Honours Biology: Mitosis
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Last updated 12:23 AM on 1/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
Binary Fission
How prokaryotes like bacteria and archaea reproduce
2
New cards
Chromosome
the structure that contains most of the cell’s DNA and is duplicated before the parent cell splits. One set goes to each daughter cell
3
New cards
asexual reproduction
the creation of genetically identical offspring by a single parent, without the participation of a sperm and egg
ex: yeast, a sea star, certain hosue plants
ex: yeast, a sea star, certain hosue plants
4
New cards
sexual reproduction
reproduction that requires fertilization of an egg by a sperm, producing variations
5
New cards
interphase
when a cell’s metabolic activity is very high and the cell performs various functions within the organism, a cell spends 90% of its time here
6
New cards
cell cycle
an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two cells
7
New cards
G2 phase
when the cell grows in preparation for mitosis
8
New cards
mitotic phase
the part of the cell cycle when the cell actually divides, only 10% of the cell cycle is spent here
9
New cards
apoptosis
cell self-destruction, occurs when the cell cannot fix the problem preventing it from moving past the checkpoint
10
New cards
G0 phase
where cells still perform cell functions but do not divide and is either temporary because it does not have the right resources at the moment or is permanent (ex: neurons)
11
New cards
S phase
here the cell grows and chromosomes are duplicated, resulting in sister chromatids
12
New cards
G1 phase
in this subphase of interphase, the cell grows
13
New cards
chromatin
the name for DNA when it is stretched out and in its loose form
14
New cards
sister chromatids
the result of chromosome duplication, two identical copies of the DNA molecule
15
New cards
centromere
the “waist” where the two sister chromatids are joined
16
New cards
centrosomes
only found in animal cells; clouds of cytoplasmic material that contain pairs of centrioles
17
New cards
cleavage furrow
a shallow indentation in the cell surface, the first sign of the process by which cytokinesis occurs in an animal cell
18
New cards
cell plate
vesicles within a plant cell fuse ti form this membranous disk during cytokinesis
19
New cards
anchorage dependence
when a cell must be in contact with a solid surface to divide
20
New cards
malignant tumor
an abnormally growing mass of body cells that can spread into neighbouring tissues n other parts of the body, displacing normal tissue and interrupting organ function
21
New cards
benign tumor
abnormally growing mas of body cells that remains at the original site
22
New cards
metastasis
the spread of cancer cells beyond their original site
23
New cards
gametes
egg and sperm- cell division for these occur only in reproductive organs and has one half as many chromosomes as the parent cell
24
New cards
cell division
cell reproduction and results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the original parent cell
25
New cards
mitotic spindle
a football shaped structure of microtubules that guide the separation of the two sets of daughter chromosomes
26
New cards
growth factor
a protein secreted by certain body cells to tell other body cells to divide
27
New cards
carcinomas
cancers that originate in the external or internal coverings of the body
Ex: cancer of the skin or lining of intestines
Ex: cancer of the skin or lining of intestines
28
New cards
density-dependent inhibition
a phenomenon in which crowded cells stop dividing because they have filled up the space
29
New cards
leukemias and lymphomas
cancers of blood forming tissues, such as bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes
30
New cards
sarcomas
cancers in tissues that support the body, such as bone and muscle
31
New cards
How do some cancer cells divide constantly?
they ignore the checkpoints because they have deflective control systems and can also synthesize their own growth factors
32
New cards
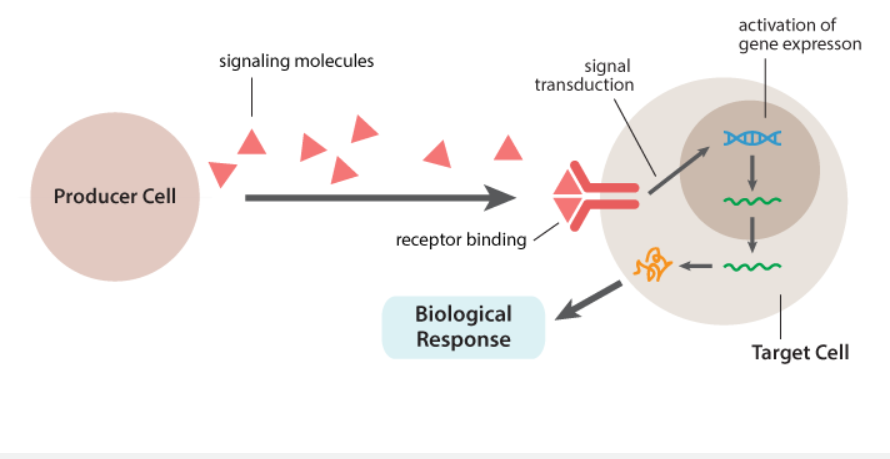
what does this image show?
A cell receiving a signal, or growth factor
33
New cards
At which of the checkpoints in the Cell Cycle do chromosomes exist as duplicates sister chromatids?
G2 and M (answer to a question)
34
New cards
When is an individual said to have cancer?
When their tumor is malignant (answer to a question)
35
New cards
The body cells of an elephant have 56 chromosomes. If an elephant’s skin cell with 56 chromosomes divides b mitosis, each daughter cell will have ________ chromosomes.
56 (answer to a question)
36
New cards
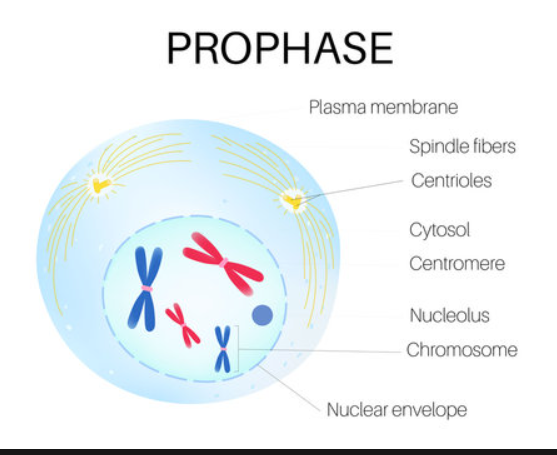
What phase of the cell cycle is this?
Prophase (answer to a question)
37
New cards
What is a characteristic that distinguishes cancerous cells from normal cells? (answer is not about differences in how fast the cells divide)
cancer cells do not have density-dependent inhibition, so they will continue to grow and pile up (answer to a question)
38
New cards
Compared to a control culture, the cells in an experimental culture are fewer but much larger in size when they cover the dish surface and stop growing. What is a reasonable hypothesis for this difference?
The experimental culture is deficient in one or more growth factors
(answer to a question)
(answer to a question)
39
New cards
What’s the difference between cytokinesis in plant and animal cells?
Animal cells have cleavage furrow while plant cells have cell plates that they create during cytokinesis (answer to a question)
40
New cards
You view an animal cell through a microscope and observe dense, duplicated chromosomes scattered throughout the cell. Which state of mitosis are you looking at?
Prophase, in prophase the chromosomes have duplicated and are condensed but are not yet aligned (answer to a question)
41
New cards
A researcher treats cells with a chemical that prevents DNA synthesis from starting. This treatment would trap the cells in which part of the cell cycle?
G1 (answer to a question)
42
New cards
What must a cell do before it can undergo cell division?
The DNA must be compacted into manageable packages (answer to a question)
43
New cards
What happens in mitosis?
the nucleus and its contents (most importantly, chromosomes) are divided and equally distributed, forming daughter nuclei (answer to a question)
44
New cards
What cells in the human body do not divide?
mature muscle cells; ex: cells in the heart and brain not repairing after injury (answer to a question)
45
New cards
What phase of the cell cycle does the cell spend most of its time in?
Interphase (answer to a question)
46
New cards
What are the two main stages of the cell cycle?
Interphase (when growing happens) and mitotic phase (when cells divide)
(answer to a question)
(answer to a question)
47
New cards
What happens during interphase?
cell makes more, cytoplasm, cytoplasmic organelles (like mitochondria and ribosomes), increases supply of proteins, grow in size, and duplicates chromosomes (answer to a question)
48
New cards
Where does a chromosome consist of two identical chromatids?
after chromosome duplication and before chromosome distribution (answer to a question)
49
New cards
3 steps of Binary fission
1. chromosomes are duplicated and separate
2. Cell becomes elongated and chromosomes move
3. cell divides into two daughter cells (answer to a question)
50
New cards
Why is it necessary for chromatins to form chromosomes before division?
When the chromatins condense into chromosomes it makes things easier to transport, its like whe someone is moving and packs all of their things into boxes (answer to a question)
51
New cards
What happens during cytokinesis?
This stage begins before mitosis ends, the cytoplasm is divided into two (answer to a question)
52
New cards
Do prokaryotes go through mitosis?
No- mitosis is unique to eukaryotes (answer to a question)
53
New cards
What is different about cancer cell division and regular cell division?
Cancer cells do not stop at checkpoints and are uncontrolled, communicate, carry out normal cell functions, and anchor. They also can make their own growth factors- taking nutrients away from other cells (answer to a question)
54
New cards
Why is binary fission classified as asexual reproduction?
because its genetically identical to its singular parent cell (answer to a question)
55
New cards
How do multicellular organisms grow?
They produce more cells (answer to a question)
56
New cards
What are the 3 subphases of interphase, in order?
G1, S, G2 (answer to a question)
57
New cards
Where is the third checkpoint in the cell cycle and what does it check for?
This checkpoint is in the M phase of mitosis and makes sure the chromosomes are aligned and attached to the spindle correctly. (answer to a question)
58
New cards
Where is the first checkpoint in the Cell Cycle and what does it check for?
It is in G1 and checks that the DNA is not damaged,cell growth, and that the cell has the resources needed to move on (answer to a question)
59
New cards
What are the overlapping phases of the mitotic phase?
cytokinesis and mitosis (answer to a question)
60
New cards
How does chemotherapy work?
It attacks cells that divide frequently; someone undergoing chemotherapy will lose their hair because hair follicles divide frequently, so the chemo attacks it
61
New cards
Where is the second checkpoint in the cell cycle and what does it check for?
It is in G2 and checks that the DNA has replicated correctly, that the cell has grown, and that it has what it needs to move on