Unit 4: AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Nation state + example
Geographic area with population area, recognition, sovereignty, people have a common culture (or nation) EX: Japan, Poland, Slovakia
Stateless nation + example
A group of people that share a common culture but aren’t a state. EX: Kuros, Basques, Scots
Multinational State + example
A state with many ethnic groups. EX: USA, Russia, China
Multi-State nation + example
Ethnic groups that are linked culturally but live in several geographically connected states. EX: Arabs, Koreans
True or false: Multi nation states spans borders
True
Autonomous region/semi autonomous region
People given a degree of freedom to run their homeland while still under the authority of a state
Sovereignty
To have complete authority over your state
What is self determination?
the process by which a country determines its own statehood and forms its own allegiances and governments.
How does self-determination impact a territory?
People have freedom to exhibit their culture, less likely to independence
Territoriality
Area of land or water that is chained by a group or individual as their own
neocolonialism
Colonized countries get pressured into giving resources to the colonizing country
How has china been using neocolonialism in Africa?
China is building infrastructure in order to export raw materials
Identify 2 problems that a country in the shatter belt region may experience
Conflict, genocide
Where is the shatter belt region?
Balkanization
Region breaking into small units
Brexit
When Britain exited the EU
Colonialism vs Imperialism
Colonialism is where one country physically exerts complete control over another country. Imperialism is formal or informal economic and political domination of one country over the other.
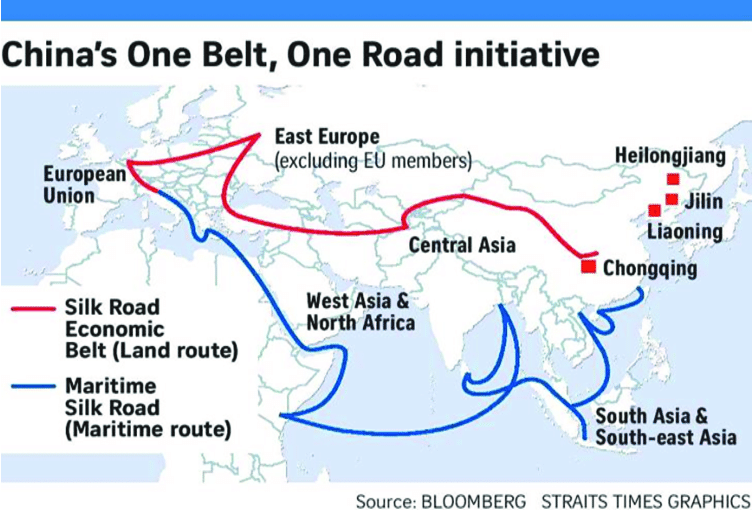
China’s one belt, one road initiative
Choke point
A choke point is a body of water that dan be closed off, and international trade could be delayed
Antecedent boundary
a boundary between two states that is created before the area is populated with human society.
Relic boundary
A boundary that is no longer there
Superimposed boundary
a political boundary that is forcibly imposed on the landscape by an outside power, without regard for existing cultural or ethnic divisions
Subsequent boundary
A boundary to group together ethnic groups; A boundary that is established after the settlement with an attempt to accommodate cultural differences
Boundary dispute
2 countries have a different idea where the boundary should be
Frontier
A zone of territory where no state has governing authority.
Locational boundary dispute
Boundary dispute over the physical location
Operational dispute
A dispute over how the boundary will function
allocational boundary dispute
A dispute over the right to resources
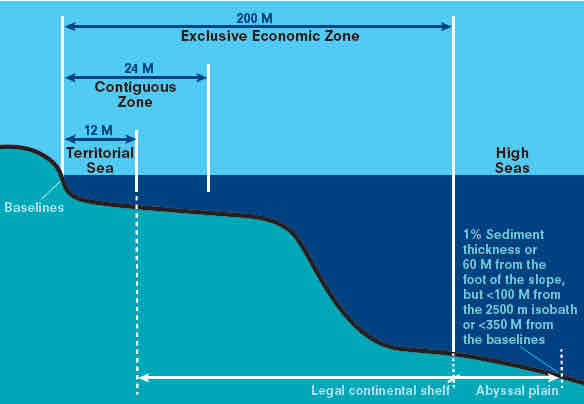
UNCLOS 200 mile EEZ
Gerrymandering
manipulate the boundaries of (an electoralconstituency) so as to favor one party or class.
2 ways gerrymandering impacts political elections
It can create unfair advantage to other running politicians
Could impact communities of color
Unitary vs federal forms of governance
Unitary has 1 level of government, federal has 2 forms
Shapes of states
Prorupt, fragmented, compact, elongated, enclave, exclave
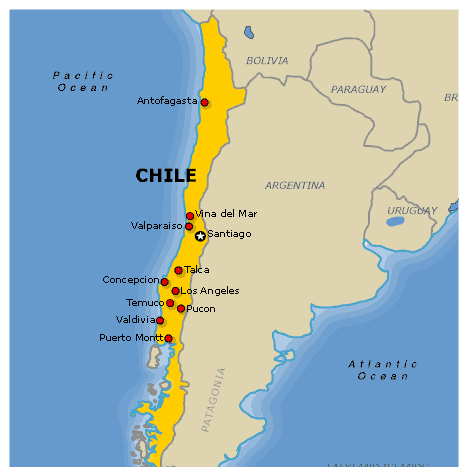
Prorupted shape
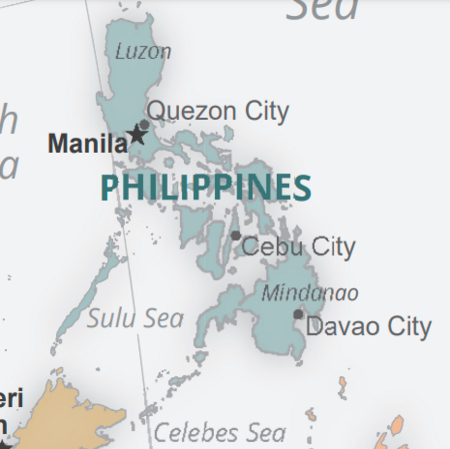
Fragmented
Elongated
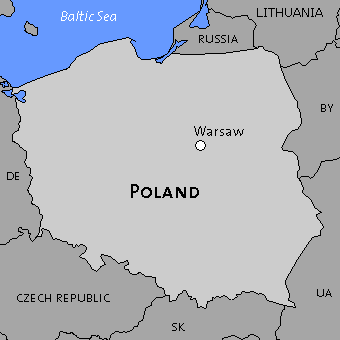
Compact
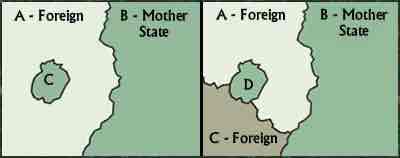
Exclave/enclave
a region of a country that is completely separated from the main body of that country, usually by the borders of another country
Devolution
The opposite of evolution. Some causes may be ethnic desires for independence, and civil war
Identify 2 Supranational organizations and explain how they impact the countries in them.
ASEAN and EU.
Countries enjoy the ‘power in numbers’ benefit but countries have to abide by what all the countries decide
Centripetal and centrifugal forces examples in political ways
Centripetal=government creates laws that are fair for all citizens
Centrifugal=ethnic minorities mistreated by police
Centripetal and centrifugal forces examples in economic ways
Centripetal=equal distribution of wealth
Centrifugal=ethnic minorities living in poverty
Centripetal and centrifugal forces examples in cultural ways
Centripetal=multiculturalism
Centrifugal=assimilation