Equine husbandry
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is box-walking?
When a horse circles arounds its stall, leaving a characteristic circular indentation in its bedding.
What is weaving?
When a horse sways its head from side to side, while shifting its weight between its forelimbs.
What is self-mutilation?
Biting, stomping, kicking, rubbing, lunging into objects.
What is crab-biting?
When a horse latches onto an object such as the stable door with its teeth and gulps in air.
What is wind sucking?
When a horse gulps in air.
Why might a horse show stereotypical behaviours?
- Health problems
- Limited natural behaviours, like too long spent boxed, insufficient foraging, lack of exercise, grooming, companionship
- Stress
- Being stabled away from similar aged equines as a foal.
What different sounds do horses make and what do they mean?
Squeals and grunts - aggression or excitement.
Snorts - interest or excitement.
Whinny - locating herd or excitement.
Whickering softly - reassurance.
What is bad body language to use around a horse?
- Square shoulders
- Increased respiration
- Eye to eye contact
What is a snaffle bridle used for?
Riding and driving to control the horse.
What is a chifney bit used for?
A special bit used to lead a horse that is particularly strong and difficult to handle. It must not be used when the horse is tied up or being ridden or lunged.
What is a twitch used for?
Twitches work by applying pressure, causing endorphins to be released, which raise the pain threshold, allowing the horse to enter a sedative state. Twitches should not be left on for more than 5- 10 mins and car should be taken to prevent it rubbing the skin or gums.
What are the different kinds of horse rugs?
- Sweat rug
- Stable rug
- Turn out rug
- Summer sheet
What are stable bandages?
Bandages around a horse's cannon. Used to provide protection, warmth and reduce swelling.
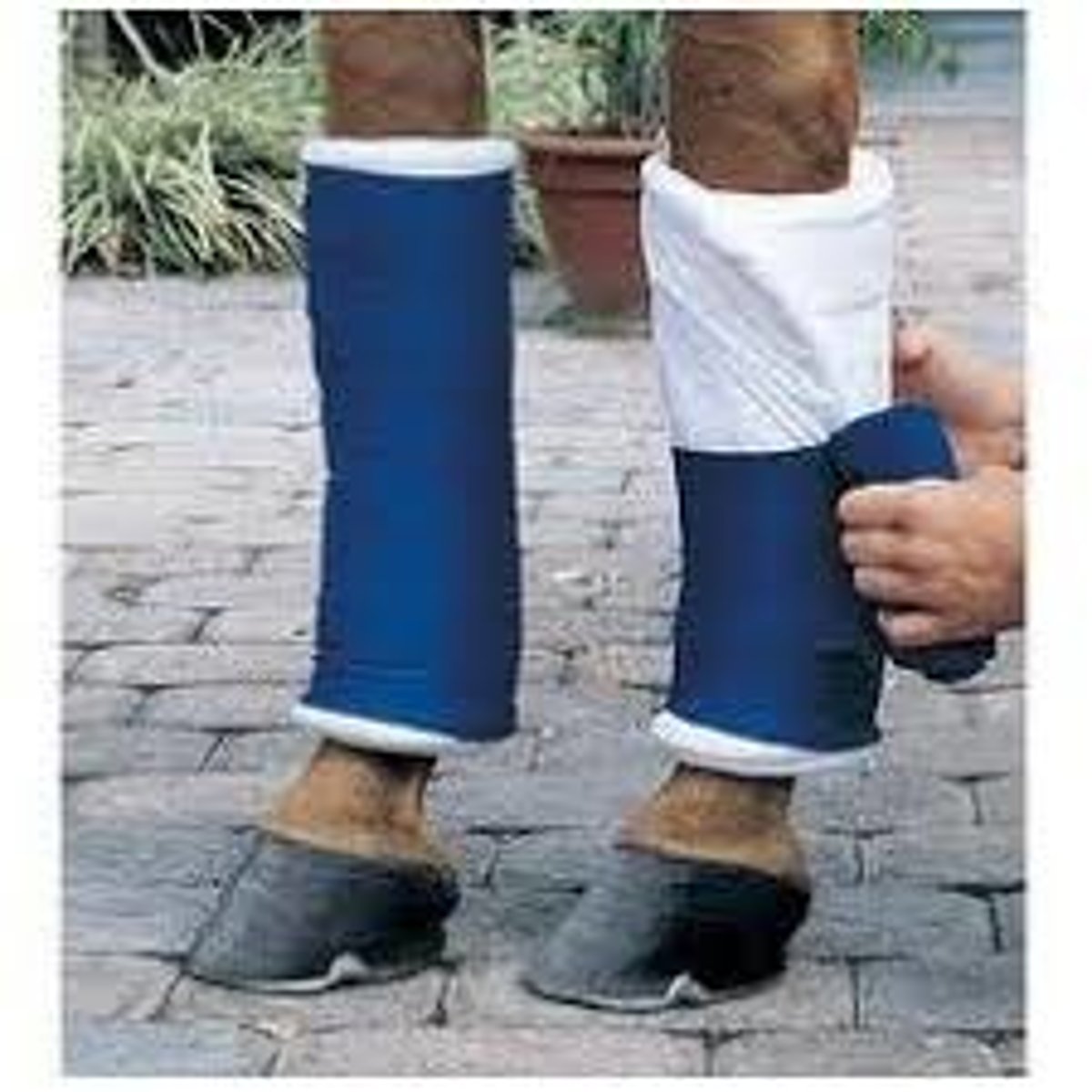
What are tendon/brushing boots?
Used for jumping to prevent damage to the cannon.
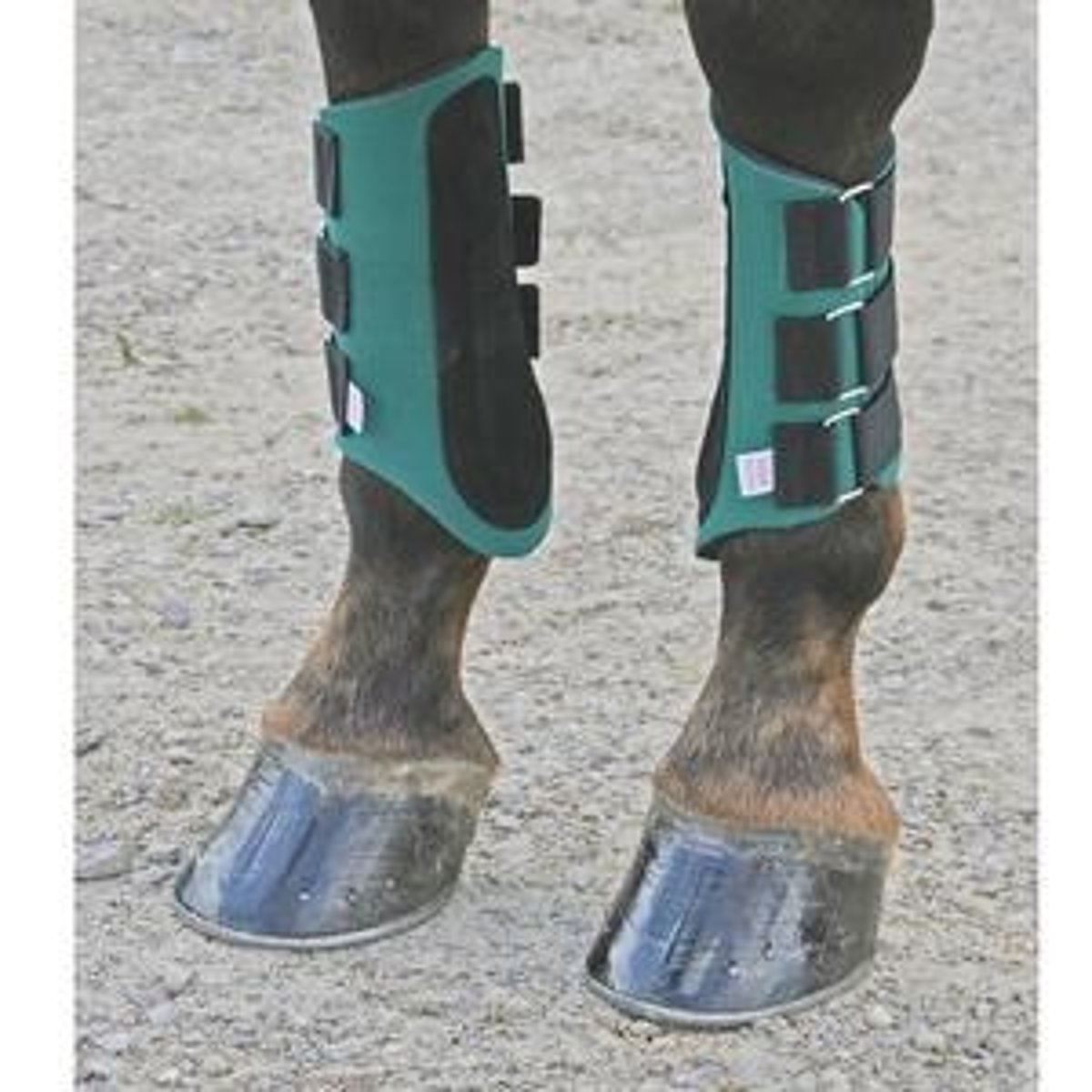

What are overreach boots?
Boots that surround the entire hoof, preventing the hind hooves kicking the front hooves.
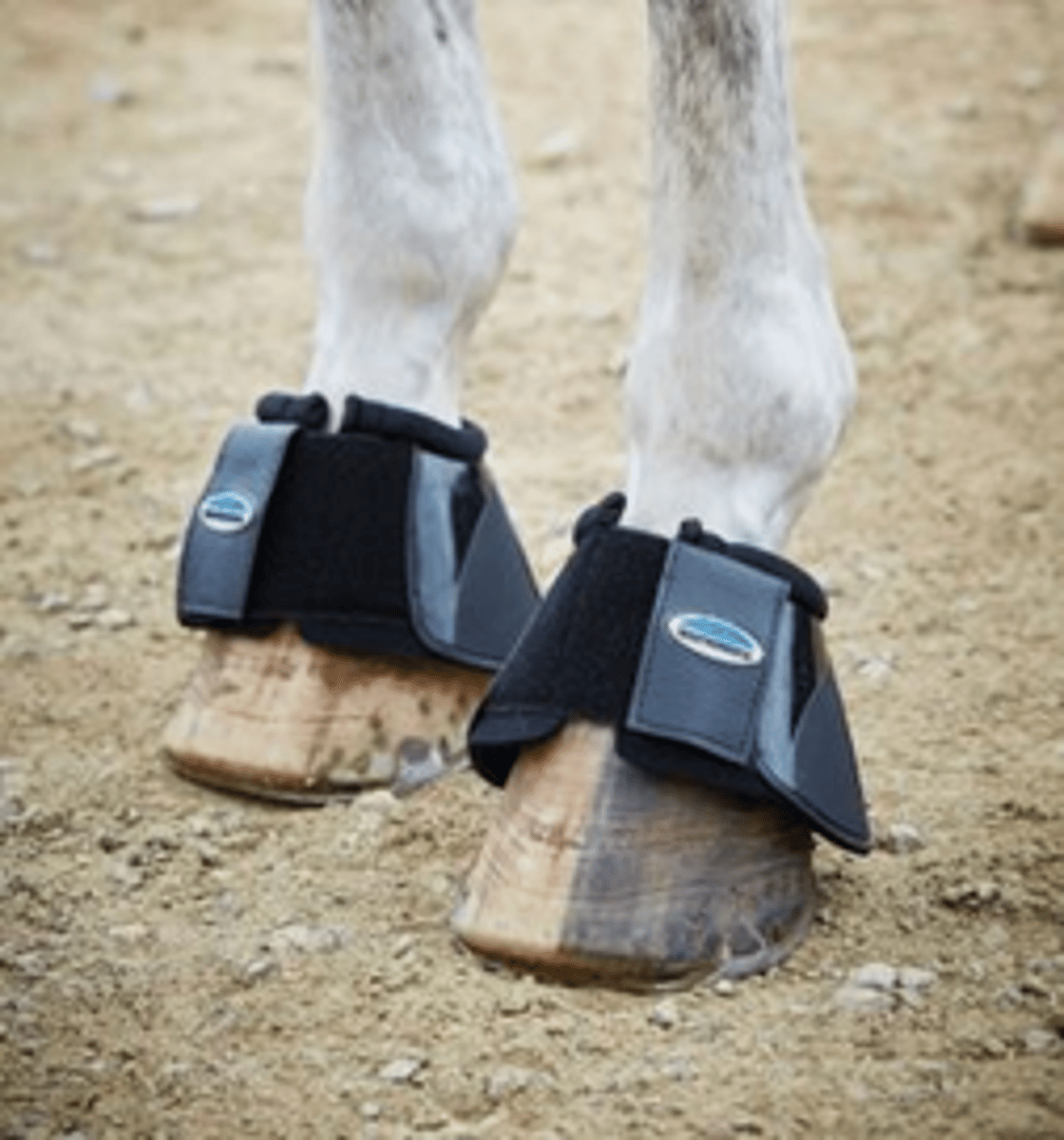

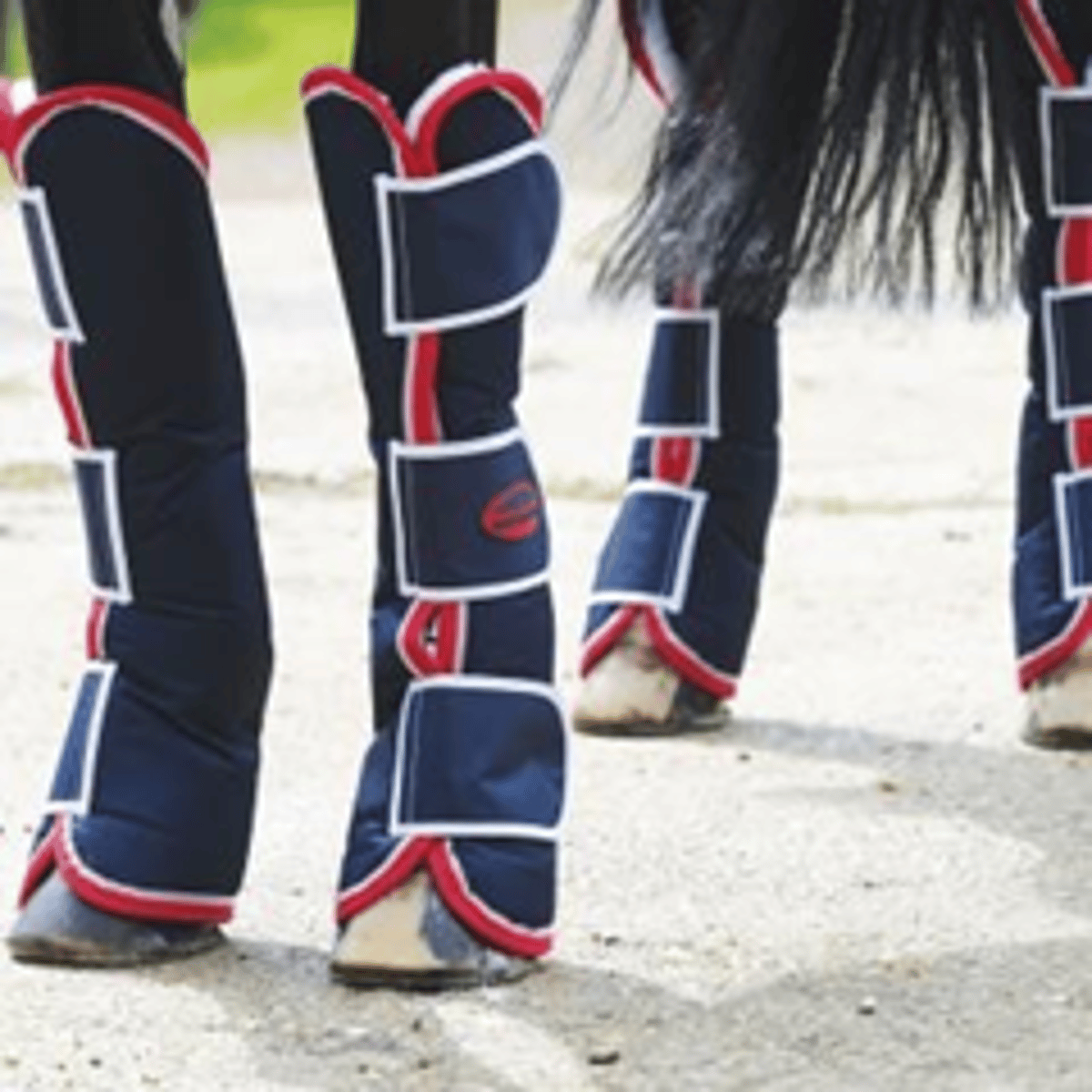
What are tail bandages and travel boots used for?
To protect the horses from rubbing during transport, or knocking and injuring their limbs.

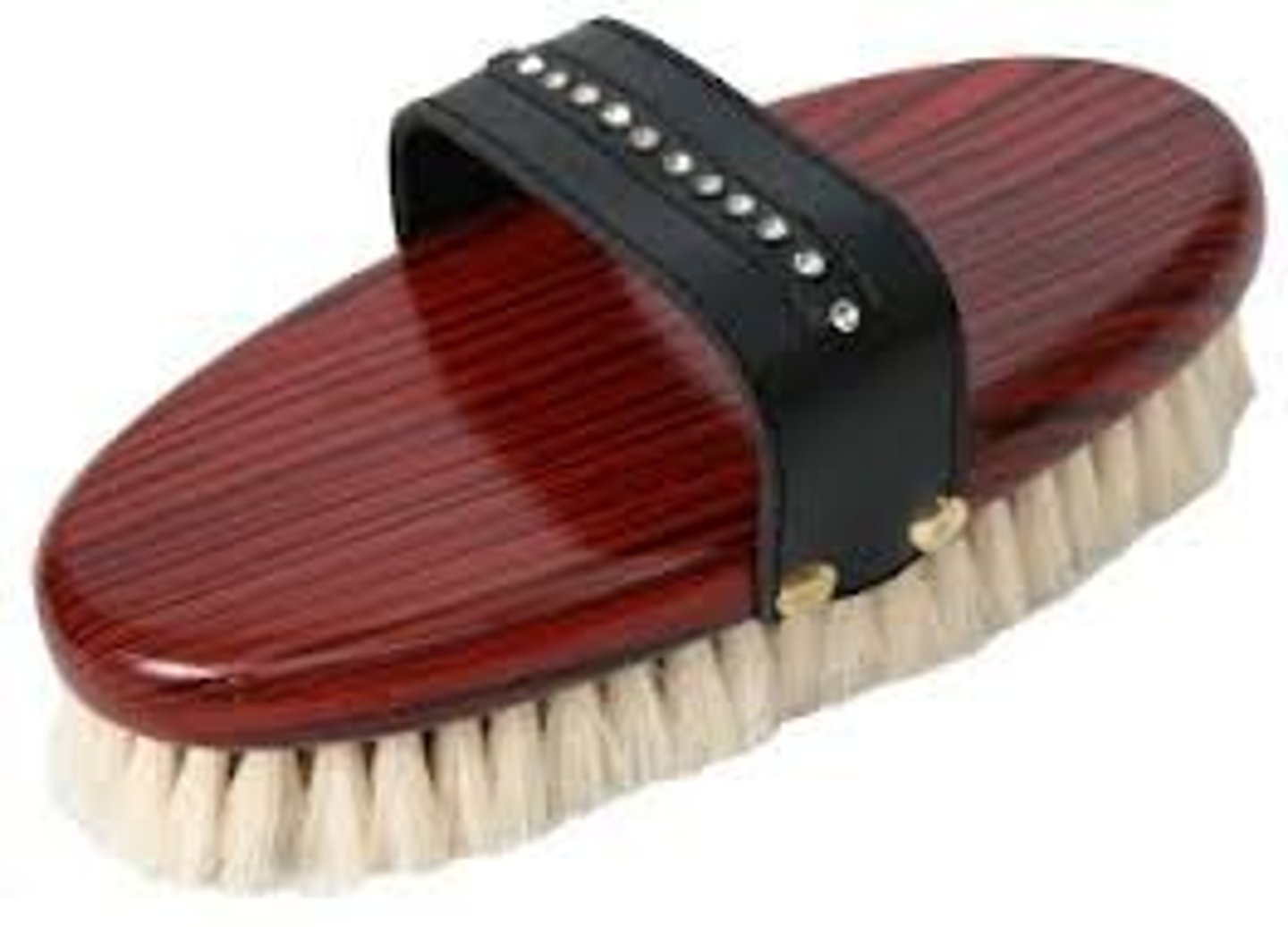
What is a body brush and what is it used for?
A soft-bristled brush used to remove small particles and grease from the fur, as well as providing a soothing sensation to the horse. Can be used anywhere.

What is a curry comb and what is it used for?
A brush made from rubber or plastic, used to loosen hair and dirt as well as stimulating the skin. It must not be used on the head or legs.
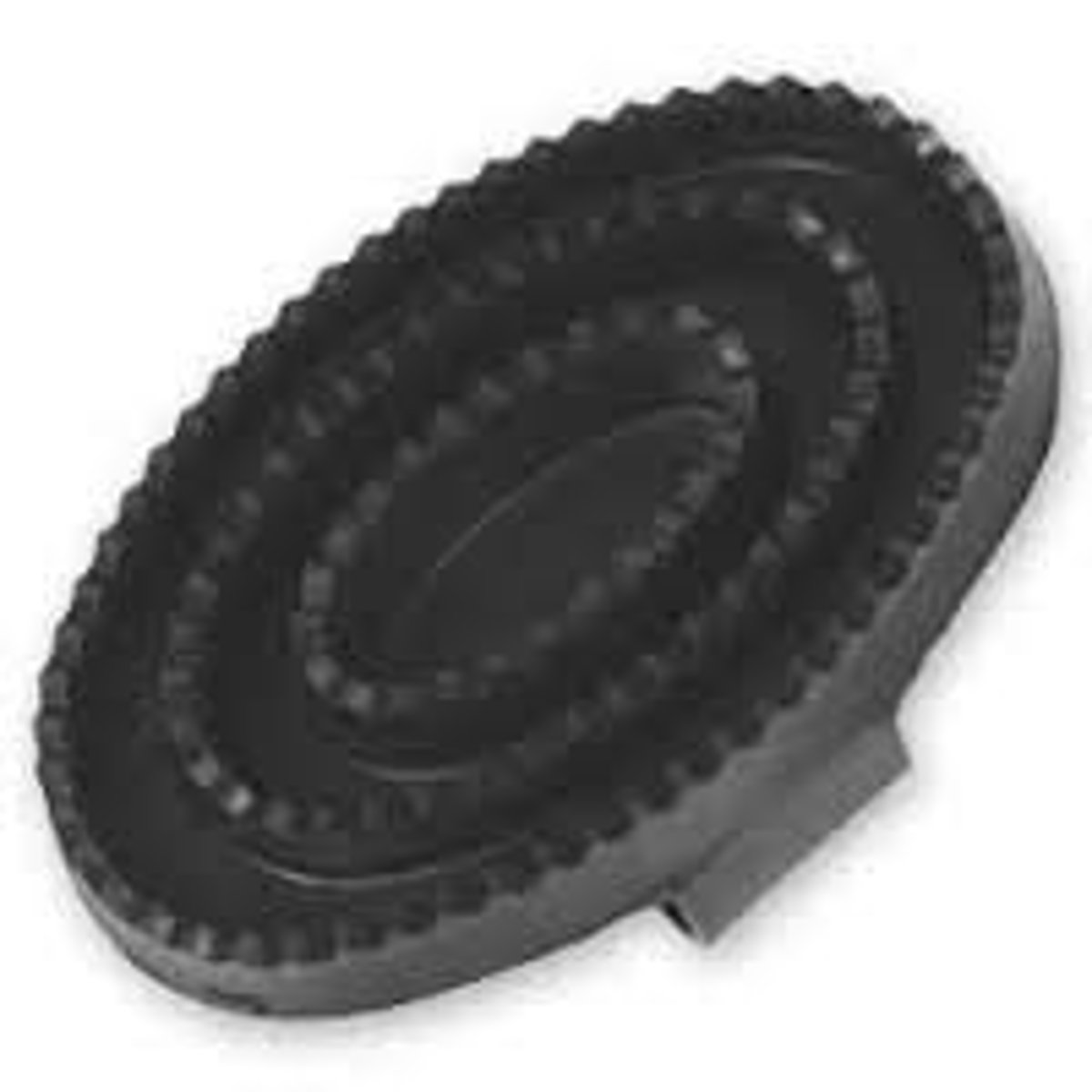

What is a metal curry comb and what is it used for?
Used to remove hair and dirt from a body brush.
What is a dandy brush and what is it used for?
Used to remove dirt and hair that has been loosened by the curry comb. Must not be used on the head or legs.
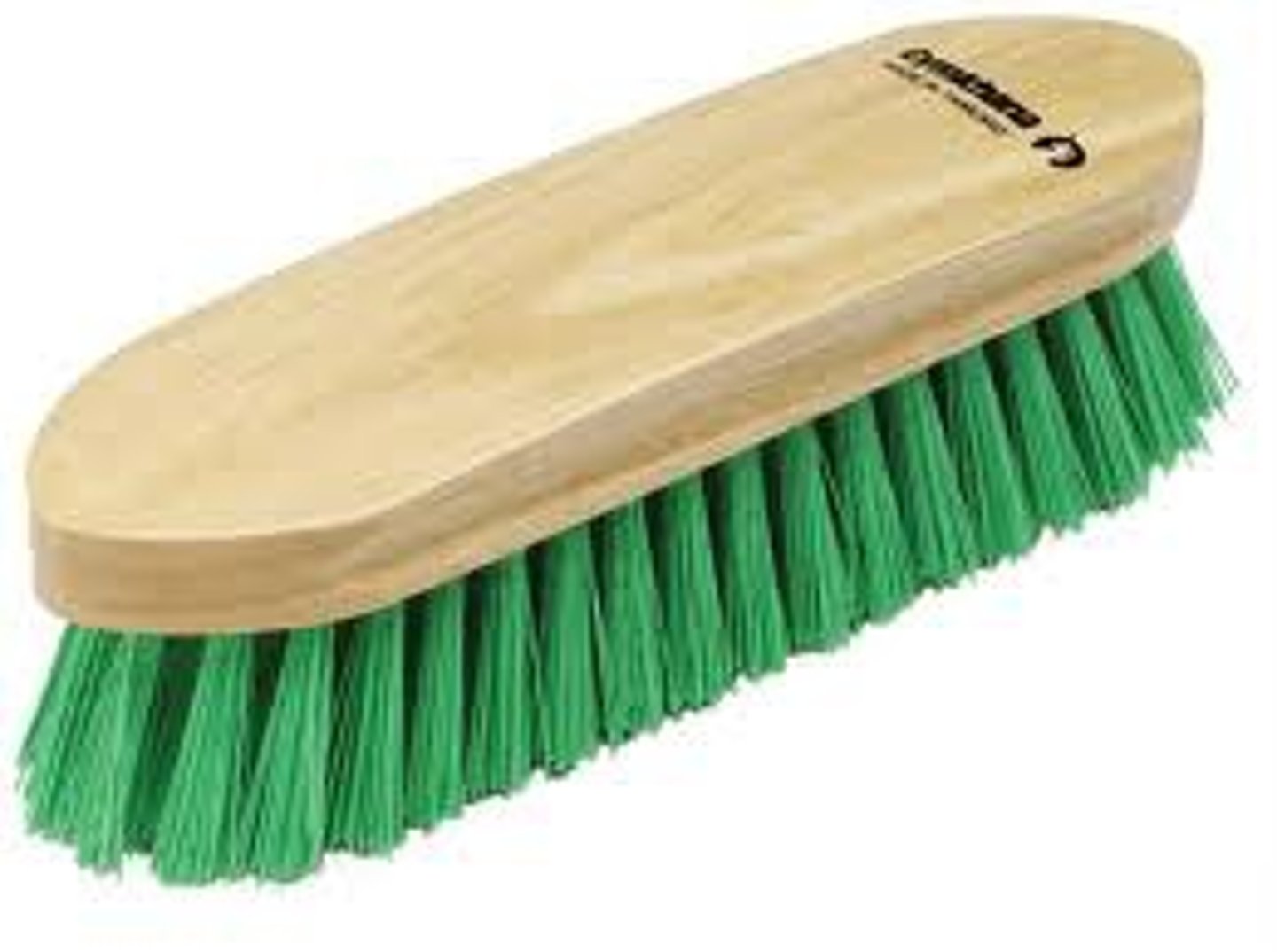

What is a grooming mitt and what is it used for?
To remove mud, dirt, dust, debris and loose hair. Can be used anywhere on the body.
What is a hoof pick used for?
To remove dirt, mud and stones to prevent bruising and infection.
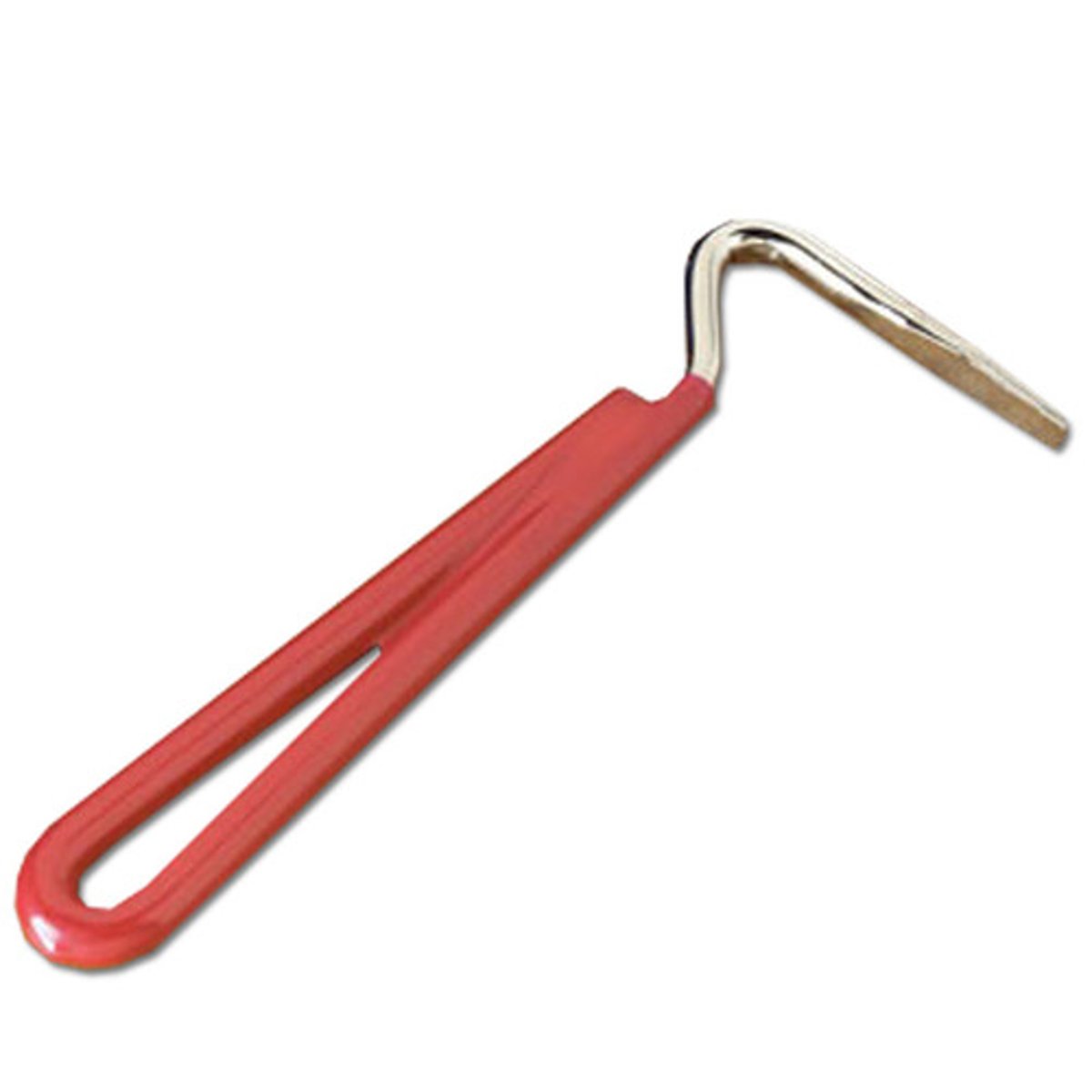

What is hoof oil and a brush used for?
To keep the hooves moisturised and prevent cracking which could make the horse more susceptible to lameness and infection.
What is a sweat scraper and what is it used for?
Used to remove sweat or water from a horse that has been washed. Water on a horse's coat can make it harder for the horse to regulate its own body temperature.
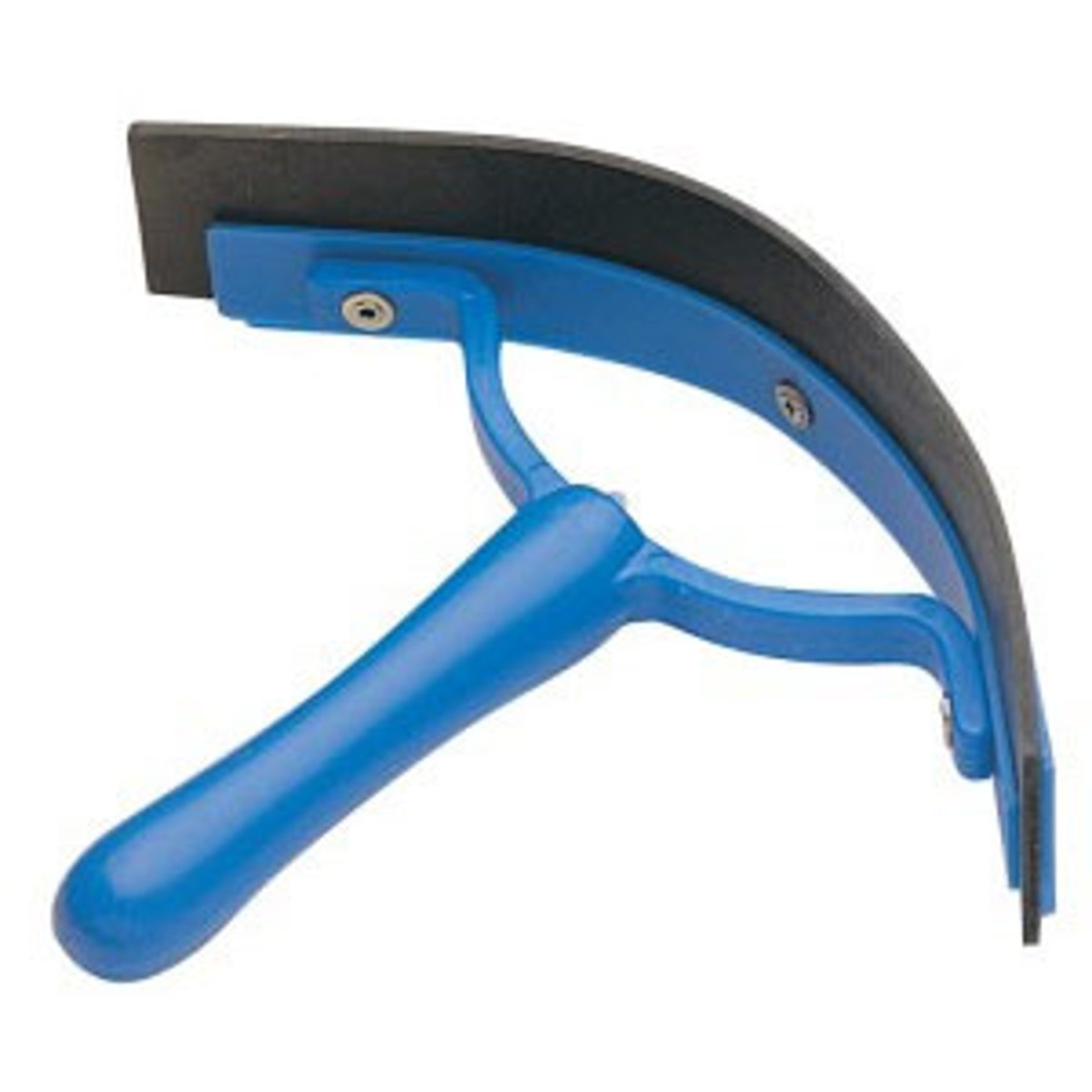

What is a water brush and what is it used for?
To apply water to the horse for washing.
Why is grooming so important to horses?
- It is a natural behaviour.
- Improves skin and coat health by increasing blood flow and massaging the muscles.
- Prevents chaffing under tack.
- Allows the owner to bond with their horse.
- Allows the owner to check for abnormalities.
- Improves the horse's mood and wellbeing.
How often should horses be groomed?
At least once a week or before each ride.
What are warmblood horse breeds?
Smart and agile breeds used for leisure and competitive riding. Examples include the Hanoverian, Irish Sport Horse, Trakehner, Quarter Horse, Tennessee Walking Horse.
What are coldblood horse breeds?
Big and strong breeds usually used for carriage pulling. Examples include Shires, Percherons, Ardennes, Suffolk Punches.
What are hotblood horse breeds?
Adaptable, intelligent breeds used for polo and racing mostly. Examples include Thoroughbred, Arabian, Barb, Akhal-teke.
What are equine passports?
Every equine must have a passport, although there is a special exception for semi-wild ponies in Dartmoor, Exmoor and the New Forest. Passport applications are made through the Passport Issuing Organisation (PIO) and passports are valid for life. If the horse is sold or dies, they must be returned to the PIO.
Do horses need to be microchipped?
Yes it became a requirement by law in 2020. Horses must have a microchip in order to have a passport.
How are white markings indicated on a horse passport?
They are outlined in red ball point pen and hatched with diagonal lines.
How are a few white hairs indicated on a horse passport?
With a few short red lines.
How are scares indicated on a horse passport?
By arrows pointing to the site of the scar.
How are brand marks indicated on a horse passport?
They are drawn in black. If the shape is not visible, they should be considered as a scar.
How are whorls indicated on a horse passport?
They are indicated by an X drawn in black ink. If the whorl is elongated, this is shown by a continual line from the X.
How are flesh marks indicated on a horse passport?
They are outlined and block-shaded in red.
How is a prophet's thumb mark indicated on a horse passport?
They are indicated by a small black triangle.
What are ermine marks and how are they indicated on a horse passport?
Dark sports occurring on white marks, usually seen around the coronet band. They are outlined in black ink and not shaded.
How are chestnuts indicated on a horse passport?
Chestnuts only need to be indicated if the horse doesn't have any other markings or if the horse has less than 4 whorls. They are outlined in black pen.
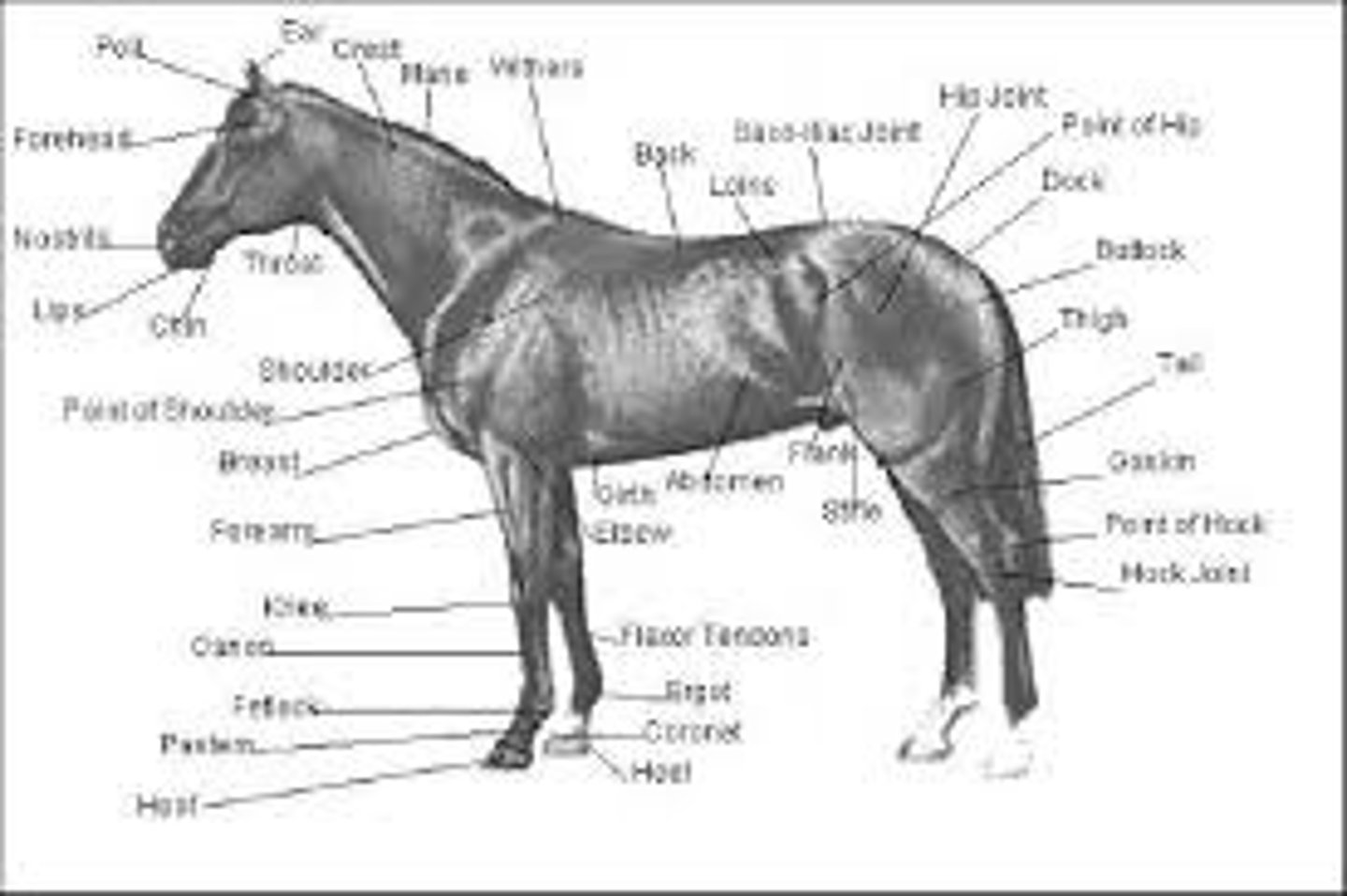
What are the points of a horse?
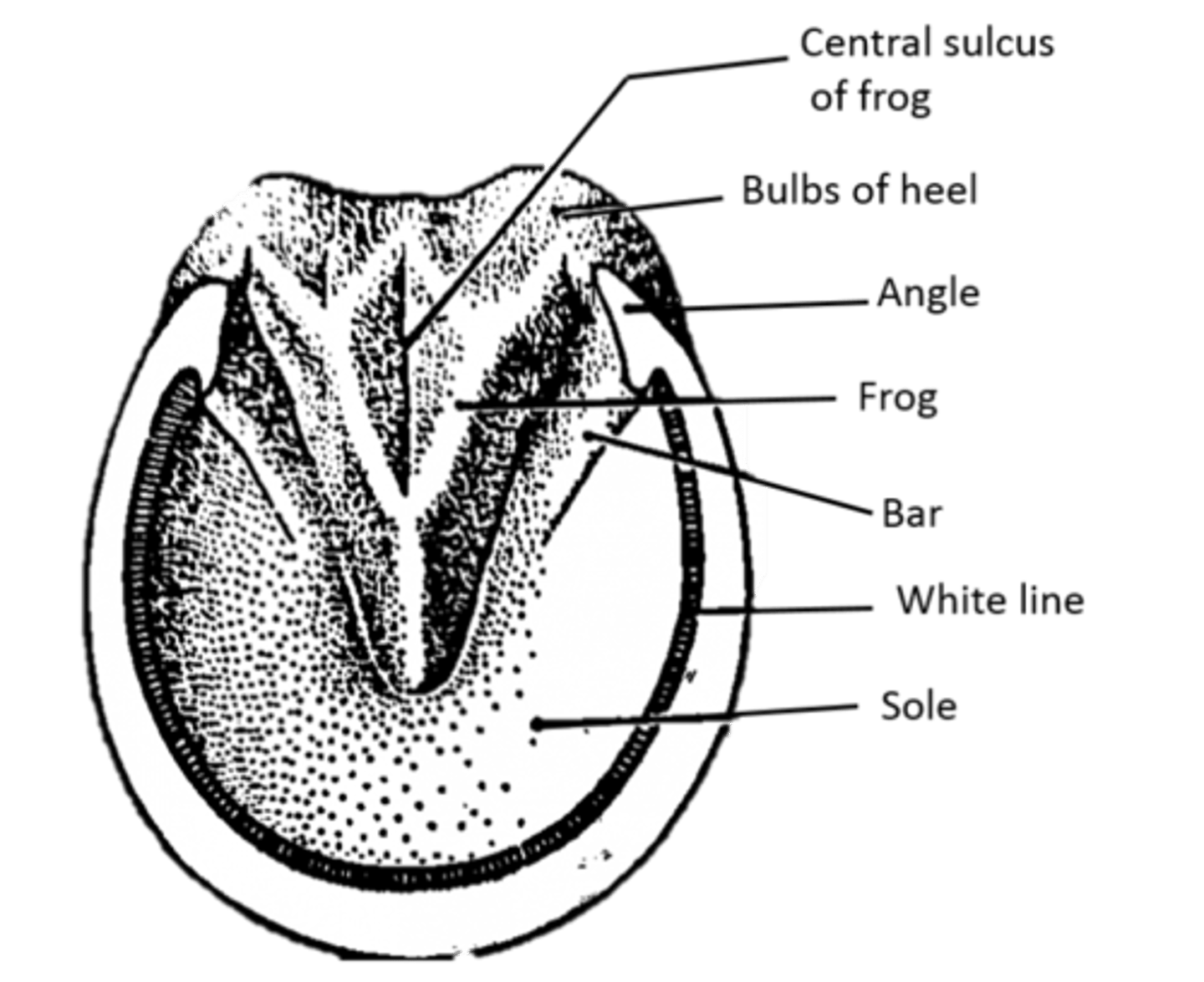
What is the anatomy of a horse's hoof?
What is the British Equine Federation (BEF)?
The national governing body for horse sports in the UK, it is affiliated with the Federation Equestrian Internationale (FEI) which is the international governing body of equestrian sports.
What is the British Horse racing Authority (BHA)?
The governing body responsible for the administration and regulation of horse racing in Britain.
What is the Thoroughbred Breeders Association (TBA)?
They regulate and support thoroughbred breeders to ensure British thoroughbreds maintain excellent bloodlines.
What are the requirements of horse stabling?
- Good drainage and ventilation
- Non-slip flooring
- Horses should be able to see over the stable door
- Enough space to turn around, lie down and stand up
What are some bedding materials used for horses?
- Wood shavings. They are non-palatable so useful if the horse needs to starved. They are easy to store, cheap and widely available but their quality varies.
- Wood pellets. They are eco-friendly, dust-free and require water added to make them expand.
- Straw. Cheap, edible, and able to create bigger beds. Can be dusty and smell.
- Chopped Straw. Dust-free and non-palatable but expensive.
What are the requirements that a horse's pasture must meet?
Each horse requires 1 -1.5 acres of pasture. Horses must have access to shelter, shade, water.
What are poisonous plants to horses?
- Foxglove
- Sycamore
- Oak
- Ivy
- Ragwort
- Deadly nightshade
- Buttercups can cause colic and diarrhoea. Grey horses with fleshy marks may experience blistering.
How can the quality of pasture be maintained?
- Evaluation of soil samples
- Rotational grazing
- Weed removal. Weeds compete with grass.
- Filling in rabbit holes to prevent horses stepping in them.
- Faeces removal at least twice weekly to prevent parasites. Horse will not eat where there is poo.
- Worming horses when they are moved to a new pasture to prevent the spread of parasites.
Where should horses be given IM injections?
In the triangle of the neck, or in the hindquarters (gluteals) in the triangle indicated by the tuber coxae, tuber ischium, and tuber sacrale.