Science membranes and Trasport
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
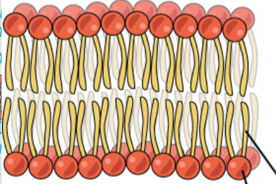
What is phospholipid bilayer
The fundamental structure of phospholipids creating the layer of cell membrane.
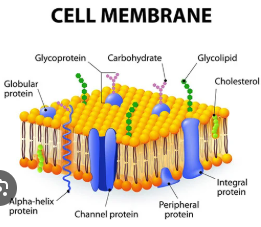
What is plasma membrane (cell membrane)?
a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds every cell, separating its internal contents from the outside environment
What is Solute
the one the is getting dissolved
What is Solvent
The one that does the dissolving
Solution
the mixture of the chemical reaction
Equilibrium
equally concentrated on both sides of the membrane
Passive transport
no extra energy needed
high to low concentration gradient
goes down the concentration gradient
Active Transport
Energy (ATP)
Moves from low to high concentration
Goes against (up) the concentration
Function of Cell Membrane
Provides protection for the cell by keeping harmful substances out and keeping harmful substance out
transports molecules and ions into the cell and waste out the cell 1. ^Semiperimeable ^
Osmosis
The simple diffusion of water across the cell membrane
water moves down the concentration gradient until equilibrium is reached
high to low concentration
Concentration
the amount of a substance (solute) within a specific volume of a mixture or solution

Concentration Gradient
the difference in the concentration of a substance between two areas
Endocytosis
Uses vesicles to move large particles into the cell (phagocytosis and Phinocytosis)
Phagocytosis
cell “eating”
engulfs solids
Phinocytosis
cell “drinking”
engulfs liquids
Diffusion
The spreading out of molecules across a membrane until equilibrium is reached. Passive (O2 AND CO2)
Protein Pumps
Active, K+,Na+,Ca2+, Cl- Muscle contractions and nerve signal conduction
Facilitated Diffusion
a transport protein that helps facilitate the diffusion that can’t pass through the cell membrane
Tonicity
relative solute of a solutions (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic
Hypertonic
water in solution is lower than cells cytoplasm ; cell shrivels; plants generating turgor pressure
Hypotonic
water in solution is higher than cells cytoplasm; cells swell
Isotonic
water in solution is equal amount as the cell cytoplasm; animals
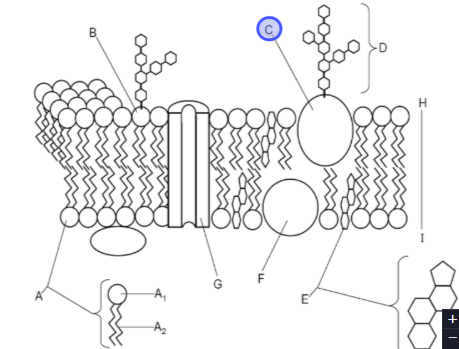
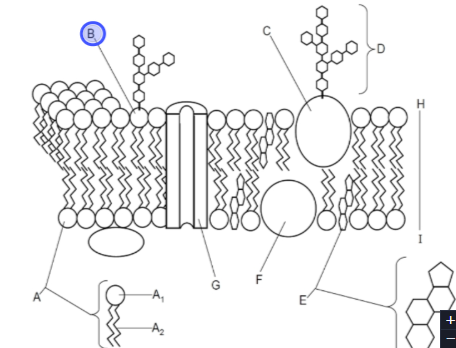
What is this
Glycoprotein
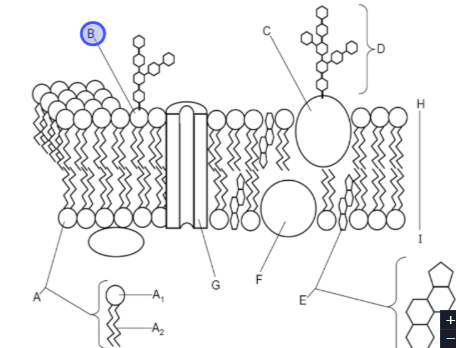
What is this
Glycolipid
Important equation
C1*V1=C2*V2 (concentration swelling before*volume swelling before=concentration swelling after*volume swelling after)
Facilitated Diffusion substances transported in what way
glucose
Diffusion substances transported in what way
CO2 and O2
Osmosis substances transported in what way
water
Endocytosis substances transported in what way
captures bacteria
Exocytosis substances transported in what way
Neurotransmitters
What cannot pass through the plasma membrane with the help of transport proteins
ions and sodium
Plasma membrane is mainly made out of
Proteins and phospholipid
How does the molecules enter and leave the cell without the use of the cell’s energy
Molecullar Transport- Small molecules and ions are carried across the membranes by protiein
Bulk Transport- larger molecules and even solid clumps of material depending on size and shape
Endocytosis
exocytosis