Unit 3 - Chemistry 2024
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Why did we build our labratory calirimteers out of stryofoam
stryfoam helps keeps the contents of the calormiteter isolated form the air int he room
stryfoam reacts with acids and bases, making it managable to record temps
strydoam cups can be reused after the lb session for beverages
stryofoam contans water molecules trapped within its structure, improving its insulation
stryfoam helps keeps the contents of the calormiteter isolated form the air int he room
Which choice best describes the pauli exclusion principle?
high energy orbitals in an atom are excluded from accepting electrons
no two electrons in an atom may possess the same set of quantum numbers
the possible values of ml exclude those greater than +l and those less than -L
knowing an objects position precisely excludes us from knowing its speed
no two electrons in an atom may possess the same set of quantum numbers
diamagnetic vs paramagnetic
diamagnetic = A diamagnetic atom has a net spin of zero as all electrons are paired up in its orbitals.
paramagnetic = A paramagnetic atom has unpaired electrons, resulting in a non-zero net spin.
what is the best description of an open shell atom
it lacks the full octet in the valence shell
the ns and d orbital are completly filled
the open shell atoms are defined as alements 57=71 and 89-103
open shell atoms have one or more unpaired electrons
open sell atoms have one or more unpaired electrons
What is the big equation for finding Tf
mcdelta T = mcdelta T
bigger number - Tf, and then Tf - smaller number
what is observed when an ednothermic reaction is run in a calorimeter?
the temp of the water increases
the temp of the water decreases
if the heat capacity of the reaction chemicals is greater than water, the temp of the water increases
if the heat capacity of the reaction chemicals is greater than water, the temp of the water decreases
the temp of the water decreases
if the heat capacity of the reaction chemicals is greater than water, the temp of the water increases
When an endothermic reaction is run in a calorimeter, the most observable change is a decrease in the temperature of the calorimeter as the reaction absorbs heat from its surroundings, causing the solution inside to cool down; essentially, the calorimeter loses heat to the reaction.
what is the best description of the shape of an orbital with L=0
sphere
electron affinity for fluorine rxn
F (g) + e- → F- (g)
which is true about electromagnetic radiation
as wavelenght increases, frequency increases
as wavelenght increases, energy increases
as wavelength increases, amplitude increases
as frequency increases, energy increases
as frequency increases, energy increases
Explanation: Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional, meaning as wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and consequently, energy also decreases.
Key points:
Higher frequency = higher energy and Longer wavelength = lower energy
why do we not observe effetcs of quantum mechanics in every day life
because objects in everyday life are to massive to observe quantum behavior
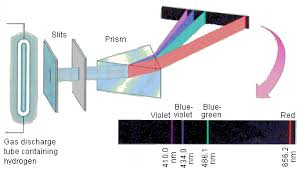
what is the best explanation for why we only see certian colors, rather than a continum of light?
light behaves as a particle, which is called a photon
blackbody radiation must be desribed using quantization to avoid the ultraviolet catastrophe
electrons in a H atom can only occupy certain orbits around the nucelus
electrons in a H atom can only adopt certain energy levels
electrons in a H atom can only adopt certain energy levels
atoms can only absorb or emit light at specific wavelengths corresponding to the energy differences between their electron energy levels
which was not observed in the photoelectric effect experiement
as light intensity increased, the speef of the ejected electrons increased
as light frequencly increased, the speed of the ejected electrons increased
as lighr wavelenght increased, the speed oft eh ejected electrons decreased
below certain light frequencies, no electrosn were emitted
which was not observed in the photoelectric effect experiement
as light intensity increased, the speef of the ejected electrons increased
When light shines on a metal, electrons can be ejected from the surface of the metal i
how does bohr’s model of the H atom differ from quantum mechanics
bohrs modeel uses wate functions while quantum mechanics uses orbiting electrons
bohrs models uses orbitiong electrons, while quantum mechanis uses wave functions
bohrs model permits and electron energy, while quantum mechanics only allow certainelectron energuies
bohrs models works for multi electron atoms, while quantum mechanics only works for Hydrogen
what is quantum mehanics
bohrs models uses orbitiong electrons, while quantum mechanis uses wave function
the application of the principles of quantum physics to study the behavior of atoms and molecules at the atomic level
how to find core electrons
To find the number of core electrons in an atom, you need to first determine the total number of electrons (based on the atomic number) and then subtract the number of valence electrons
z eff
The effective nuclear charge (Z effective or Zeff) is defined as the net positive charge pulling these electrons towards the nucleus.
electron affinity rules
right = increases
down = decreases
not noble gases (He and down)
ionization energy trends
and get elements off of I energies
right = increases
down = decreases
look for big jump, first big jump = valence electrons
rules for n, l, ml, and ms
n = 1 → infinity
l = 0 → n-1
ml = -l → +l
ms = +- ½ i think
idk
idk
each quantum number name describes?
n = principle quantum number, size
l = angular momentum quantum number, shape
ml = magnetic quantum number, orientation in space
ms = spin quantum number, describes electron spin
know how to draw electron configurations
know it
if its 4s2 and 3d 5 it becomes:
4s1 and 3d10
know condensed electron configurations
know it
know wavelengths
Gamma rays
X rays
Ultraviolet (10 nm < λ < 400
Visible (400 nm < λ < 700 nm)
Infrared (700 nm < λ < 300 µm)
Micerwave
Radio Frequency
experiment with interference pattern is a =
double slit
light sent through double slit
electrons sent through a double slit
know how to reach energy state graph
know it
exceptions for general trend ionization energy
1→ 2
2 → 13
15 → 16
going across the periodic table, we observe an exception to the general trend for electron affinity when moving from C to N. why
the electron being added to N goes into an already singly occupied orbital, so it feels extra electron-electron repulsion
(not rly sure)
remember how to draw orbitals
know it
equation for E (with wavelength stuff)
E = hc / wavelength
h = planks constant
c = speed of light
(given on exam)
to go to mols, multiply by avos number
WORK ON THE NI AND NF STUFF ASAP
WORK ON
how to find q with the enthalpy change stuff
q = mol x delta H
WORK ON SHORT ANSWER STUFF ASAP
DO IT
Q =
QH2O= -Q RXN