Human Bio Quiz: Cardiovascular, Respiratory, & Muskoseletal System
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
3 Components of Blood Pressure
Blood volume
Cardiac output
Peripheral resistance
Systolic
Pressure in arteries/veins when blood is pumping through
Diastolic
Pressure in arteries/veins when at rest
Orthostatic hypotension
Standing up too fast and feeling like you’re going to pass out
Tachycardia
Rapid heart rate
Heart rate over 100 bpm
Bradycardia
Heart rate below 60 bpm
A-fib
inconsistent
high risk of stroke s
blood thinners
can live with
Ventricular Fibrillation
Start CPR
Ventricles are not constricting as a unit. They are quivering.
Structures of the heart
Superior/inferior vena cava
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Pulmonary trunk
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Aorta
P - T
Heartbeat
QRS
Ventricular depolarization (making artial depolarization)
Female Musculoskeletal System
Shorter stature
Contoured Mandible
Thinner Skull
Slender long bones
Wide pelvis
Male Musculoskeletal System
Higher Density
Rigid Skull Features
Thicker Long Bones
Narrow Pelvis
Higher calcium deposits at muscle insertions
Joints (Articulations)
Fibrous — Skull
Cartilaginous — Intervertebral Disc
Synovial — Shoulder, elbow, hip, knee
Bones of the Lower Limb
Sacrum
Pelvic bone
Pelvic gridle
Femur
Patella
Tibia
Fibula
Tarsal bones
Metatarsal bones
Phalanges
Bones of the Upper Limb
Pectoral Girdle: Clavicle, Scapula
Humerus
Ulna
Radius
Carpal bones
Metacarpal bones
Phanlanges
Sutures
Anterior Fontanel
Coronal suture
Frontal suture
Cranial Bones (8)
Frontal bone
Parietal bone
Sphenoid bone
Ethmoid bone
Temporal bone
Occipital bone
Facial Bones (14)
Nasal bones
Lacrimal bones
Palatine bone
Zygomatic bone
Inferior nasal concha
Vomer
Maxilla
Mandible
Innate Immune System
Non-specific
Responds to everything the same way
Fast-acting
Examples:
Barriers: Skin/membrane
Cellular: phagocytes, NK cells, inflammatory response
Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
Redness (Rubor): Due to increased blood flow
Heat (Calor): Also due to increased blood flow
Swelling (Tumor): Caused by fluid accumulation in tissues
Pain (Dolor): resulting from the release of chemicals that stimulate nerve endings
Loss of function: Can occur due to pain and swelling, affecting mobility or function in the affected area
Adaptive Immune System
Respond to antigens
Cell mediated
Antibody mediated
Has “memory”
Must be exposed to specific antigen to develop this immunity
Upper Respiratory Tract
Nose
Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Lower Respiratory Tract
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchiole
Alveoli
Larynx
Vestibular folds — False vocal cords
Vocal Folds — True vocal cords → airflow and ligaments
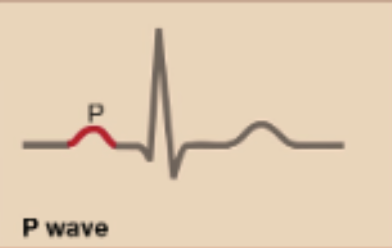
P- Wave
Atrial depolariation
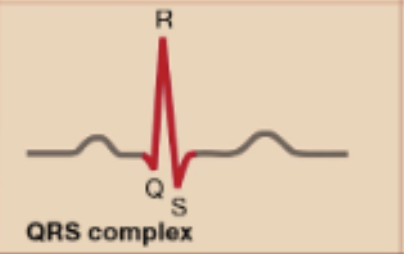
QRS Complex
Ventricular Depolarization (masking atrial repolarization)
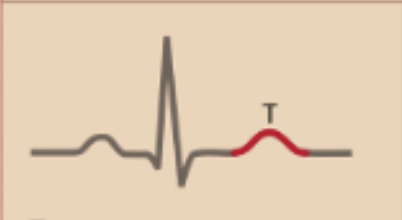
T-wave
Ventricular Repolarization
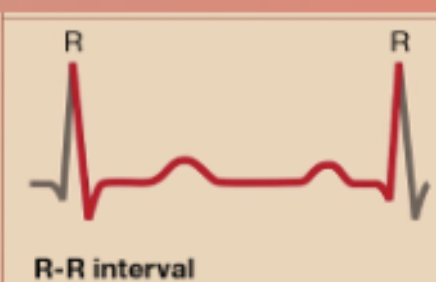
R-R Interval
Entire duration of a cardiac action potential
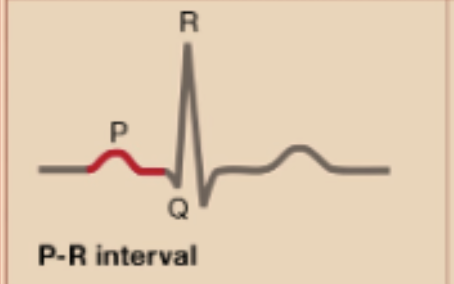
P-R Interval
Duration of atrial depolarization and AV node delay
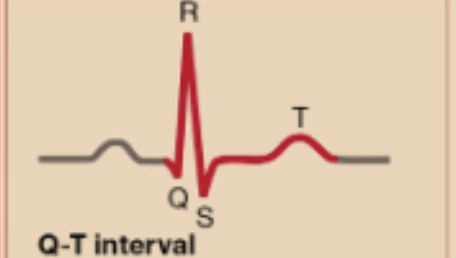
Q-T Interval
Entire Duration of a ventricular action potential
S-T Segment
Ventricular plateau phase
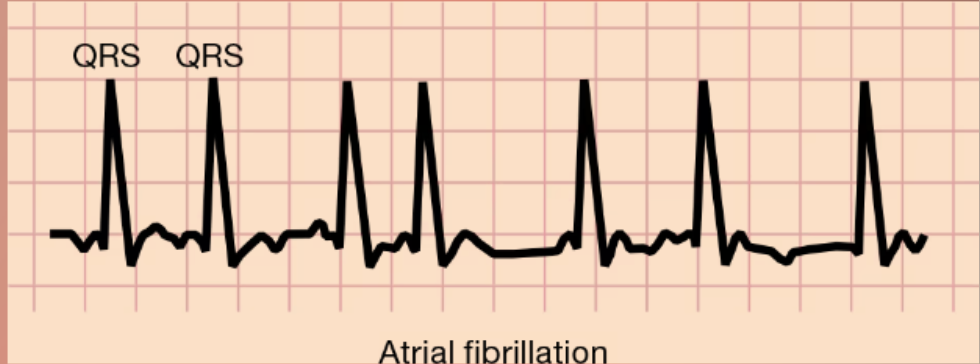
Atrial Fibrillation
Irregular, rapid heartbeat
The upper right chamber of the heart quivers instead of beating normal
Blood is still pumping through the body
Can live with
SA Node (Sinoatrial node)
Where normal electrical activity
Atrial contraction
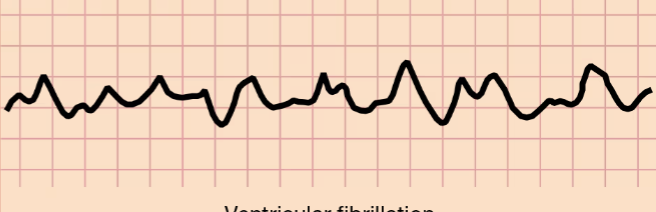
Ventricular Fibrillation
The lower chambers of the heart quiver, preventing blood from being pumped through the body.
START CPR
Muscle Shapes
Parallel
Circular
Pennate
Convergent
Fusiform
Example of Parallel Muscle Shape
Sartorius
Example of Convergent Muscle
Pectoralis
Example of Pennate Muscle Shape
Uni, bi, multi
Flexor pollicis longus
Rectus femoris
Deltoid
Example of Circular Muscle Shapes
Sphincters
Example of Fusiform Muscle Shape
Biceps
Scoliosis
Sideways curvature of the spine
Lordosis
Exaggerated inward curvature of the spine
Think Trump
Kyphosis
Excessive outward curvature of the upper spine