Emergency Care and Transportation of the Sick and injured
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
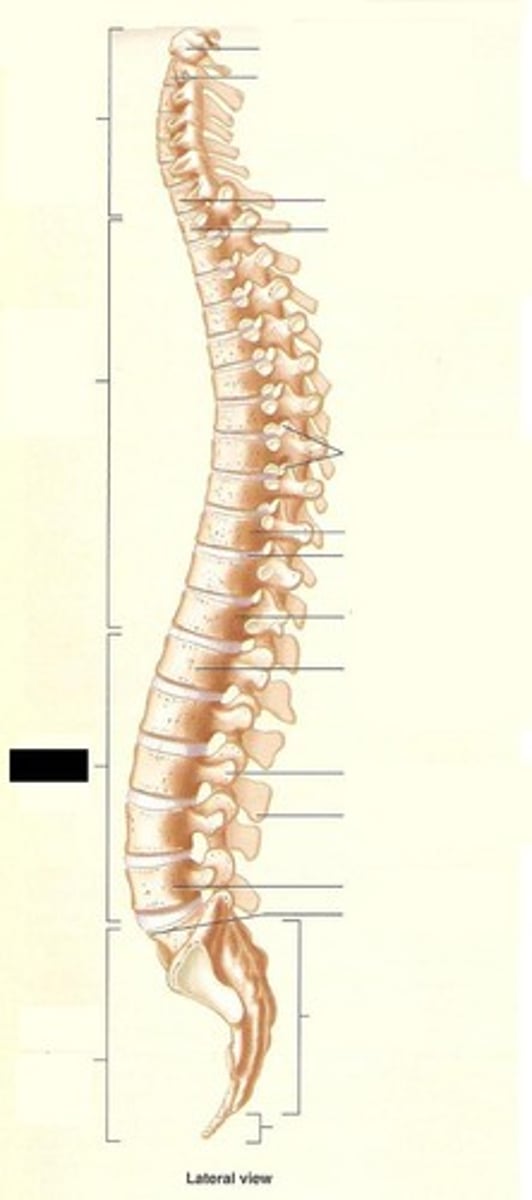
Vertebrae
The bones of the vertebral column
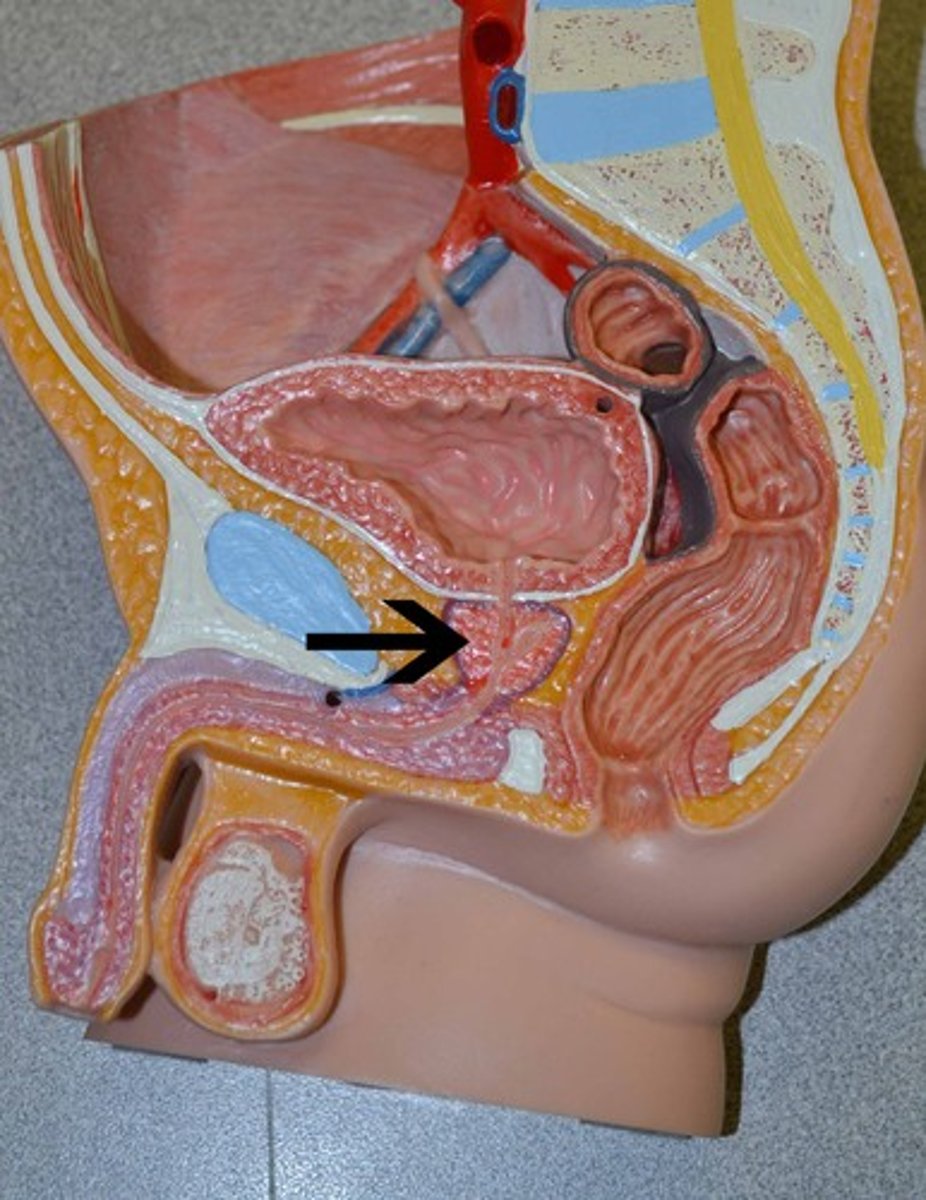
prostate gland
A small gland that surrounds the male urethra where it emerges from the urinary bladder; it secretes a fluid that is part of the ejaculatory fluid.
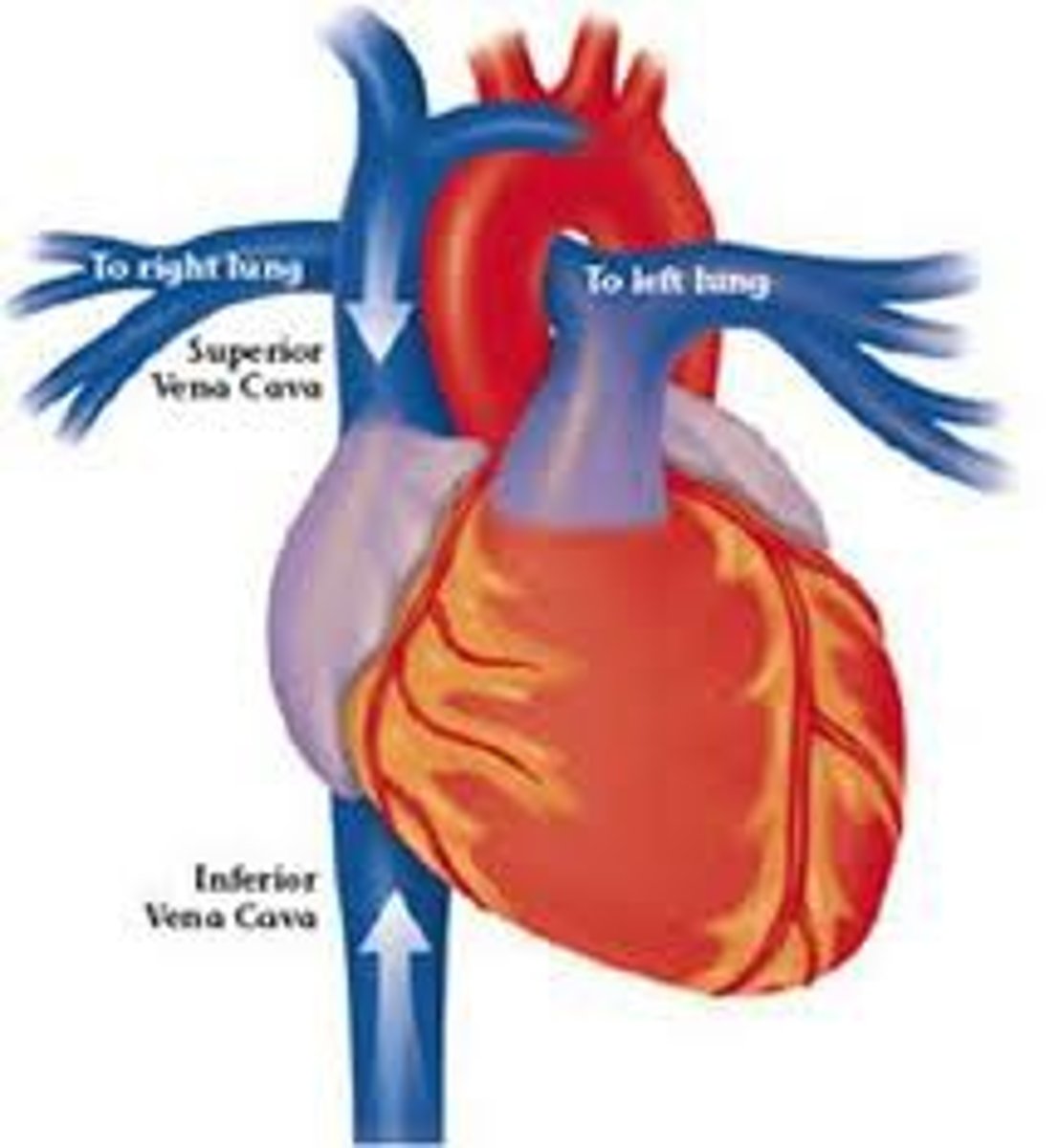
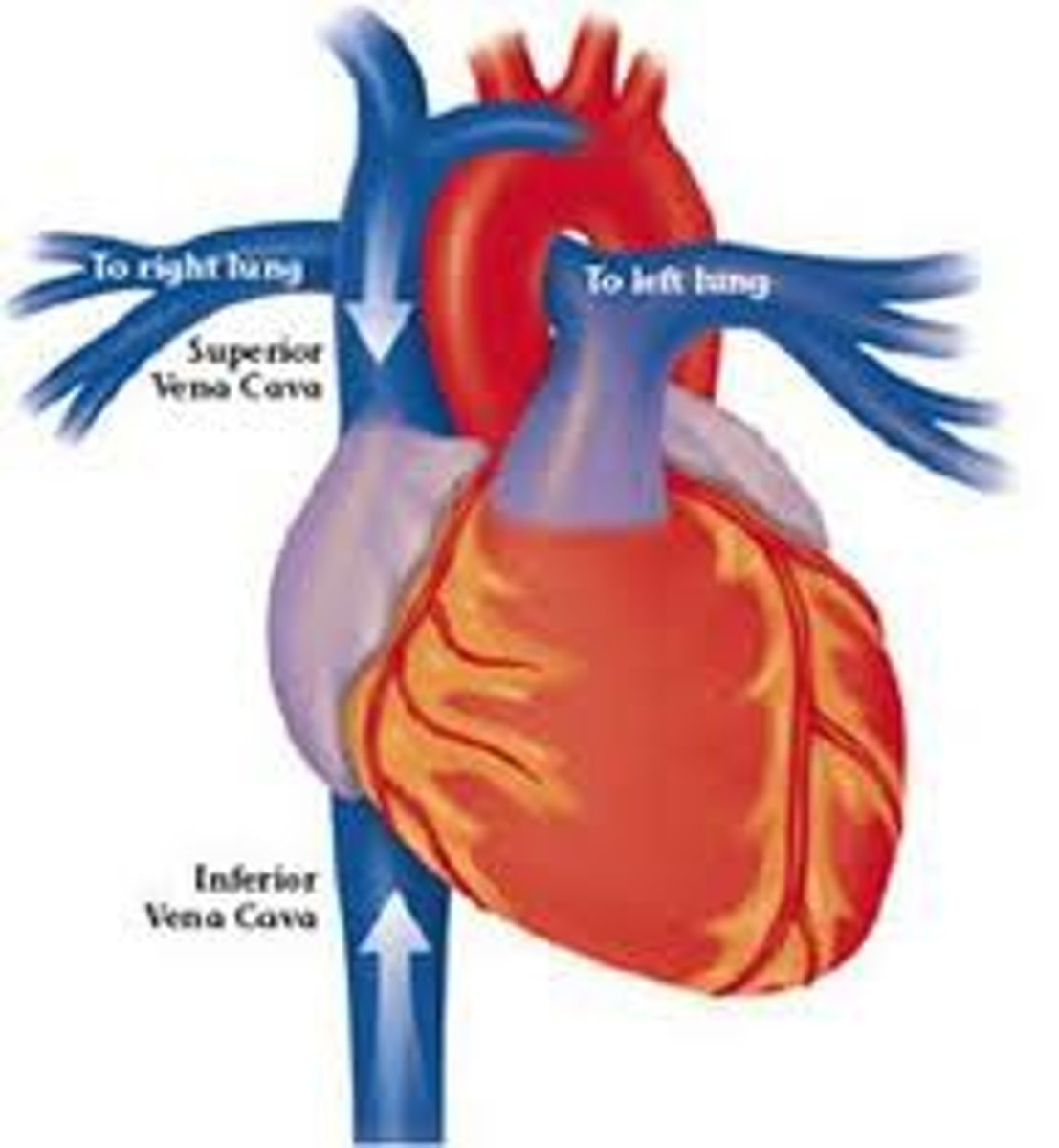
inferior vena cava
One of the two largest veins in the body; carries blood from the lower extremities and the pelvis and the abdominal organs to the heart
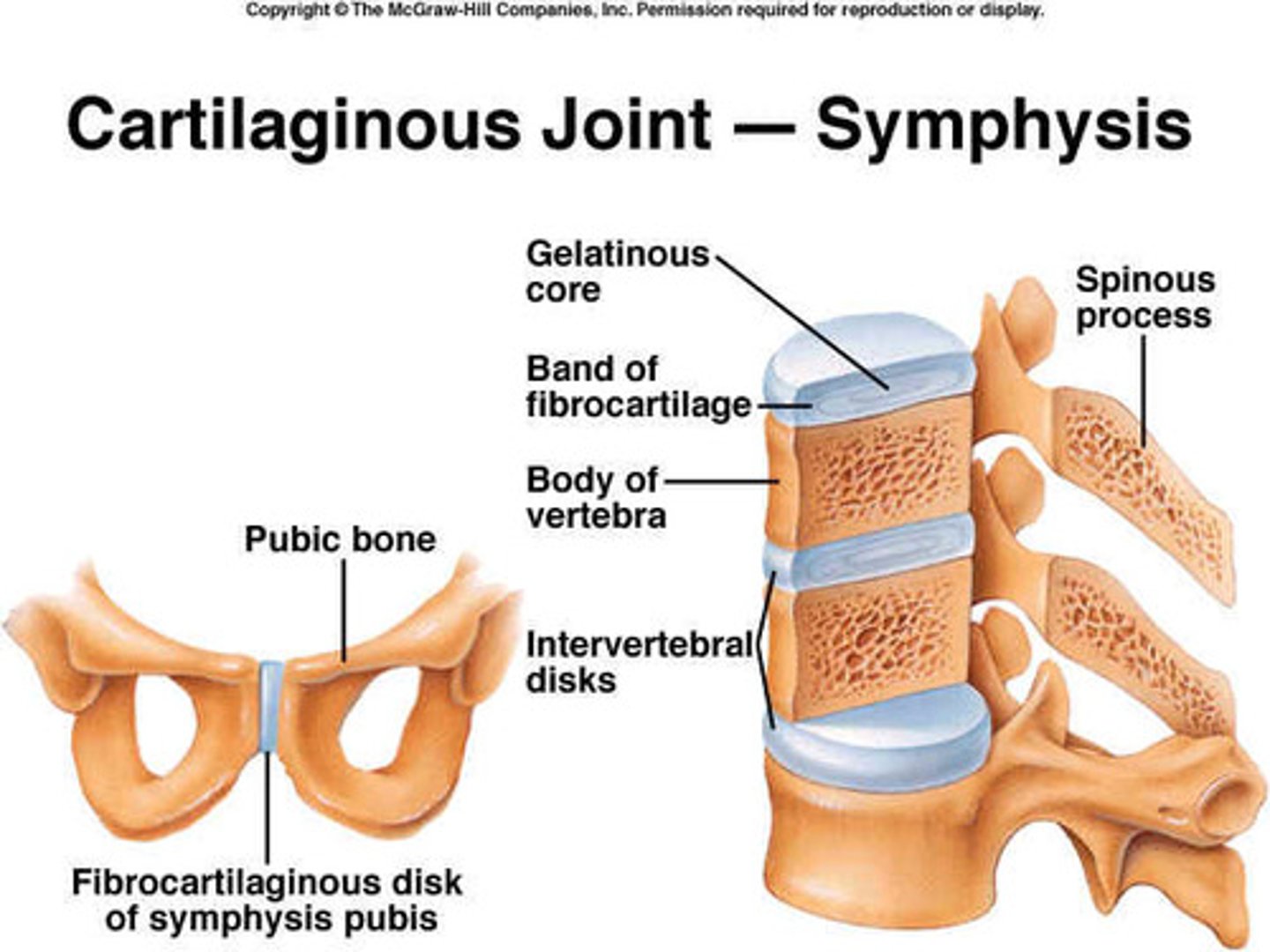
Symphyses
Joints that have grown together to form a very stable connection.
labored breathing
The use of muscles of the chest, back, and abdomen to assist in expanding the chest; occurs when air movement is impaired.
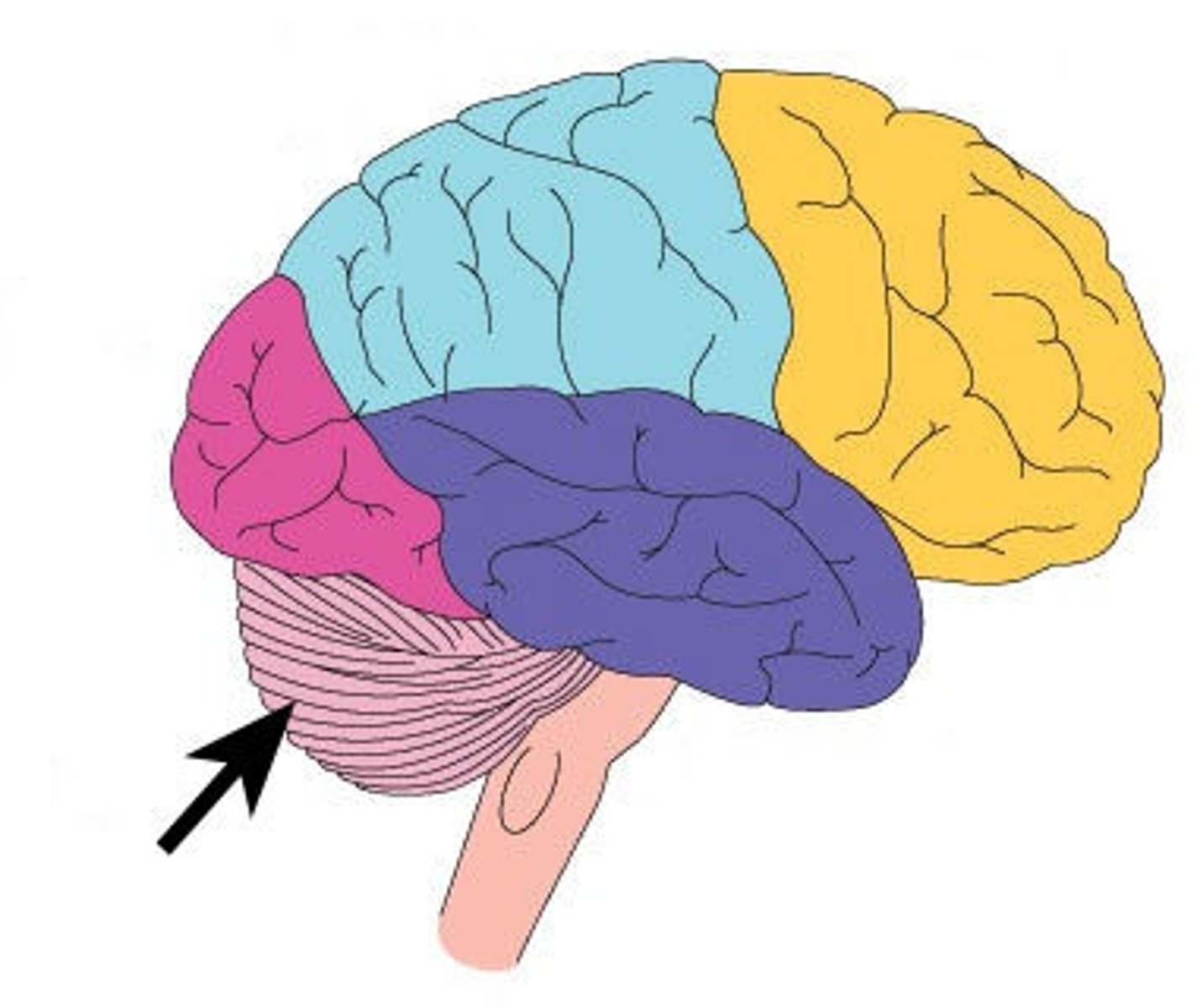
Cerebellum
One of the three major subdivisions of the brain, sometimes called the little brain; coordinates the various activities of the brain, particularly fine body movements.
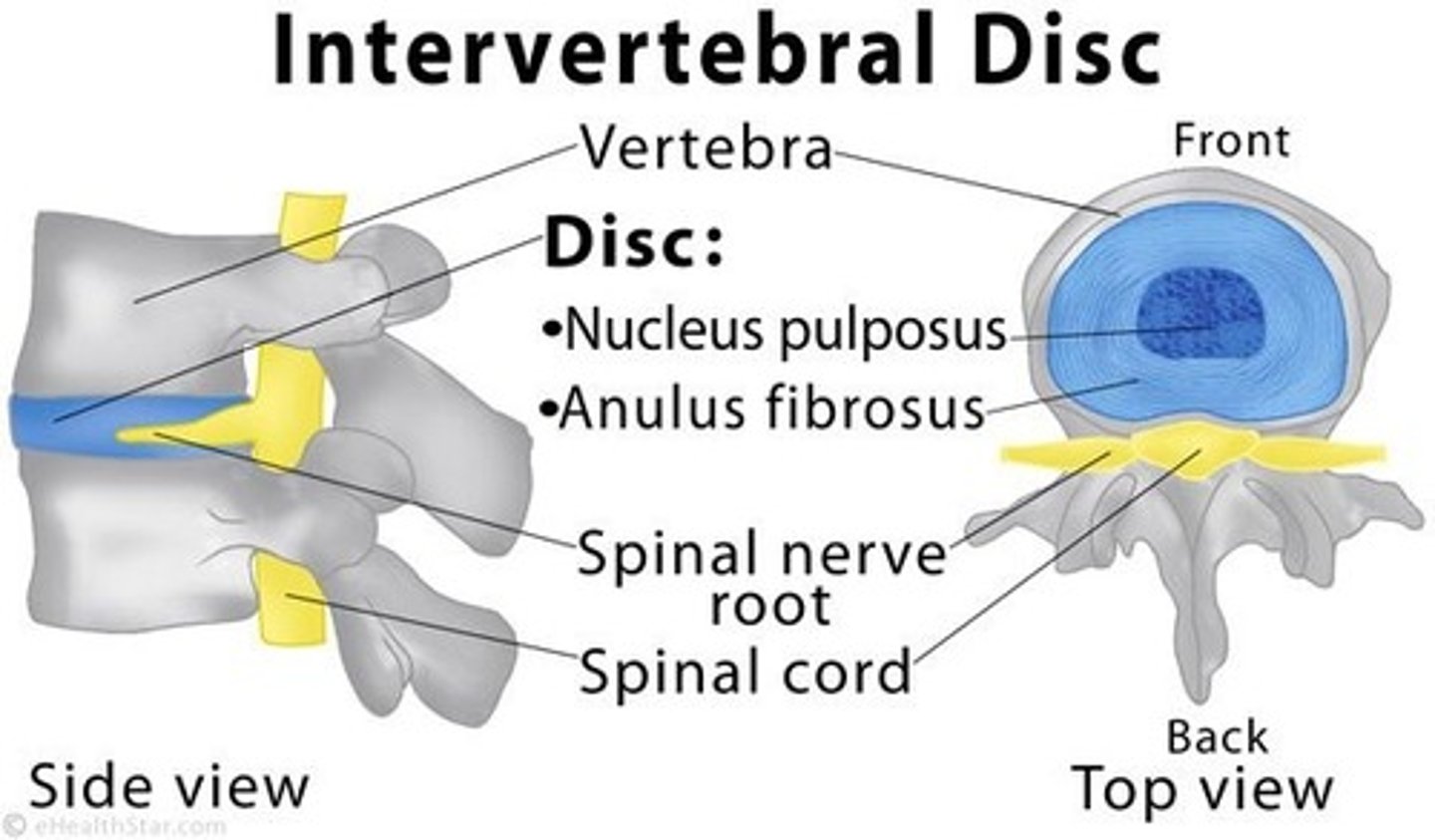
Inverterbral discs
Tough, elastic structures between adjoining vertebrae that act as shock absorbers.
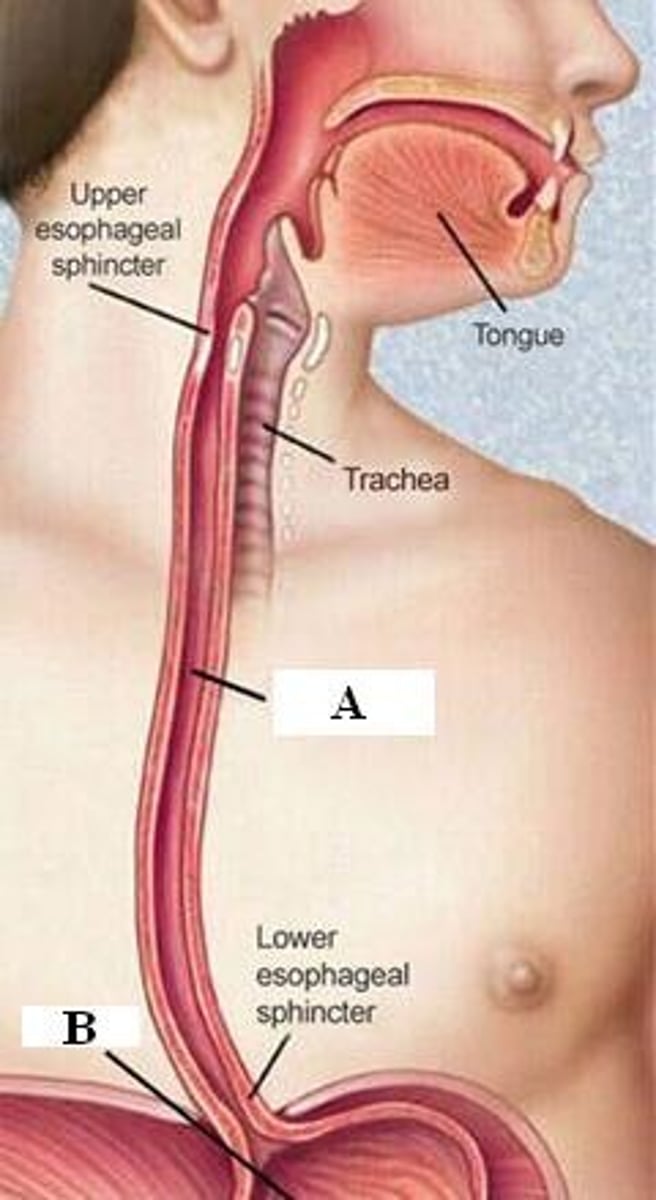
Peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
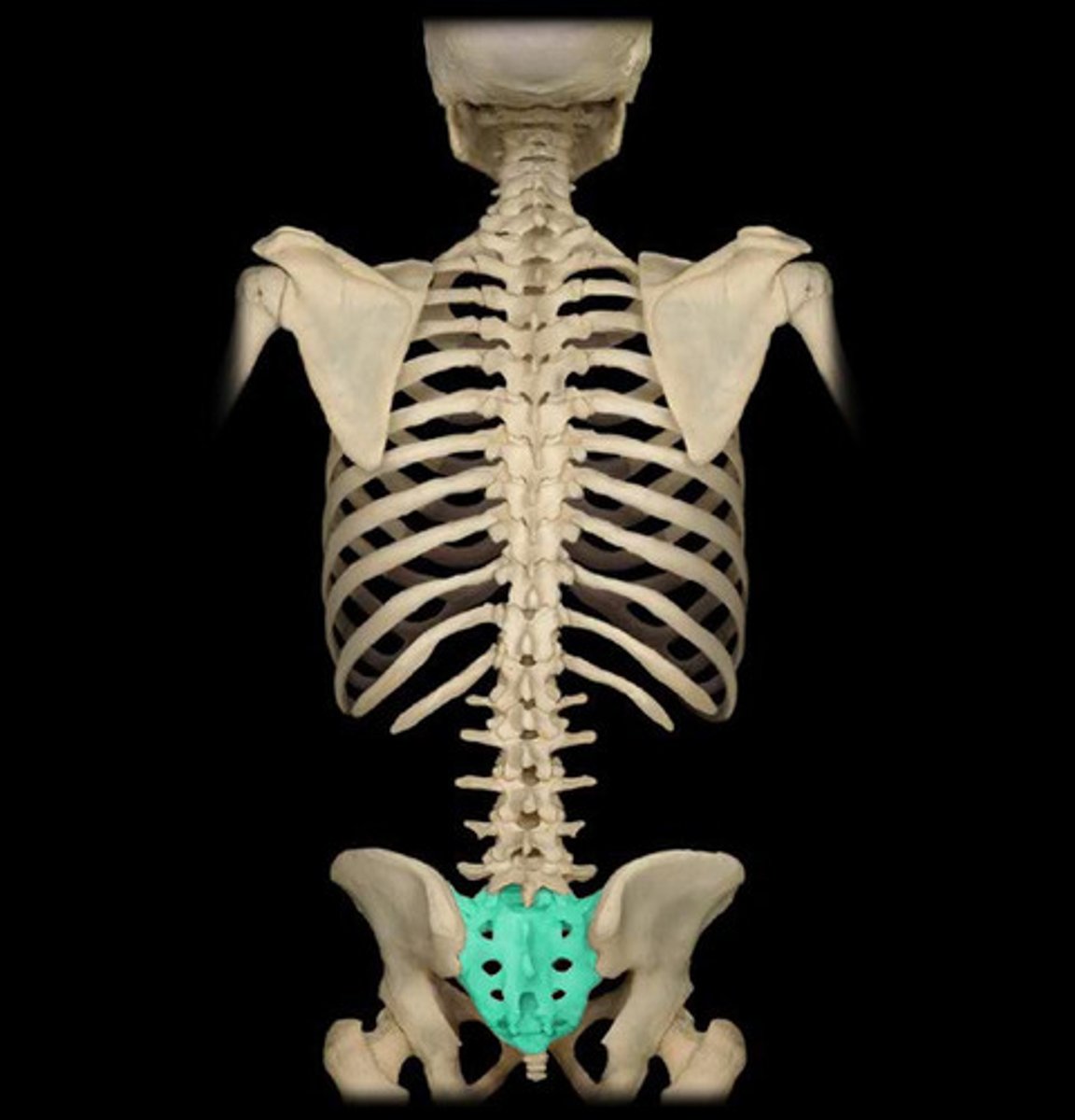
Sacrum
One of three bones that make up the pelvic ring; consists of five fused sacral vertebrae.
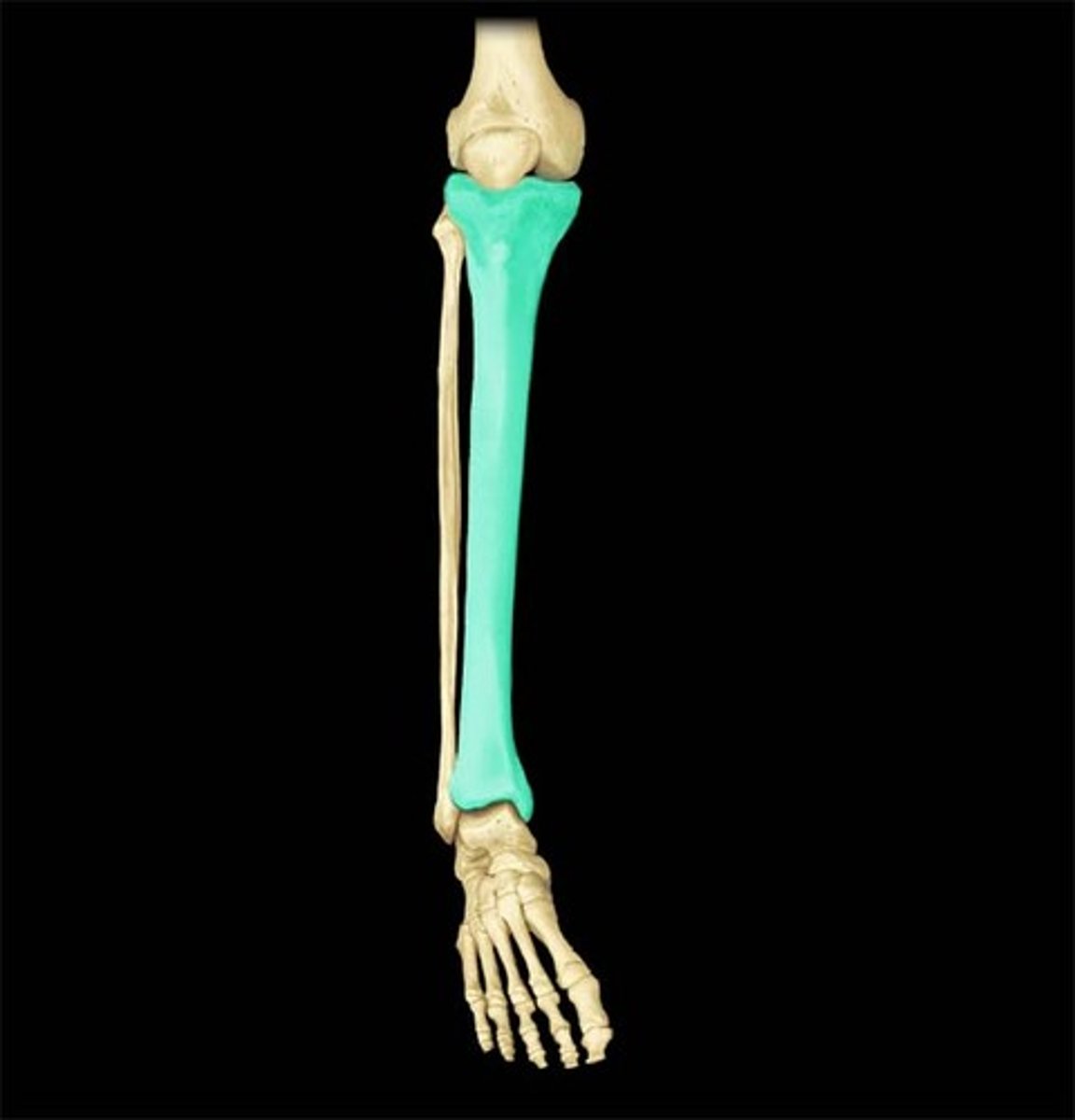
Tibia
The shinbone; the larger of the two bones of the lower leg.
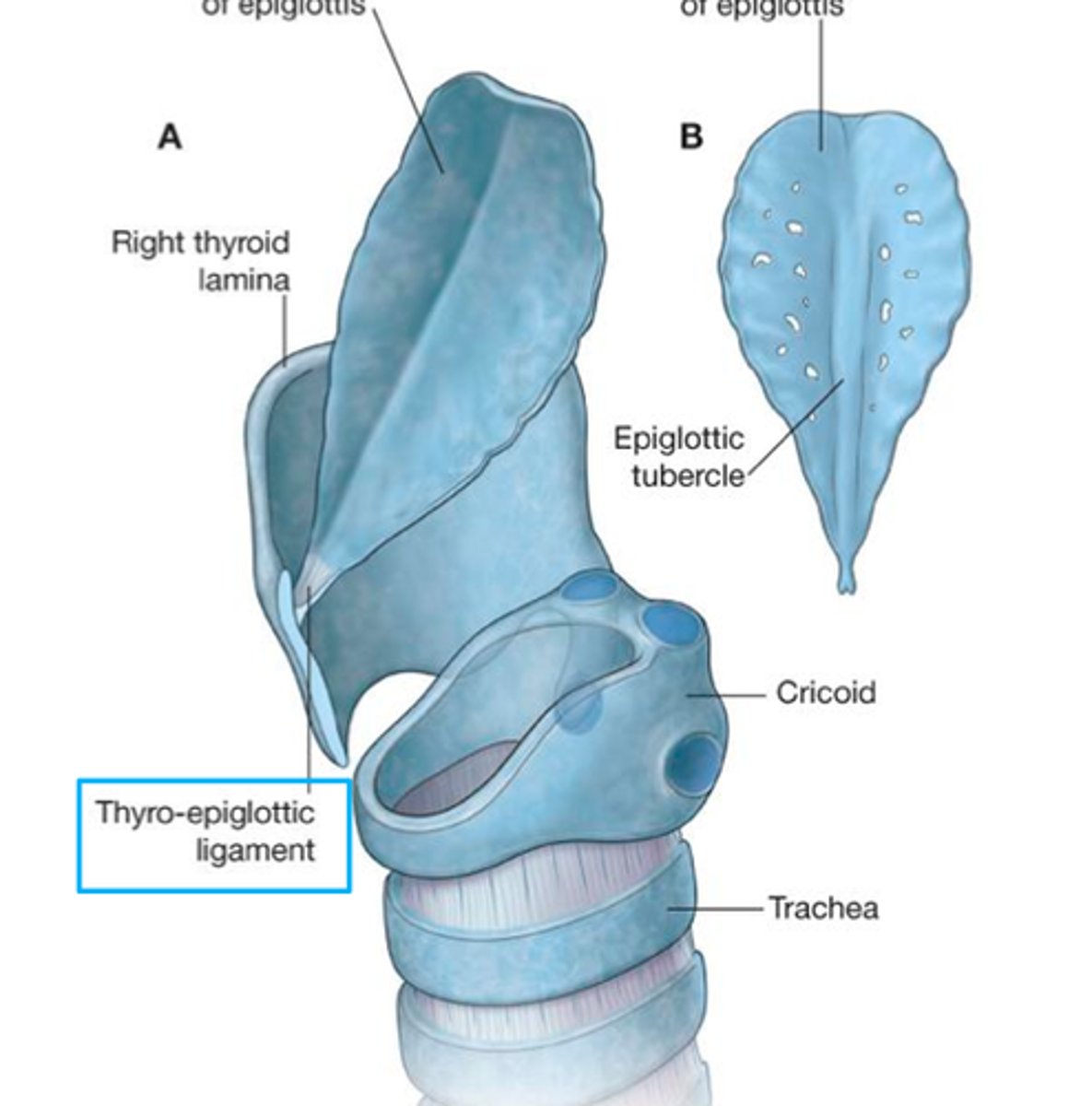
Eppiglottis
A thin, leaf-shaped valve that allows air to pass into the trachea but prevents food and liquid from entering.
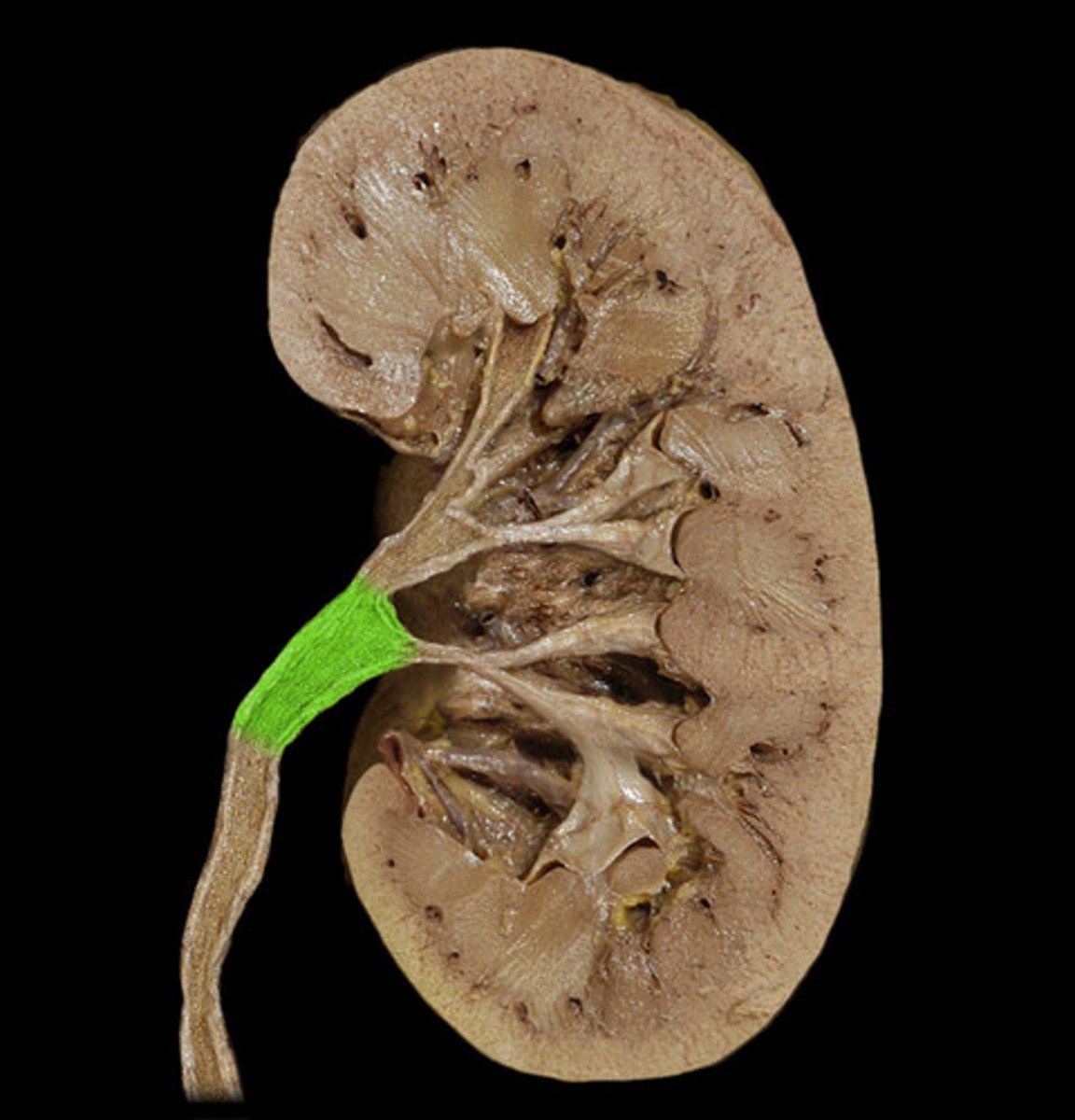
renal pelvis
A cone-shaped area that collects urine from the kidneys and funnels it through the ureter into the bladder.
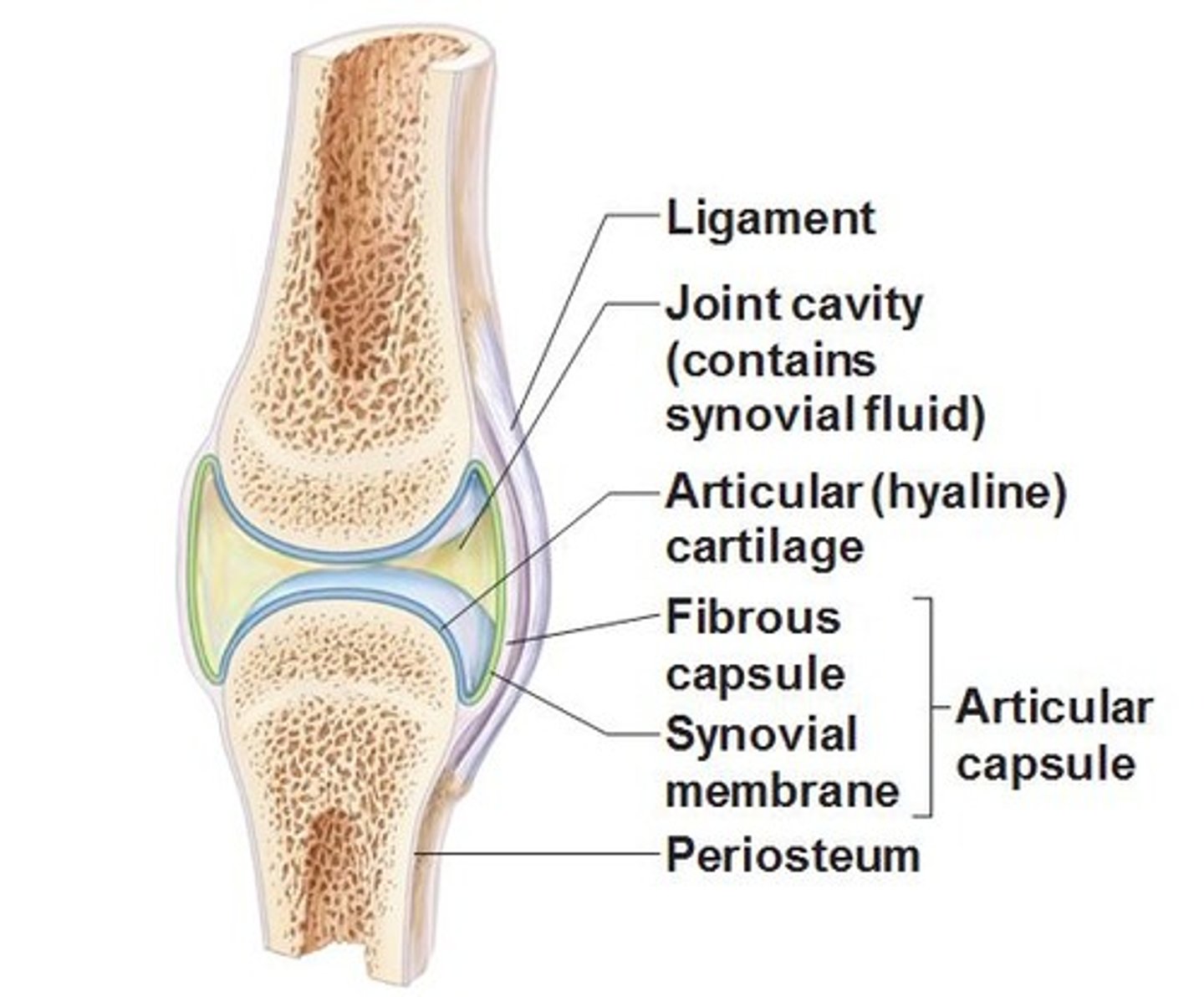
synovial membrane
The lining of a joint that secretes synovial fluid into the joint space.
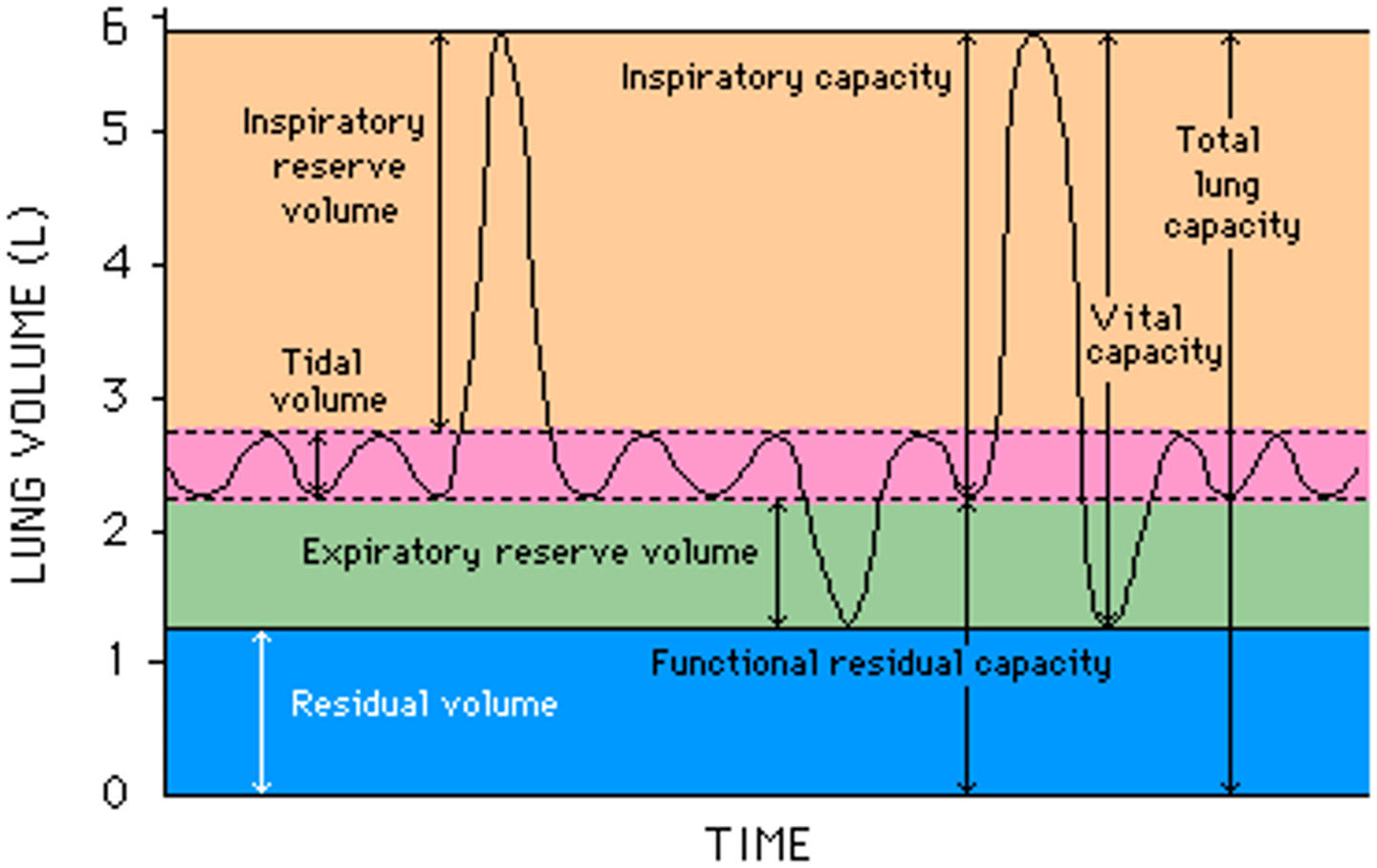
Residial volume (RV)
The air that remains in the lungs after maximal expiration.
minute ventilation
The volume of air that moves in and out of the lungs per minute; calculated by multiplying the tidal volume and respiratory rate
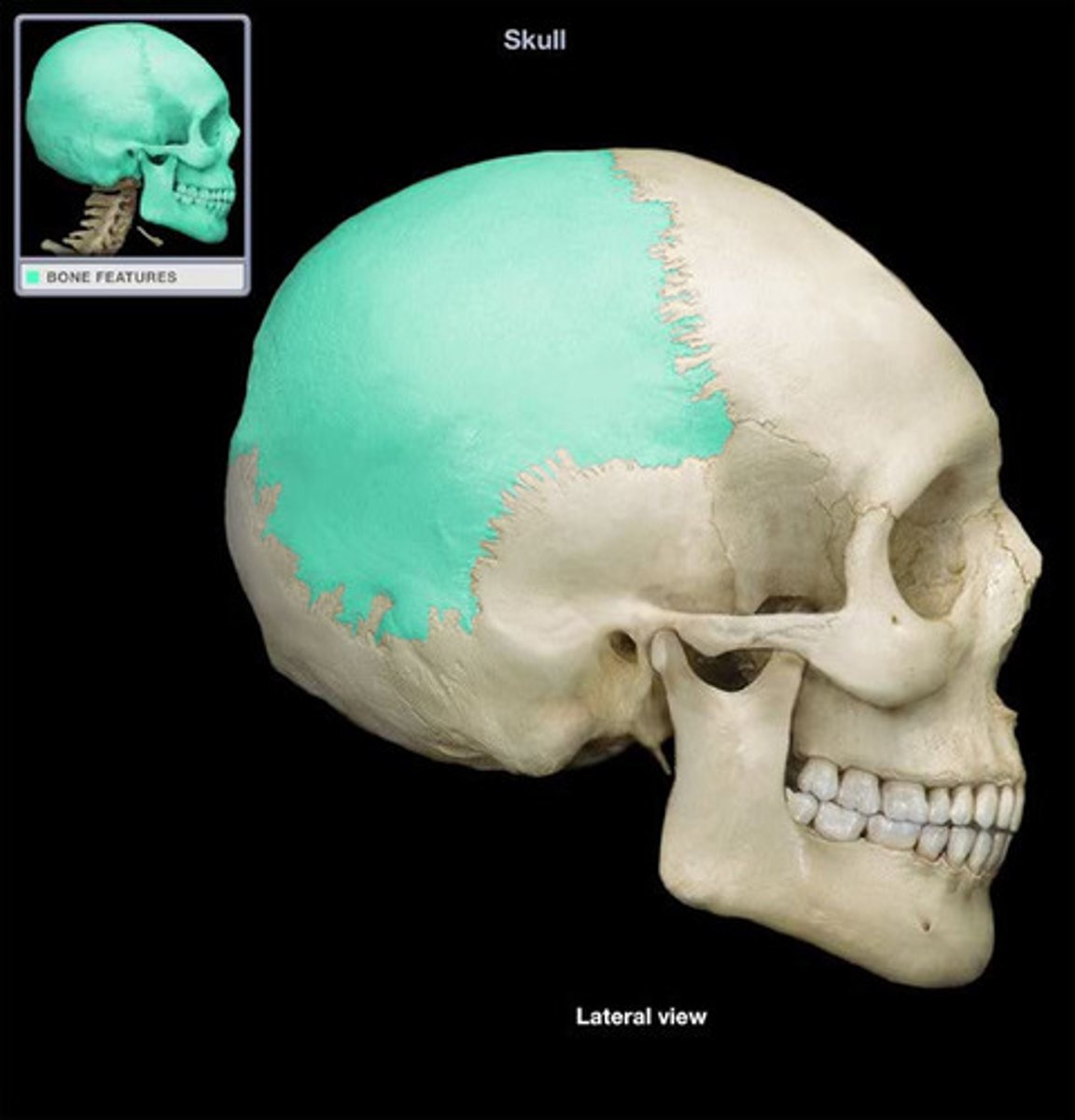
parietal bone of skull
The bones that lie between the temporal and occipital regions of the cranium.
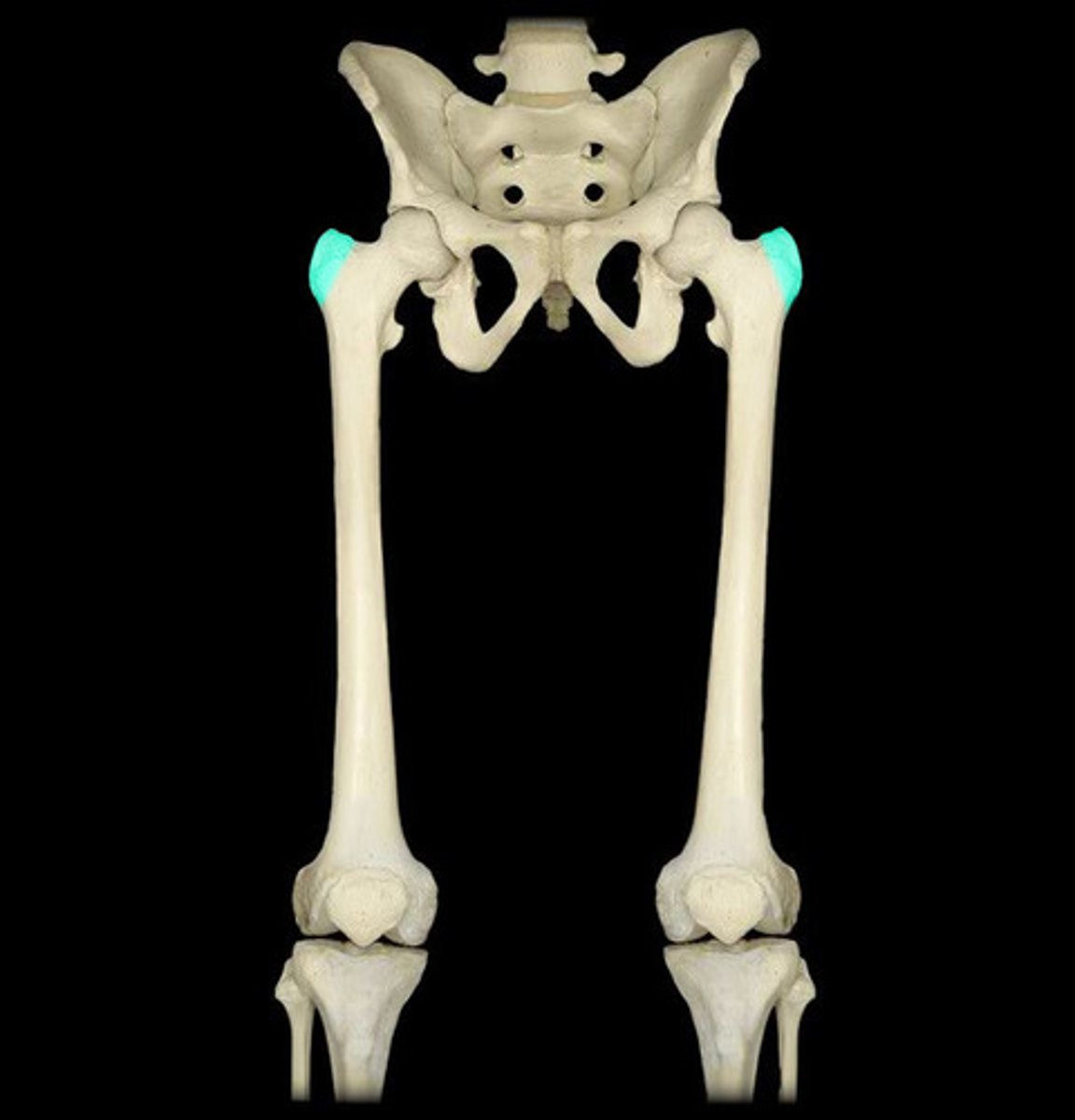
greater trochanter
A bony prominence on the proximal lateral side of the thigh, just below the hip joint.
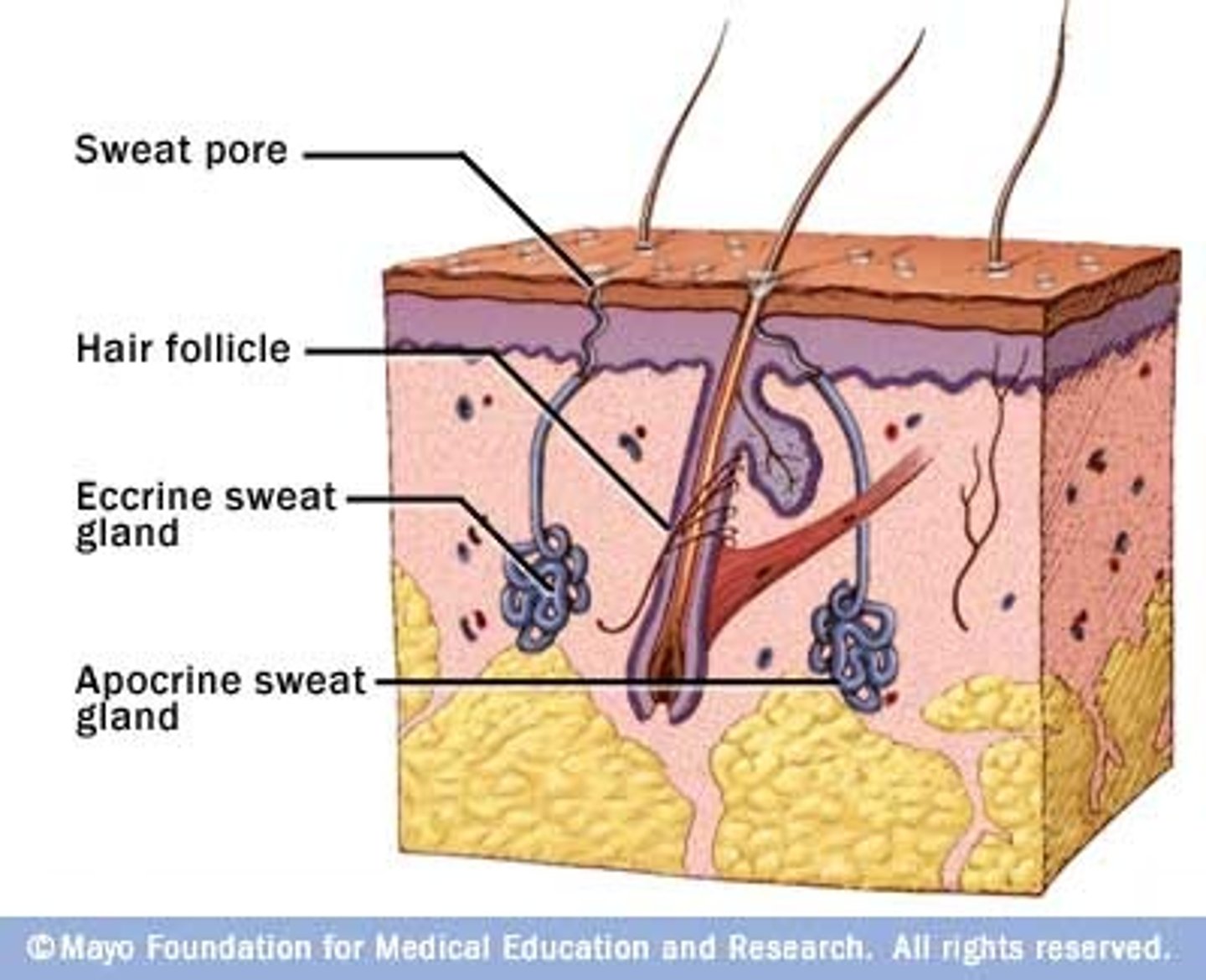
sweat glands
The glands that secrete sweat, located in the dermal layer of the skin.
lactic acid
A metabolic by-product of the breakdown of glucose that accumulates when metabolism proceeds in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic metabolism)

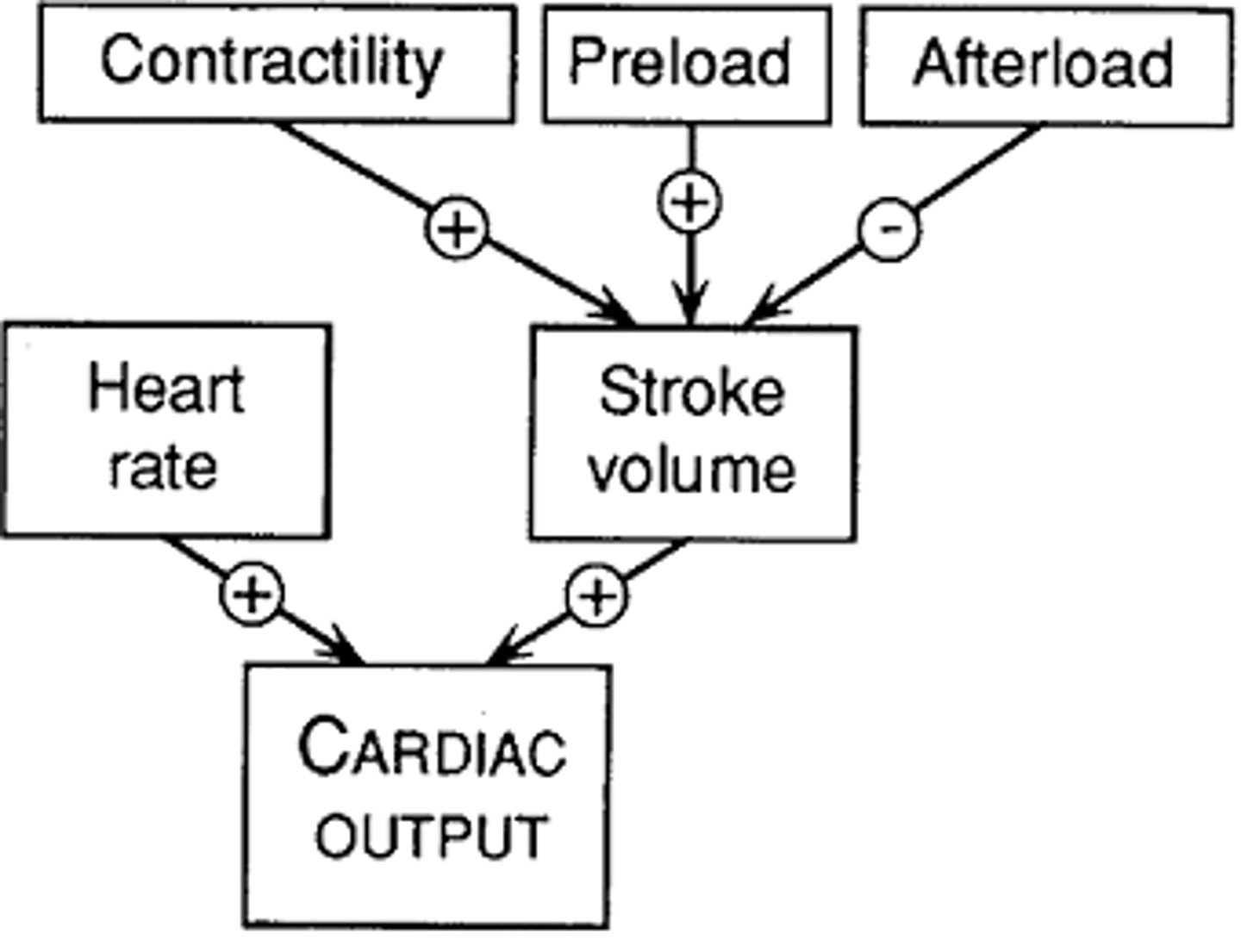
cardiac output
A measure of the volume of blood circulated by the heart in 1 minute, calculated by multiplying the stroke volume by the heart rate.
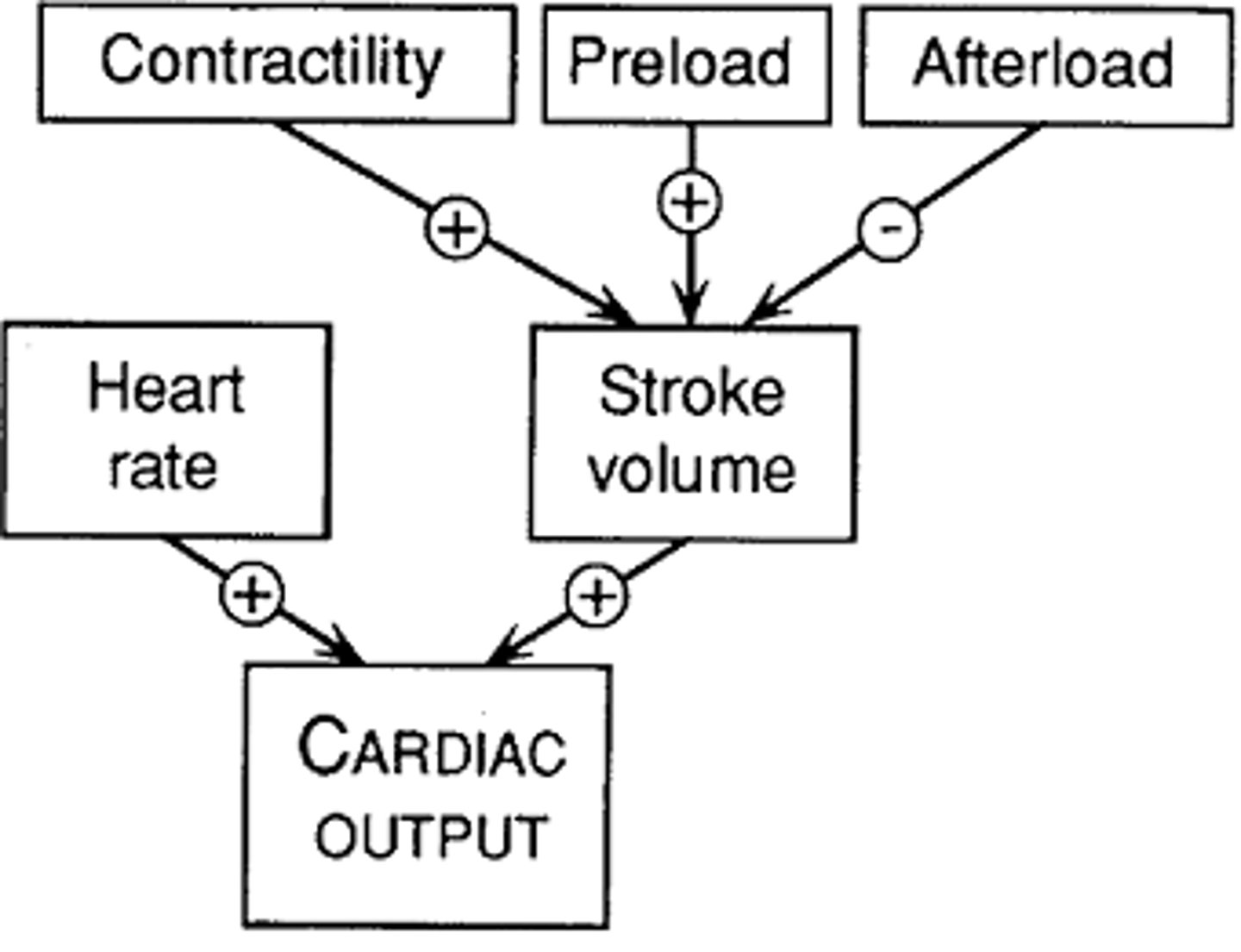
stroke volume
The volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle of the heart in one contraction
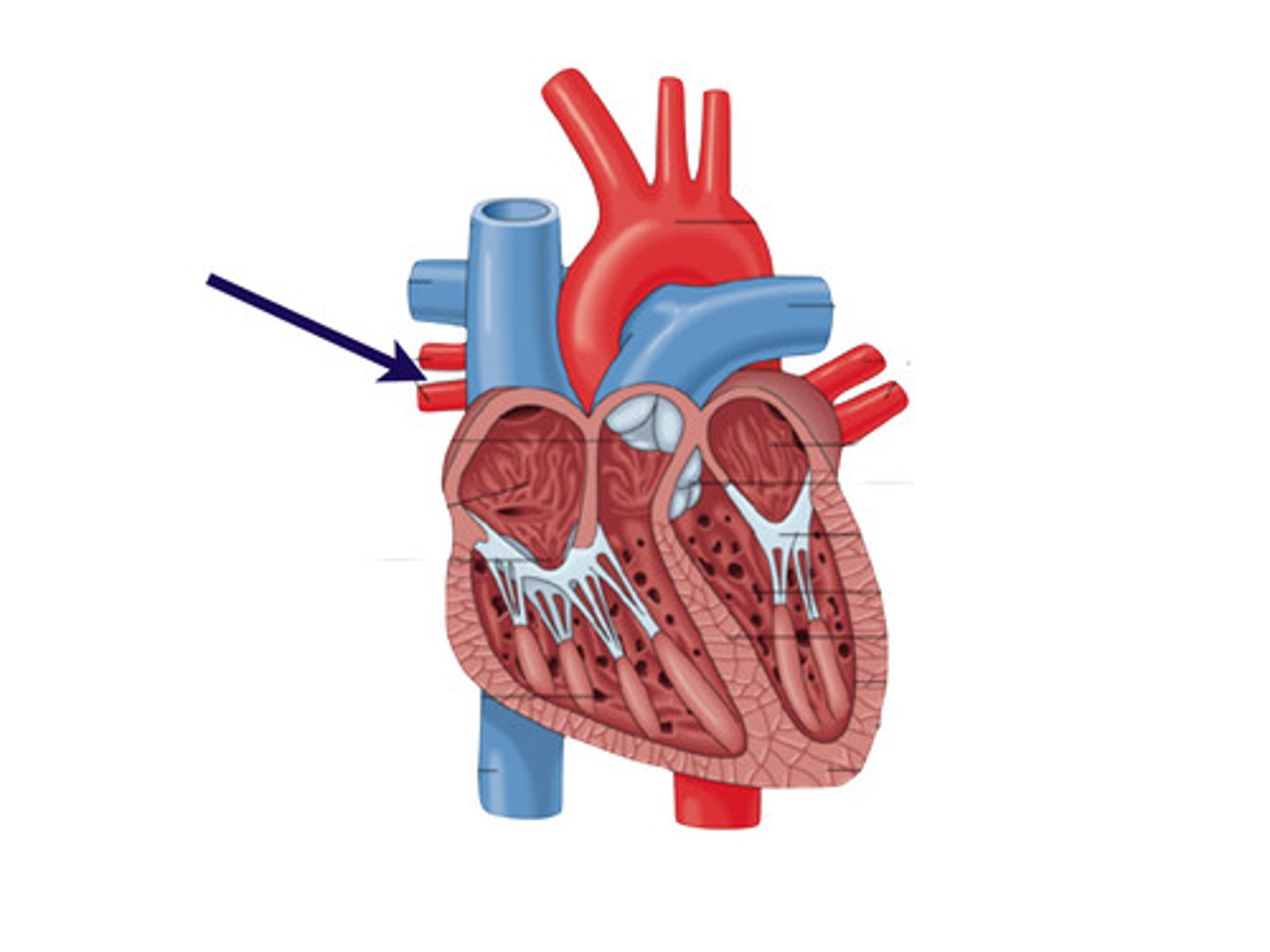
pulmonary veins
The four veins that return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
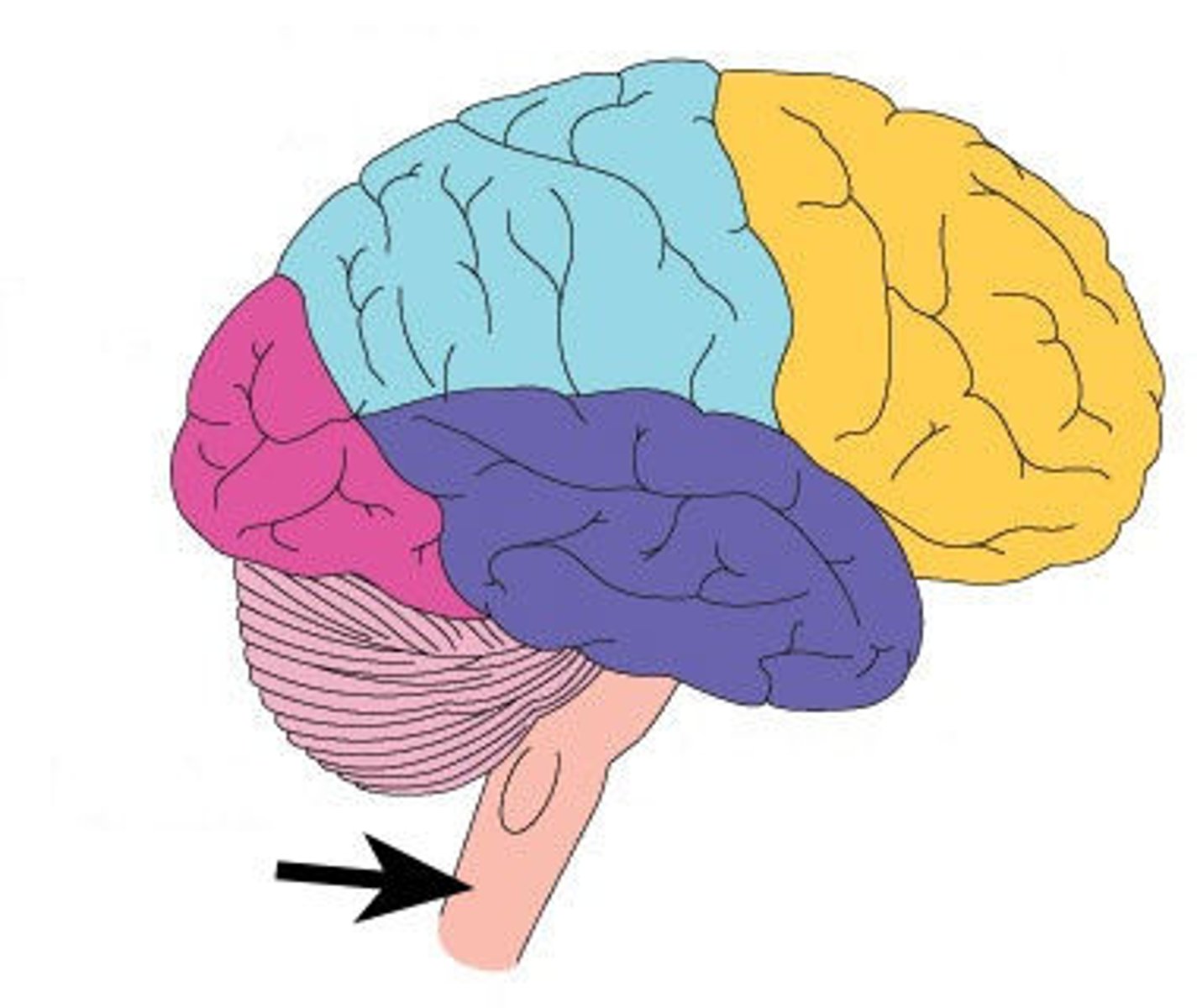
Brainstem
The area of the brain between the spinal cord and cerebrum, surrounded by the cerebellum; controls functions that are necessary for life, such as respiration.
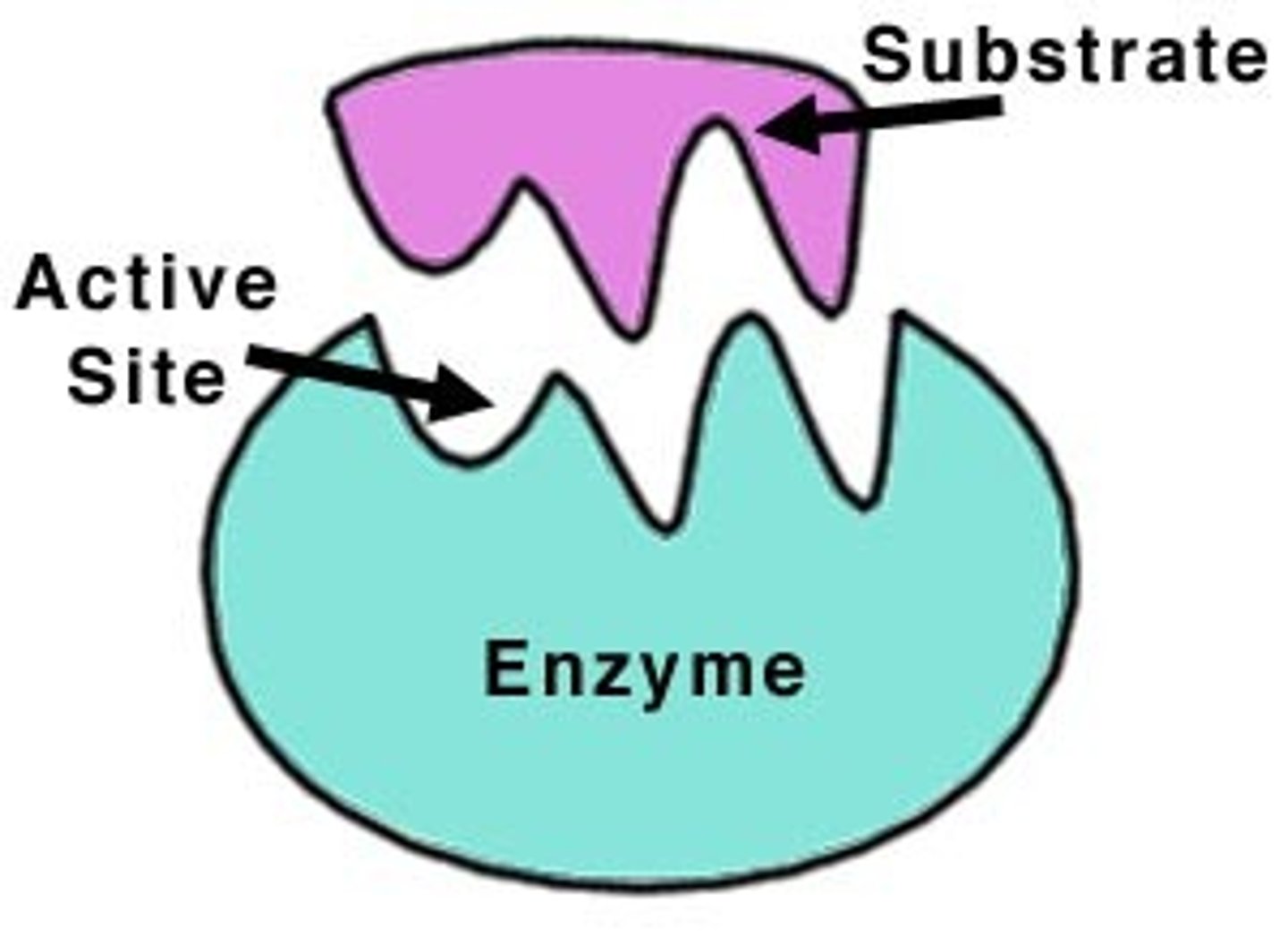
Enzymes
Proteins designed to speed up the rate of specific chemical reactions.
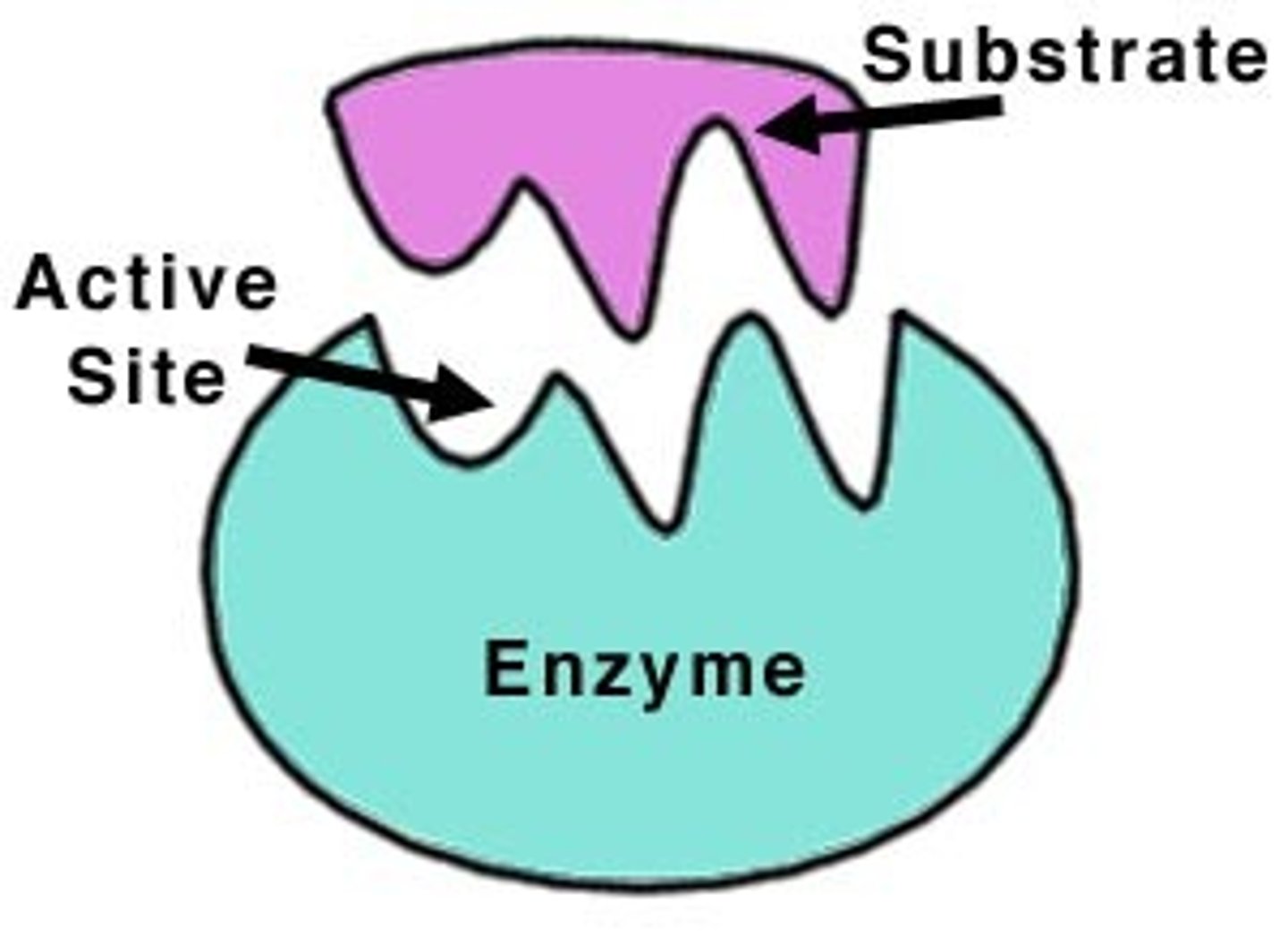
Substrate
The reactant on which an enzyme works.
Platelets
Tiny, disc-shaped elements that are much smaller than the cells; they are essential in the initial formation of a blood clot, the mechanism that stops bleeding.
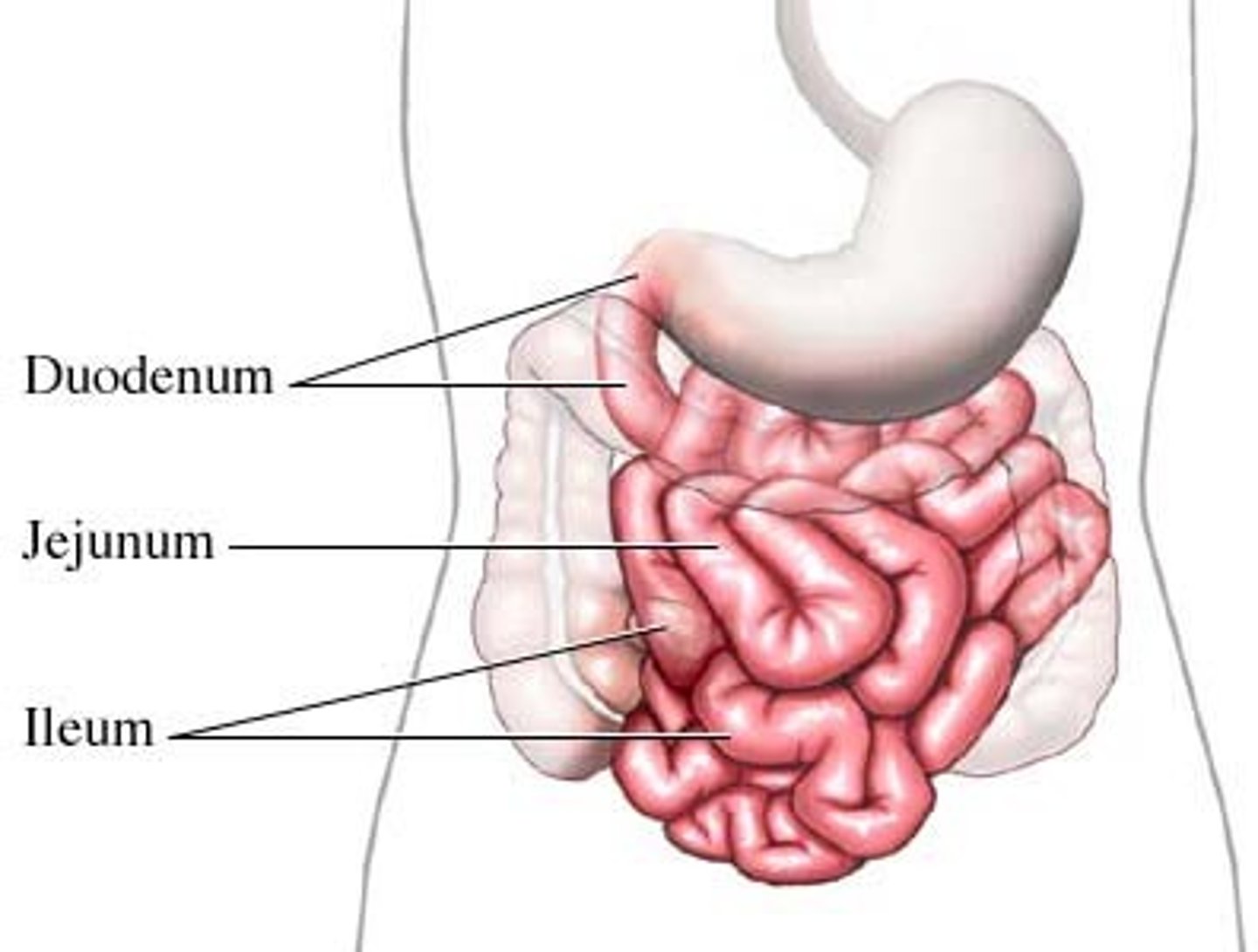
small intestine
The portion of the digestive tube between the stomach and the cecum, consisting of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
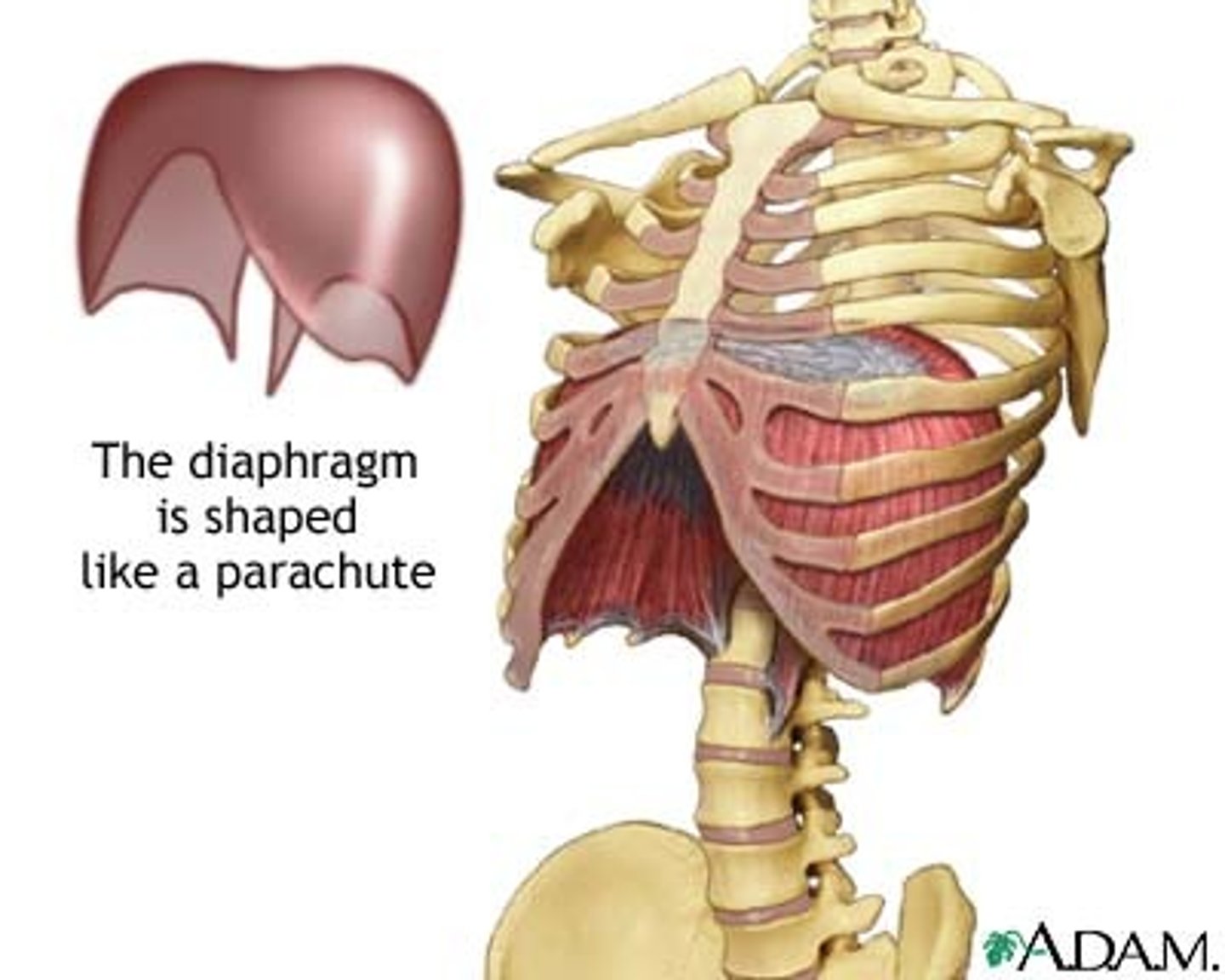
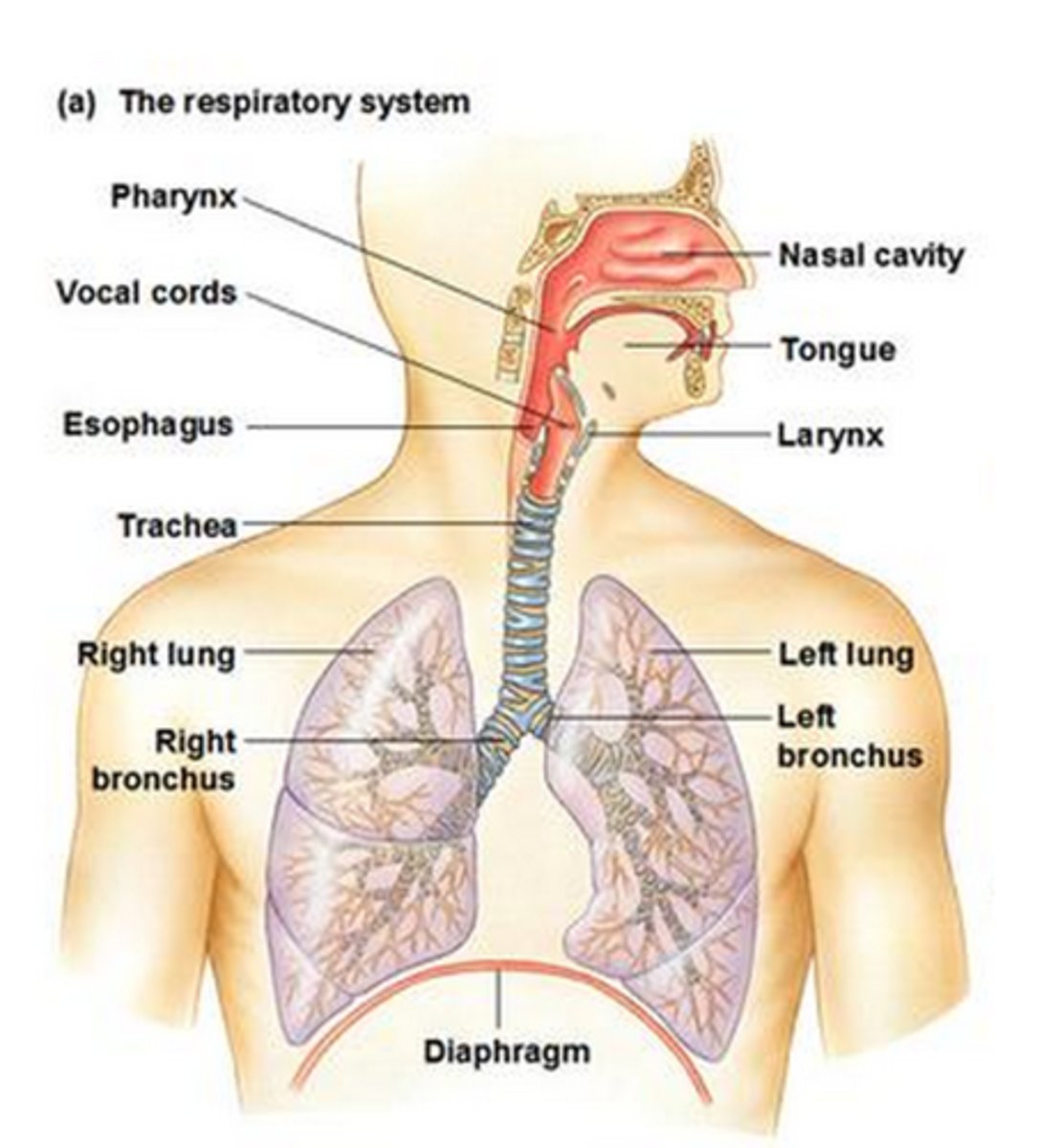
Diaphragm
A muscular dome that forms the undersurface of the thorax, separating the chest from the abdominal cavity. Contraction of this (and the chest wall muscles) brings air into the lungs. Relaxation allows air to be expelled from the lungs.
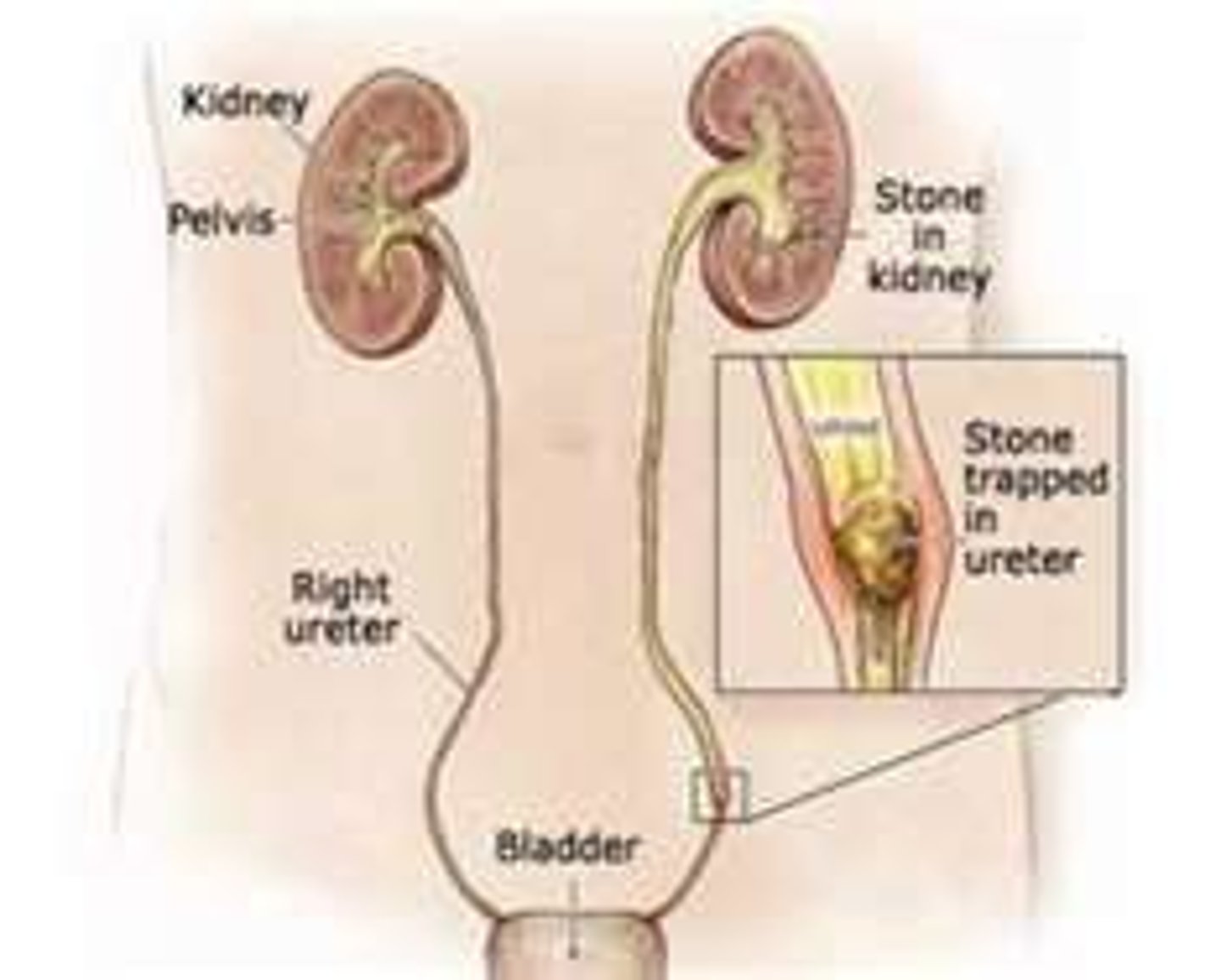
ureter
A small, hollow tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
blood pressure
The pressure that the blood exerts against the walls of the arteries as it passes through them.
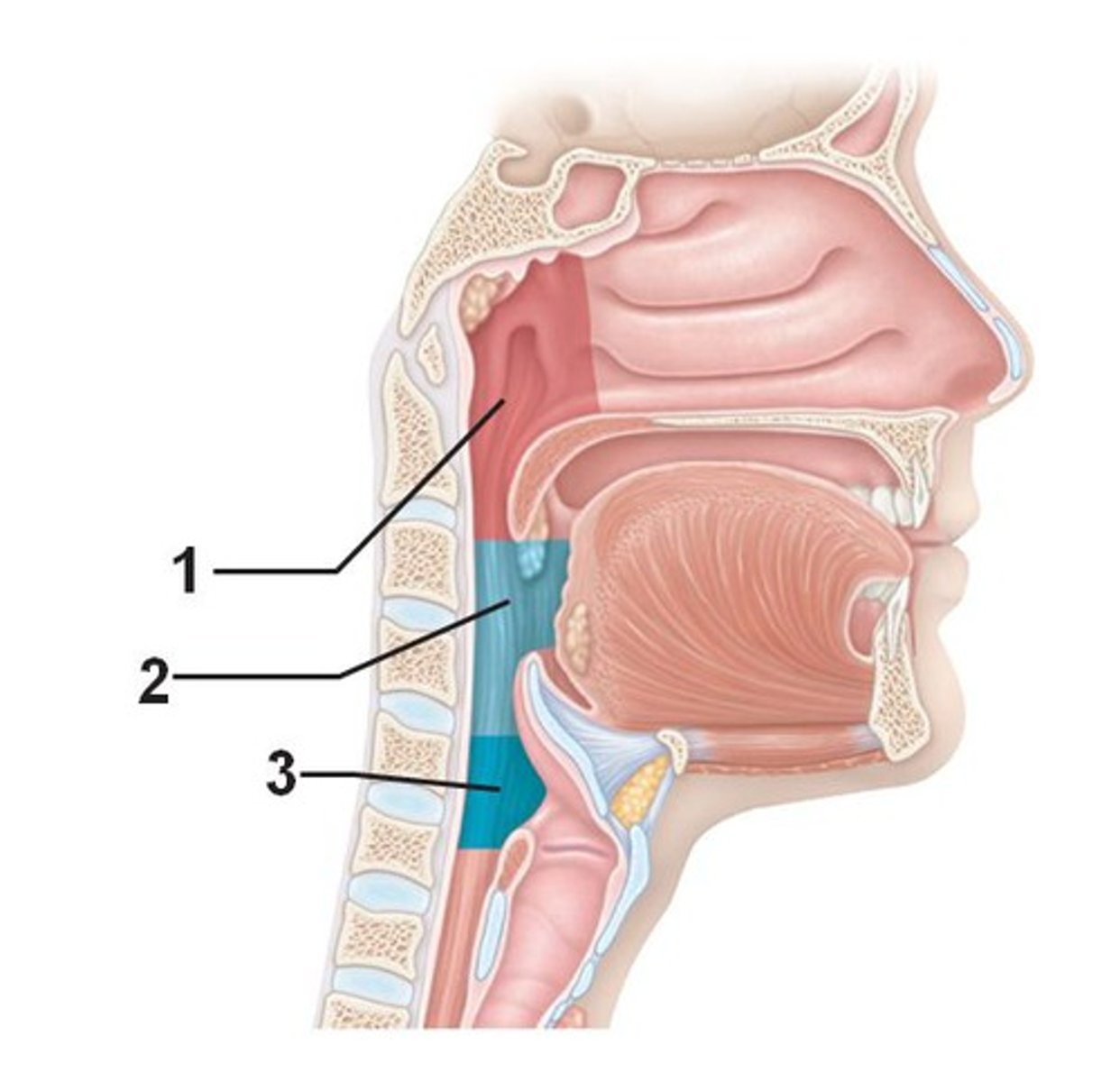
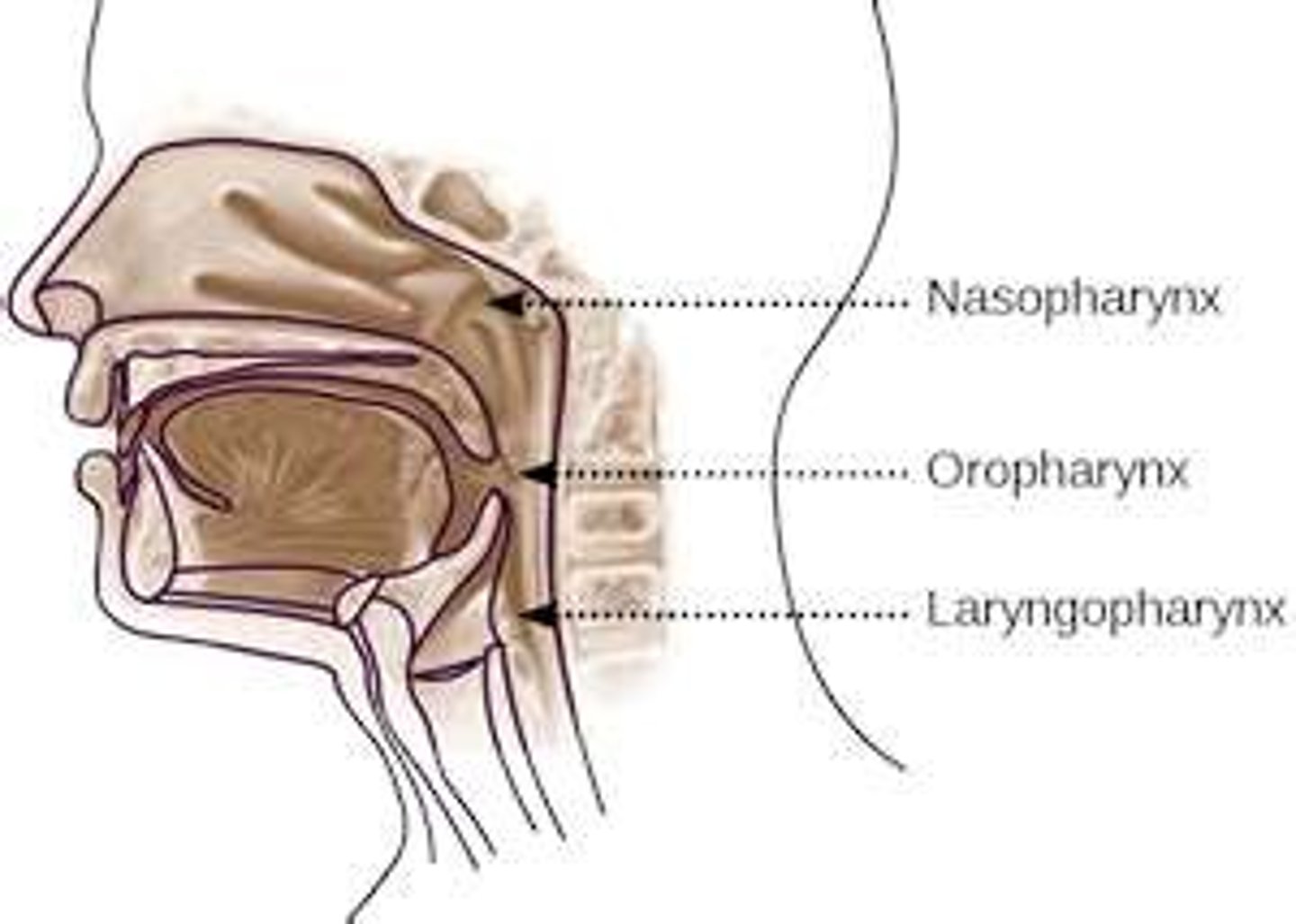
oropharynx
A tubular structure that extends vertically from the back of the mouth to the esophagus and trachea.
topographic anatomy
The superficial landmarks of the body that serve as guides to the structures that lie beneath them.
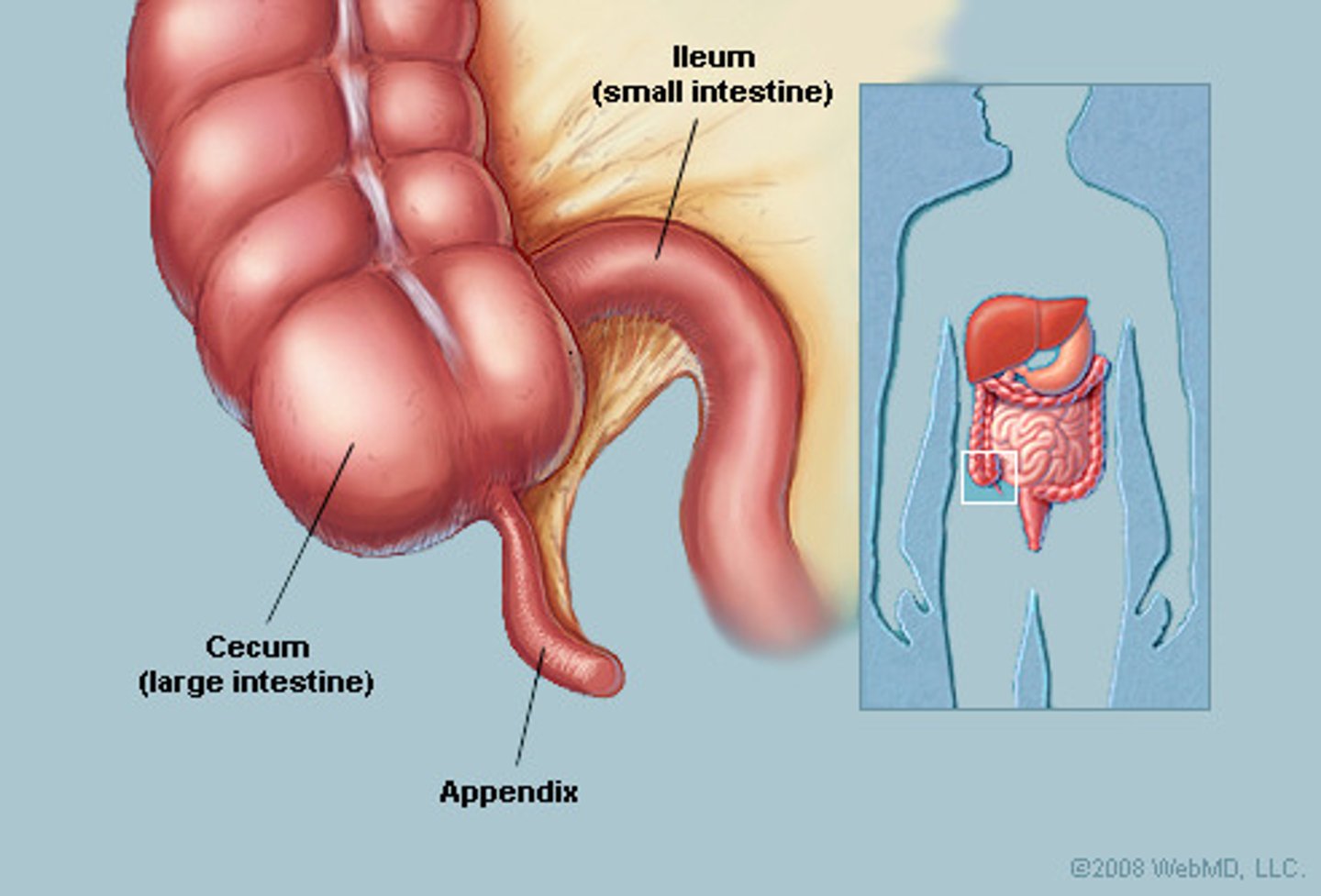
appendix
A small, tubular structure that is attached to the lower border of the cecum in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen.
malleous
A rounded bony prominence on either side of the ankle; also called the ankle bone.
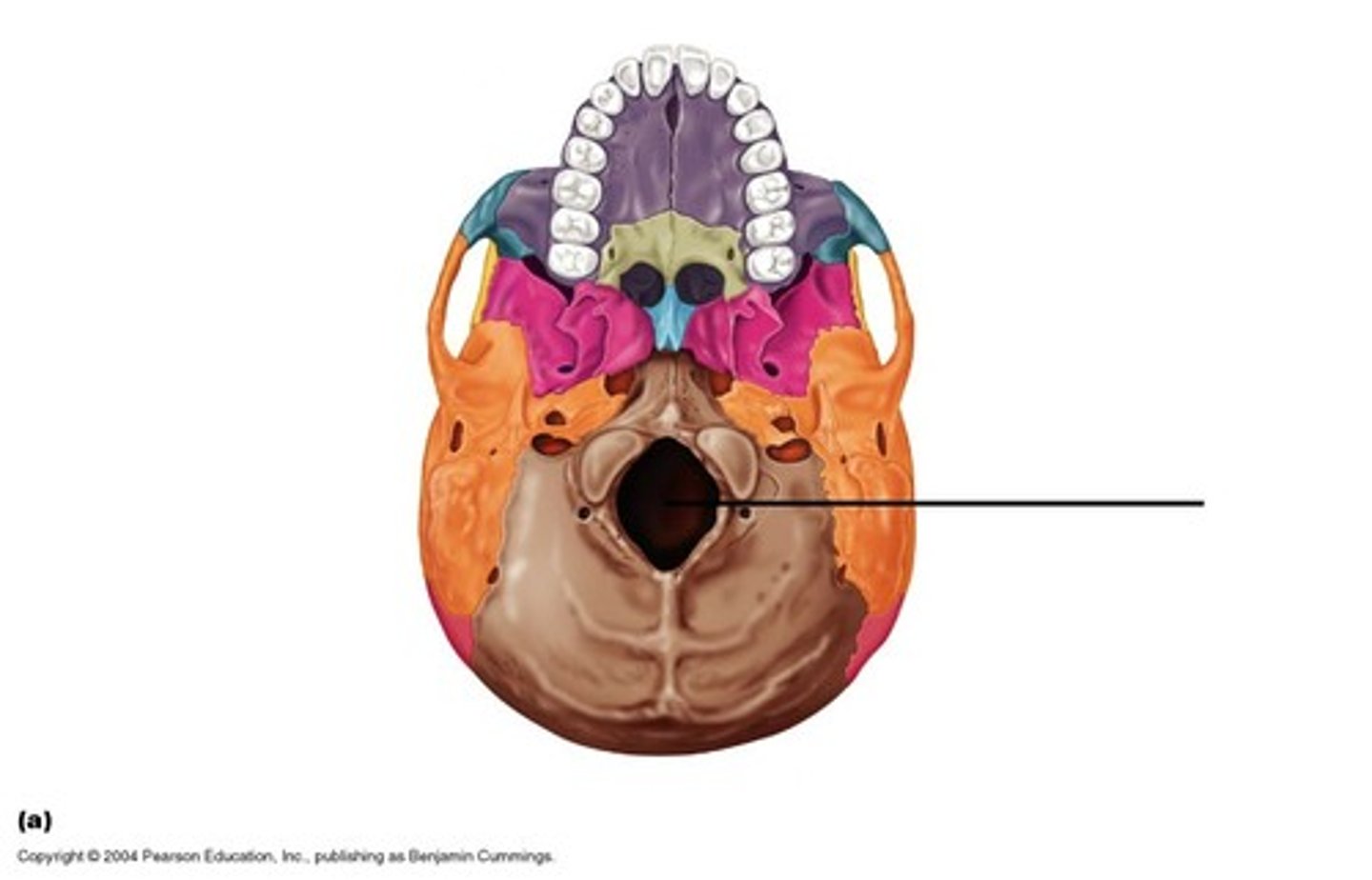
foramen magnum
A large opening at the base of the skull through which the brain connects to the spinal cord.
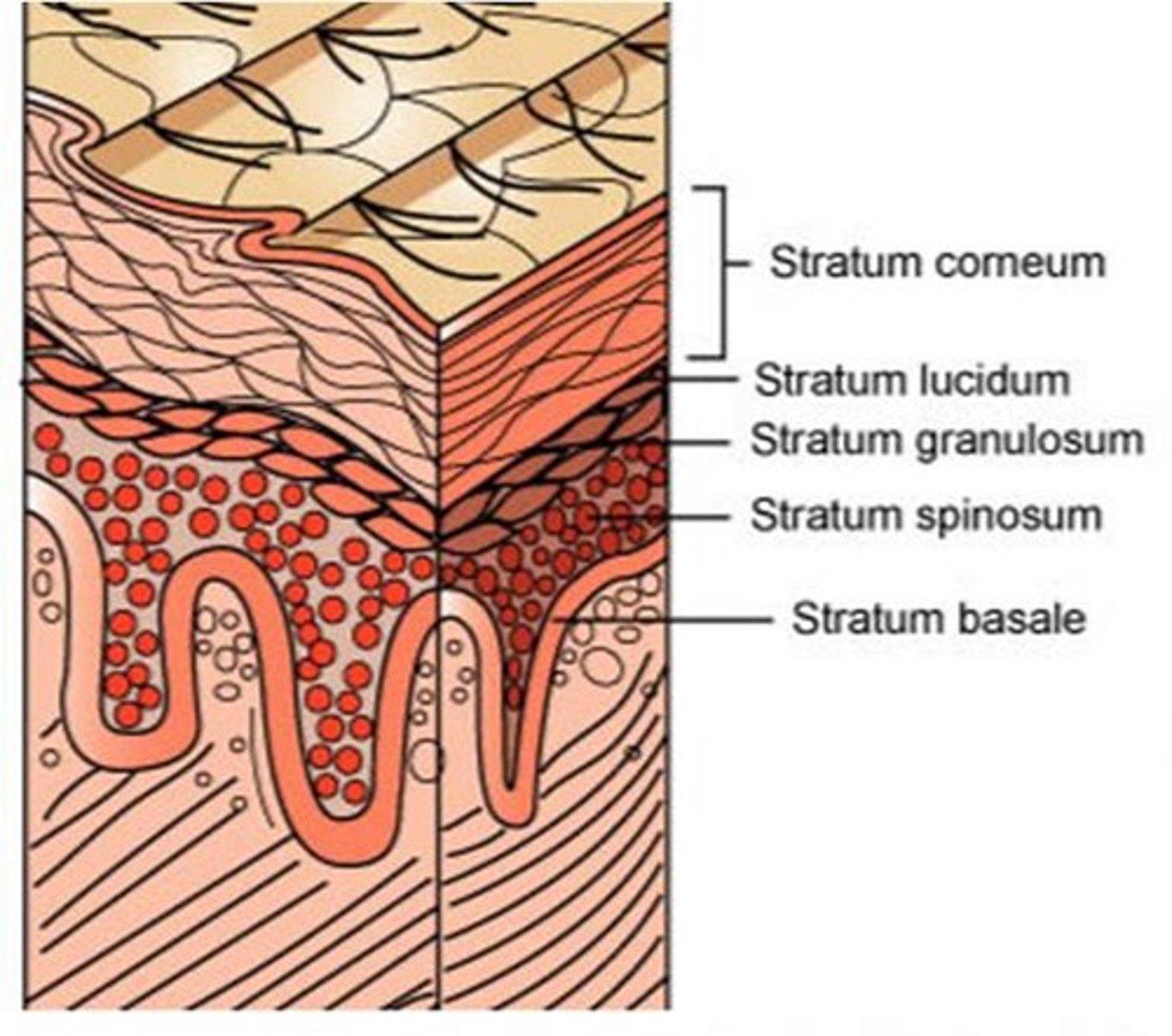
germinal layer
The deepest layer of the epidermis, where new skin cells are formed.
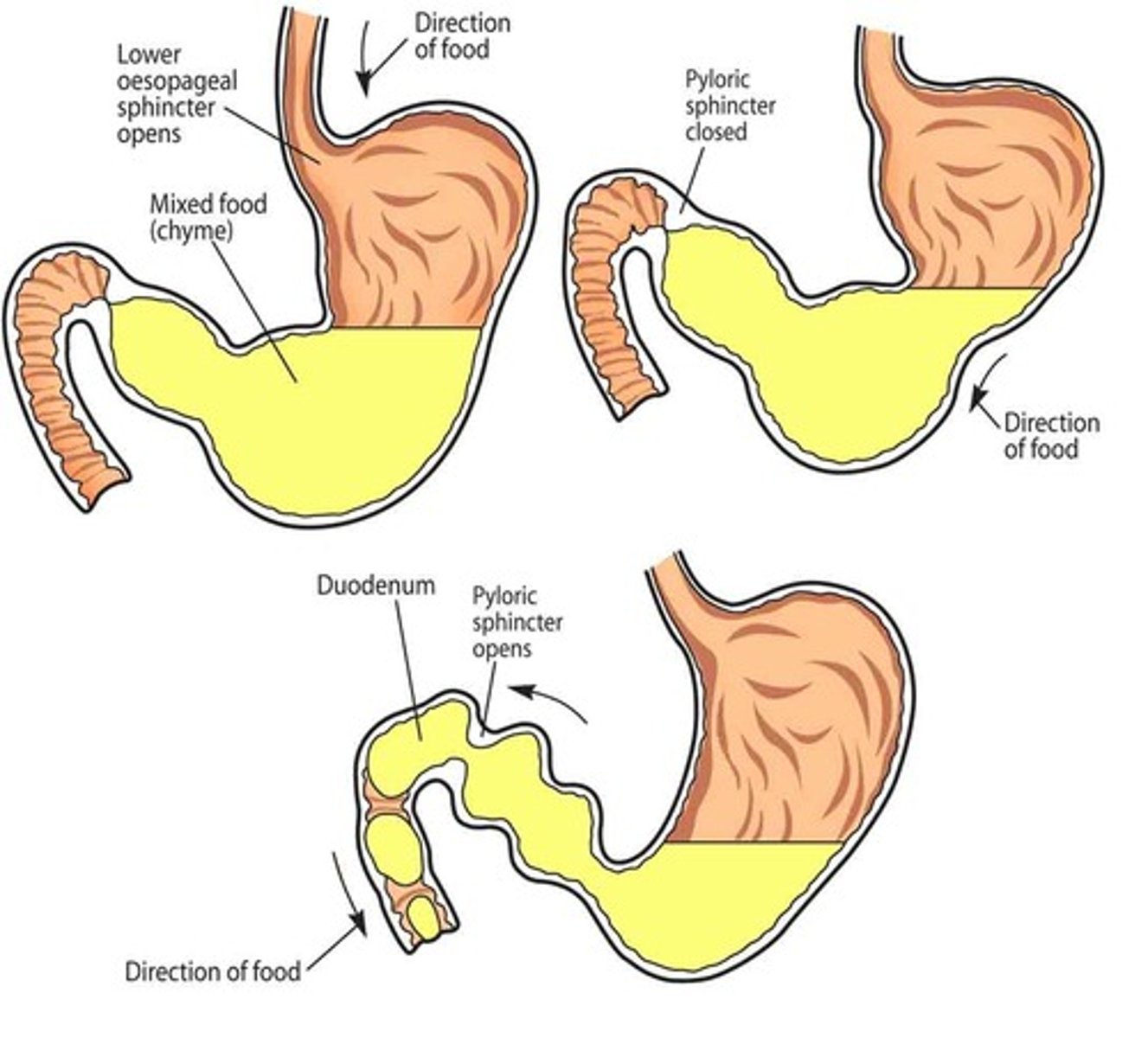
Chyme
The substance that leaves the stomach. It is a combination of all of the eaten foods with added stomach acids.
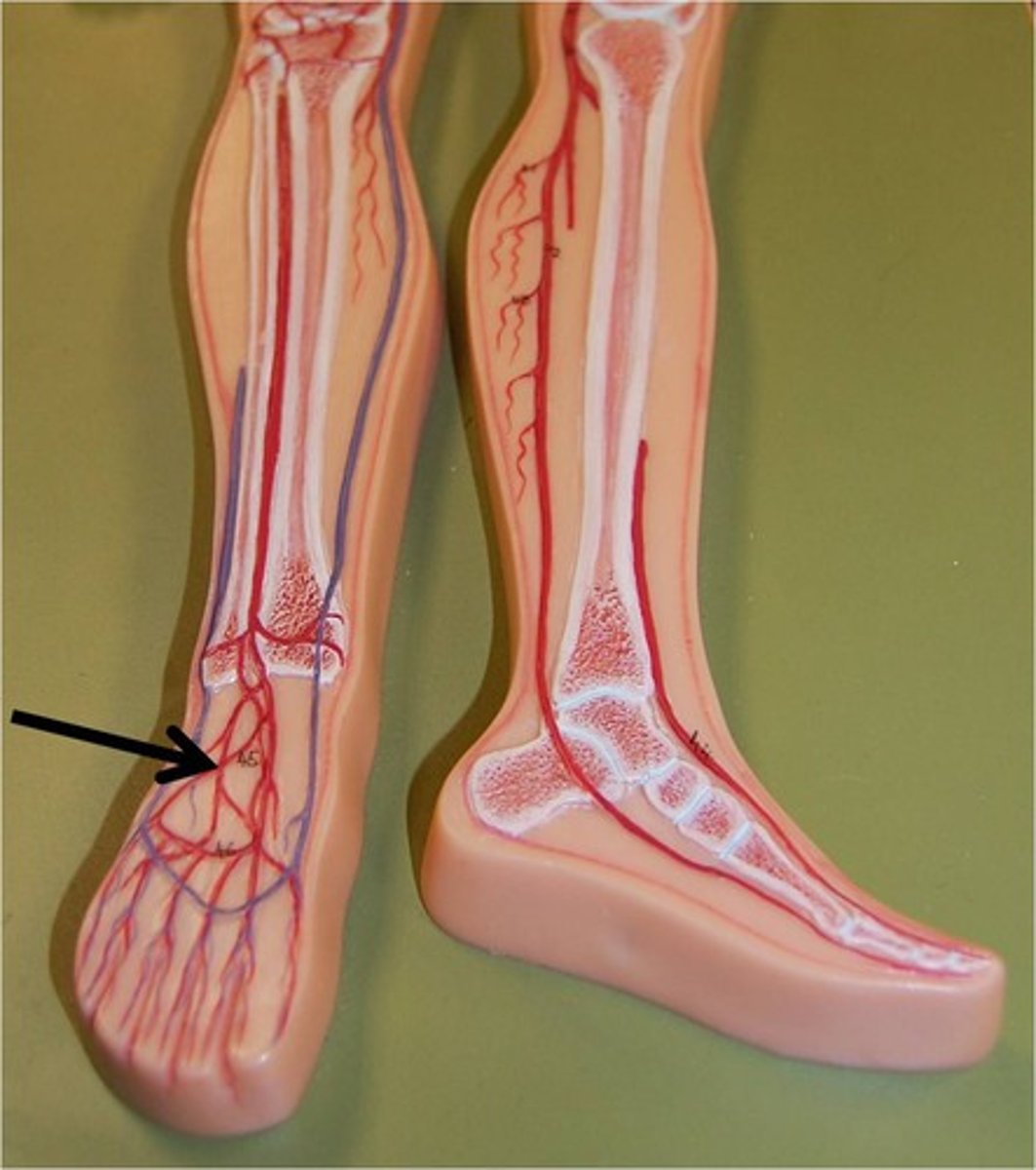
dorsalis pedis artery
The artery on the anterior surface of the foot between the first and second metatarsals.
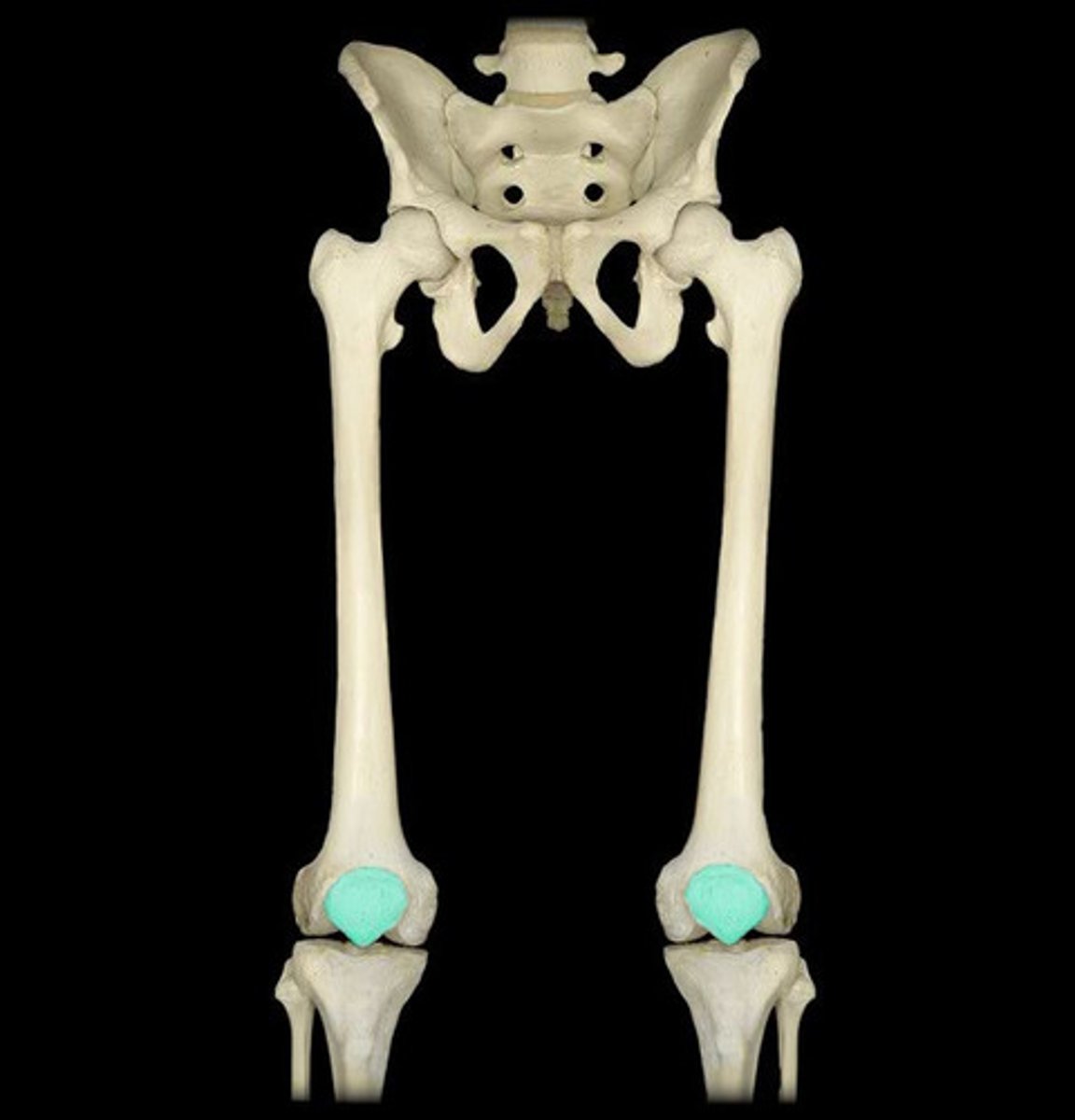
patella
The knee cap; a specialized bone that lies within the tendon of the quadriceps muscle.
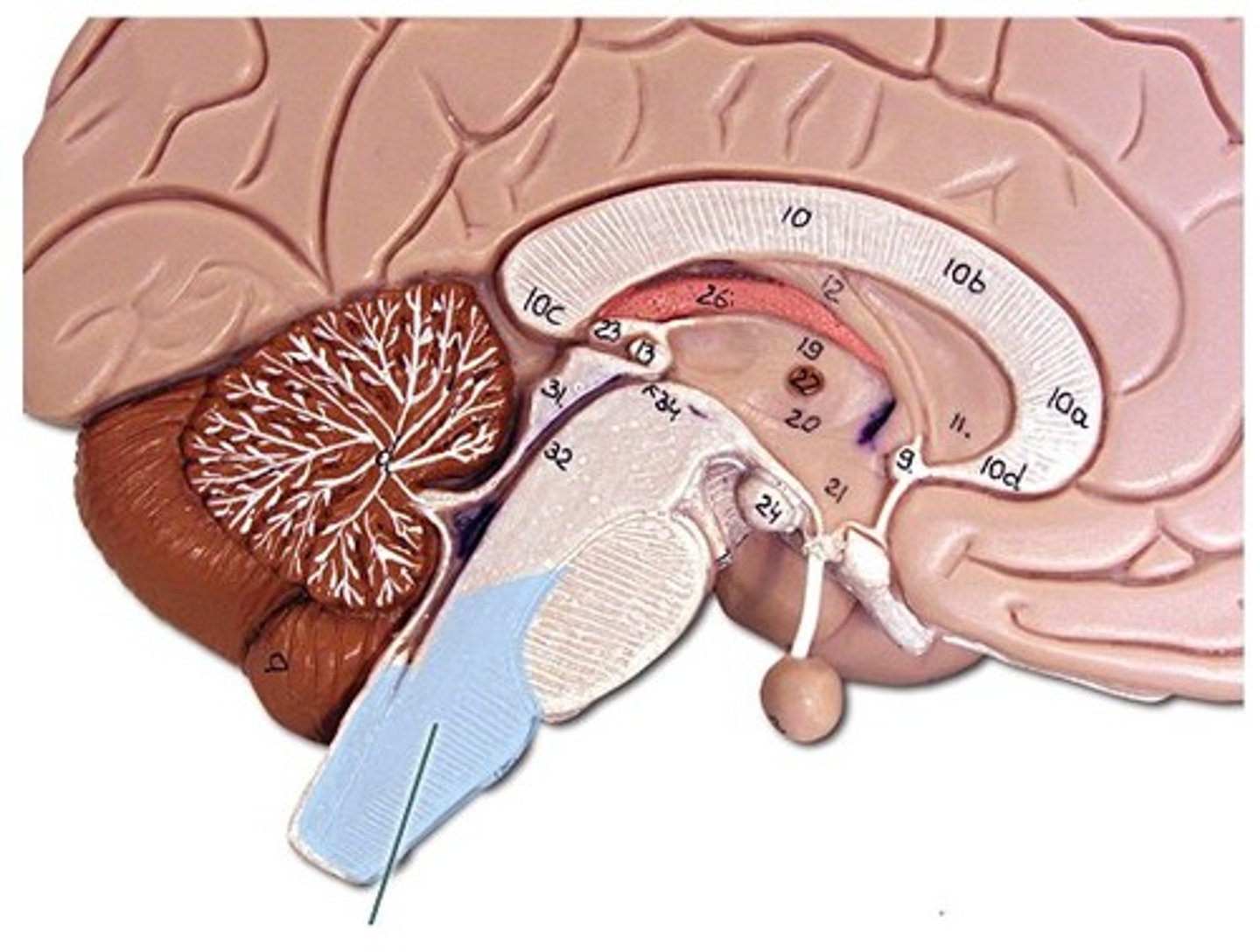
medulla oblongata
Nerve tissue that is continuous inferiorly with the spinal cord; serves as a conduction pathway for ascending and descending nerve tracts; coordinates heart rate, blood vessel diameter, breathing, swallowing, vomiting, coughing, and sneezing.
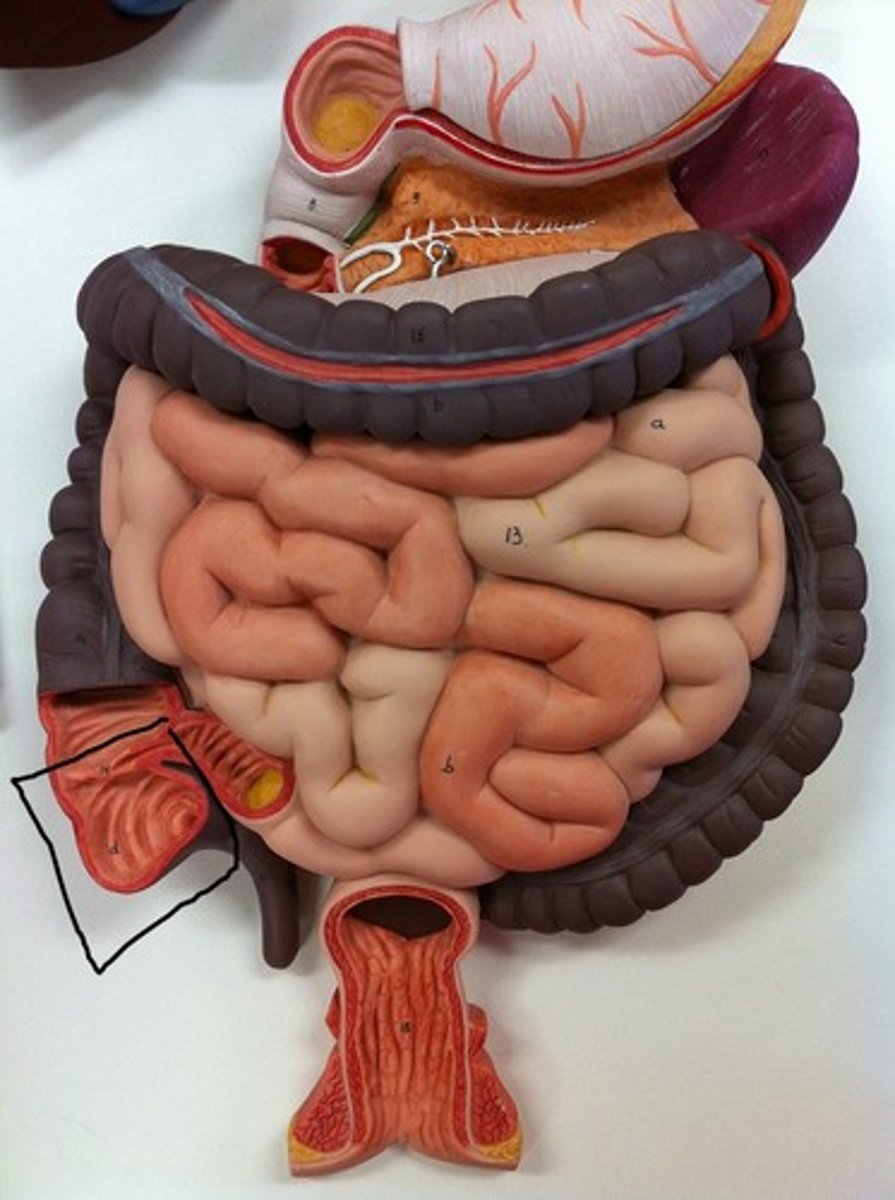
cecum
The first part of the large intestine, into which the ileum opens.
Musculoskeltal System
The bones and voluntary muscles of the body.
appendicular skeleton
The portion of the skeletal system that comprises the arms, legs, pelvis, and shoulder girdle.
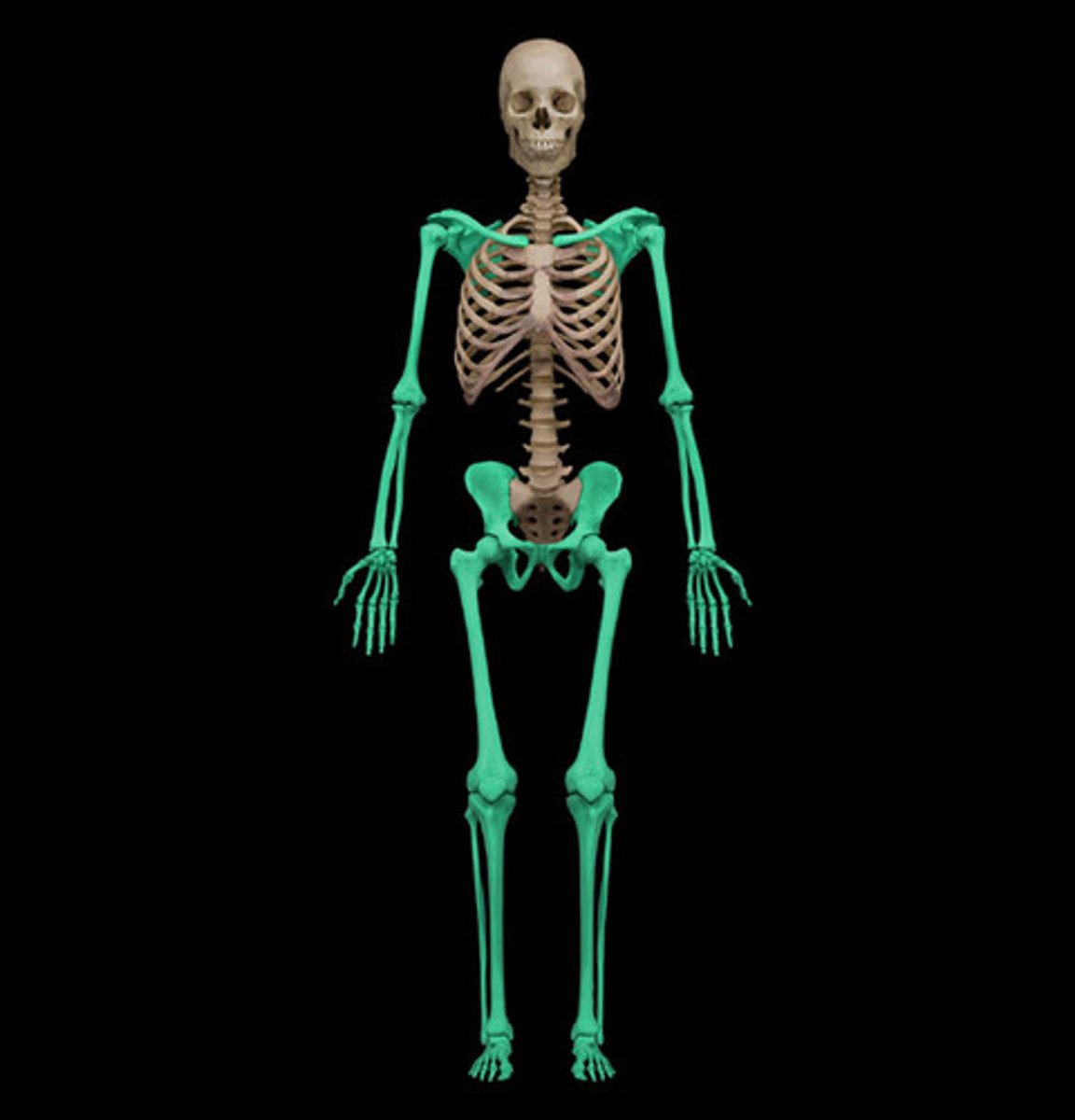
Skeletal Sytem
The framework of the body, composed of bones and other connective tissues, that supports and protects internal organs and other body tissues.
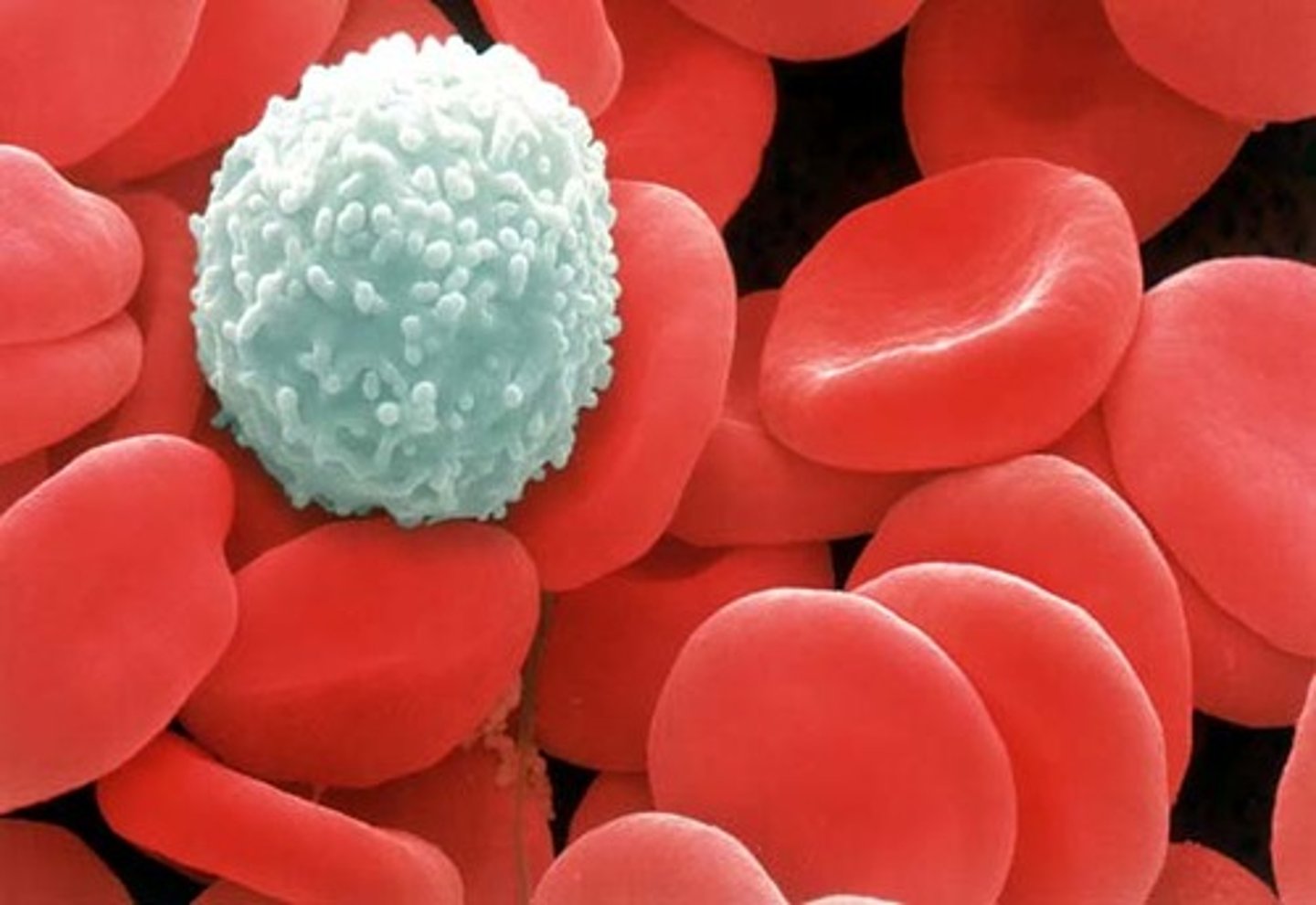
white blood cells
Blood cells that have a role in the body's immune defense mechanisms against infection; also called leukocytes.
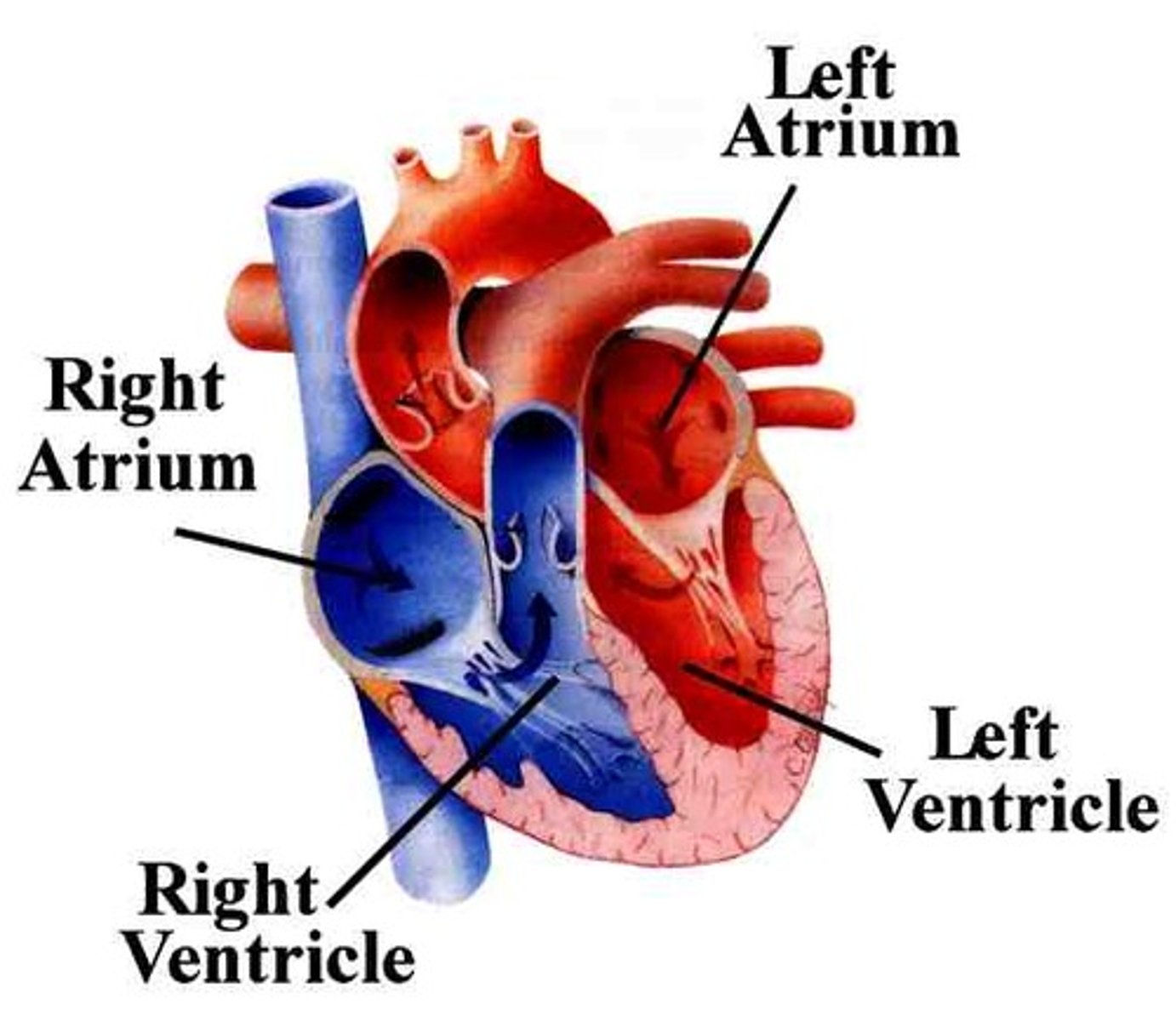
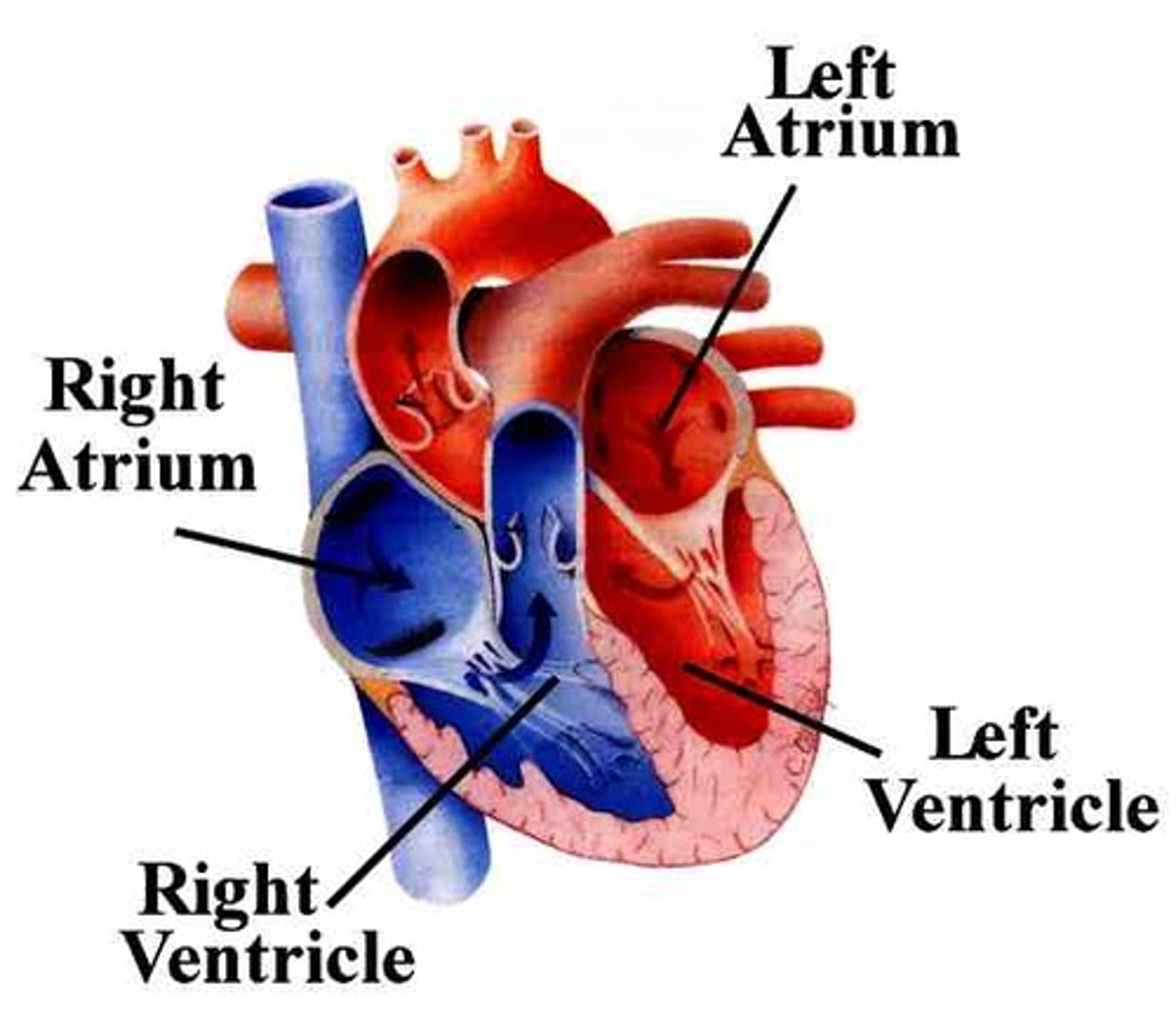
heart
A hollow muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
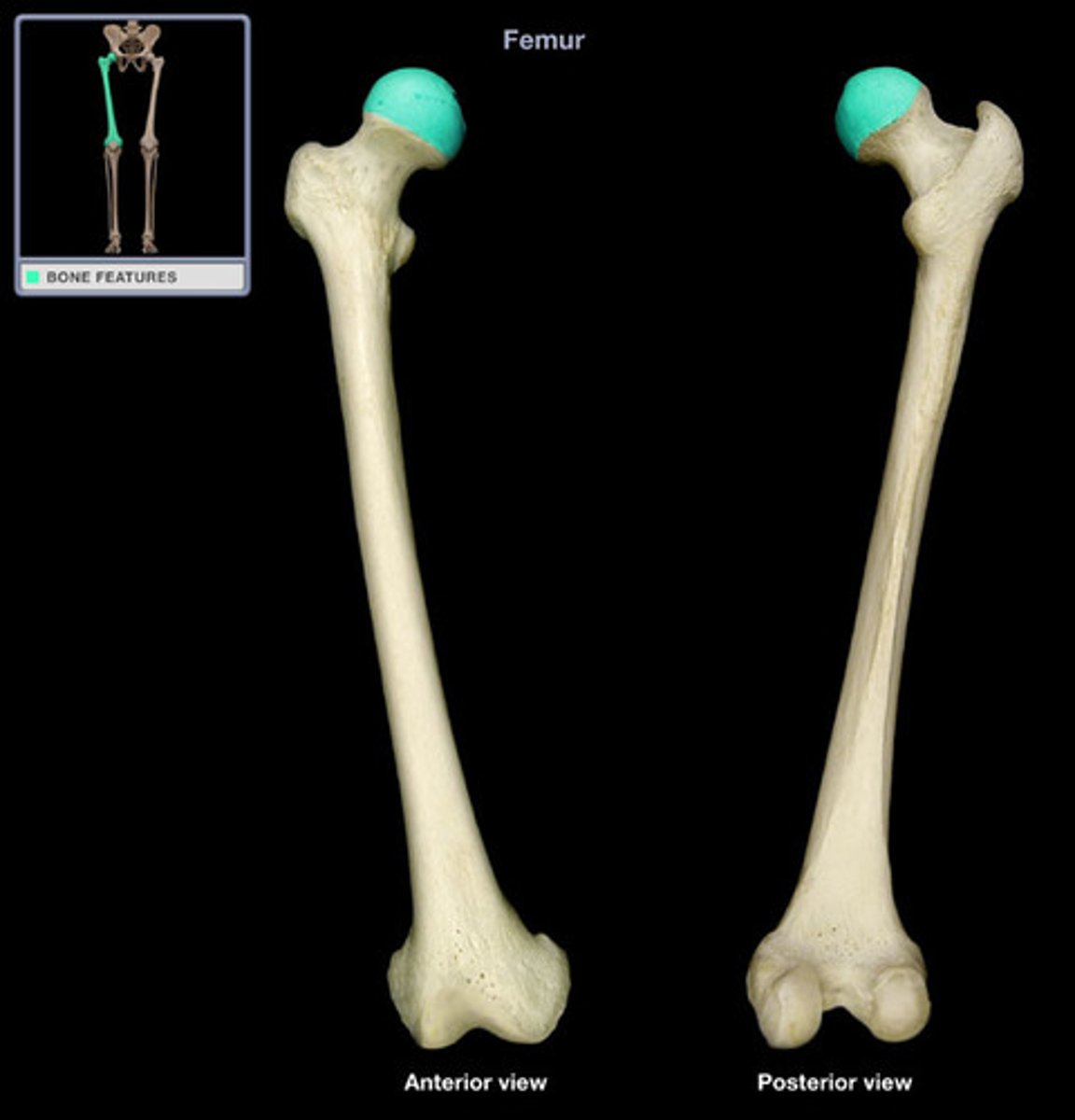
femoral head
The proximal end of the femur, articulating with the acetabulum to form the hip joint.
expiratory reserve volume
The amount of air that can be exhaled following a normal exhalation; average volume is about 1,200 mL in the average adult man.
cellular metabolism
A set of chemical reactions that supplies cells with energy. Includes both anaerobic and aerobic metabolism.
zygomas
The quadrangular bones of the cheek, articulating with the frontal bone, the maxillae, the zygomatic processes of the temporal bone, and the great wings of the sphenoid bone.
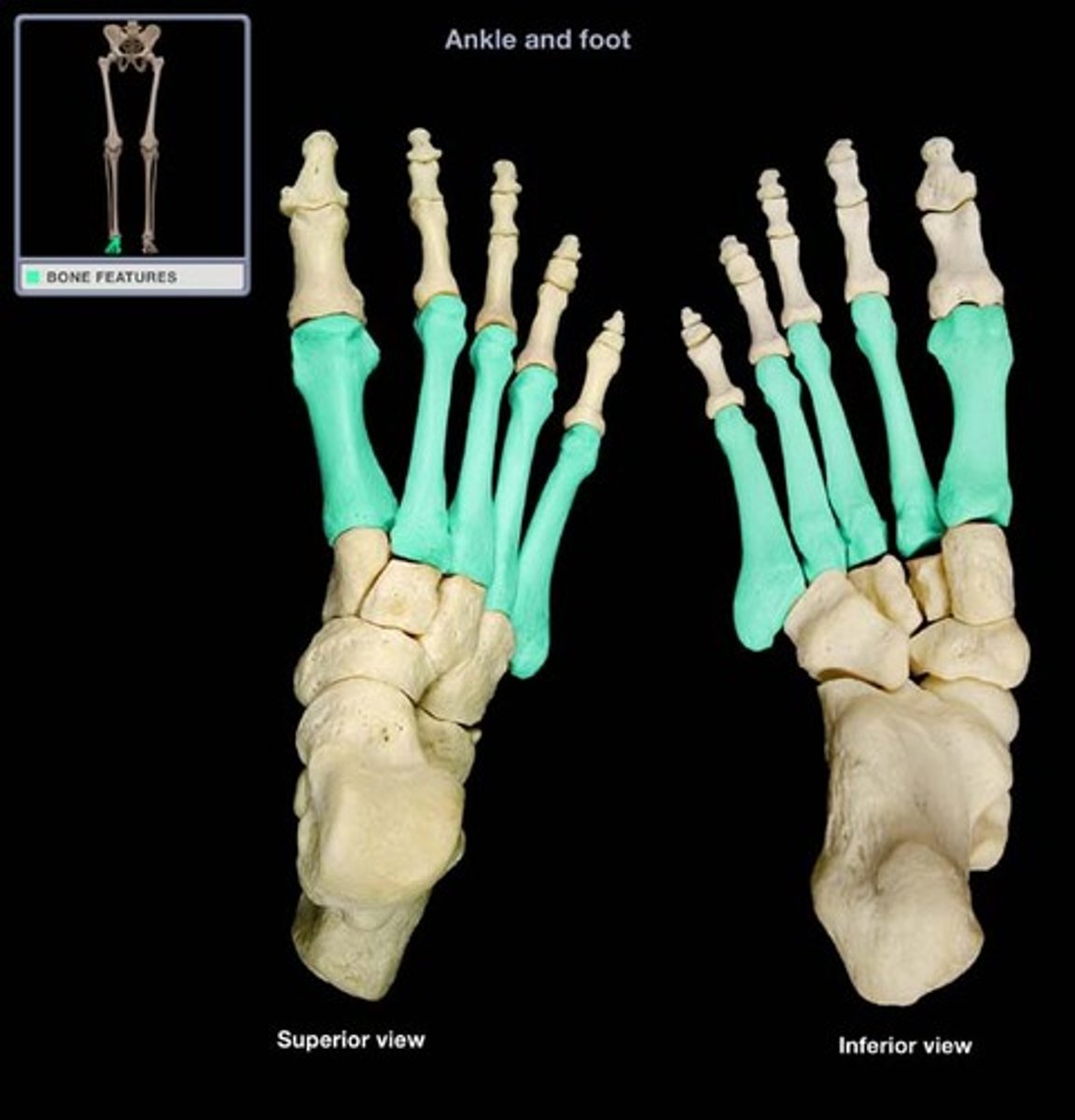
metatarsals
Bones of the foot, situated between the tarsals and phalanges.
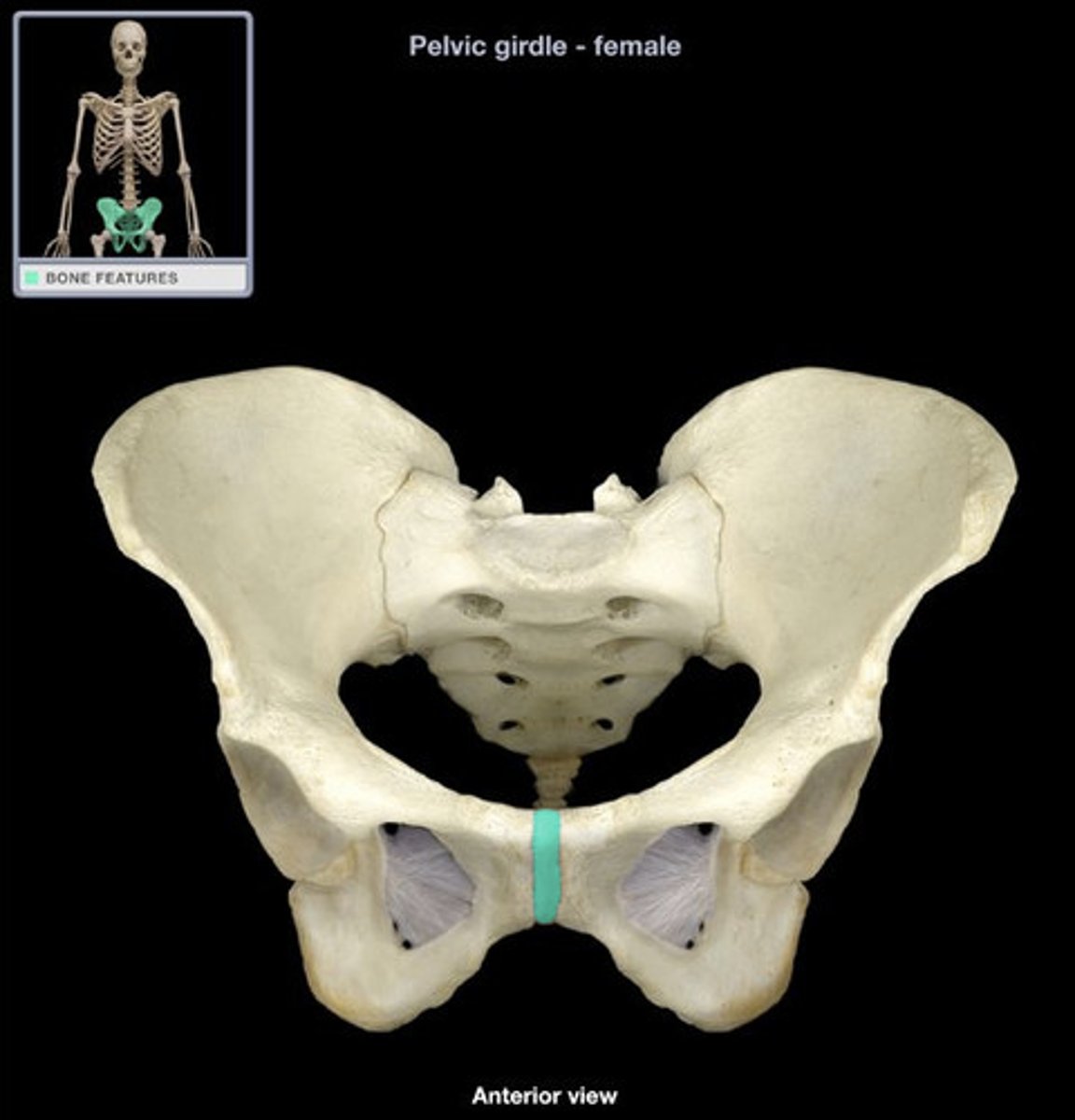
pubic symphysis
A hard, bony, and cartilaginous prominence found at the midline in the lowermost portion of the abdomen where the two halves of the pelvic ring are joined by cartilage at a joint with minimal motion.
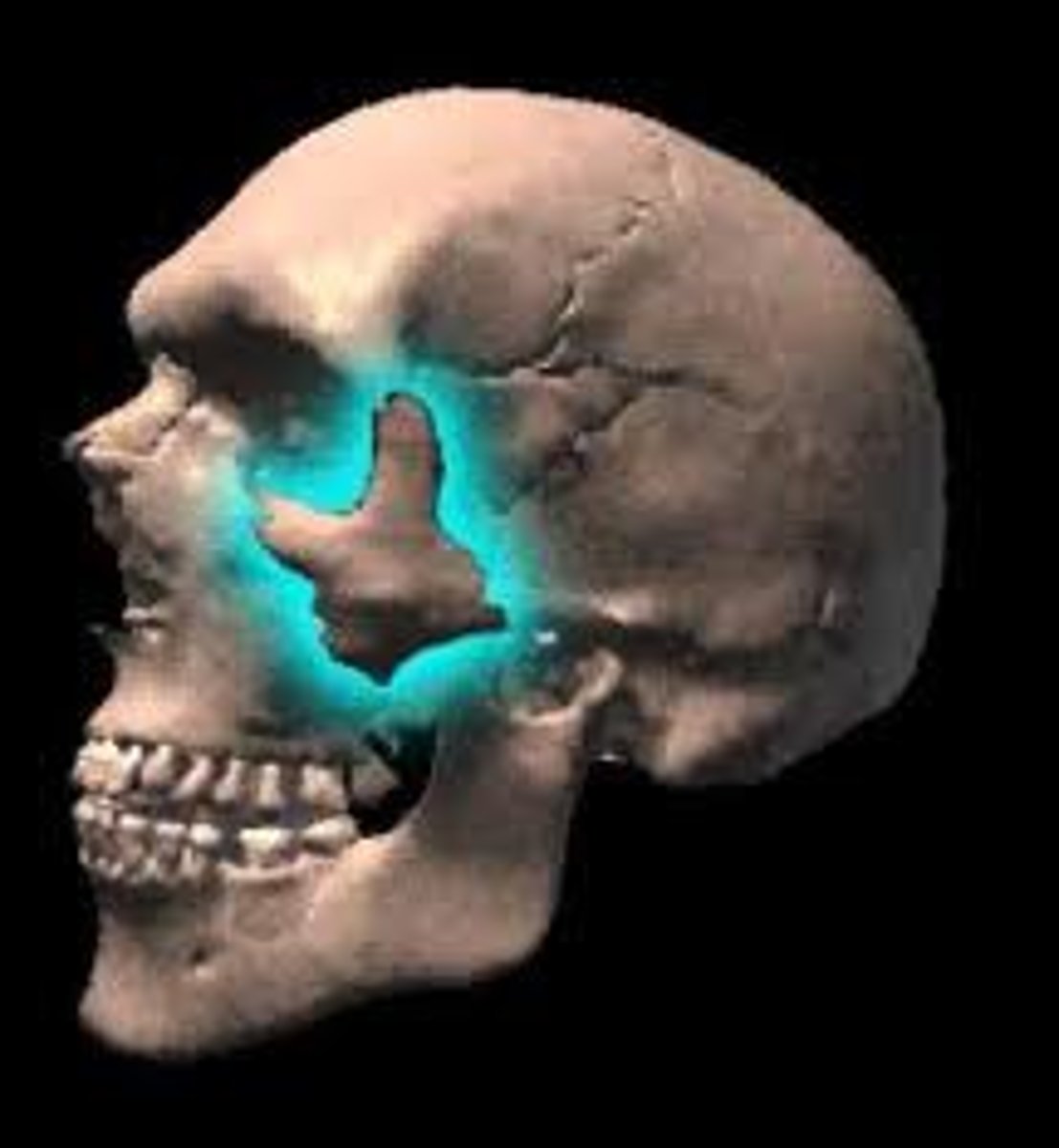
hypoxic drive
A condition in which chronically low levels of oxygen in the blood stimulate the respiratory drive; seen in patients with chronic lung diseases.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter and drug sometimes used in the treatment of shock; produces vasoconstriction through its alpha-stimulator properties.
frontal bone of skull
The bones of the cranium that form the forehead.
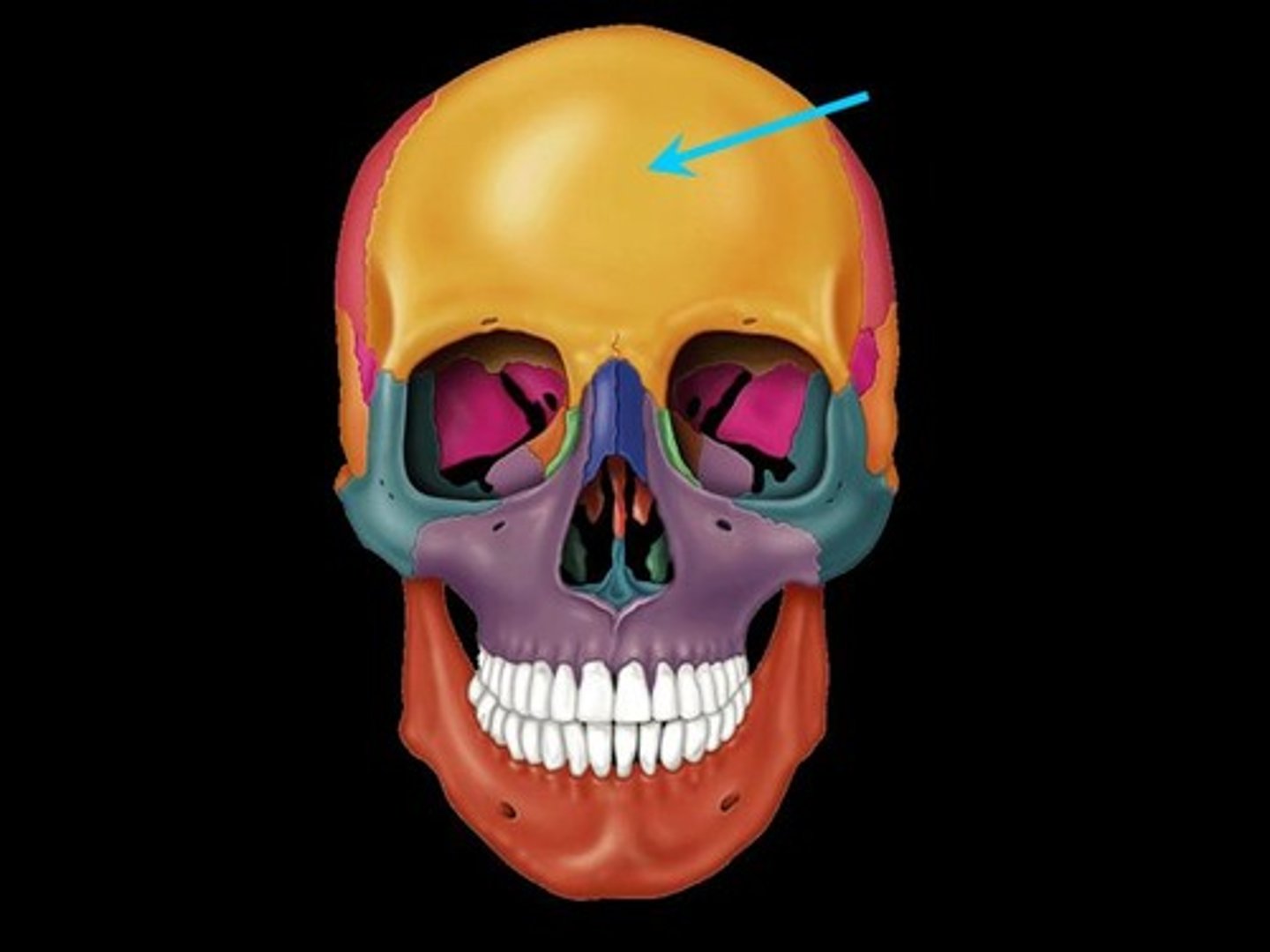
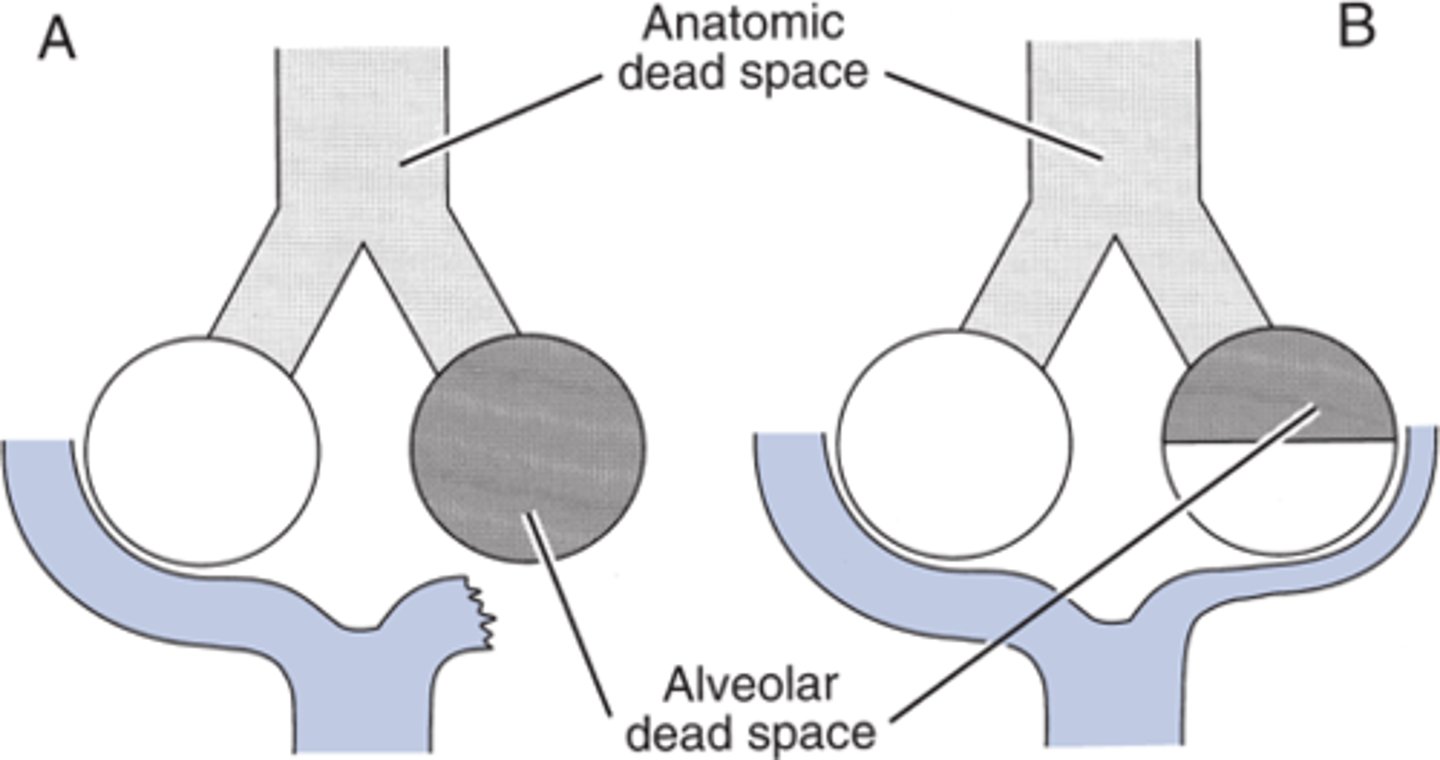
dead space
Any portion of the airway that does contain air and cannot participate in gas exchange, such as the trachea and bronchi.
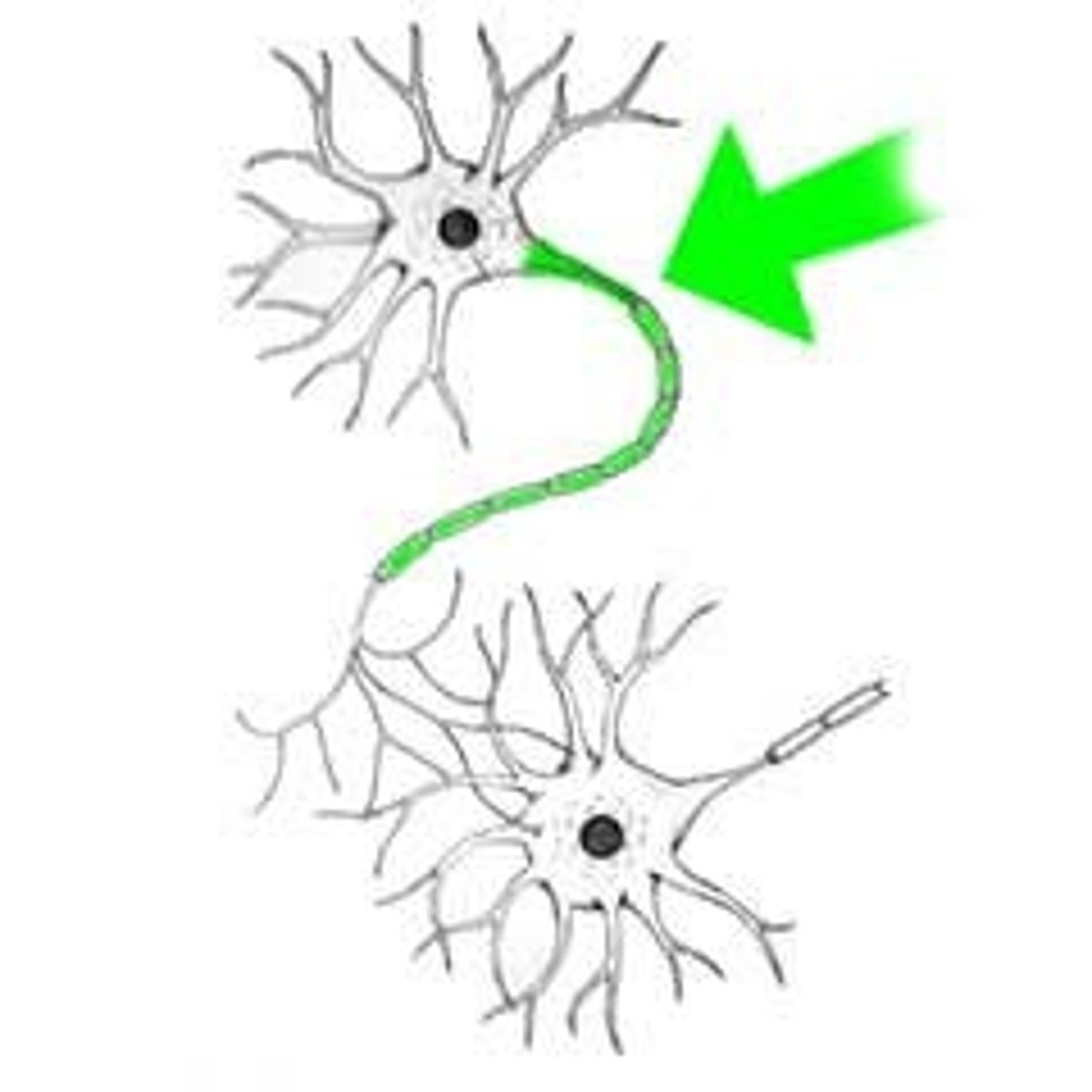
axons
Extensions of a neuron that carry impulses away from the nerve cell body to the dendrites (receivers) of another neuron.
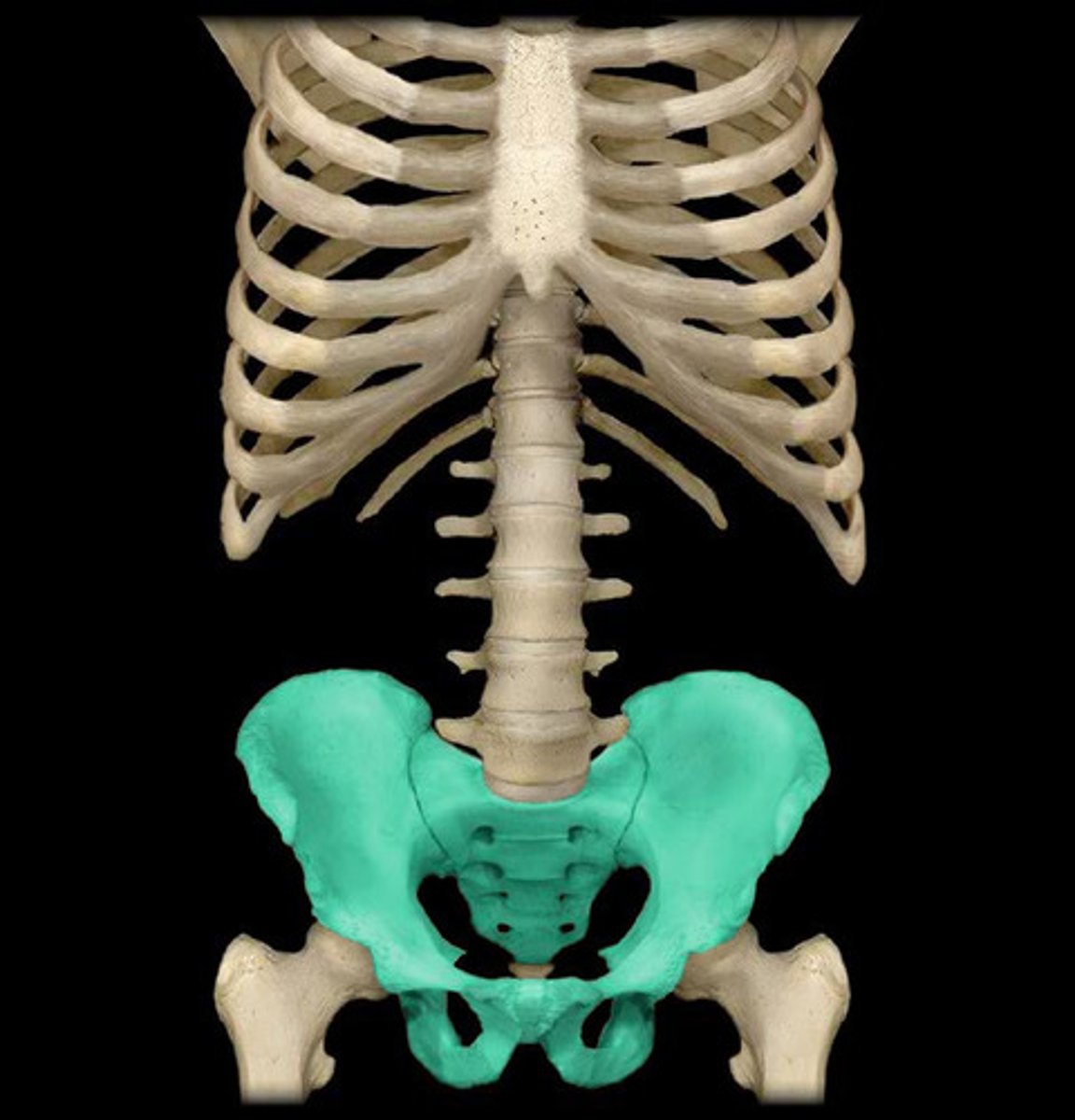
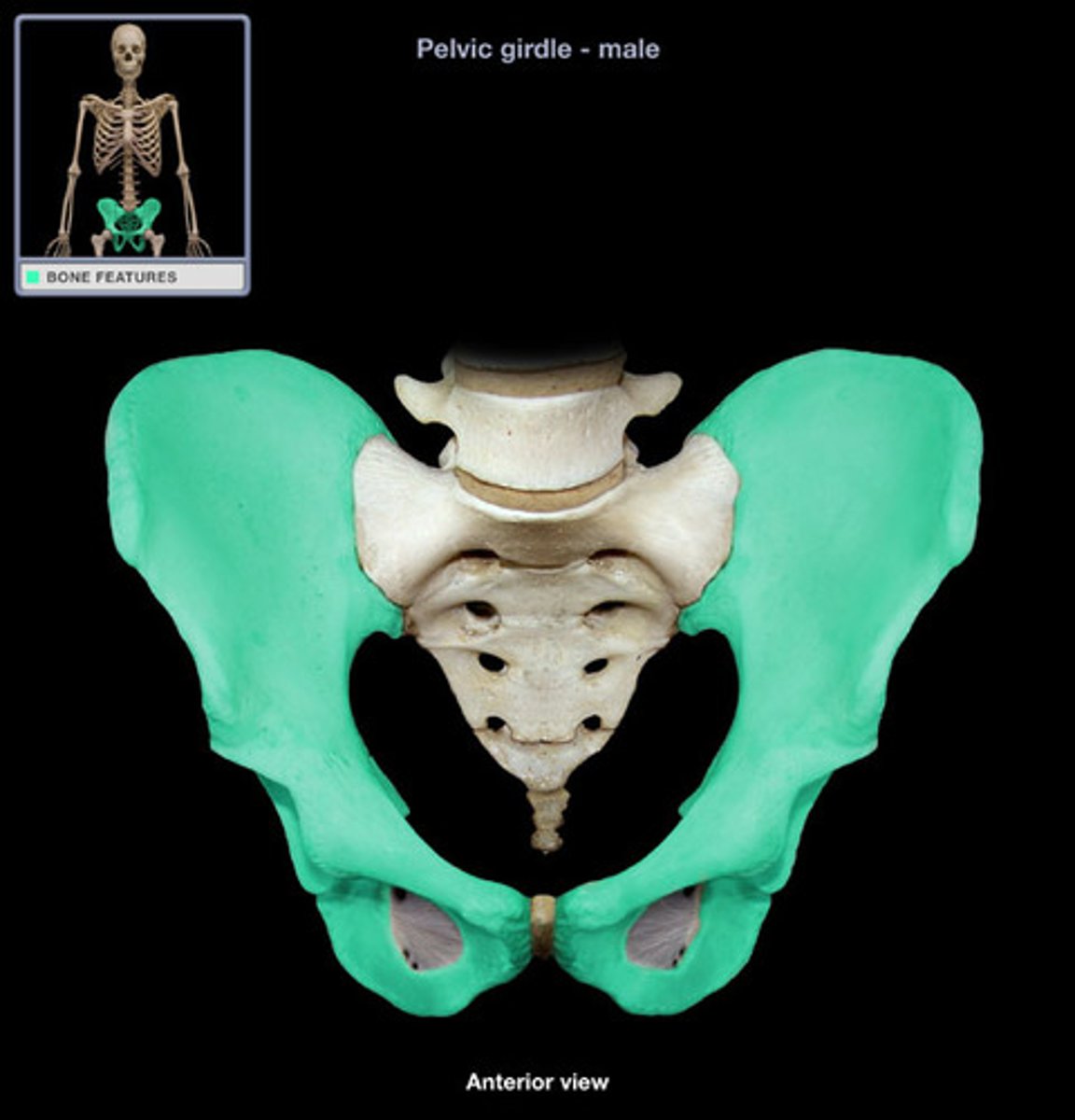
pelvic girdle
The supporting structure for the legs, which serves to connect the legs to the axial skeleton.
cardiac muscle
The heart muscle.
sphincter
Muscles that encircle and, by contracting, constrict a duct, tube, or opening. Examples are found within the rectum, bladder, and blood vessels.
Coxae
hip bones
Cartilage
The smooth connective tissue that forms the support structure of the skeletal system and provides cushioning between bones; also forms the nasal septum and portions of the outer ear.
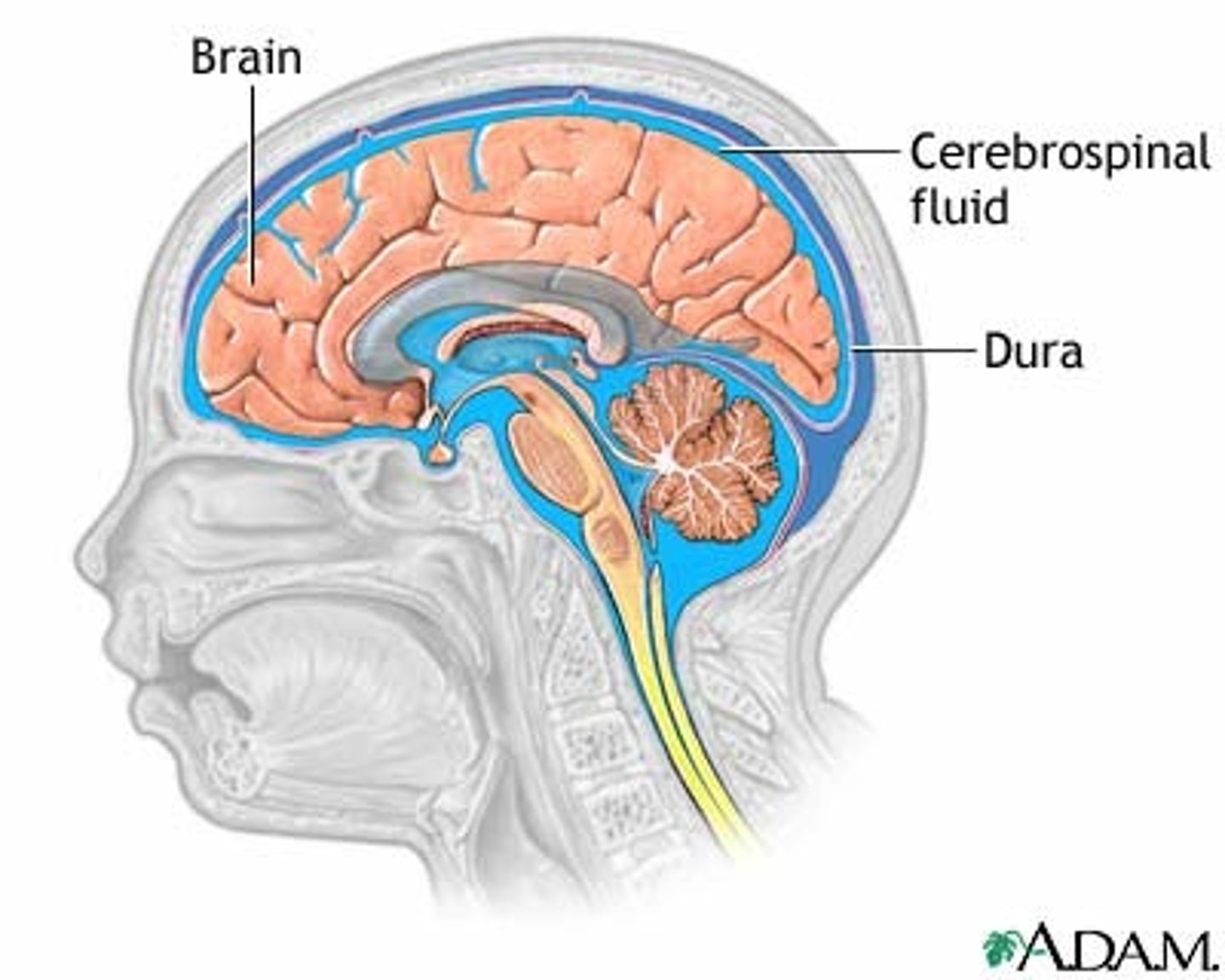
cerebrospinal fluid
Fluid produced in the ventricles of the brain that flows in the subarachnoid space and bathes the meninges.
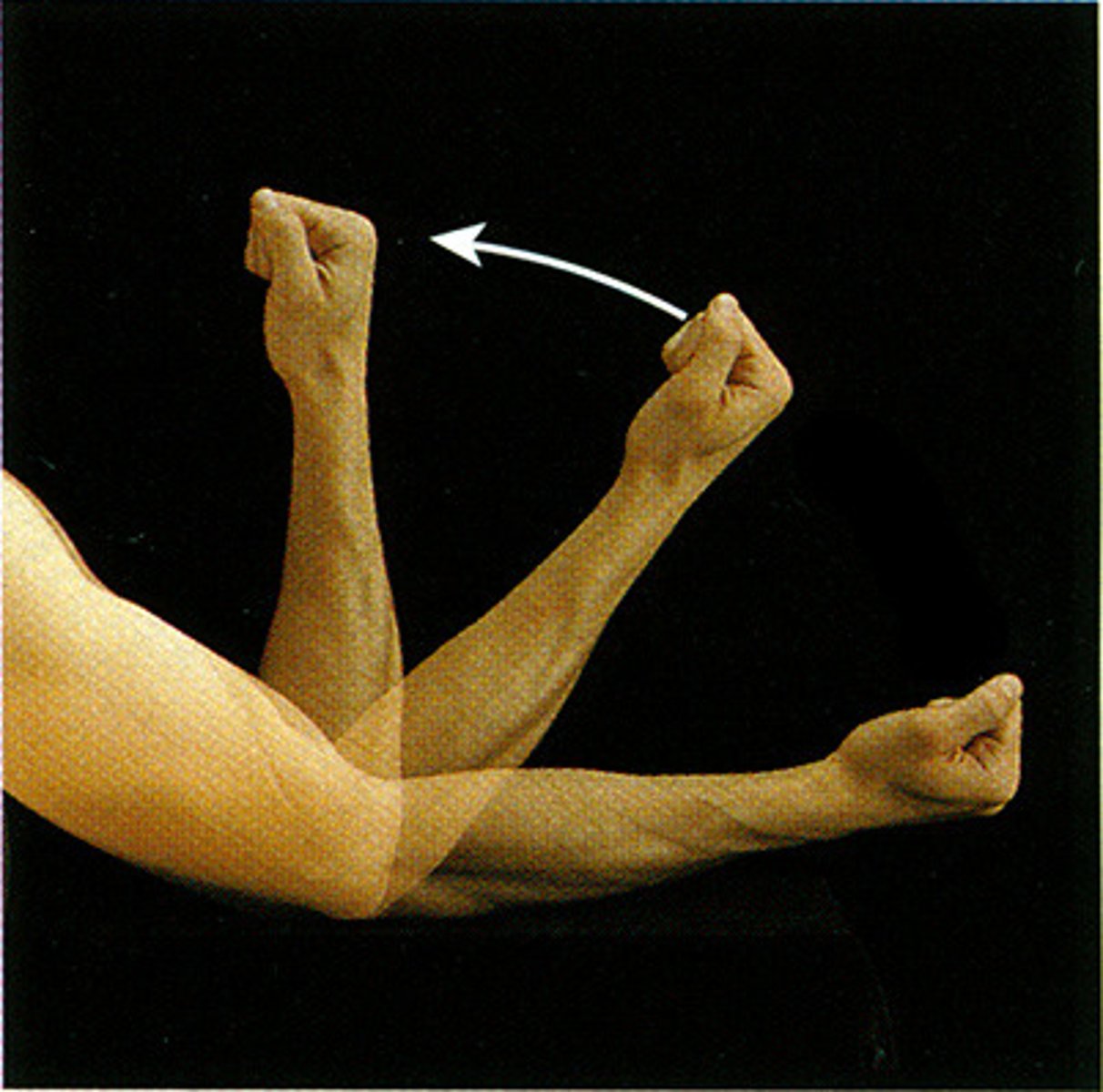
flexion
The bending of a joint.
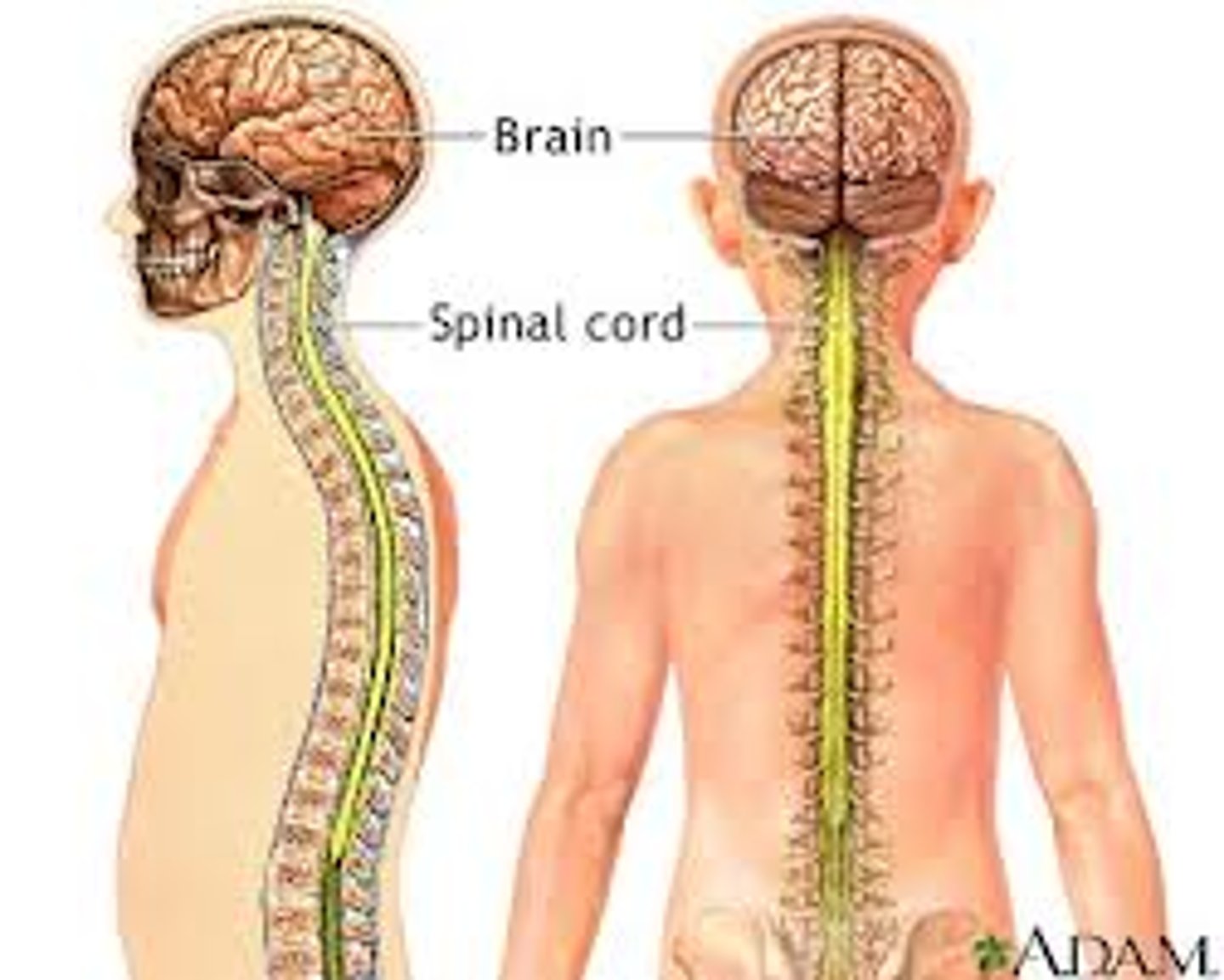
central nervous system
The brain and spinal cord.
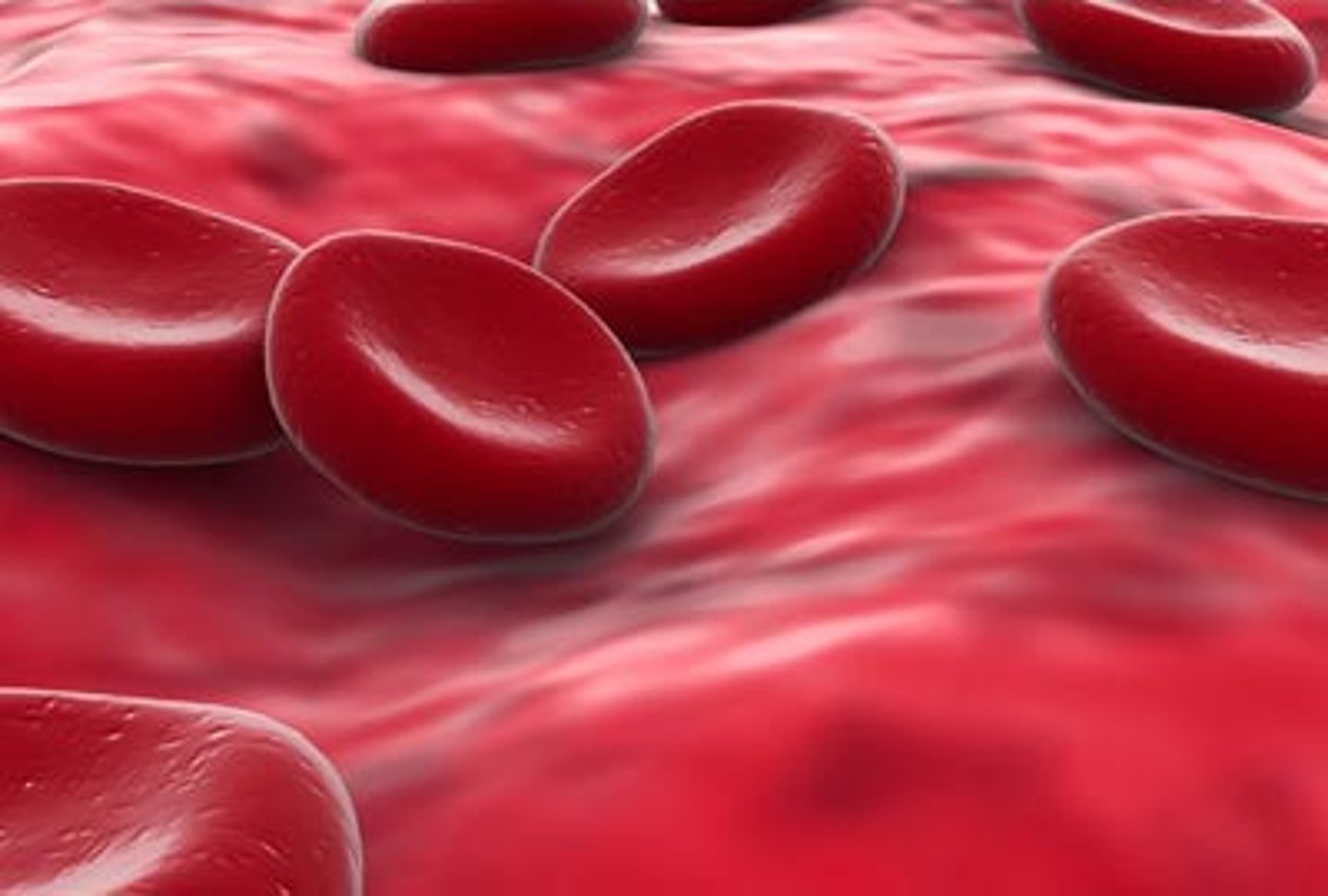
red blood cells
Cells that carry oxygen to the body's tissues; also called erythrocytes.
sensory nerves
The nerves that carry sensations such as touch, taste, smell, heat, cold, and pain from the body to the central nervous system.
mandible
The bone of the lower jaw.
respiration
The process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide.

inspiratory reserve volume
The amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal inhalation; the amount of air that can be inhaled in addition to the normal tidal volume.
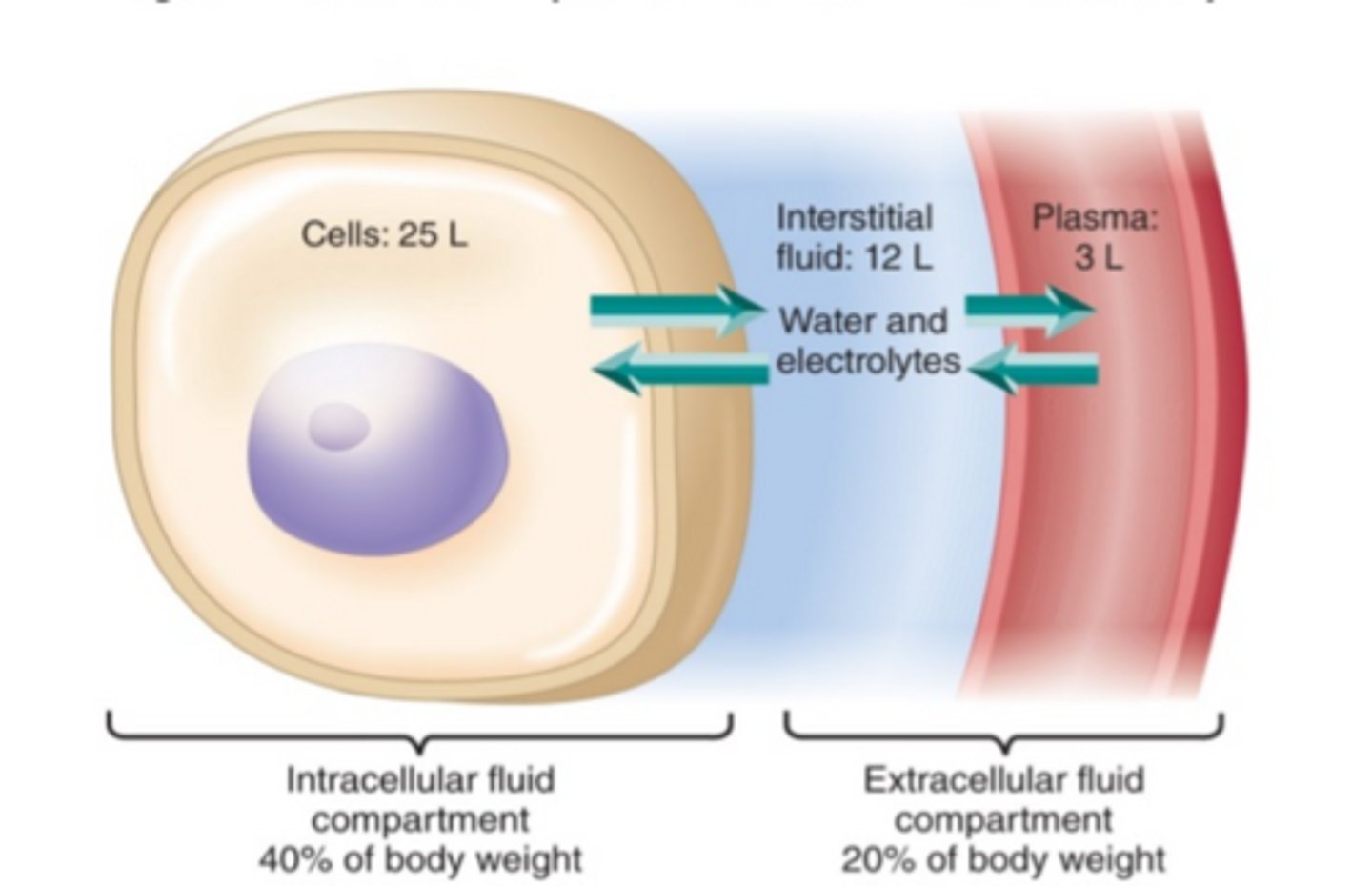
intracellular space
The space within a cell or cells.
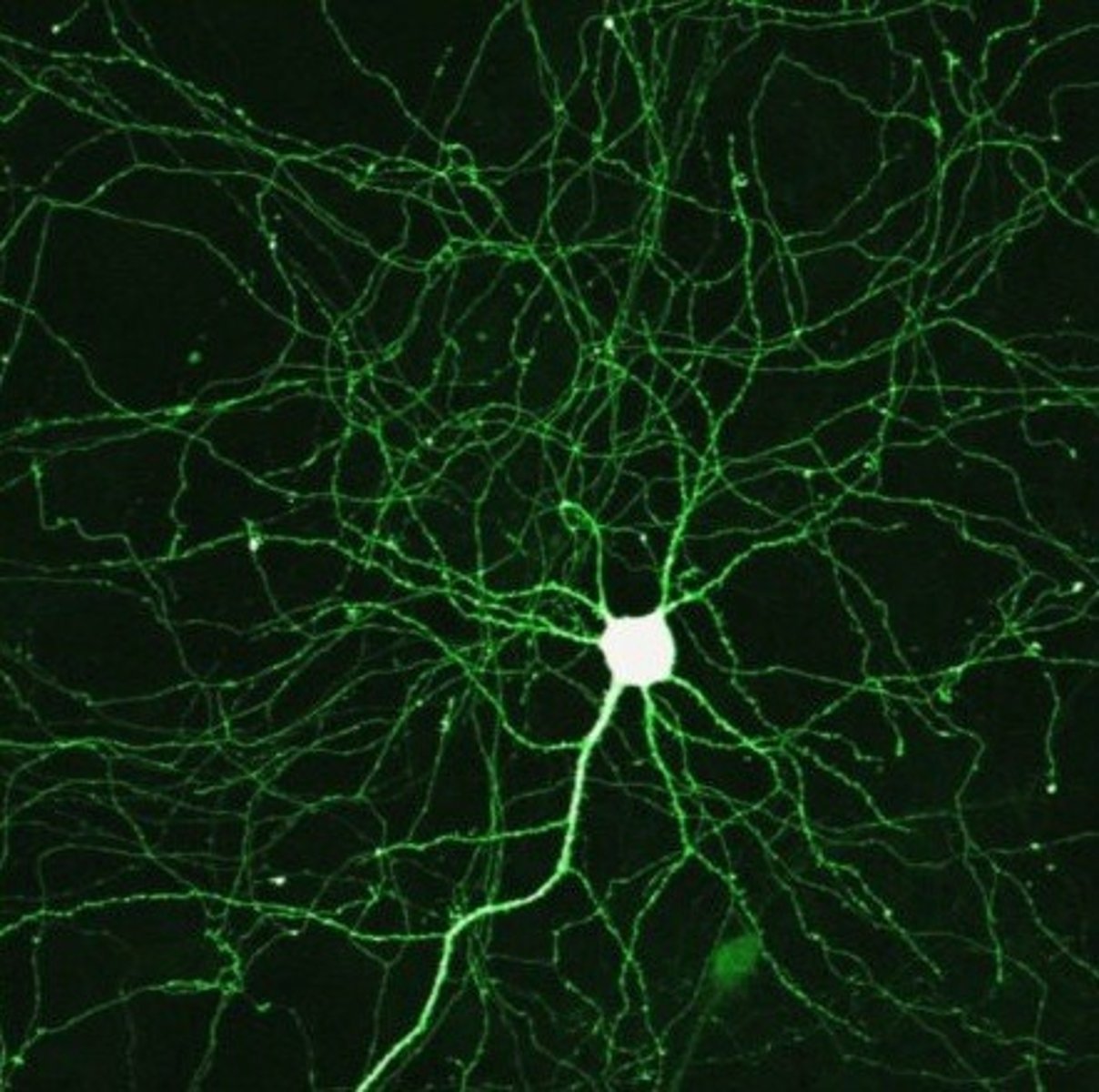
neurons
The functional units of the nervous system; also called nerve cells.
adrenergic
Pertaining to nerves that release the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, or noradrenaline; also pertains to the receptors acted on by norepinephrine.
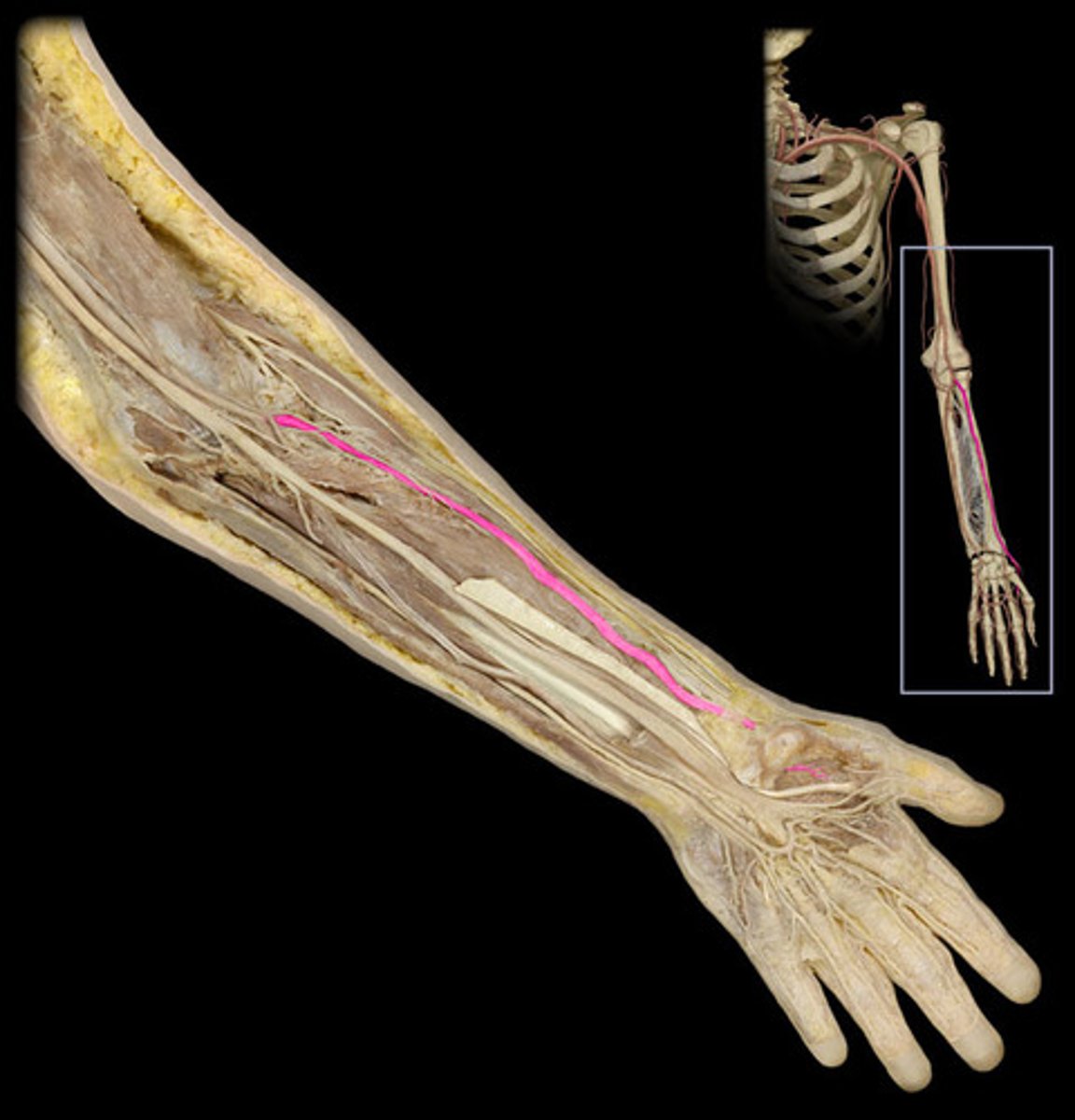
radial artery
The major artery in the forearm; it is palpable at the wrist on the thumb side.
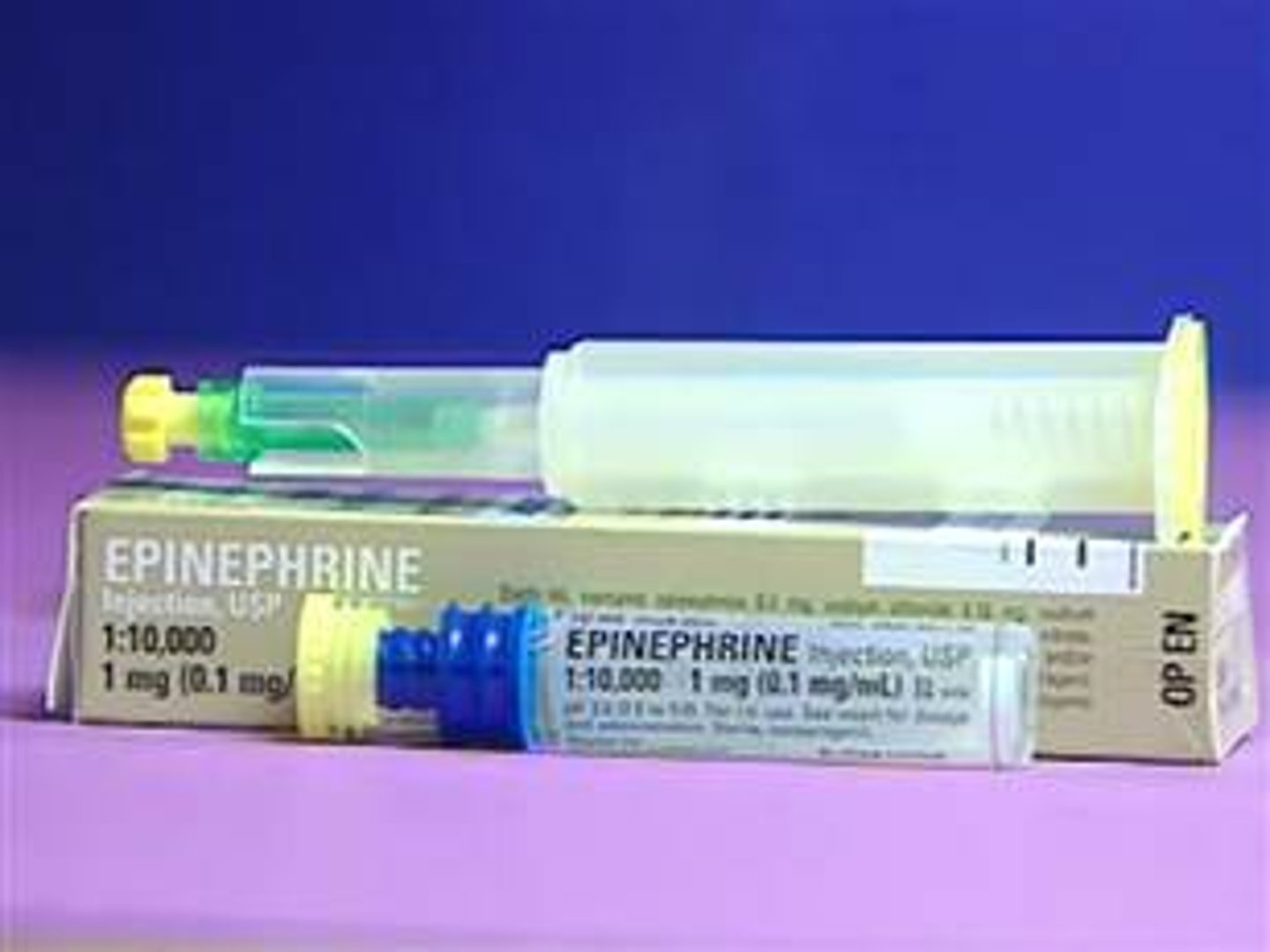
Epinephrine
A medication that increases heart rate and blood pressure but also eases breathing problems by decreasing muscle tone of the bronchiole tree; a substance produced by the body (commonly called adrenaline), and a drug produced by pharmaceutical companies that increases pulse rate and blood pressure; the drug of choice for an anaphylactic reaction.
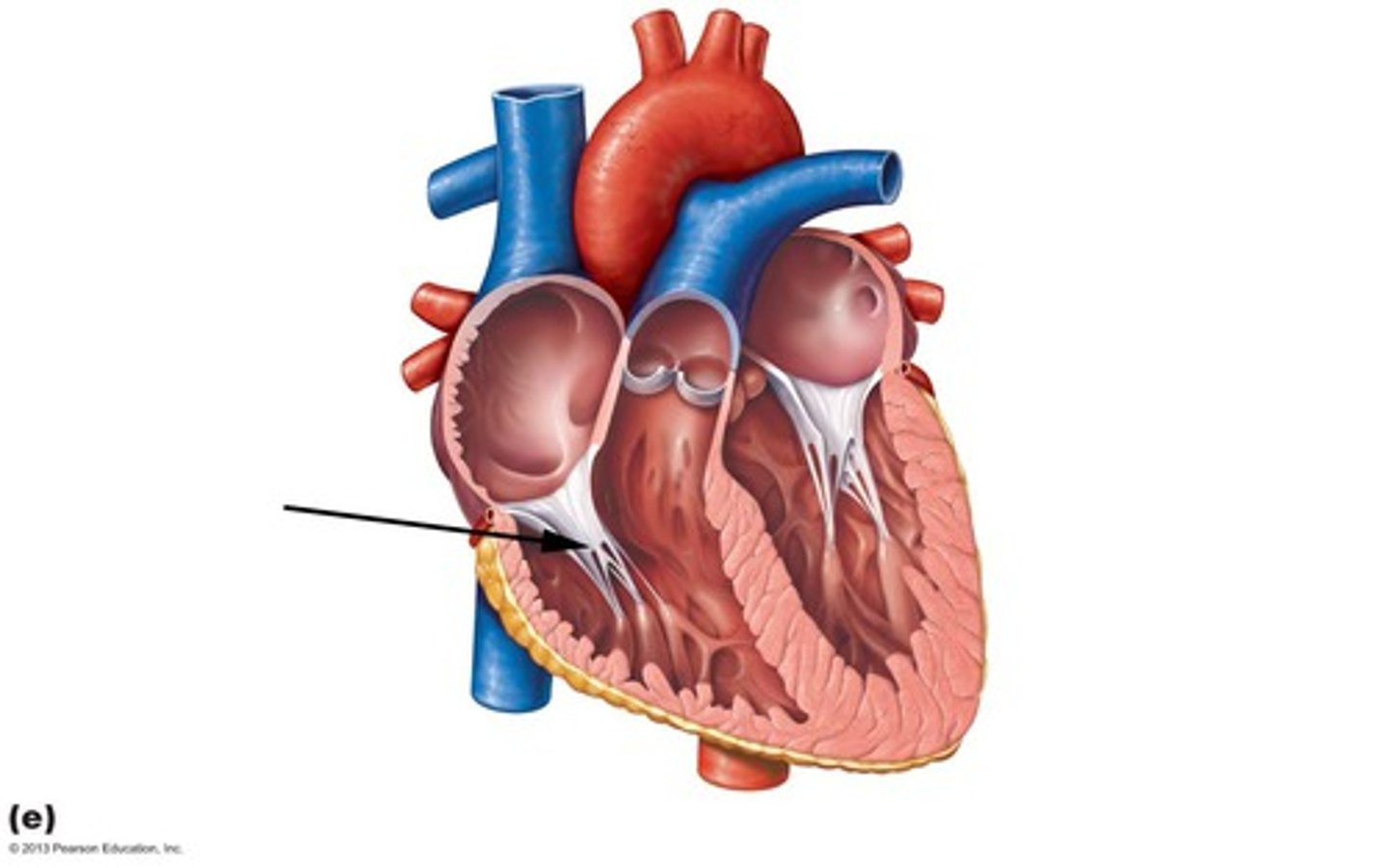
chordae tendineae
Thin bands of fibrous tissue that attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting.
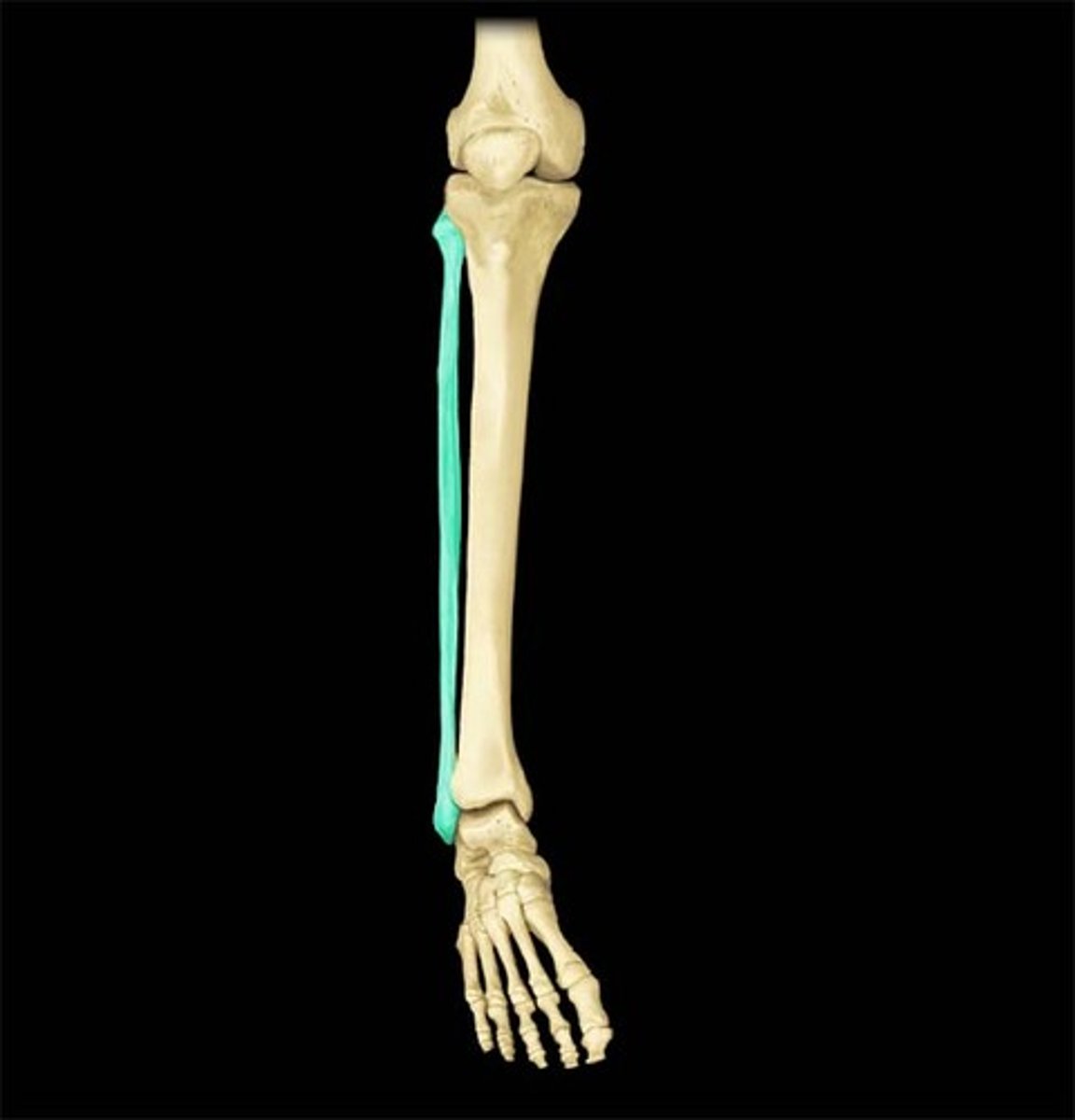
fibula
The smaller of the two bones that form the lower leg, located on the lateral side.
shock
A condition in which the circulatory system fails to provide sufficient circulation to maintain normal cellular functions; also called hypoperfusion.
atrium
One of the two upper chambers of the heart.
nasopharynx
The part of the pharynx that lies above the level of the roof of the mouth, or palate.
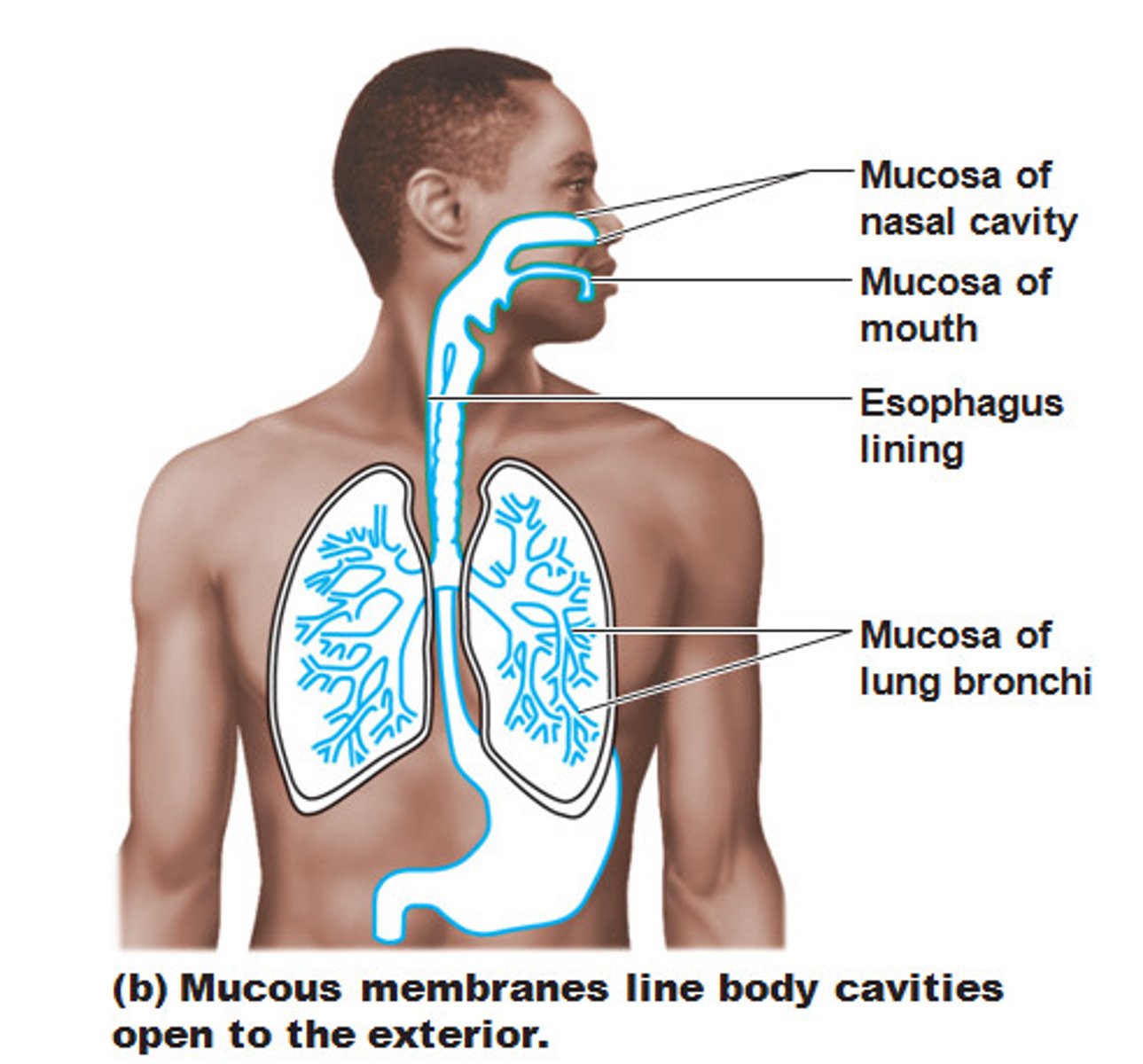
mucous membranes
The linings of body cavities and passages that communicate directly or indirectly with the environment outside the body.
vagina
The outermost cavity of a woman's reproductive tract; the lower part of the birth canal.
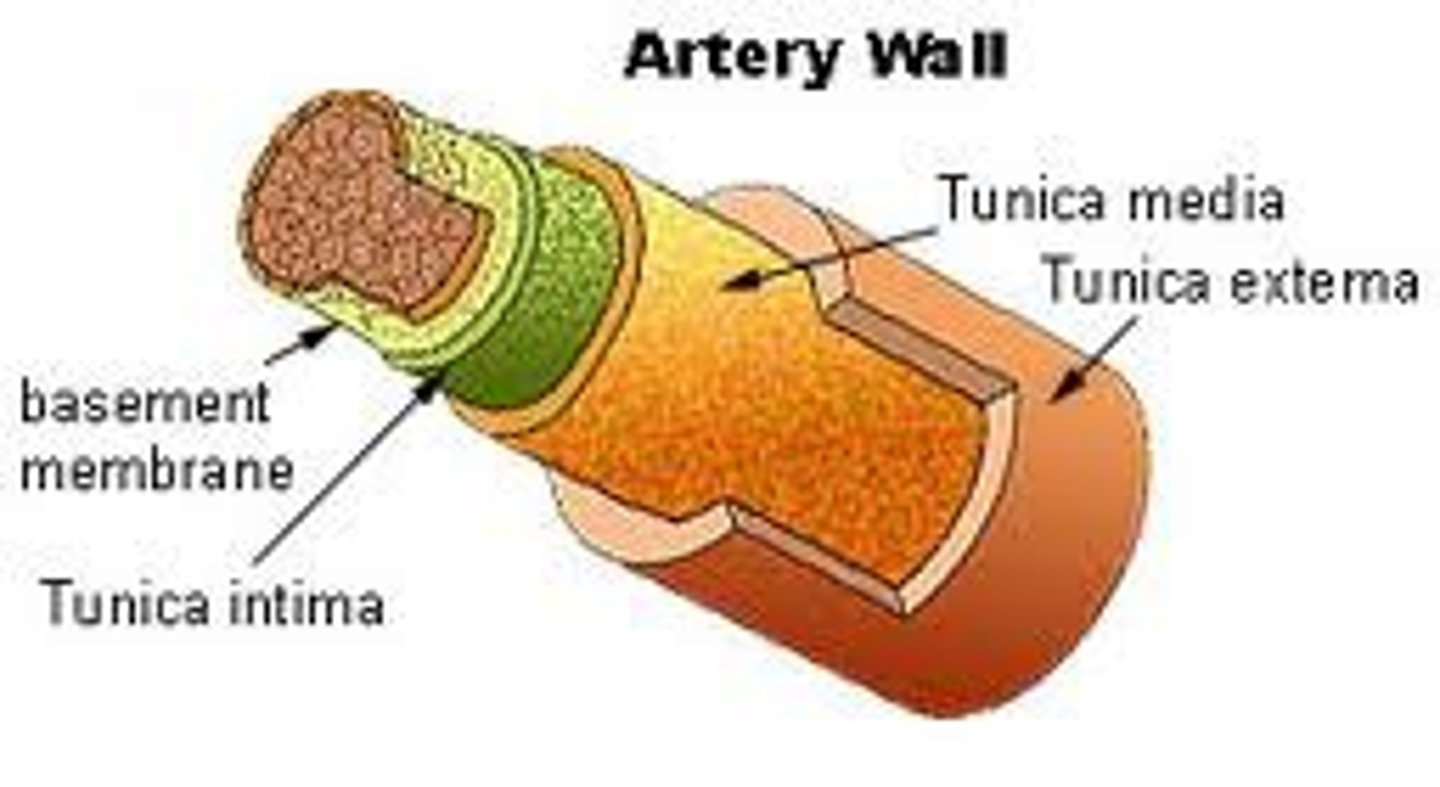
tunica media
The middle and thickest layer of tissue of a blood vessel wall, composed of elastic tissue and smooth muscle cells that allow the vessel to expand or contract in response to changes in blood pressure and tissue demand.
trachea
The windpipe; the main trunk for air passing to and from the lungs.
sternum
The breast bone.
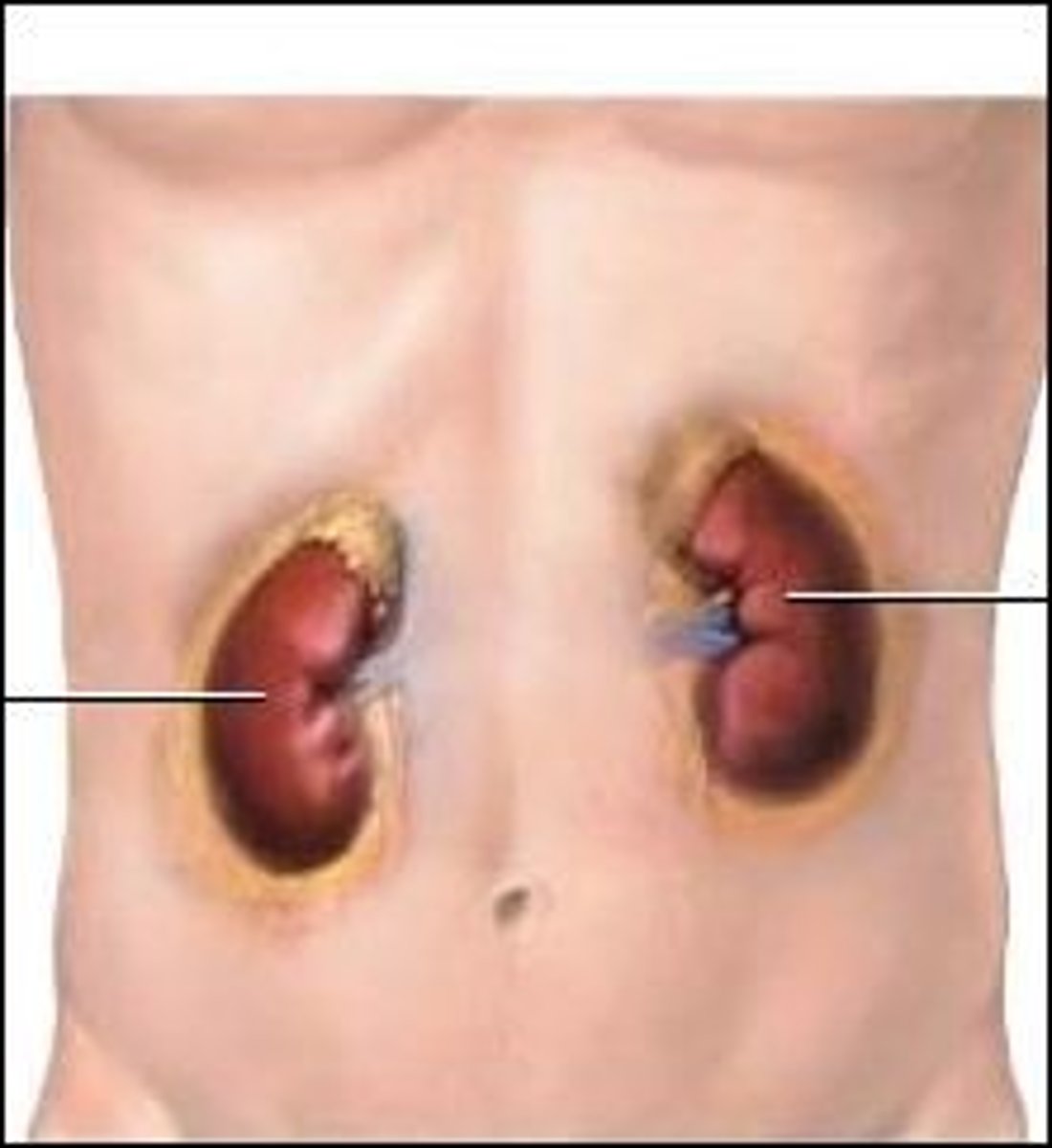
kidneys
Two retroperitoneal organs that excrete the end products of metabolism as urine and regulate the body's salt and water content.
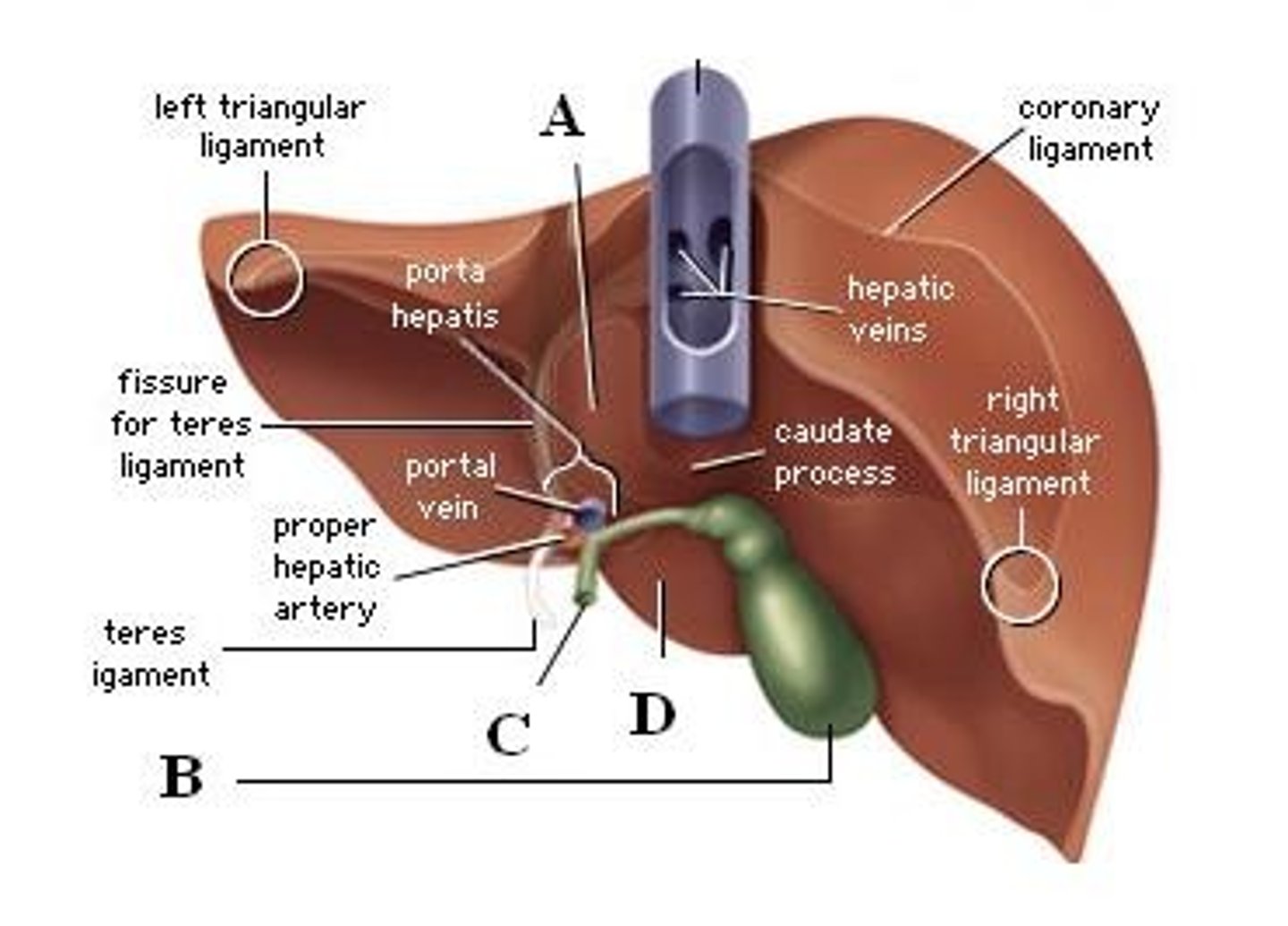
gallbladder
A sac on the undersurface of the liver that collects bile from the liver and discharges it into the duodenum through the common bile duct.
ligaments
Bands of fibrous tissue that connect bones to bones. These tissues support and strengthen a joint.
lumbar spine
The lower part of the back, formed by the lowest five nonfused vertebrae; also called the dorsal spine
parasympathetic nervous system
The part of the autonomic nervous system that controls vegetative functions such as digestion of food and relaxation.
respiratory system
All the structures of the body that contribute to the process of breathing, consisting of the upper and lower airways and their component parts.
rectum
The lowermost end of the colon.
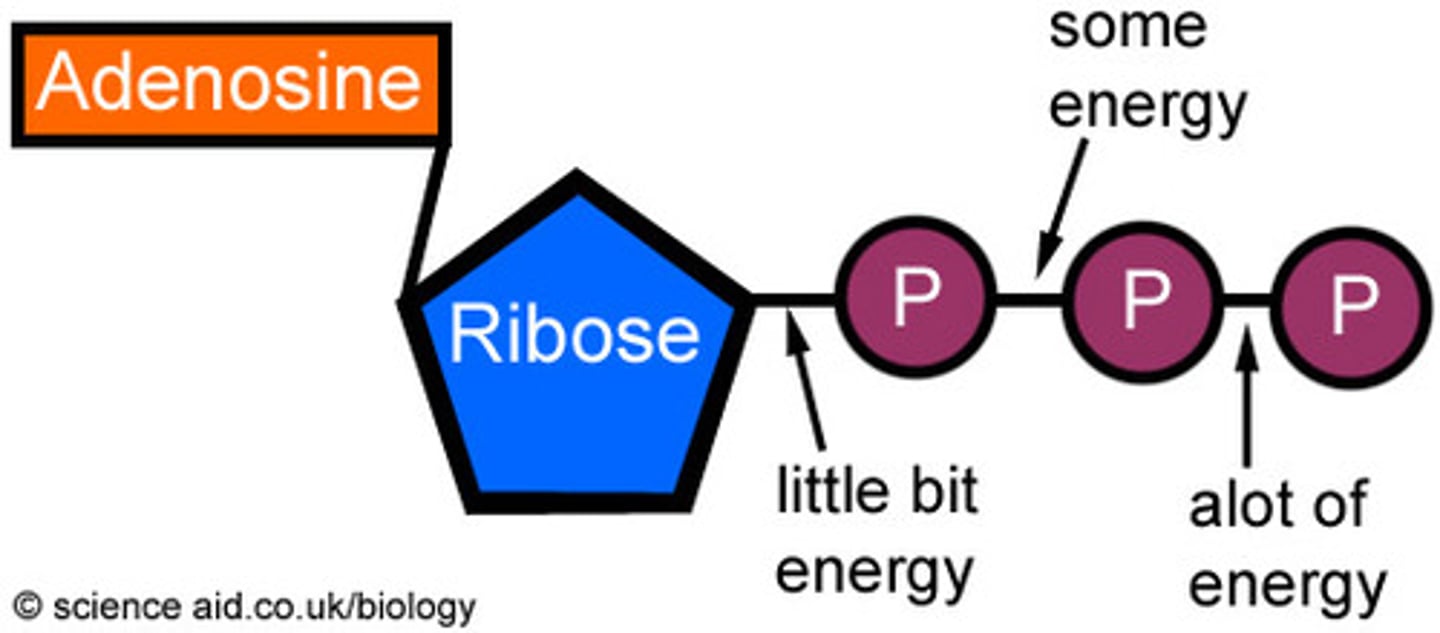
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The nucleotide involved in energy metabolism; used to store energy.
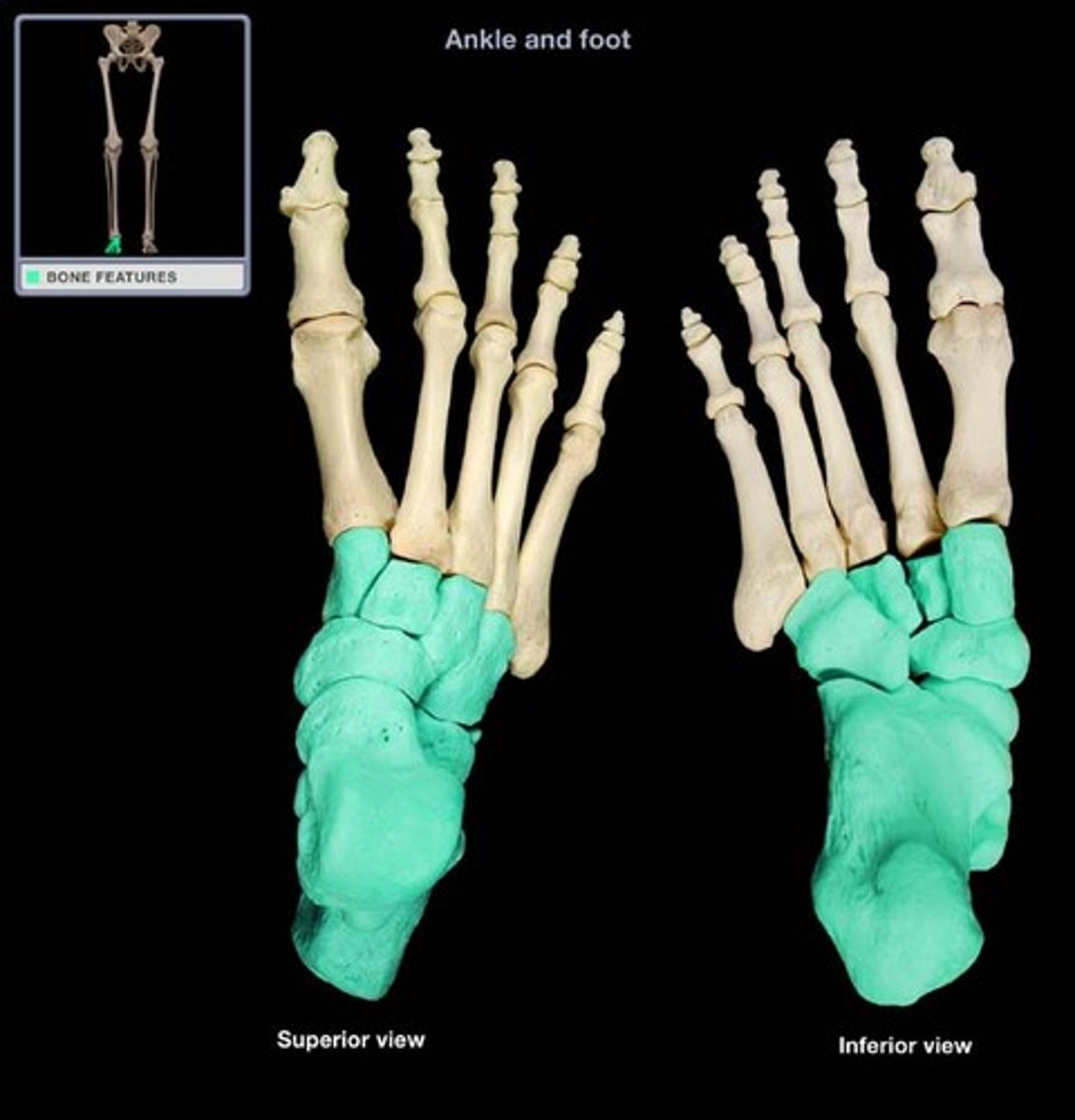
tarsals
The group of bones situated between the lower leg bones (ie, tibia and fibula) and the metatarsal bones of the foot.
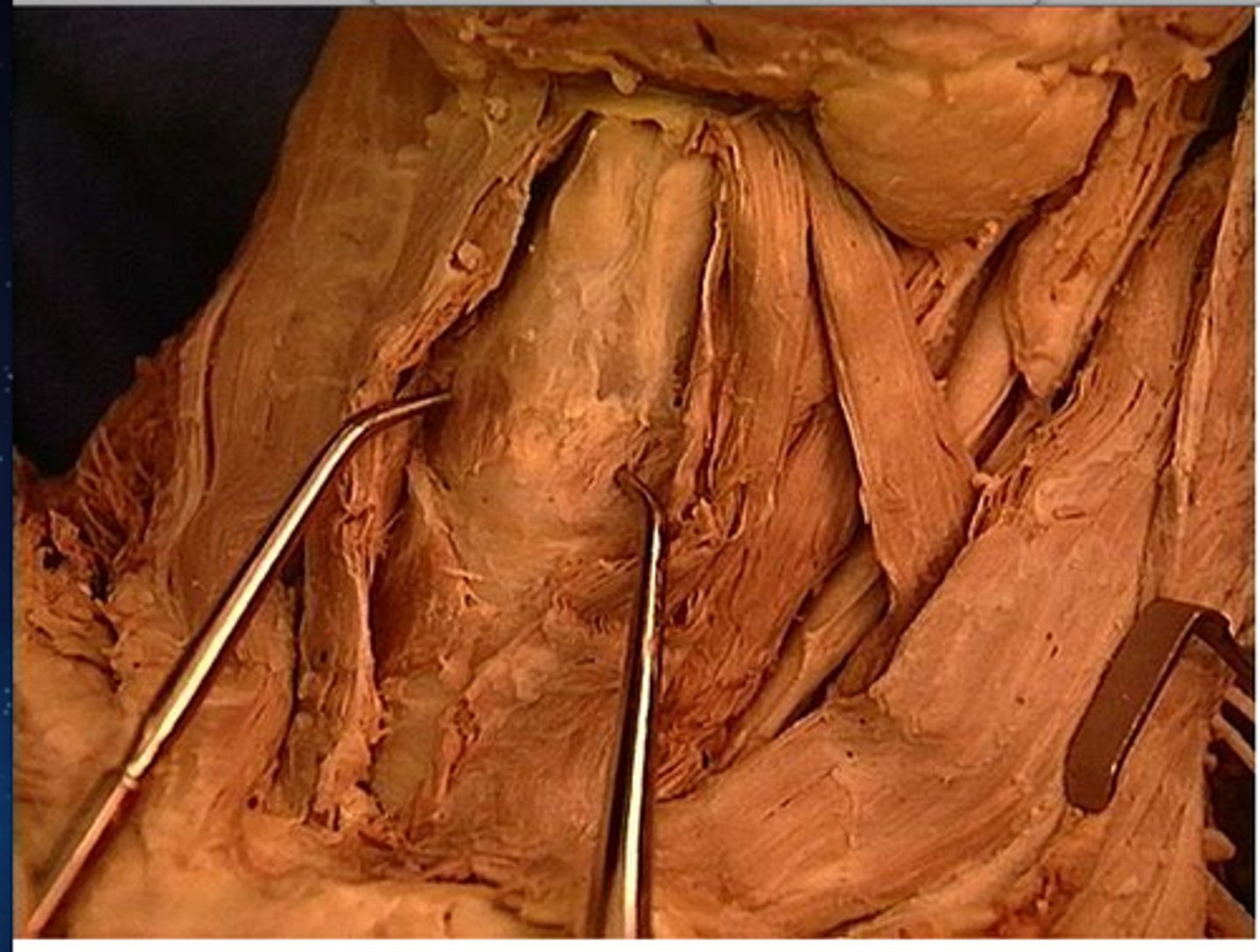
circothyroid membrane
A thin sheet of fascia that connects the thyroid and cricoid cartilages that make up the larynx.
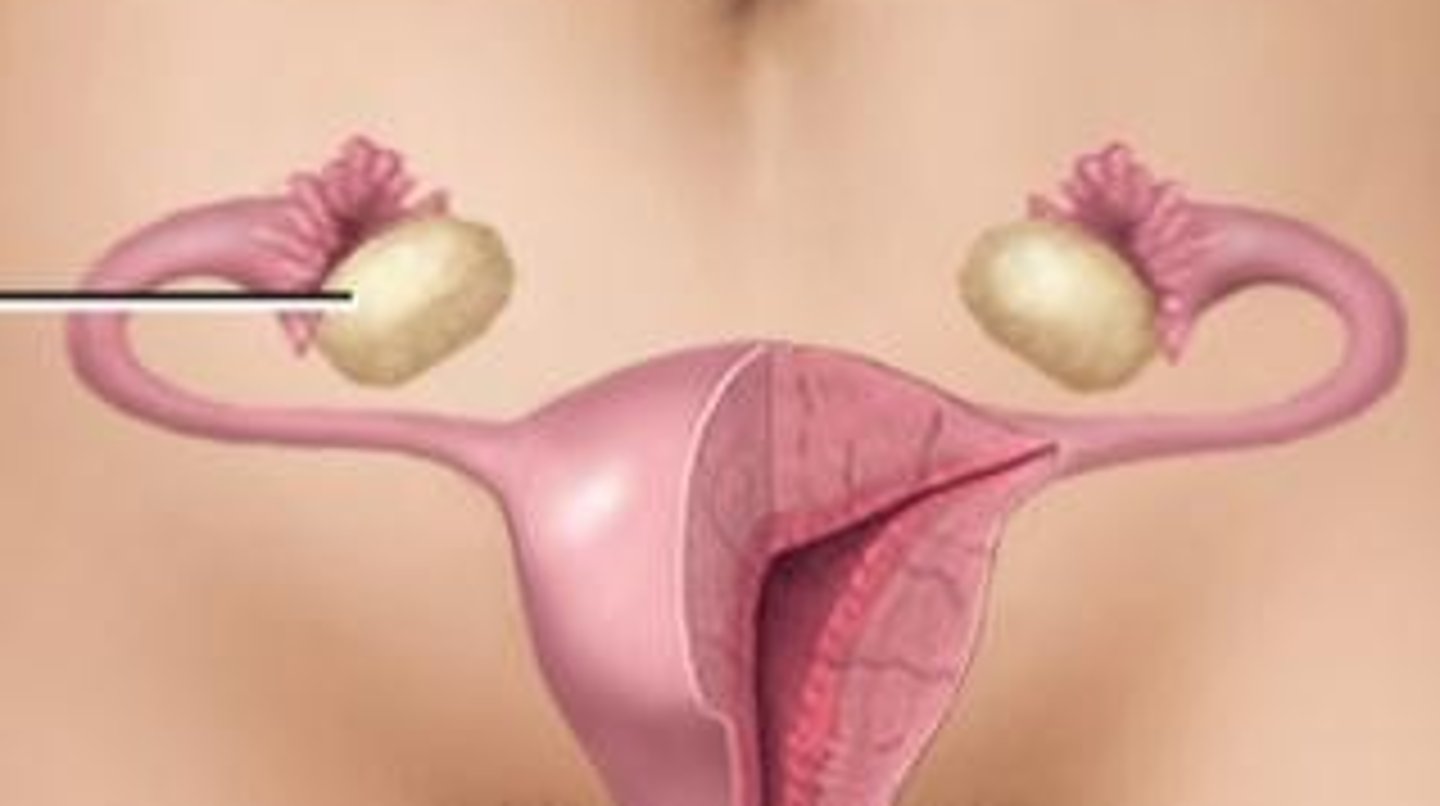
Ovaries
The primary female reproductive organs that produce an ovum, or egg, that, if fertilized, will develop into a fetus.
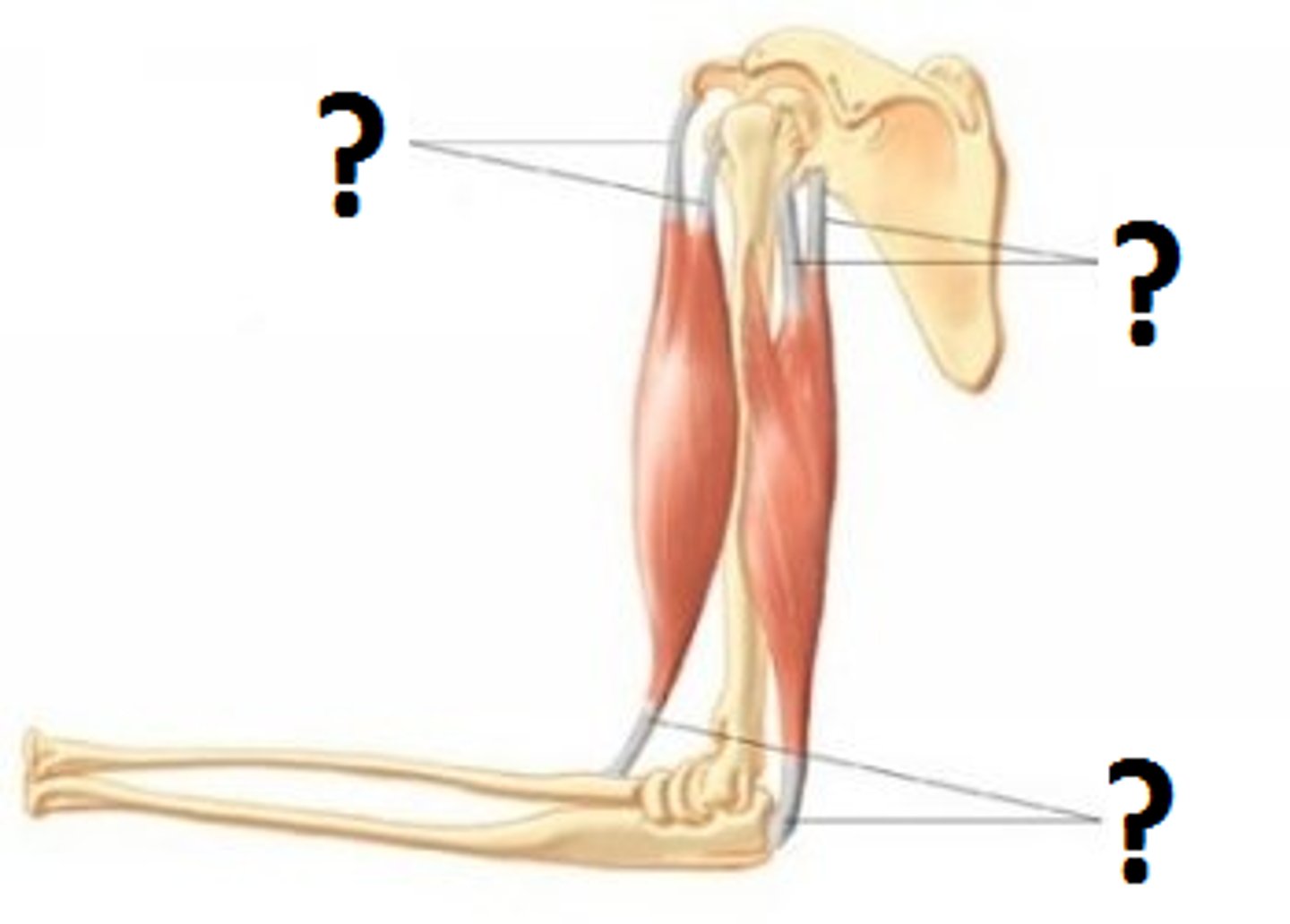
Tendons
The fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone.
mucus
The watery secretion of the mucous membranes that lubricates the body openings.

superior vena cava
One of the two largest veins in the body; carries blood from the upper extremities, head, neck, and chest into the heart.
nervous system
The system that controls virtually all activities of the body, both voluntary and involuntary.