Chemistry 12 - Equilibrium
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What is equilibrium in a chemical system?
Equilibrium is when changes are no longer observed in a system, meaning forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate.
What are the conditions necessary for a system to be in equilibrium?
Constant macroscopic properties (no visible changes), A closed system, Temperature, pressure, and concentration remain constant (No net change)
What is a closed system?
A system where everything remains there and nothing leaves.
When is a system called a Steady State System vs equilibrium?
In a steady-state system, particles enter and leave at equal rates. Seems like equilibrium but isn’t a closed system.
When is it called dynamic equilibrium?
When the same amount of particles enter a solution as particles turn solid.
How to solve "Do the moles of ___ consumed equal the moles of ___ produced?"
Look at coefficients and see if they’re equal.
Water level drops as water evaporates from it. The flask is then closed using a rubber stopper. Explain why the water level is no longer falling after this.
The rate of condensation has become equal to the rate of evaporation.
In 2NO₂ (orange) → N₂O₄ (colorless), what do you see as the reaction approaches equilibrium?
Orange would become paler.
In 2NO₂ (orange) → N₂O₄ (colorless), describe the change in concentrations of reactants and products as the reaction approaches equilibrium.
Concentration of NO₂ decreases and concentration of N₂O₄ increases.
Forward rate increases first then decreases while reverse rate increases.
In 2NO₂ (orange) → N₂O₄ (colorless), describe the change in forward and reverse rates as the reaction approaches equilibrium.
Forward rate increases first then decreases while reverse rate increases.
In the equation N₂O₄ ⇌ 2NO₂, describe in terms of molecules for the Forward reaction and then the Reverse reaction.
Forward: 1 molecule → 2 molecules; Reverse: 2 molecules → 1 molecule
For Forward rate, _____ convert into _____, For Reverse rate, _____ convert into _____.
For Forward rate, reactants convert into products; For Reverse rate, products convert back into reactants.
In the equation N₂O₄ ⇌ 2NO₂, what would a concentration-time graph look like when you add extra N₂O₄ to it?
Forward rate = Reverse rate at the beginning; Reactant increases with a spike then slowly decreases as N₂O₄ is used up; Product slowly increases as the amount of NO₂ made is increased.
How would you draw a Rate vs Time graph?
Forward rate starts high then decreases; Reverse rate starts low at zero then increases; Both meet in the middle then go horizontal.
How would you draw a Concentration-Time Graph?
Reaction starts high then decreases; Reverse rate starts low at zero then increases; They pass each other then continue horizontally.
What is Le Chatelier’s Principle?
If a system at equilibrium experiences changes (stress), shifts will occur to counteract the change.
In N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ ΔH = -92, what happens when more N₂ is added to the system? What reaction does this favor?
We want to counteract that change by shifting to the right. This favors the forward reaction.
In N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ ΔH = -92, what happens when you add NH₃?
Shifts left. N₂ is increased. H₂ is increased. NH₃ is decreased.
In N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ ΔH = -92, how does the system respond when volume is increased? How does this affect Pressure and Concentration?
Shifts towards whichever side has more moles of gas → shifts left. Pressure and Concentration are opposite, so both decrease.
When something is being diluted, what does this mean?
The concentration is being decreased (pressure is decreased and volume is increased).
In N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ ΔH = -92, how does the system respond when volume is decreased? How does this affect Pressure and Concentration?
Shifts towards whichever side has fewer moles of gas → shifts right. Pressure and Concentration are opposite, so both increase.
In N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ ΔH = -92, how does the system respond when temperature is increased?
Add heat to correct side (product side in this case). To consume some of this heat, we need to shift away from it (going left).
In N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ ΔH = -92, how does the system respond when temperature is decreased?
Add heat to correct side (product side in this case). To replace the heat, we need to shift towards it (going right).
For A (1 mol) ⇌ B (0 moles), what way does this has to shift?
needs to shift right because there’s no B to convert into A.
What are the steps to graph when Adding / removing reactants / products
Graph what is removed or added first (with a spike); Graph the effect of the shift (what arrow describes).
What are the steps to graph when changing temperature
Graph the effect of the shift (what arrow describes).
What are the steps to graph when pressure changes
Graph pressure (everything increases or decreases); Graph the effect of the shift (what arrow describes by counting gas molecules).
For Chatelier, if some random gas was added (ex: Ne, Xe, etc), how does this affect the partial pressures? What shift would this be?
The partial pressures remain the same because only the total pressure is increasing. Instead of a shift, it's “No effect.”
For Chatelier, if some random gas was added but it also includes any other gas from the equation, how does this affect the equation? Use the Example N2CL (N being not random and Cl being random in N2 (g) +3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3)
It's the same as adding N2, so shifts right. (more specifically, it increases concentration).
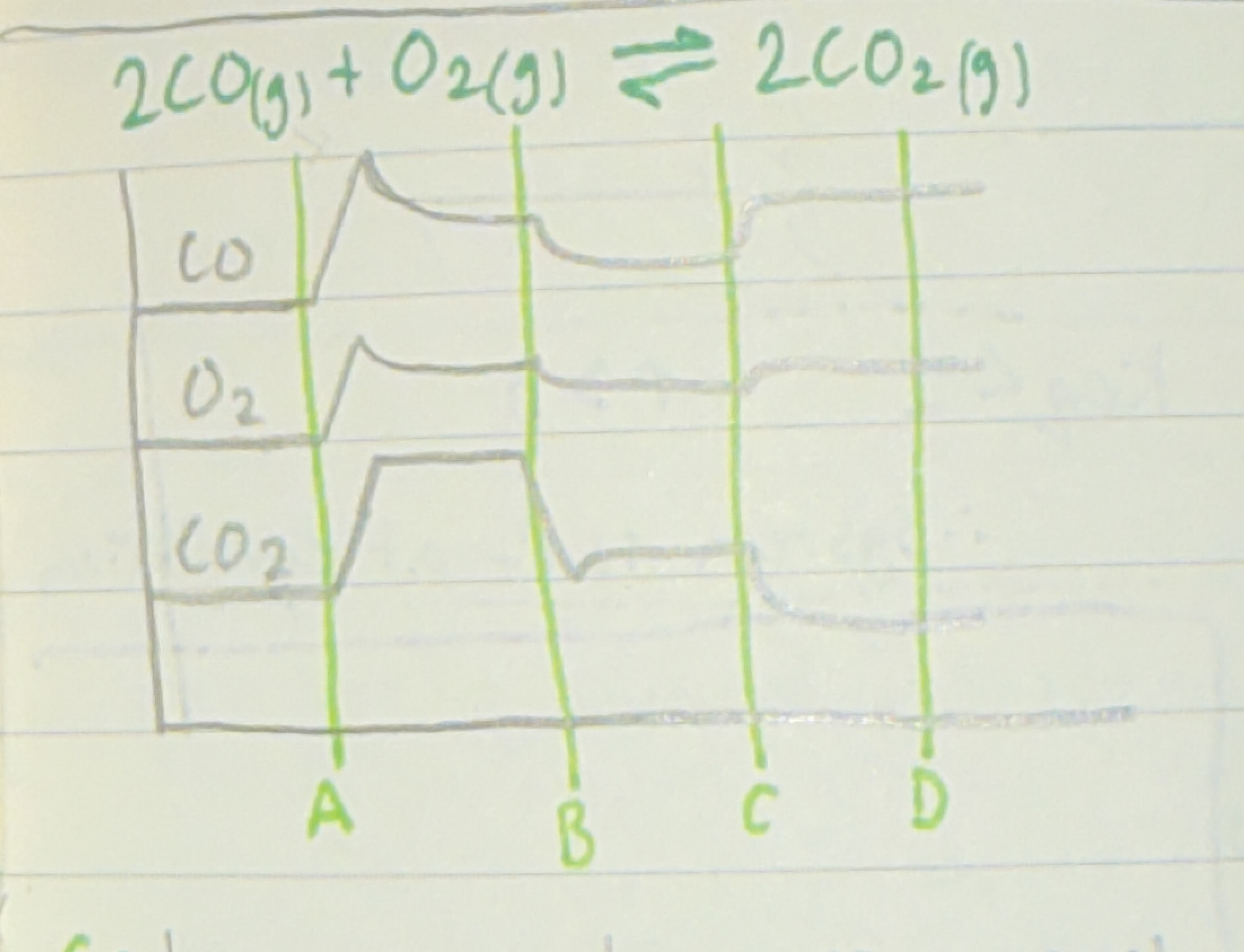
Describe what's happening in the image at A B C D and how you came to this
A: everything is increasing so pressure is increasing. —> 3:2 gas ratio so shifts right. —> Products increase after and Reactants decrease after. B: CO2 is being removed because of the spike. —> Point at what's being removed: shifts right. —> Products increase after and Reactants decrease after. C: Increase in temp since just graphing effect of shift. —> Don’t point at what's being increased: left shift. —> Products decrease after and Reactants increase after. D: All staying constant so no shift is caused. —> Catalyst or random was added.
What happens when volume is increased but coefficients are equal on both sides?
No shift occurs (no stress occurs).
What is enthalpy (ΔH)? How does it shift?
The amount of heat/energy given off or taken in during a reaction. Shifts same as when temp is increased/decreased.
Explain how Exothermic vs Endothermic relates to Ep graphs and delta H
Exothermic: resembles an Ep forward graph. It’s on the product side and it’s negative. Endothermic: resembles an Ep reversed graph. It’s on the reactant side and it’s positive.
What is entropy?
A measure of randomness in a system.
Rate states which go from lowest to highest randomness
Solids << liquids > aqueous << gas.
How does a reaction shift based on entropy?
It shifts toward the side with more random particles. —> If both sides have the same states, compare coefficients of more random state.
What does it mean when the shift for both Enthalpy and Entropy is forward?
Reaction goes to 100% completion.
What does it mean when the shift for both Enthalpy and Entropy is reversed?
Reaction goes to only 10% completion or no reaction takes place at all.
What does it mean when the shift for Enthalpy and Entropy are opposites?
Reaction is an equilibrium reaction.
What is Keq? What does it tell us about products and reactants? Give examples.
The equilibrium constant. It is a number that tells us how far a reaction has progressed when it reaches equilibrium. It compares the amount of products to the amount of reactants at equilibrium. Examples: If Keq > 1, p > r (the reaction makes mostly products) —> favors products / forward. If Keq < 1, p < r (the reaction makes mostly reactants). —> favors reactants / reverse.
What is the formula for Keq?
Keq = [B]^c / [A]^d Ratio of products with its coefficient as the exponent over ratio of reactants with its coefficient as the exponent.
Does Keq have units?
No.
What's the only thing that changes Keq?
Temperature. temp doesn’t change delta H.
What happens to Keq when temperature increases in an endothermic reaction?
Keq increases.
What happens to Keq when temperature increases in an exothermic reaction?
Keq decreases.
Does adding a catalyst affect Keq?
No, a catalyst increases both forward and reverse reactions equally.
Should solids and liquids be included in the Keq expression, including ICE Charts?
No, only gases and aqueous solutions are included. Liquids are only included if there’s 2 or more different liquids in the reaction.
What are the steps to calculate Keq in word problems?
Needs to have a balanced equation. Can use Keq formula if concentrations are given at equilibrium. Use ICE Chart if only starting concentrations are given, then use Keq formula after.
What does ICE stand for and how to use it?
First, always start with a balanced equation. I = Initial concentrations (always M not moles) —> Plug in starting [ ]s / molarity / concentration from word problem (use variables for unknowns). C = Change in concentration —> Write the coefficients for each individual gas then multiply with x (Negative x for reactants). E = Equilibrium concentration —> I row + C row (use these numbers for Keq formula).
If the starting Keq is 100 for an equation, what happens to the Keq when all of the coefficients are doubled?
(Keq)^2 —> 100^2
If the starting Keq is 100 for an equation, what happens to the Keq when all of the gases are swapped (equation is reversed)?
1/(Keq) —> 1/100
If the starting Keq is 100 for an equation, what happens to the Keq when the equation is reversed and all of the coefficients are tripled?
1/(Keq)^3 —> 1/100^3
When would you use Trial Keq?
When there’s no zeros in I row. And to see if given concentrations are at equilibrium or not.
How to use Trial Keq?
Use Keq formula to see if given info matches the Keq given. (Your answer from the formula is the trial Keq.) If answers don’t match, use ICE chart to see what Keq would be at equilibrium.
What does it mean if trial Keq ≠ Keq?
The system is not at equilibrium.
What does it mean if trial Keq < Keq?
The reaction shifts toward products.
What does it mean if trial Keq > Keq?
The reaction shifts toward reactants.
What does it mean if trial Keq = Keq?
The system is at equilibrium.
Why does equilibrium require a closed system?
To prevent loss of reactants or products, maintaining a balance between forward and reverse reactions.
What happens to the forward and reverse reaction rates when a system reaches chemical equilibrium?
At equilibrium, the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal, so the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant (but the reactions still continue at the same rate in both directions).
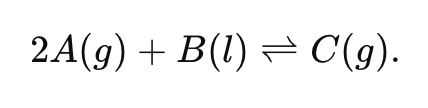
Write the Keq expression for the reaction:
(B is a liquid, so it is excluded from the expression.)
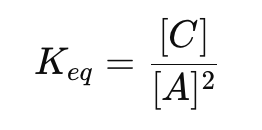
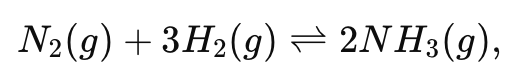
For the reaction:
how do you write the equilibrium constant expression
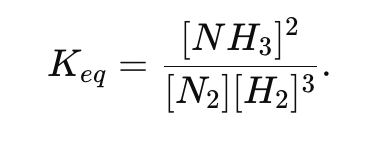
Which of the following changes affect the numerical value of Keq : adding a catalyst, changing concentration, or changing temperature?
Only temperature affects the value of Keq. Changing concentration or adding a catalyst does not change Keq ; they only affect how quickly or how far the reaction shifts to re-establish equilibrium.
According to Le Châtelier’s Principle, what happens if you remove some product from a reaction at equilibrium?
The equilibrium shifts toward the product side, producing more product to replace what was removed.
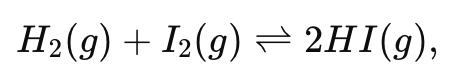
For the reaction:
initially you have 2.0 M of each H2 and I2 , and no HI. If x moles per liter of H2 react, write the equilibrium concentrations in an ICE table format.
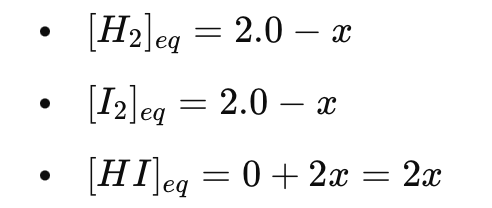
If a reaction is endothermic, how does increasing temperature affect the equilibrium?
For an endothermic reaction, increasing temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right (produces more products), because heat is treated like a reactant.
A reaction has ΔH < 0 (exothermic). What happens to Keq if you increase the temperature?
For an exothermic reaction, raising the temperature decreases Keq , because the system shifts to the left (reactants) to absorb the added heat.
How does adding a catalyst affect the equilibrium position of a reaction?
A catalyst does not change the equilibrium position or Keq ; it only speeds up how quickly equilibrium is reached by lowering the activation energy.
If you graph concentration vs. time for an equilibrium system, what does it look like once equilibrium is established?
Concentrations of reactants and products become constant (flat lines on the graph), though the forward and reverse reactions continue at equal rates.
On a concentration vs. time graph, if the product concentration jumps down at some point, what likely happened?
This indicates some product was removed. The reaction will then shift right to replace that product, so you’d see the product line go back up and the reactant lines go down.
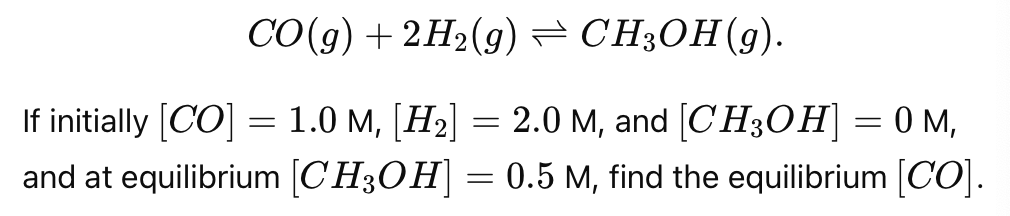
You have the reaction
[CO]eq =1.0−0.5 = 0.5 M
What does it mean if Trial KeqQ < Keq ?
the reaction shifts right to form more products until equilibrium is reached.
Why is high pressure used in the Haber process (N2 + 3H2 ⇋ 2NH3) to increase the yield of ammonia?
Because there are 4 moles of gas on the reactant side and 2 moles on the product side, high pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with fewer gas molecules (right), increasing ammonia yield.
If Keq < 1, what does that tell you about the reaction mixture at equilibrium?
the reaction favors reactants heavily at equilibrium (very little product is formed).
How do you quickly tell if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic based on ΔH values?
ΔH<0 → Exothermic (releases heat).
ΔH>0 → Endothermic (absorbs heat).
Does the reaction stop once equilibrium is reached?
No, the reaction continues in both directions at equal rates, so there’s no net change in concentrations.
Whats it asking for when it says “which of the following equilibrium systems has the highest yield of products”?
when products are increased
REMINDER
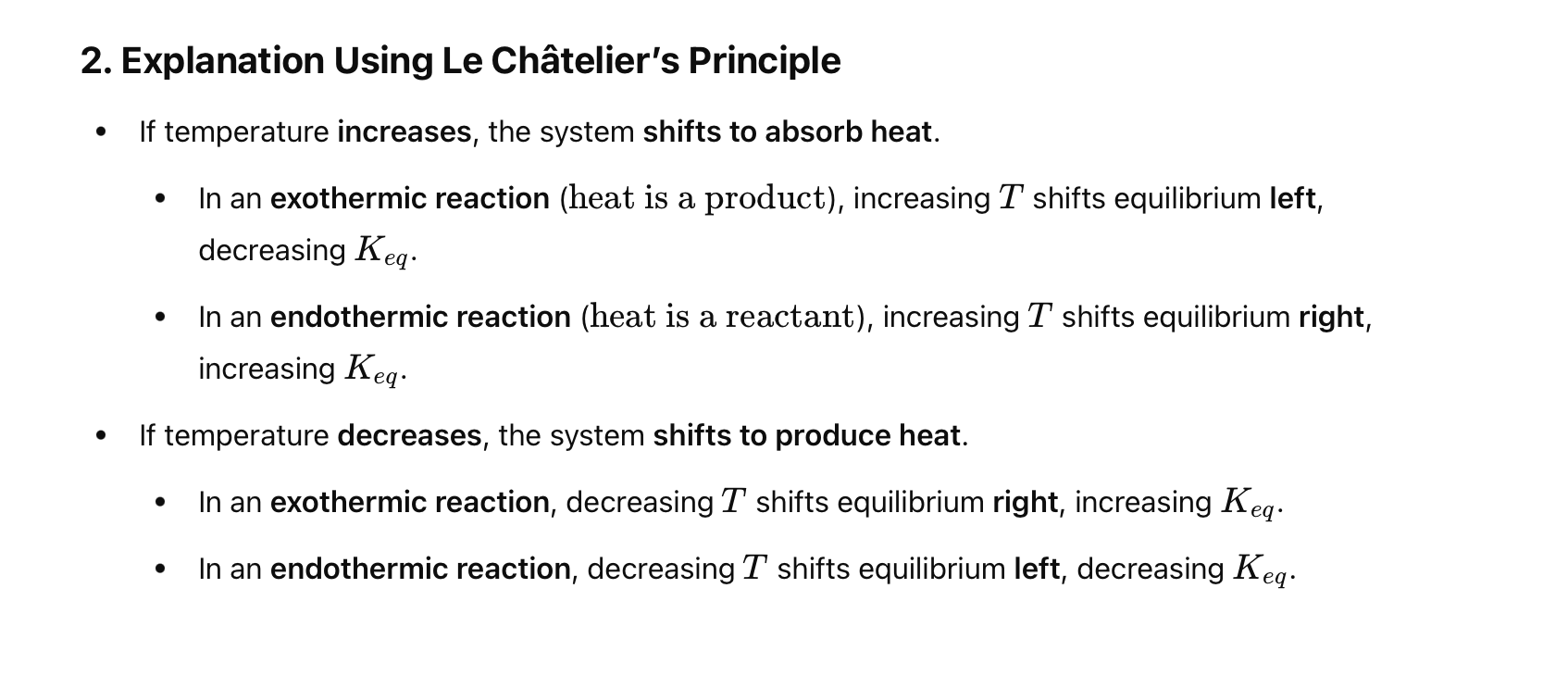
REMINDER

REMINDER
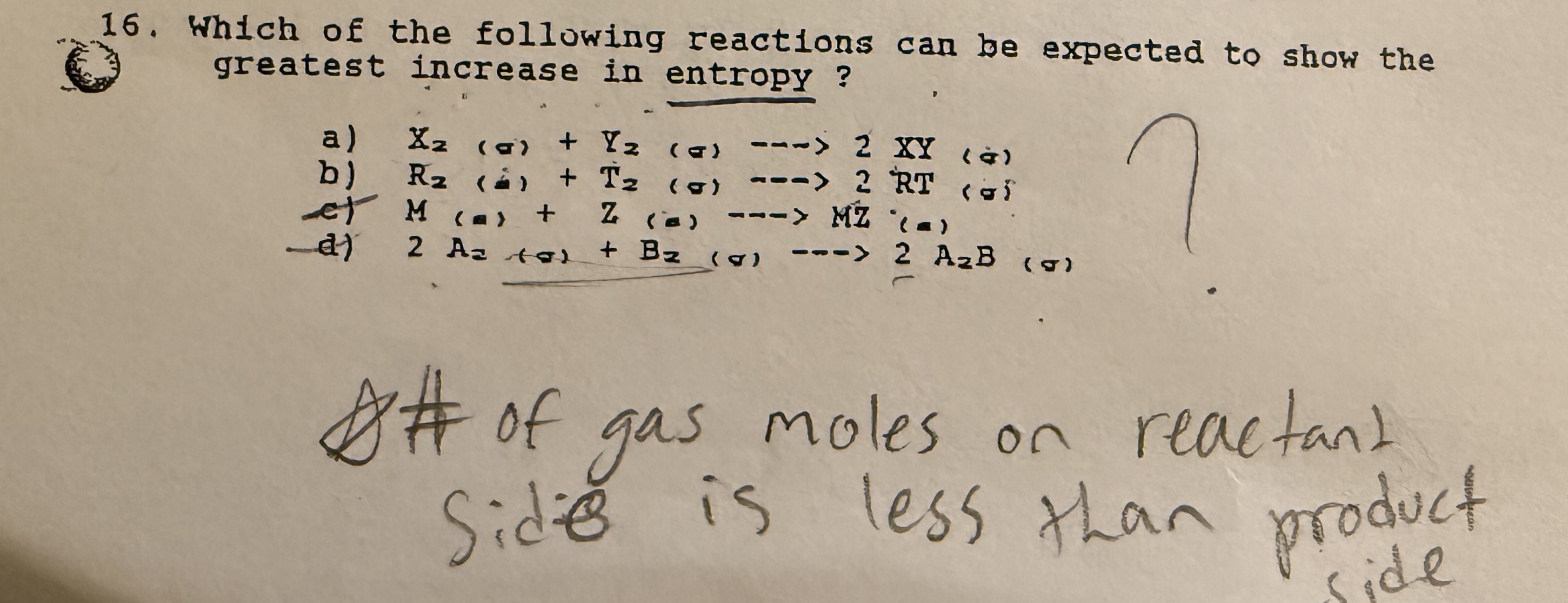
REMINDER
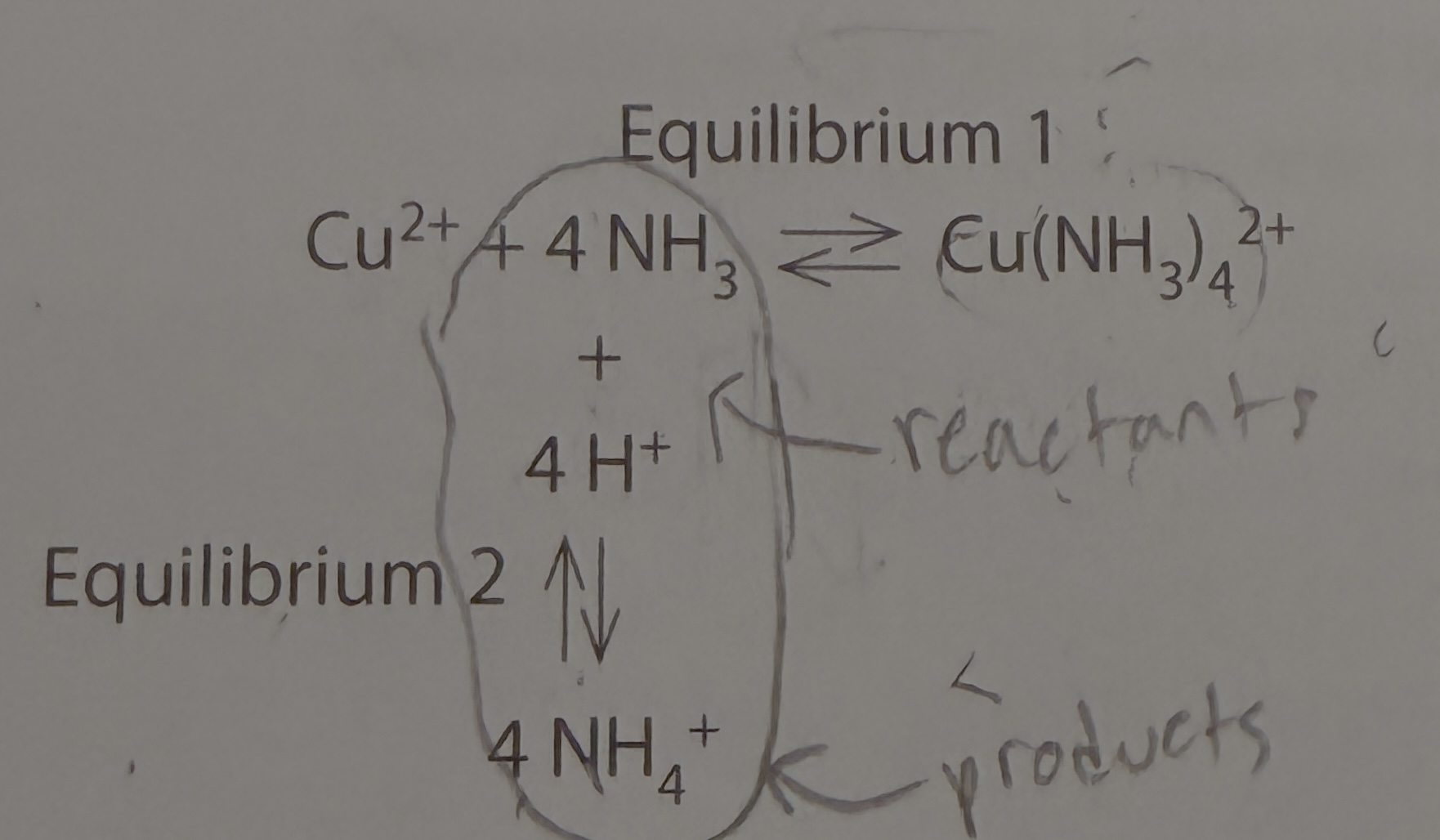
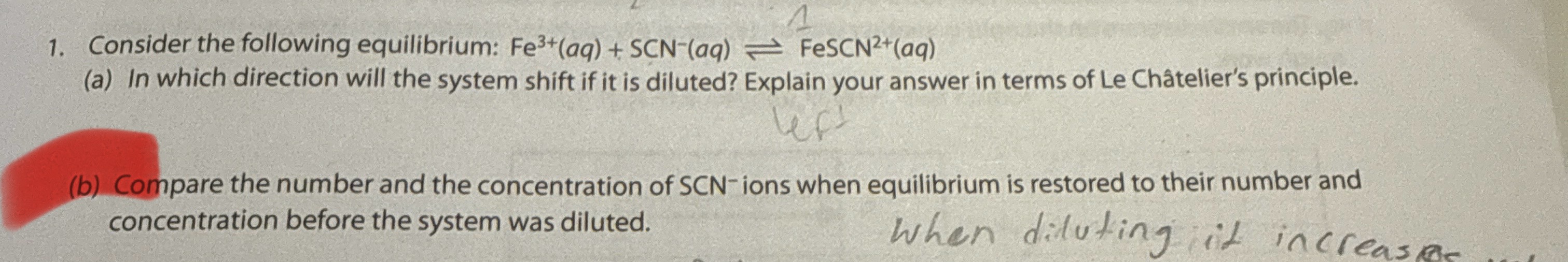
REMINDER

REMINDER
for graphs, coefficients tell us how much more they increase or decrease than one another
REMINDER
don’t include solids or liquids in concentration graphs (can include aq)
REMINDER
if a keq equation has two of the same [ ] then you can just write it with a square (might help when solving for things later by square rooting)
REMINDER
even when at equilibrium, liquid evaporation still occurs
REMINDER
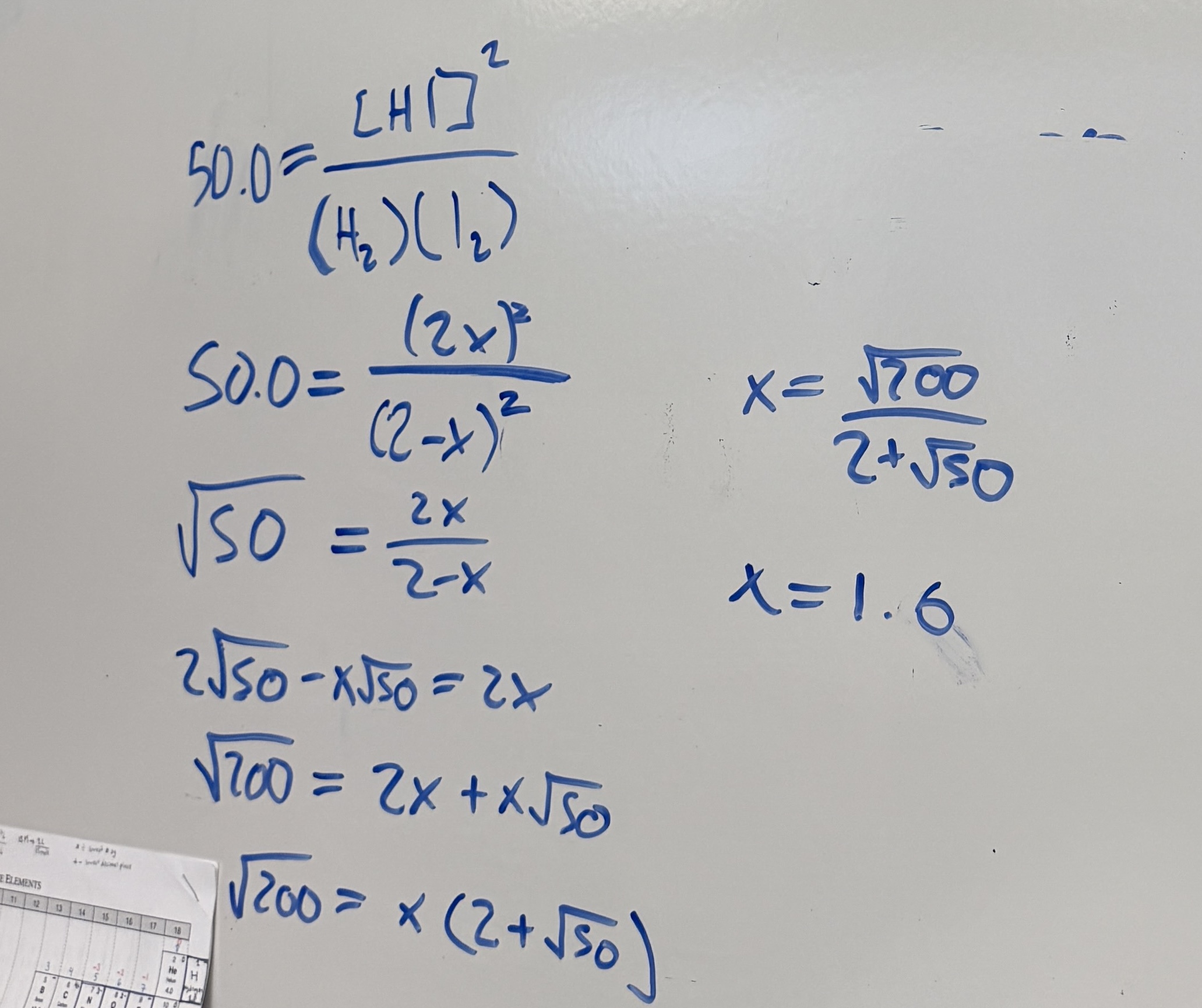
REMINDER
If a system shifts right, it means the forward reaction is favored (more products form).
If a system shifts left, it means the reverse reaction is favored (more reactants form).
REMINDER
when it talks about yield then its talking about the product
REMINDER
for kiyomis question:
do Ice chart normally and solve for x
use your E answer and multiply by molar mass to find mass