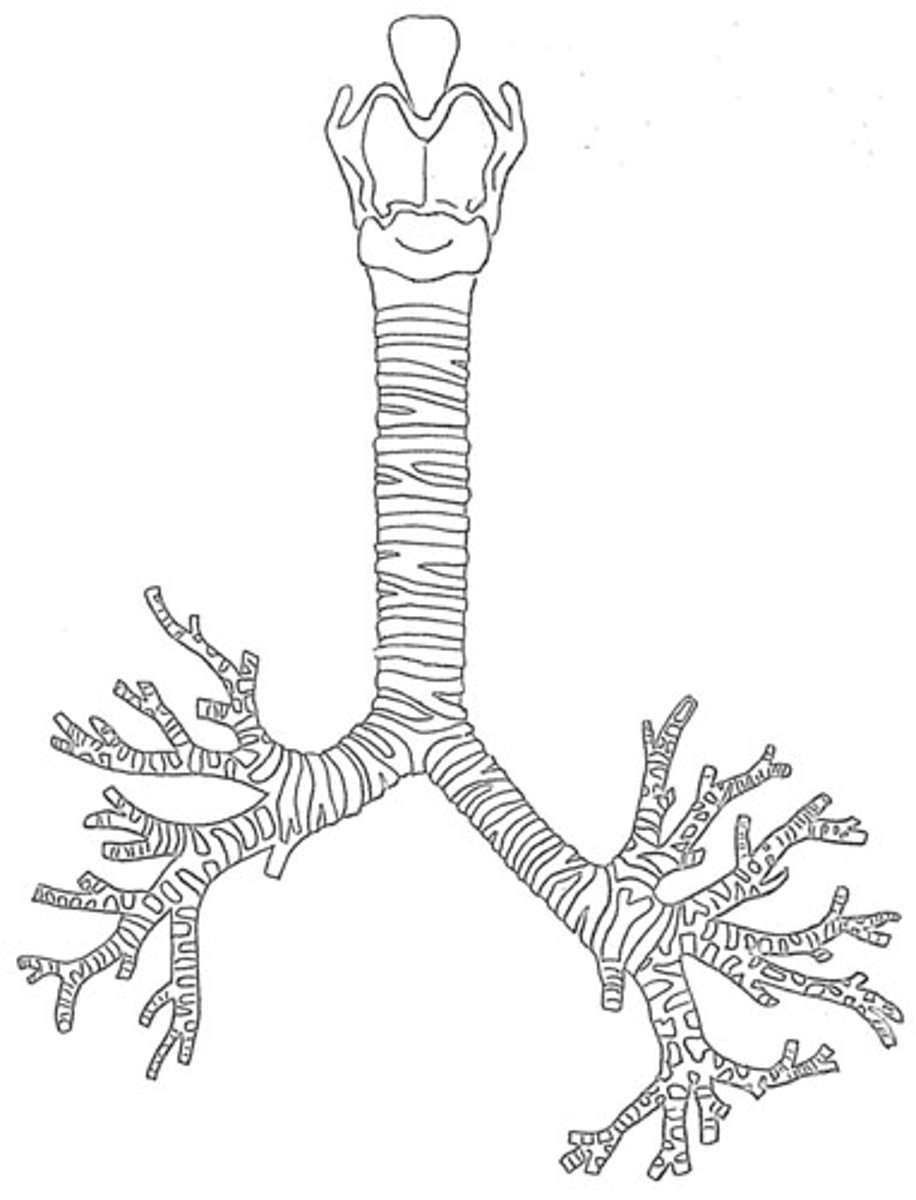
Trachea
windpipe
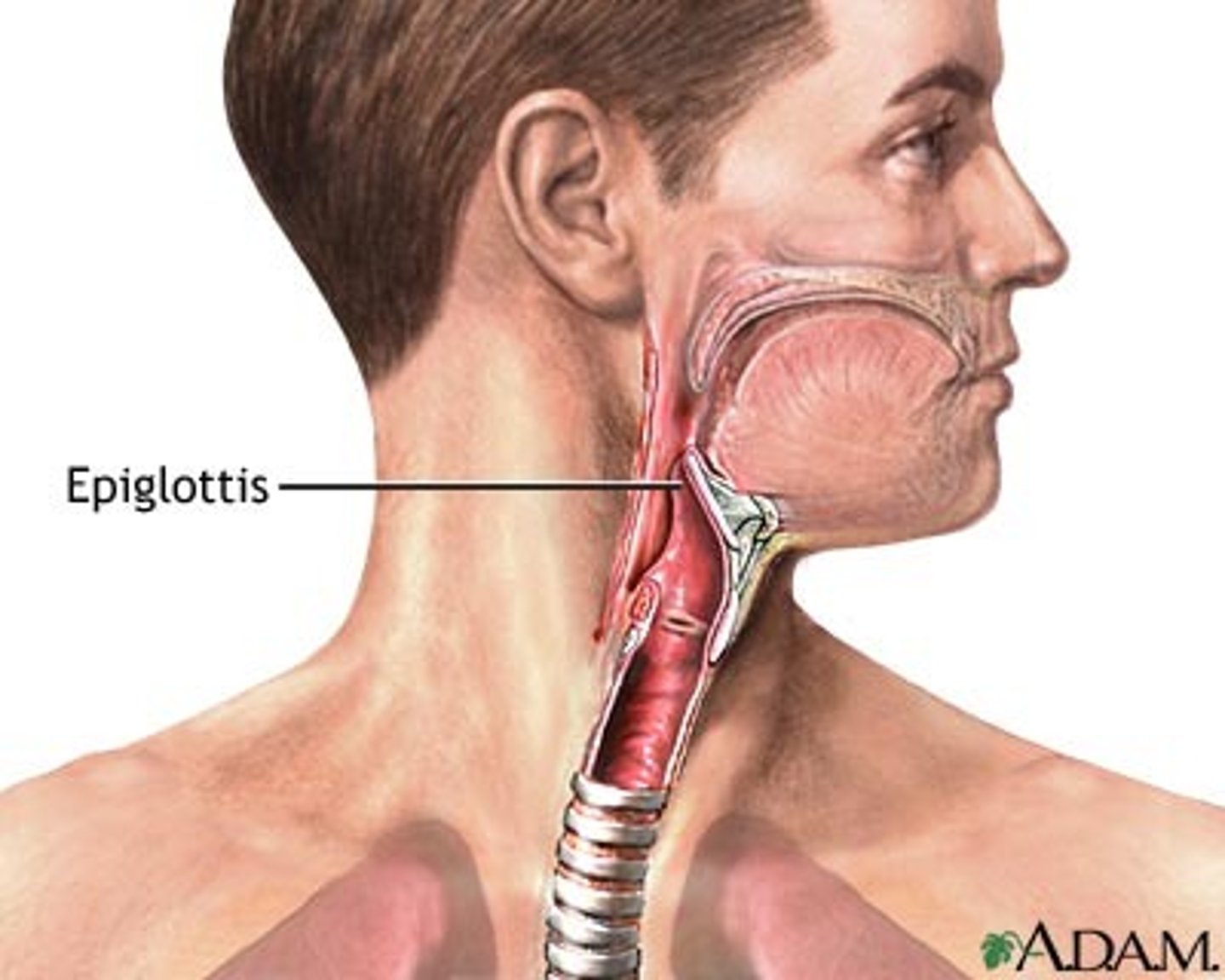
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Alveoli
Tiny sacs of lung tissue specialised for the movement of gases between air and blood.
Look like grapes.
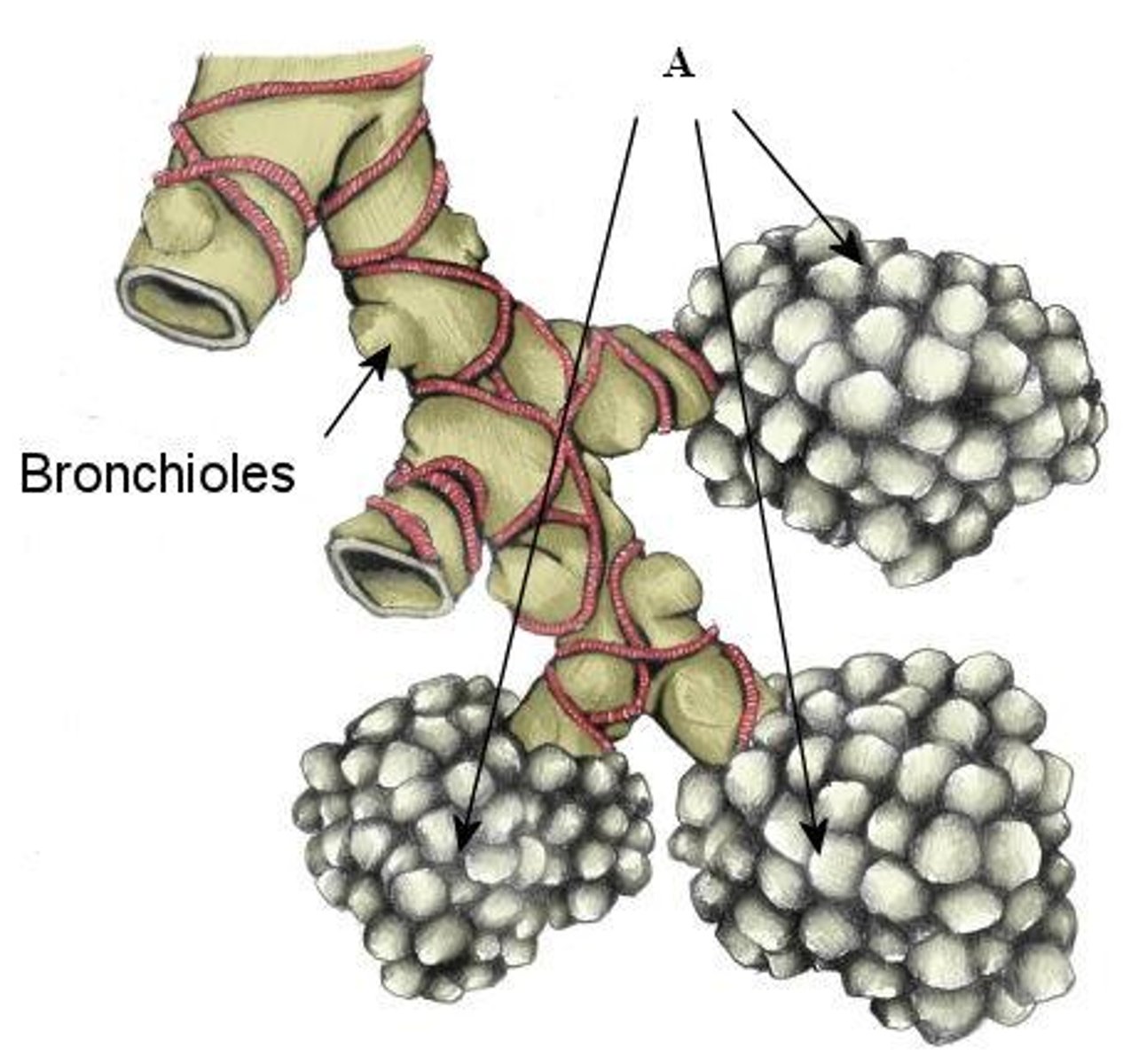
Bronchioles
smallest branches of the bronchi
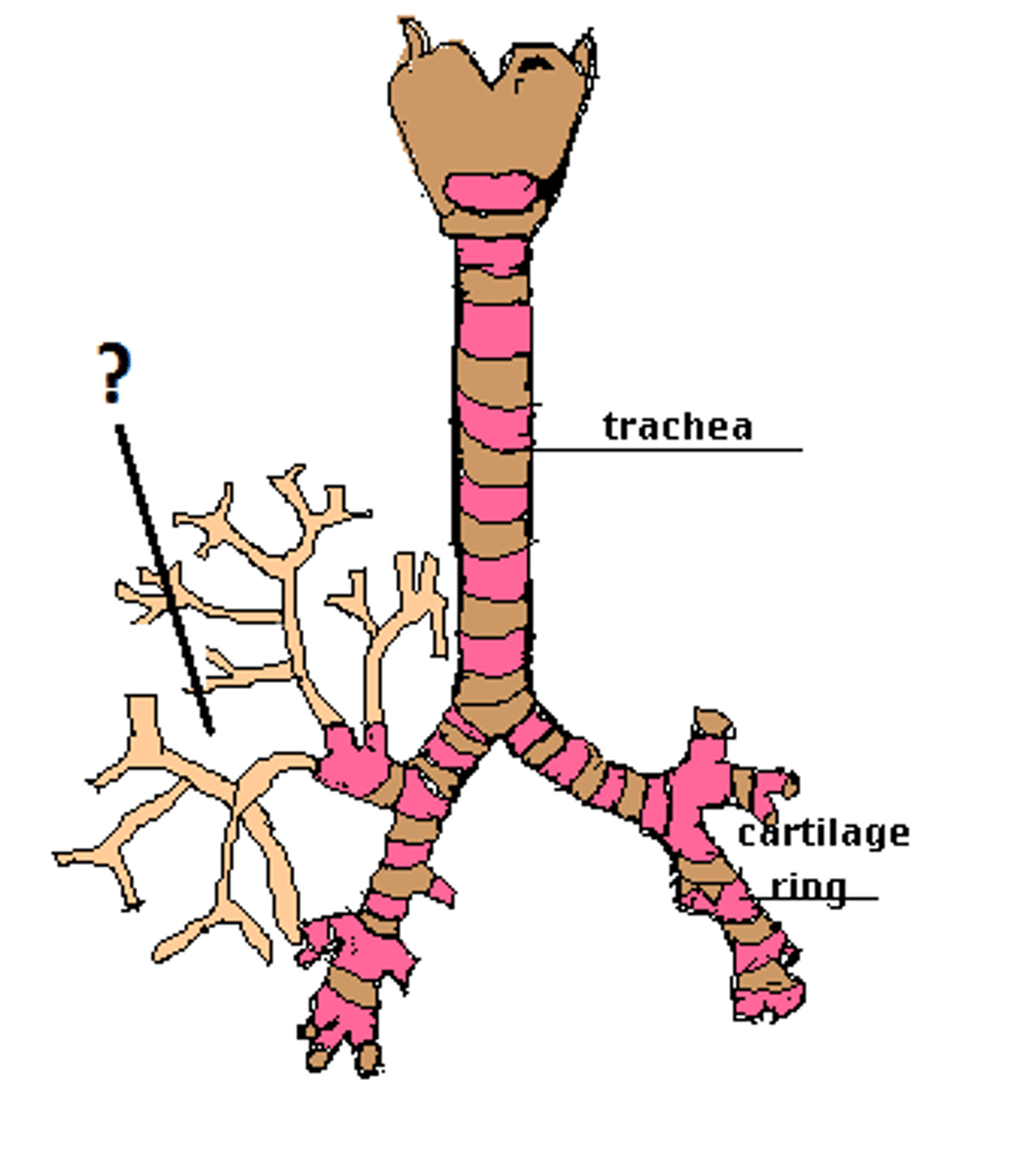
Bronchi
two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
Oxygen
gas that enters the blood through the lungs and travels to the heart to be pumped via arteries to all body cells
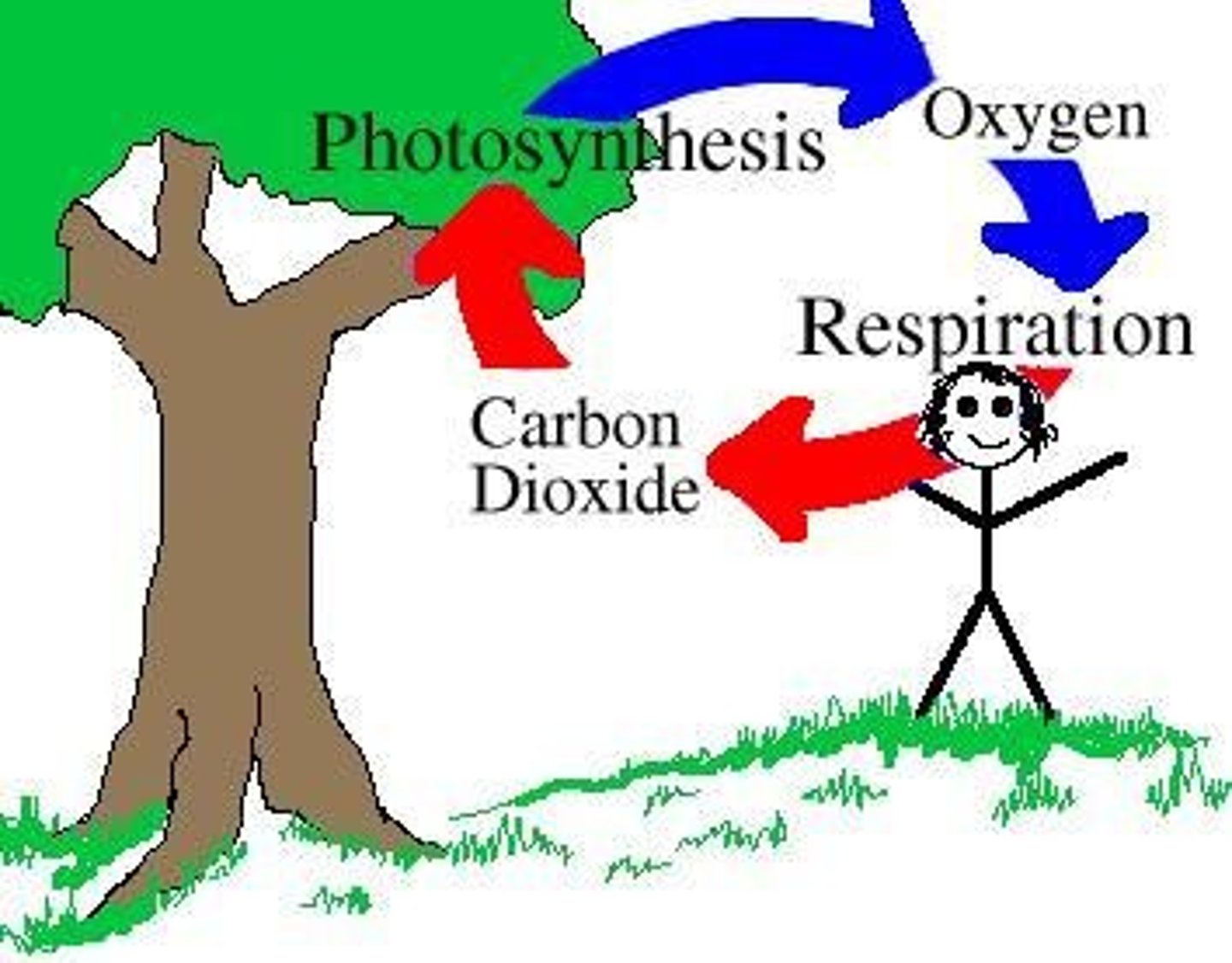
Carbon dioxide
A gas that is expelled from the body by the respiratory system.
Nutrients
Substances in food that your body needs to grow, to repair itself, and to supply you with energy
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
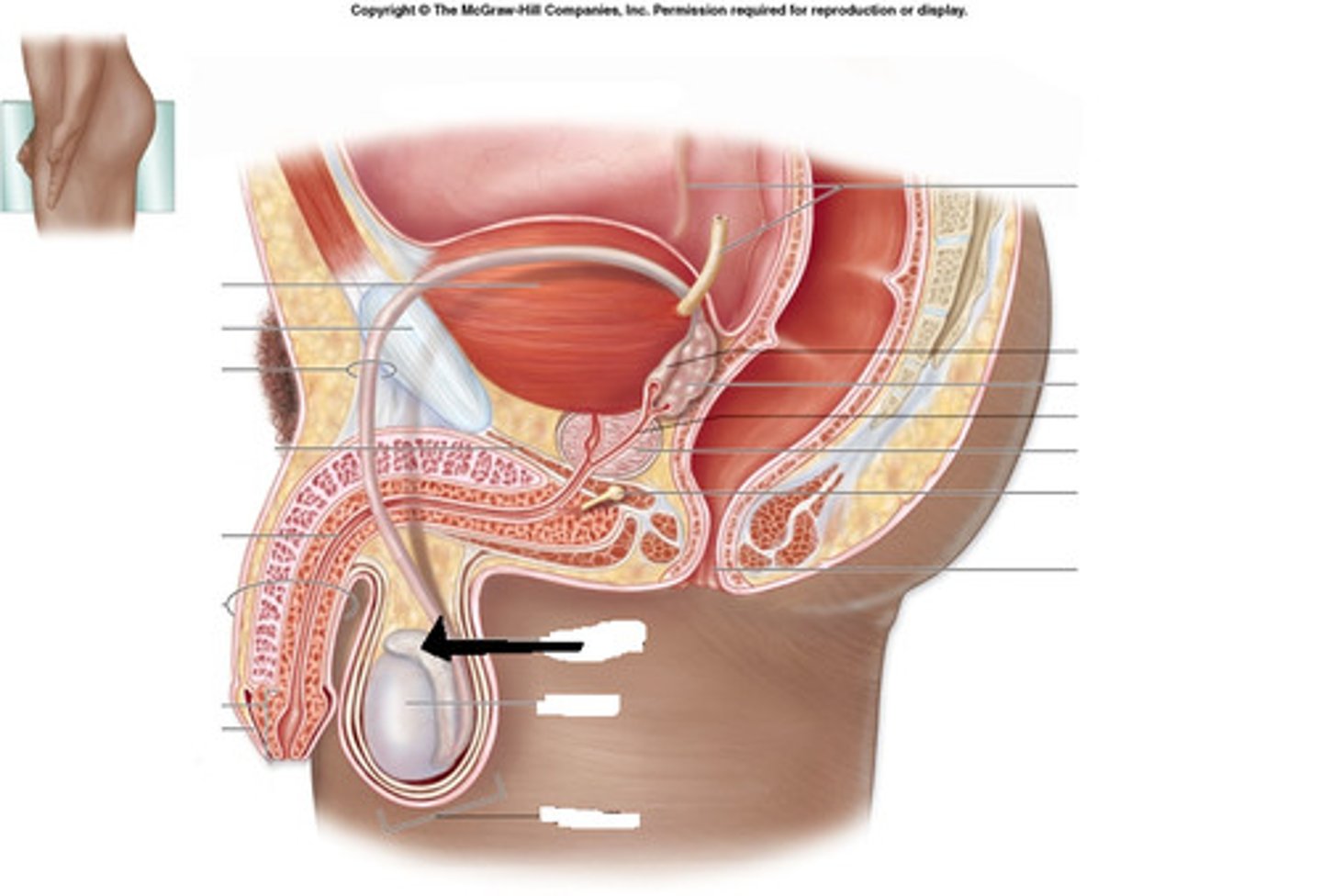
Testes
produce sperm
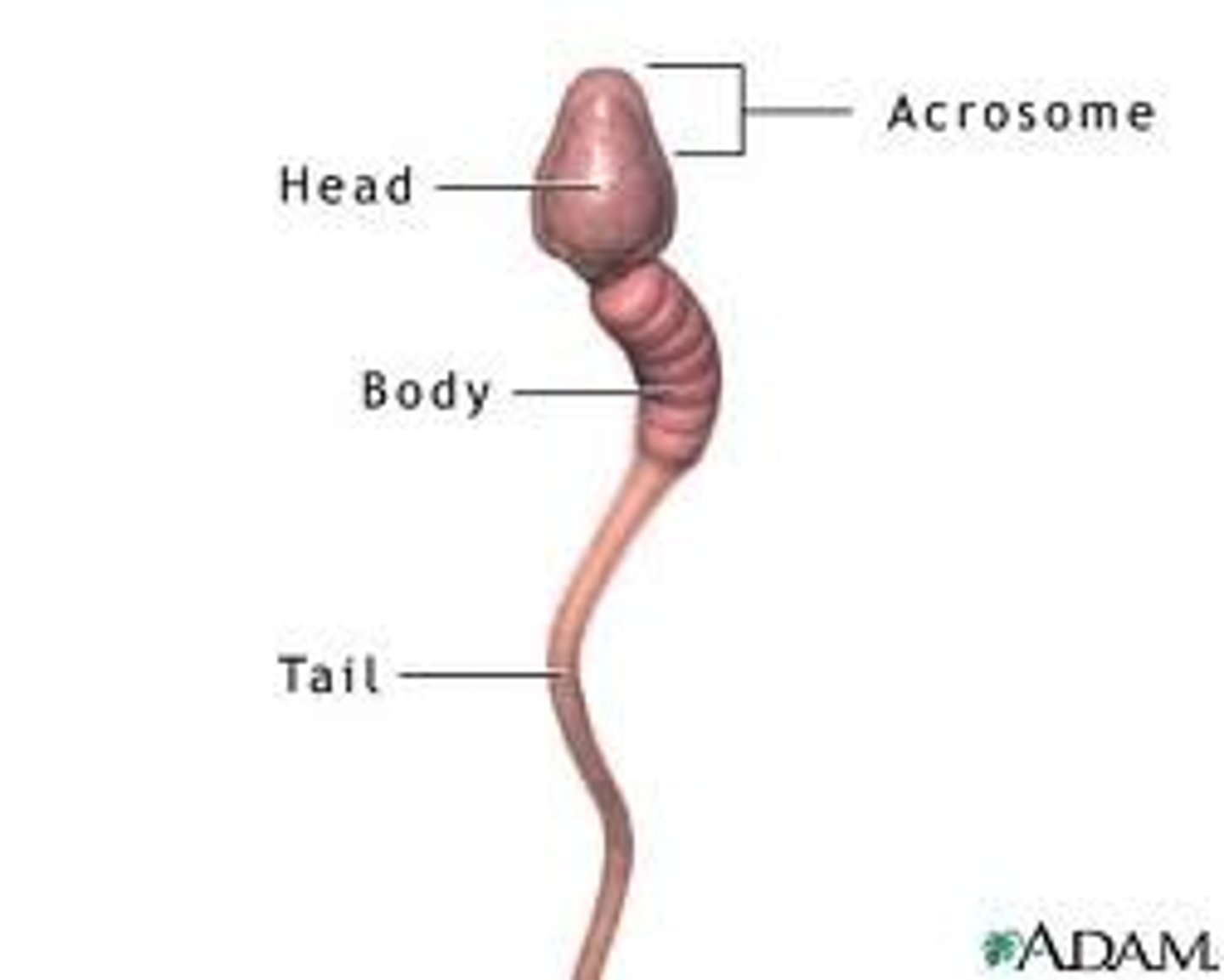
Sperm
Male sex cell
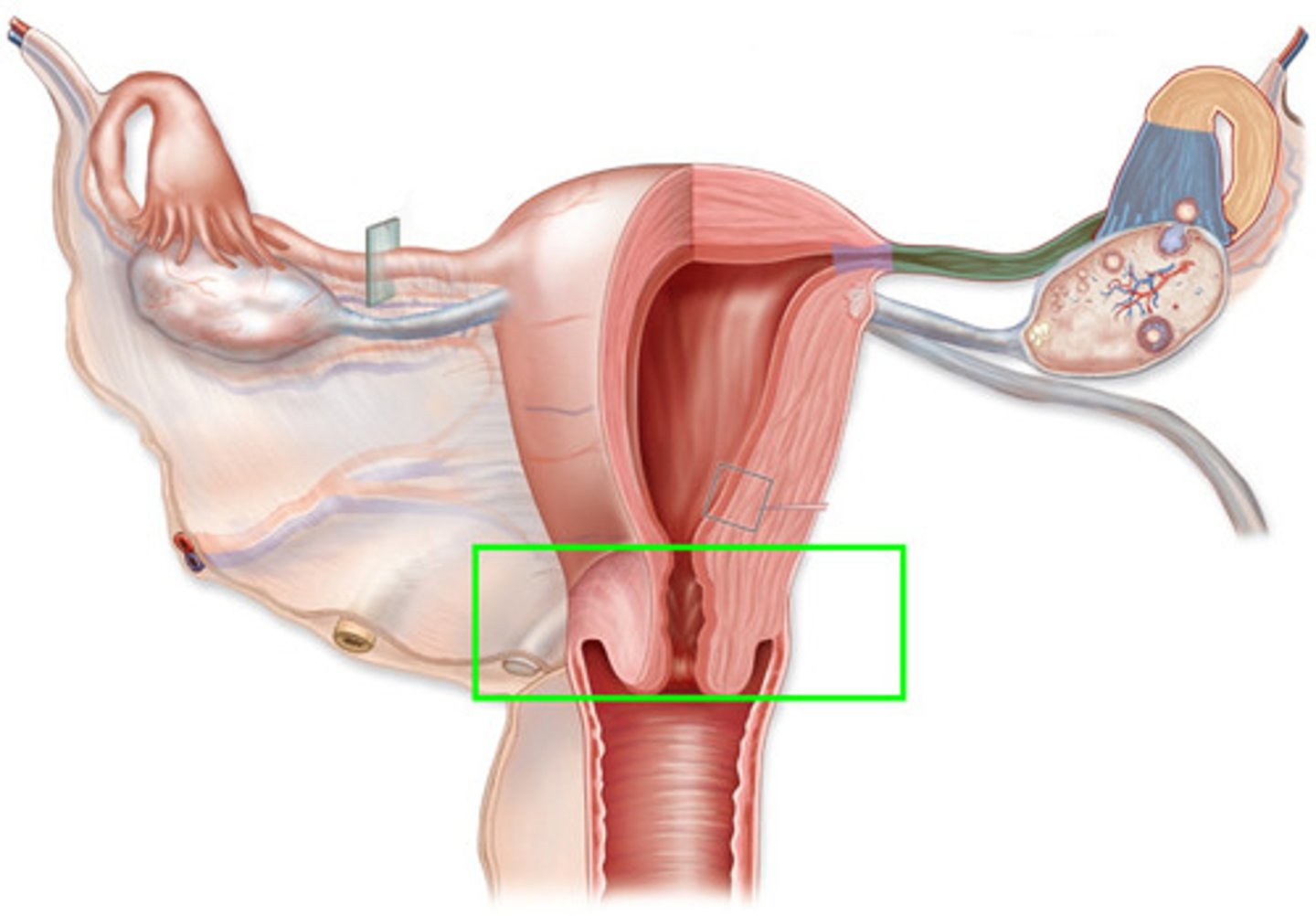
Cervix
Entrance to the uterus
Holds the baby's head in place
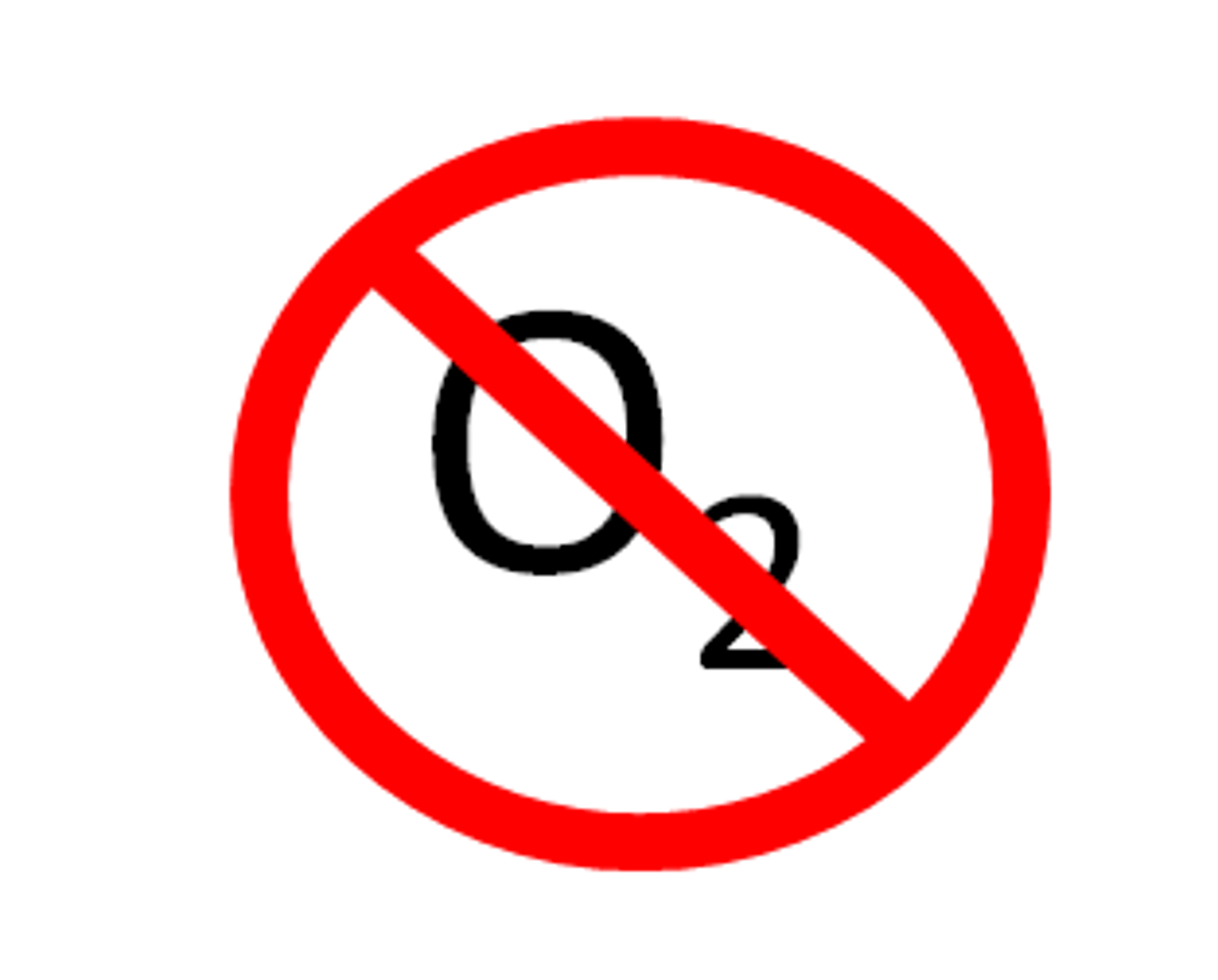
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration without oxygen. This produces lactic acid and a small amount of energy.

Aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen.
Produces energy, water and carbon dioxide.
Urethra
Tube that carries urine and semen to the outside of the body
Epididymis
A long, coiled tube on the outside of the testes in which sperm are stored and mature.
Fallopian tubes
Tubes which carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus and which provides the place where fertilisation occurs
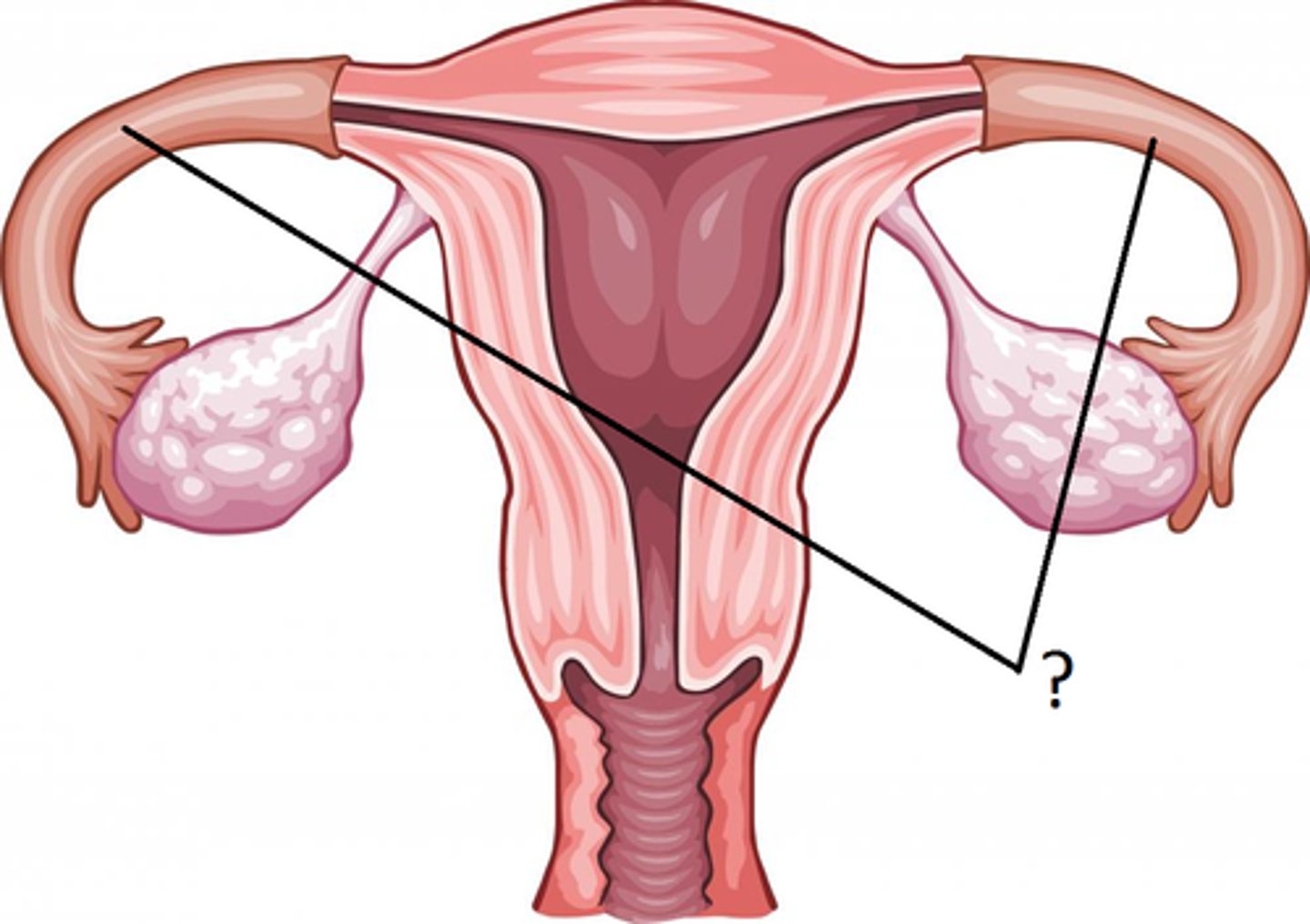
Ovary
Where eggs are produced
Egg Cells
Female sex cells
Fertilisation
Fusing of a male sex cell with a female sex cell.
Embryo
An organism in the earliest stage of development.
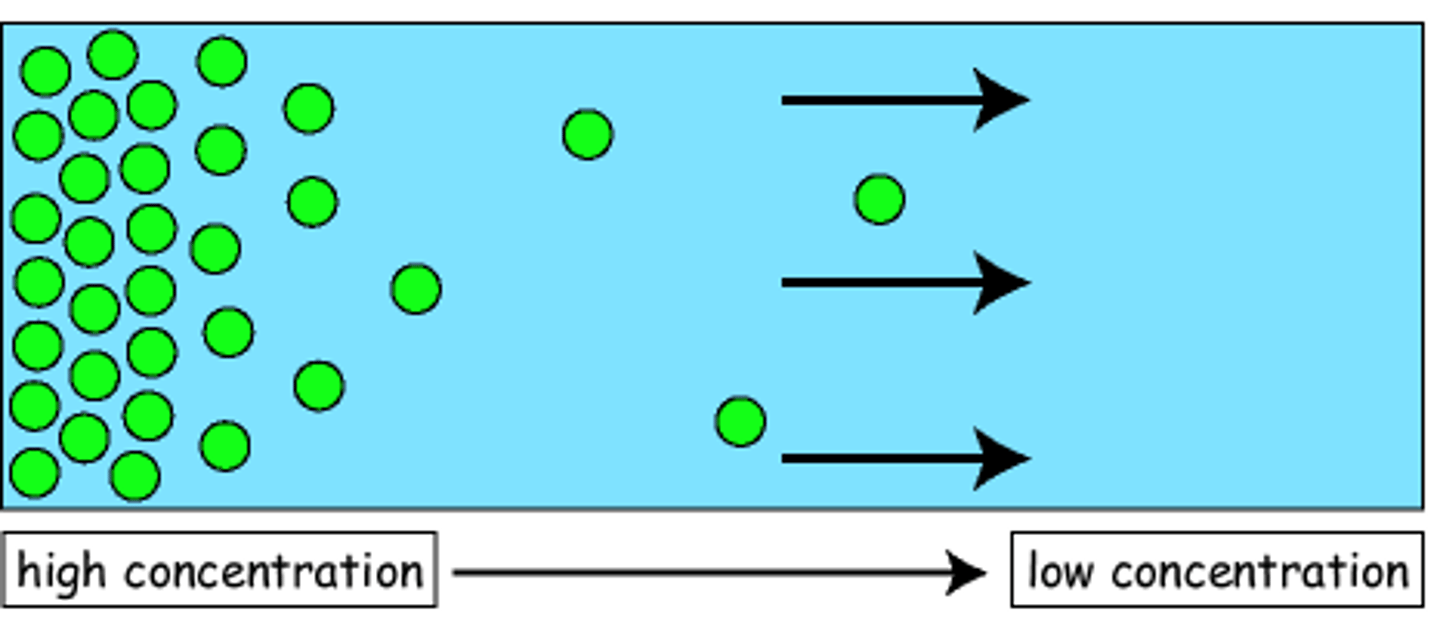
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Heart attack symptoms
Chest pain, pain in one part of the body or upper chest, feelings of a tight band around the chest, may last 20 minutes and go away, nausea, sweats, redness in the face.
Heart attack causes
Fatty plaques (atherosclerosis), blood clot, heart beats too fast
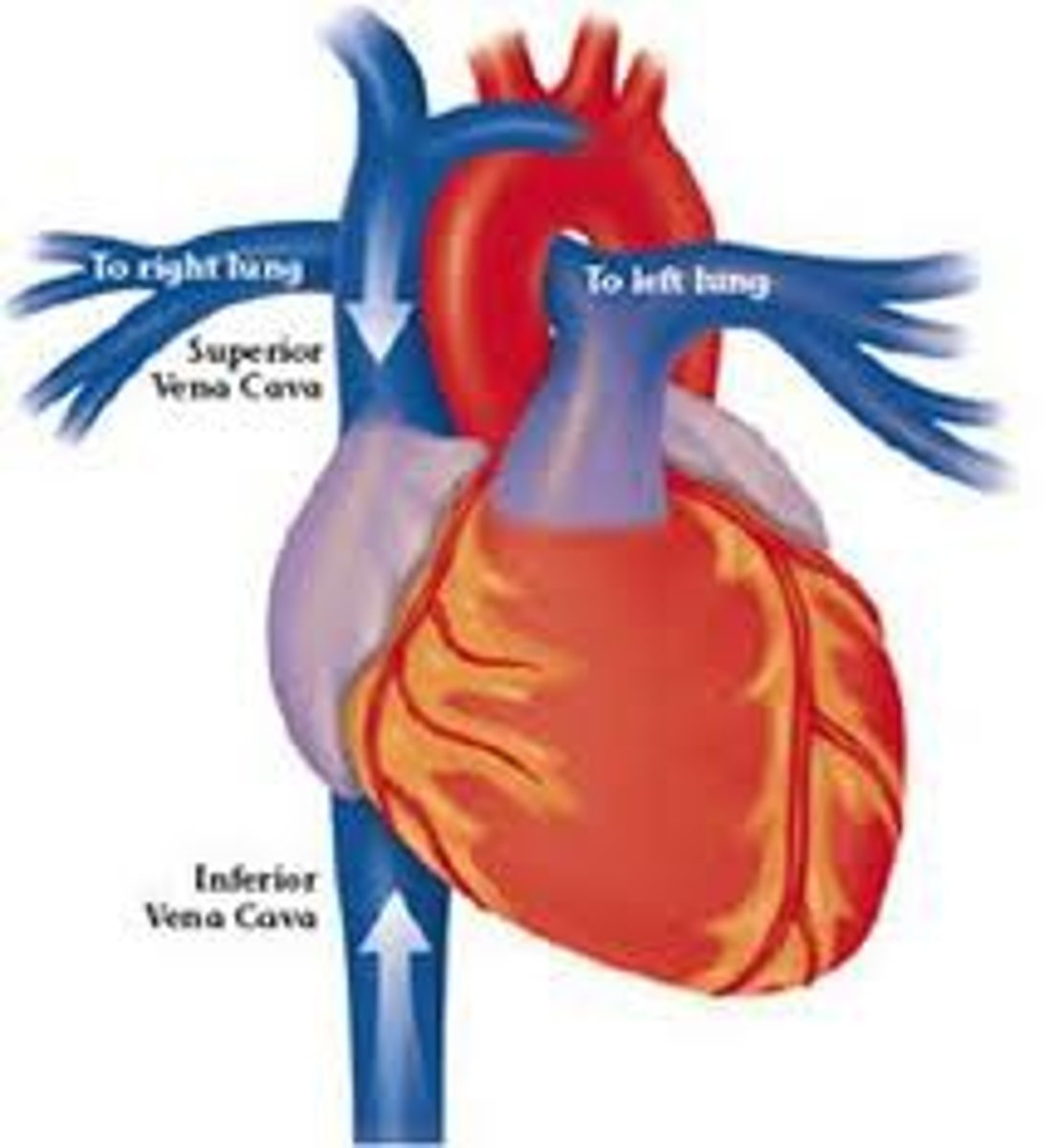
Vena cava
A large vein in the body carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart
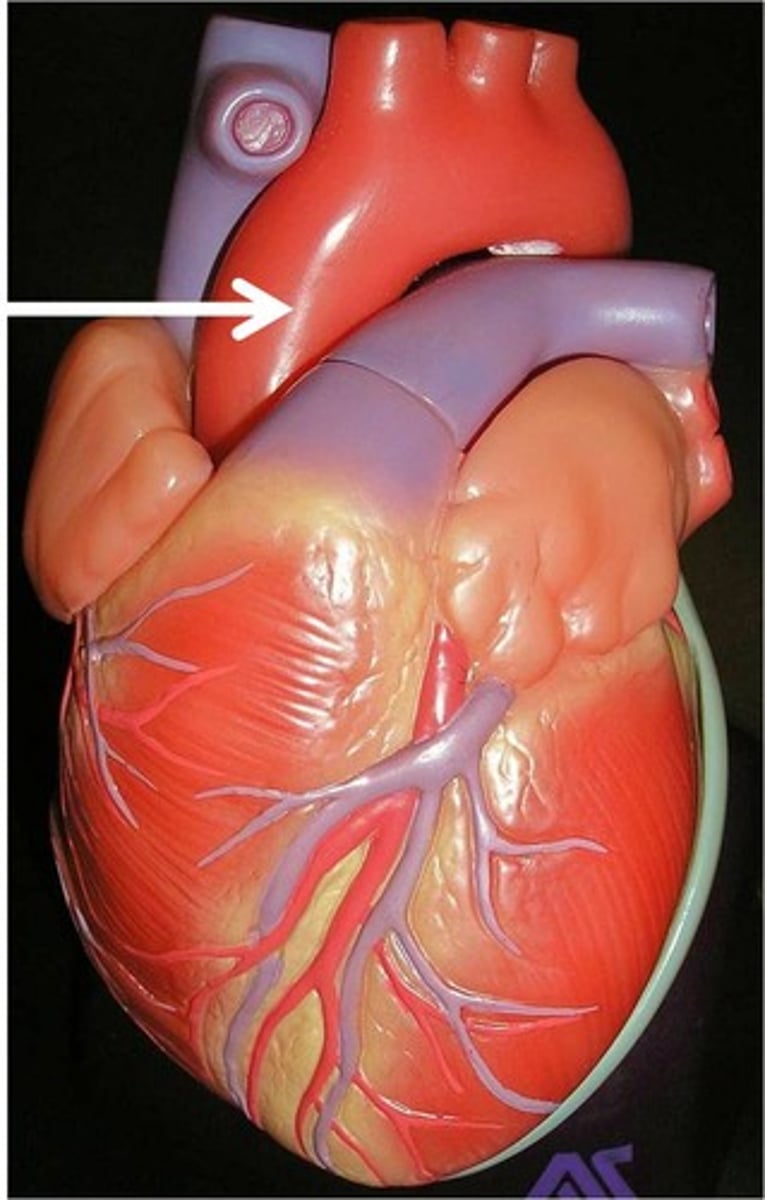
Aorta
The large arterial trunk that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to be distributed by arteries to the rest of the body cells around the body.
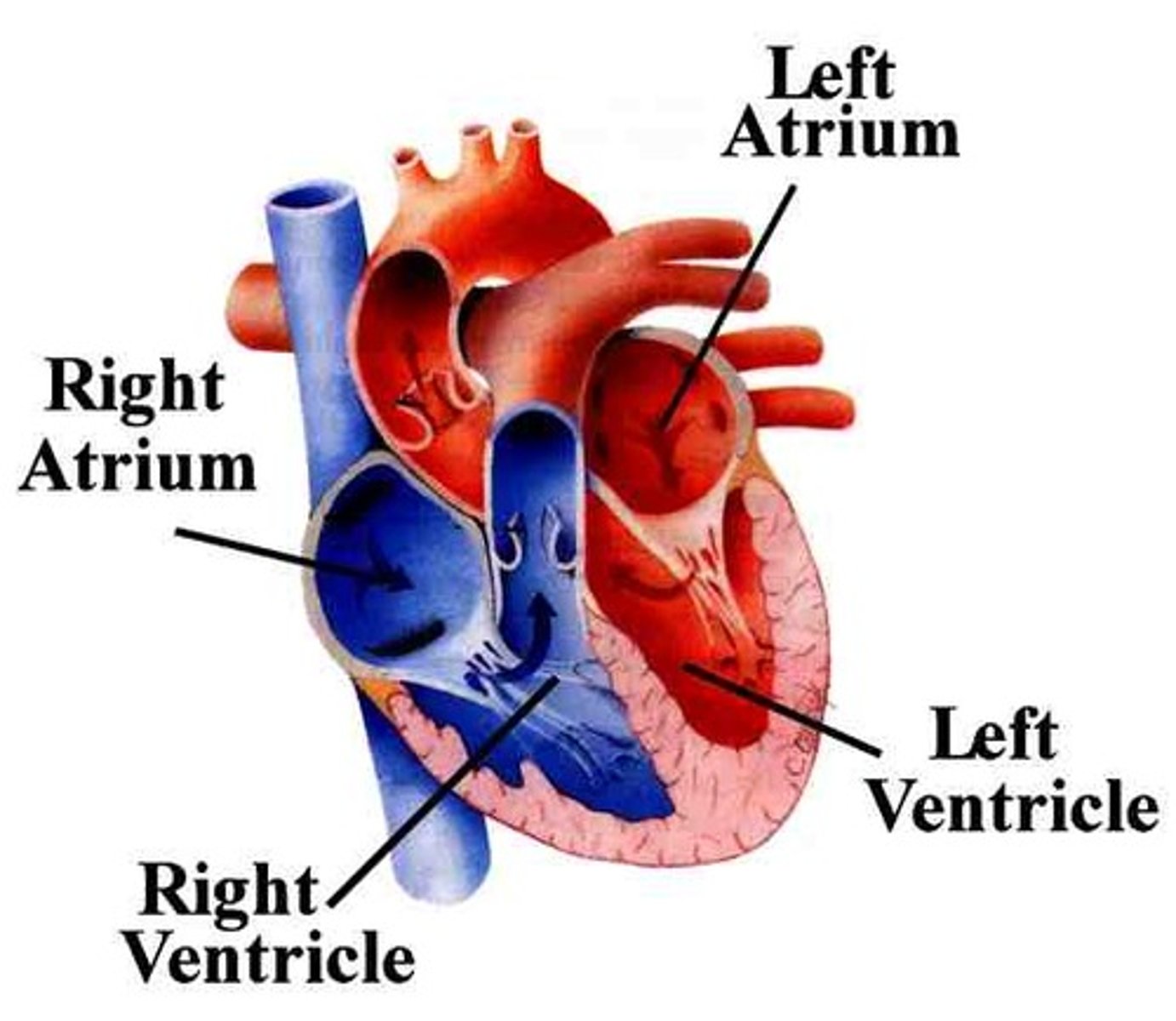
4 chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
Blood composition
Plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
Functions of blood
Transportation of nutrients, temperature regulation, protection against disease