AP Psychology Unit 2: Cognition (Memory)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
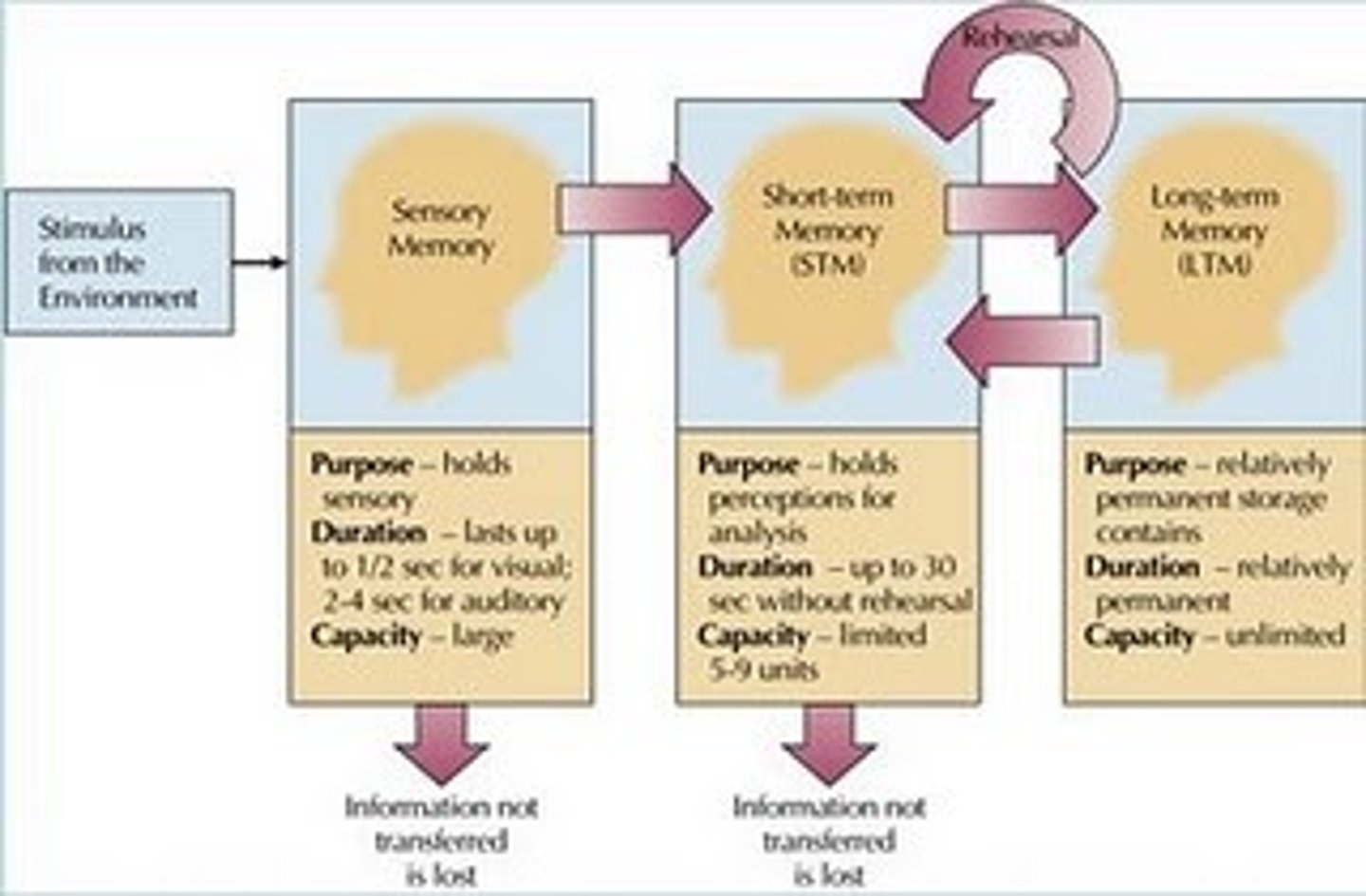
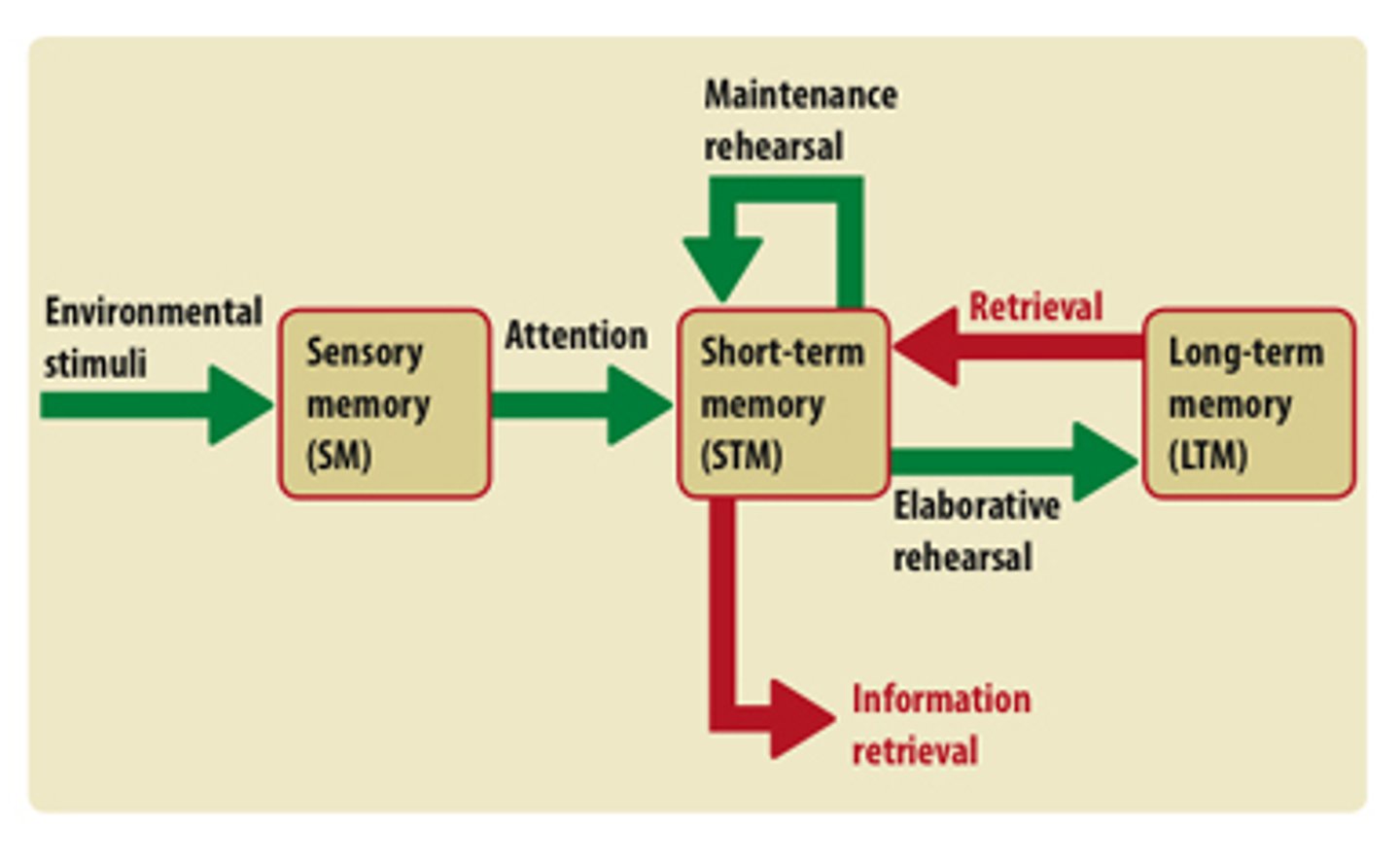
Sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
Short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten
Working memory
the part of memory that holds a limited amount of information at the ready for immediate use

Long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system; includes knowledge, skills, and experiences

Maintenance rehearsal
repeatedly verbalizing or thinking about a piece of information; allows information to be held from 20-30

Elaborative rehearsal
transferring something to long-term memory by thinking about its meaning, as opposed to simply repeating it over and over
Memory retention
the ability to retain and use information

Autobiographical memory
a form of episodic memory consisting of a person's recollections of his or her life experiences

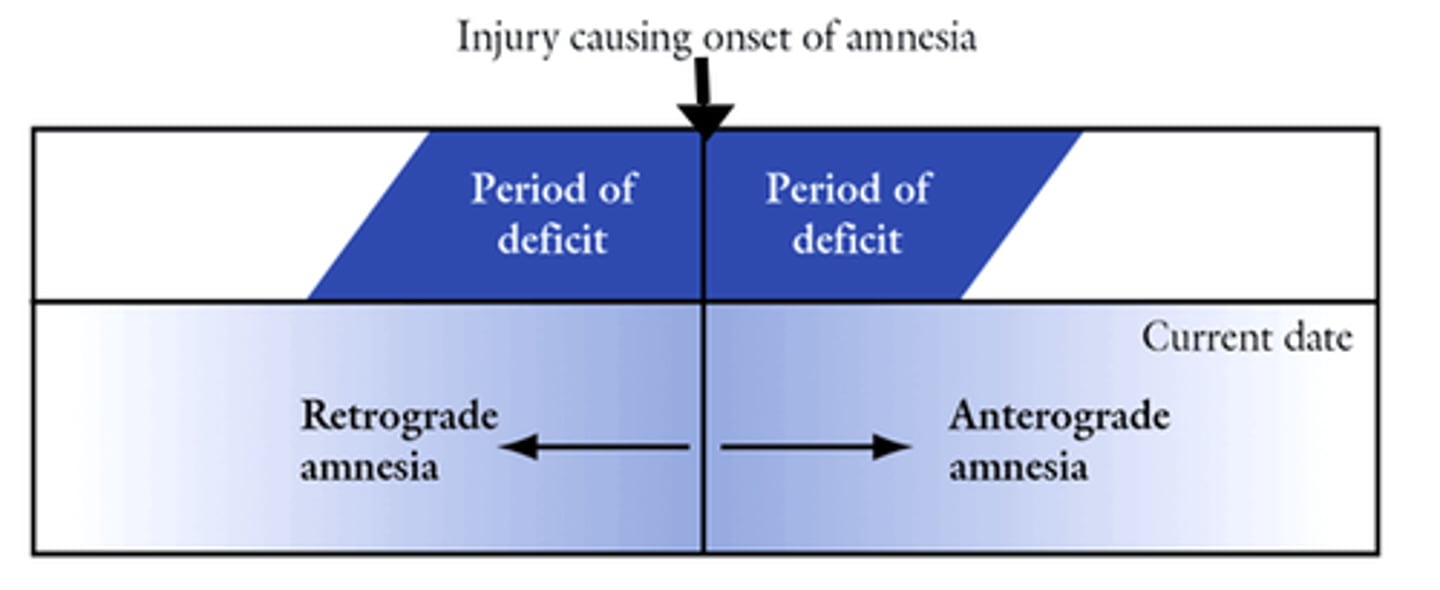
Retrograde amnesia
loss of memory from the point of some injury or trauma backwards, or loss of memory for the past
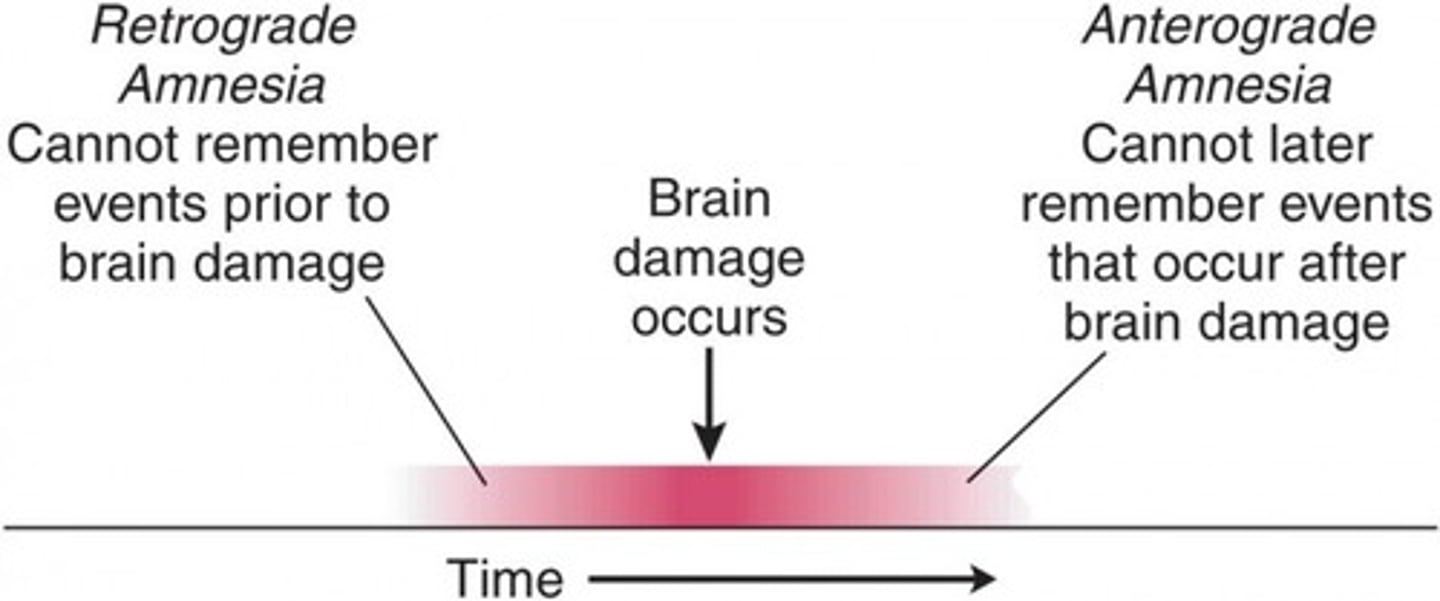
Anterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories while still maintaining past memories
Alzheimer's disease
a specific type of dementia characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive decline

Infantile amnesia
inability of adults to remember personal experiences that took place before an early age

Retrieval
the process of bringing to mind information that has been previously encoded and stored
Recall
retrieving information from past learning or experience without a memory cue

Recognition
identifying information previously learned, as on a multiple-choice test

Retrieval cues
stimuli that aid the recall or recognition of information stored in memory

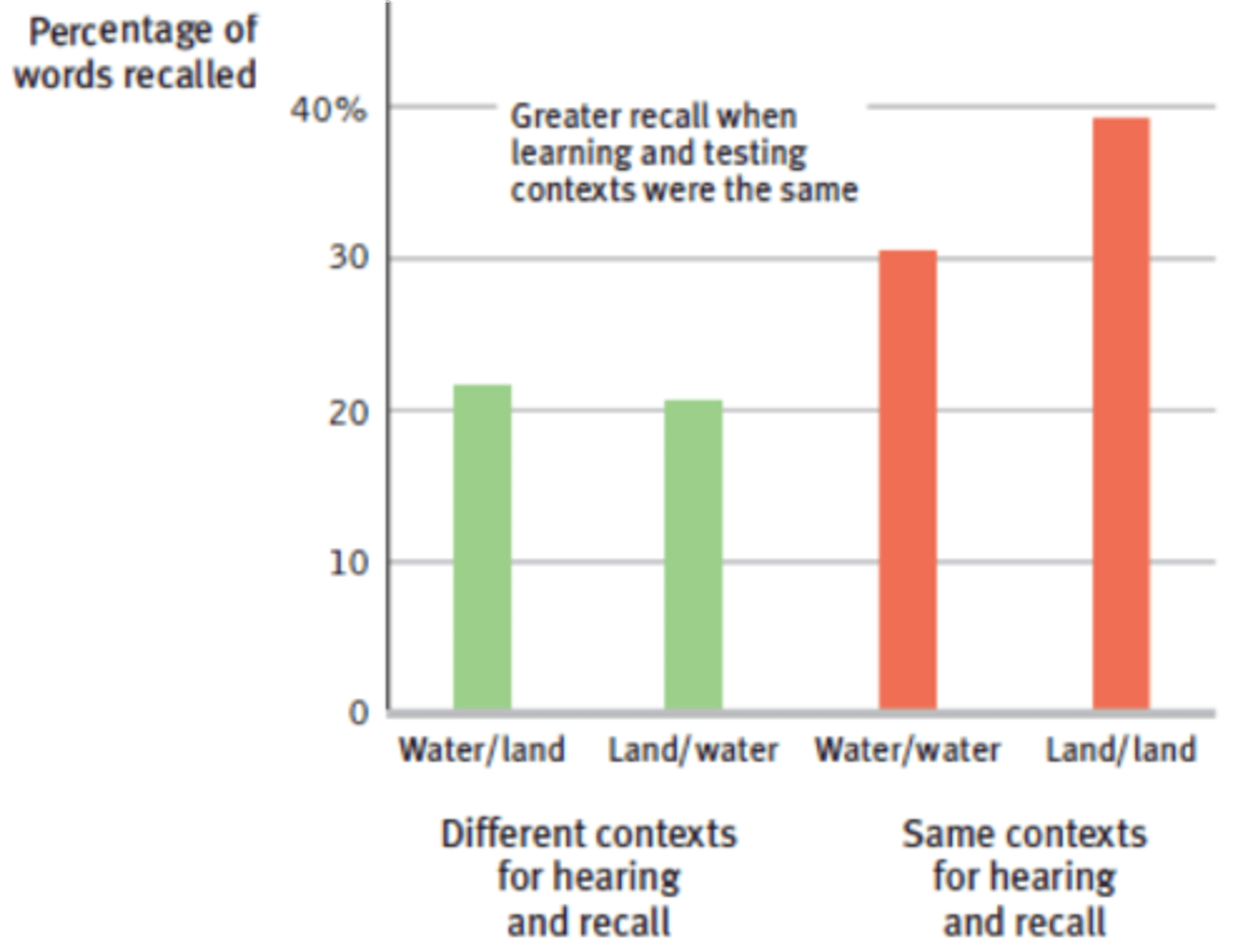
Context-dependent memory
the theory that information is better remembered when when a person is present in the same environment in which the original memory was formed
Mood-congruent memory
a phenomenon that explains how a person is able to recall a memory in more detail if it coincides with their mood at the current time

State-dependent memory
a phenomenon that explains why a memory is improved when the person is in the same biological or psychological state as when the memory was initially formed

Testing effect
the phenomenon that testing an individual's memory makes the memory stronger and easier to retrieve

Metacognition
the phenomenon that learners can improve retrieval by understanding and regulating their own learning process, including their beliefs about learning

Forgetting curve
a mathematical formula by Ebbinghaus that demonstrates the rate at which information is forgotten over time if there is no attempt to retain it
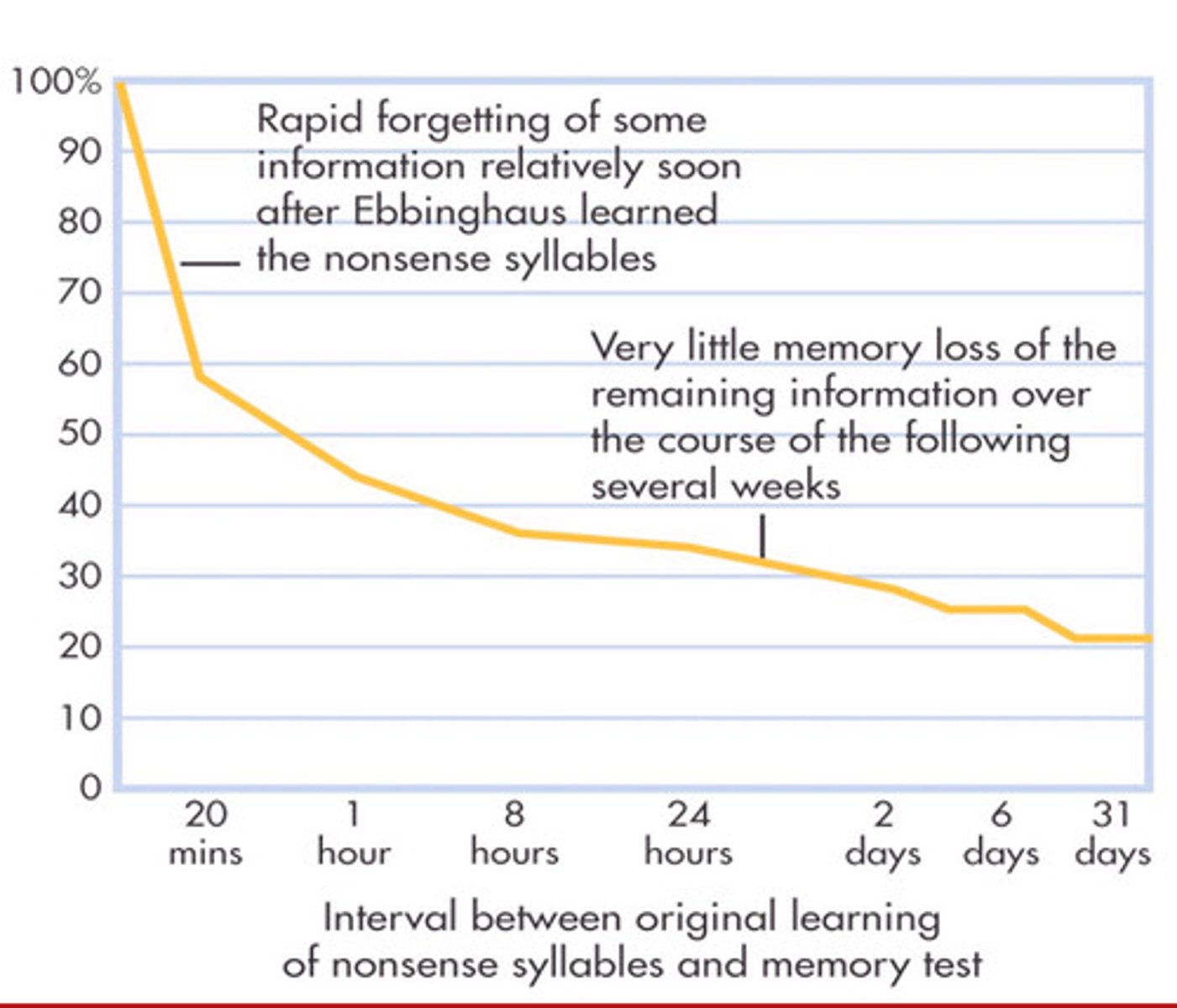
Encoding failure
the inability to recall specific information because of insufficient encoding for storage in long-term memory

Proactive interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information
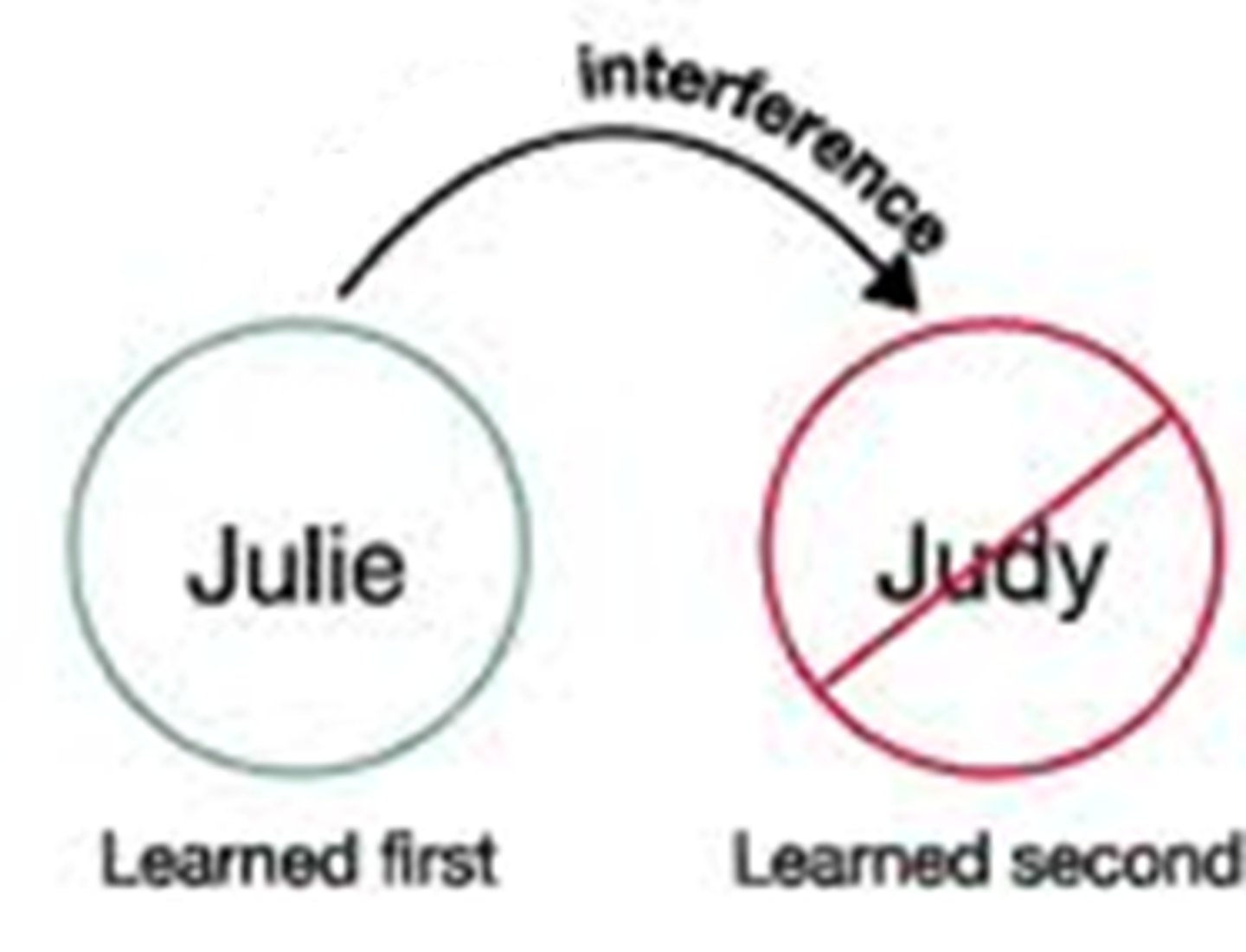
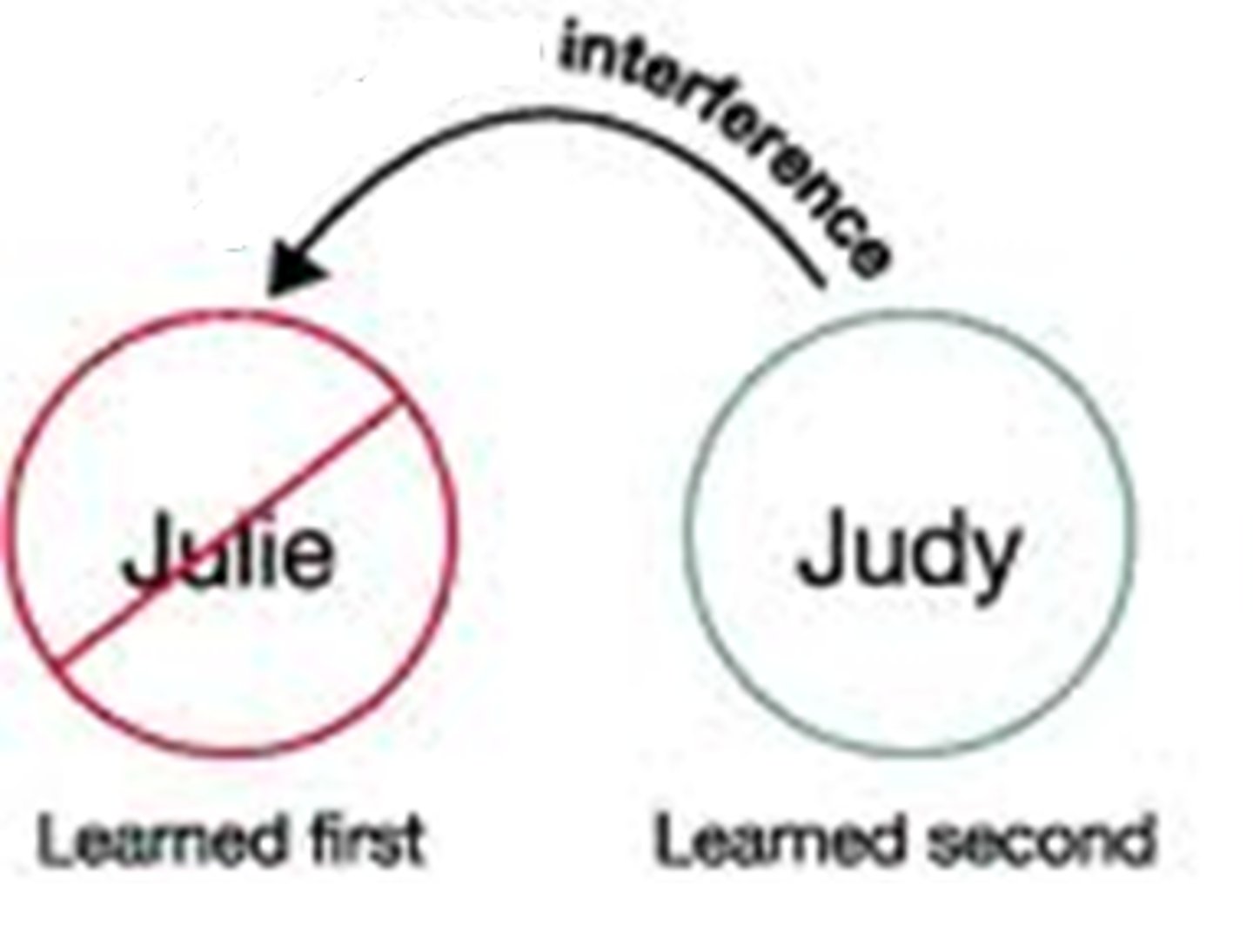
Retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information
Tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon
the temporary inability to remember something you know, accompanied by a feeling that it's just out of reach

Repression
a theory that information or memories can be forgotten to defend the mind from distress

Misinformation effect
when misleading information encountered after an event has corrupted one's memory of the event
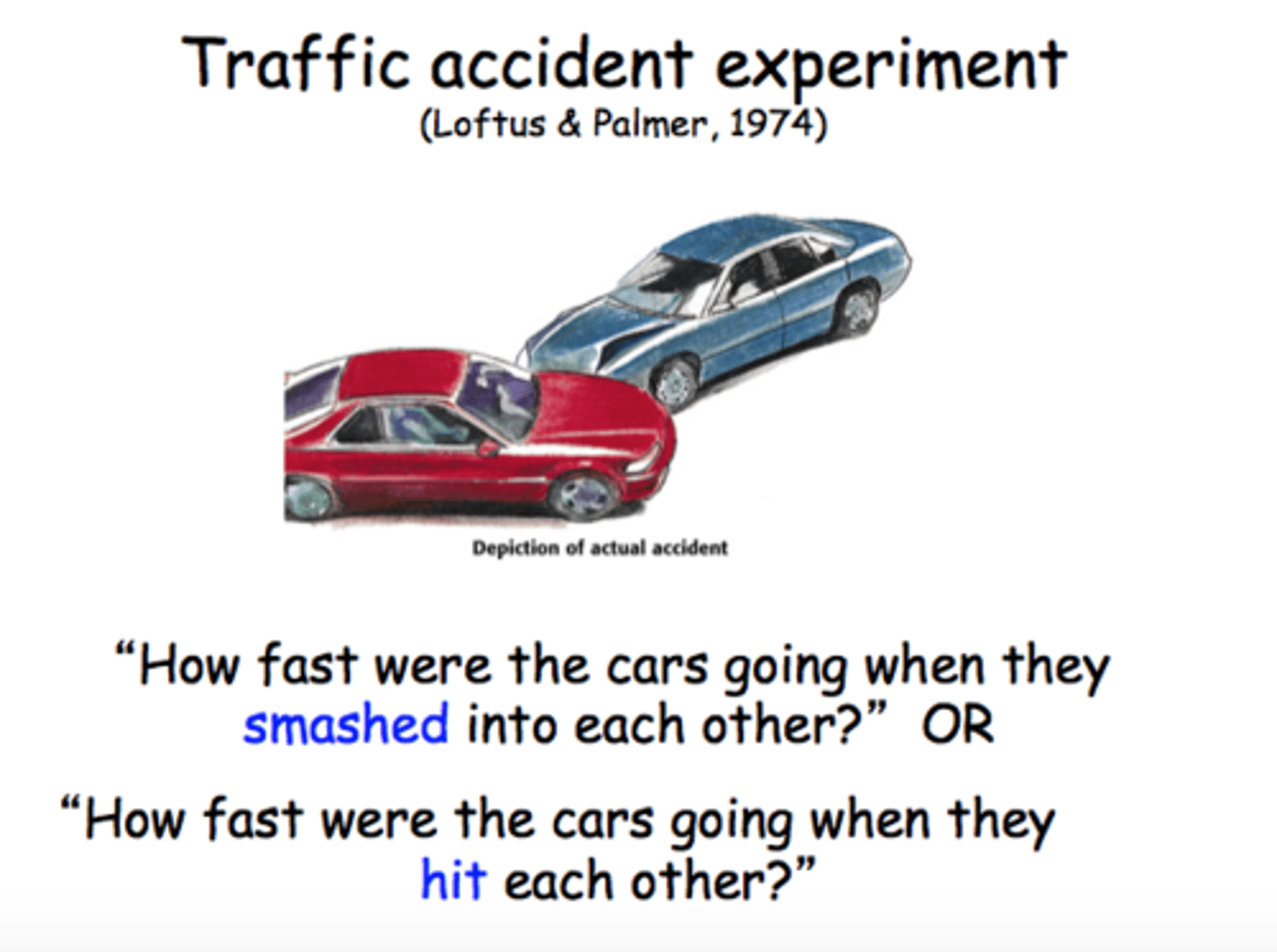
Source amnesia
the inability to recall where, when, or how one has learned something

Constructive memory
the theory that memories may not fully recall what actually happened since they can be "updated" by new information that is inaccurate
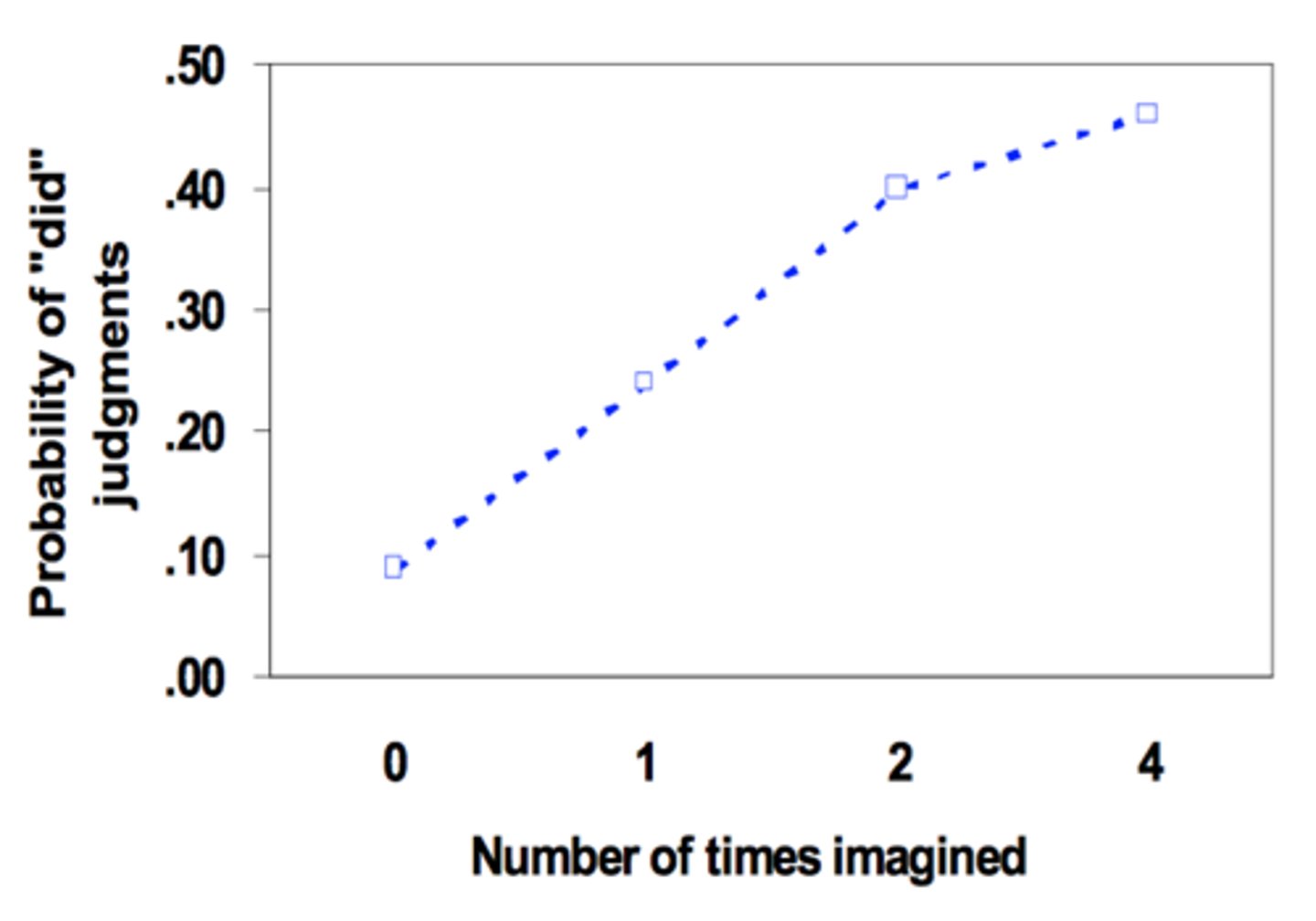
Imagination inflation
a phenomenon in which vividly imagining an event (that may not have happened) greatly increases one's confidence that the event actually occurred