Biology Terms: Lateral, Dendrite, Serotonin & More
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Dorsal
toward the back
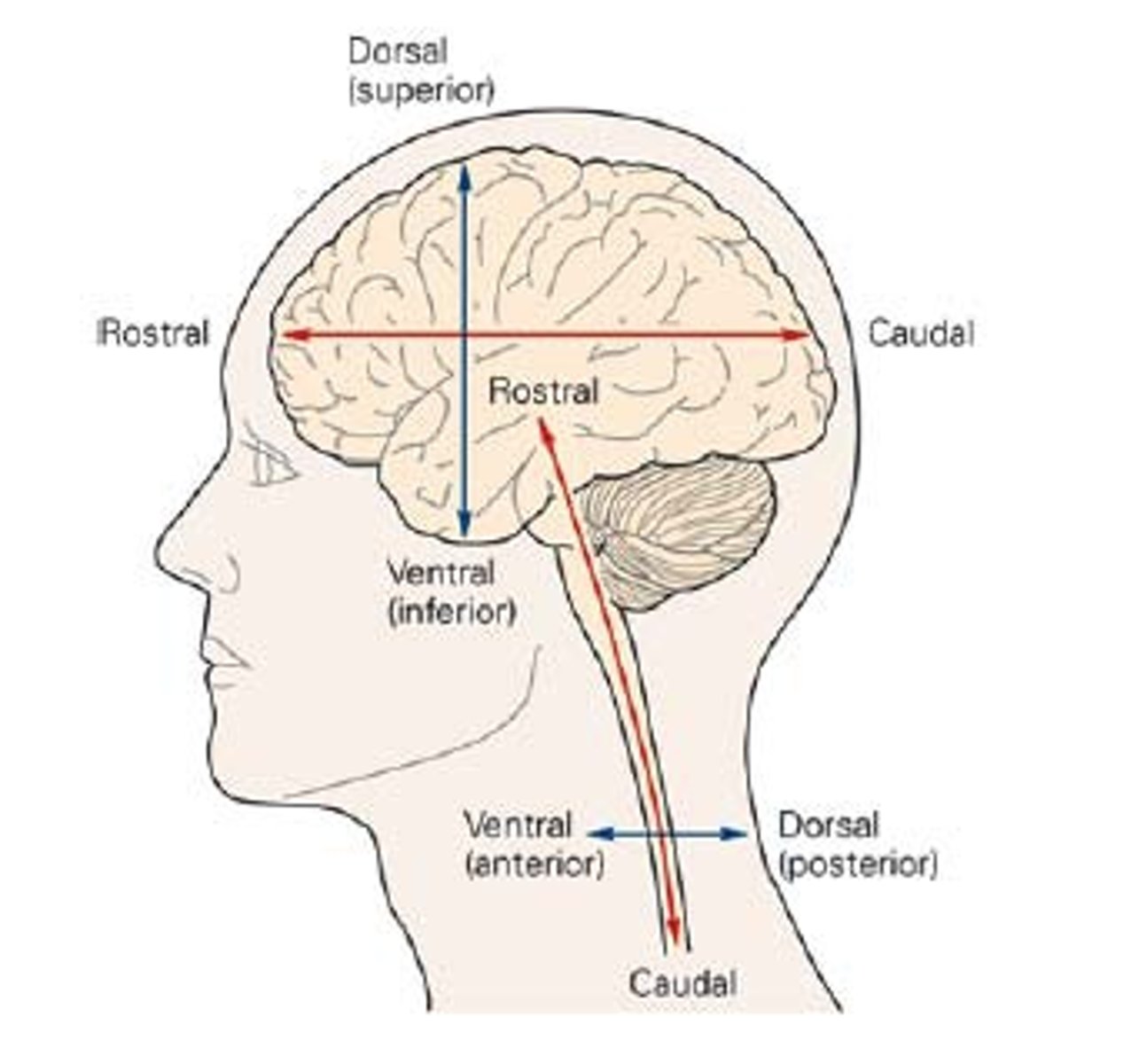
Ventral
bottom of brain
Postsynaptic side of synapse
Neurotransmitter receptors in the postsynaptic membrane are specialized proteins that react to neurotransmitter molecules.
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
Oligodendrocytes
Type of glial cell in the CNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath.
EPSP
Excitatory postsynaptic potential; a slight depolarization of a postsynaptic cell, bringing the membrane potential of that cell closer to the threshold for an action potential.
Sodium Potassium Pump
A transport protein in the plasma membrane of animal cells that actively transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
Ligand-gated Na+ channels
These are gates for Na+, and they will open when a chemical from outside the cell binds to them (like a molecule you're smelling or tasting). Then Na+ can go into the cell.
Voltage-gated Na+ channels
Open when a cell's membrane potential depolarizes, allowing sodium ions to flow into the cell.
Voltage gated K+ channels
K+ exits cell down its electrochemical gradient; ion channels, which their openings provide an outward flow of potassium ions repolarising the cell.
Gap junction
channel between two adjacent animal cells that allows ions, nutrients, and low molecular weight substances to pass between cells, enabling the cells to communicate
Bipolar cell
a bipolar neuron located in the middle layer of the retina, conveying information from the photoreceptors to the ganglion cells
Pyramidal cell
A type of large nerve cell that has a roughly pyramid-shaped cell body; found in the cerebral cortex; transform synaptic inputs into a patterned output of action potentials
Anterior
front of brain
Posterior
back of brain
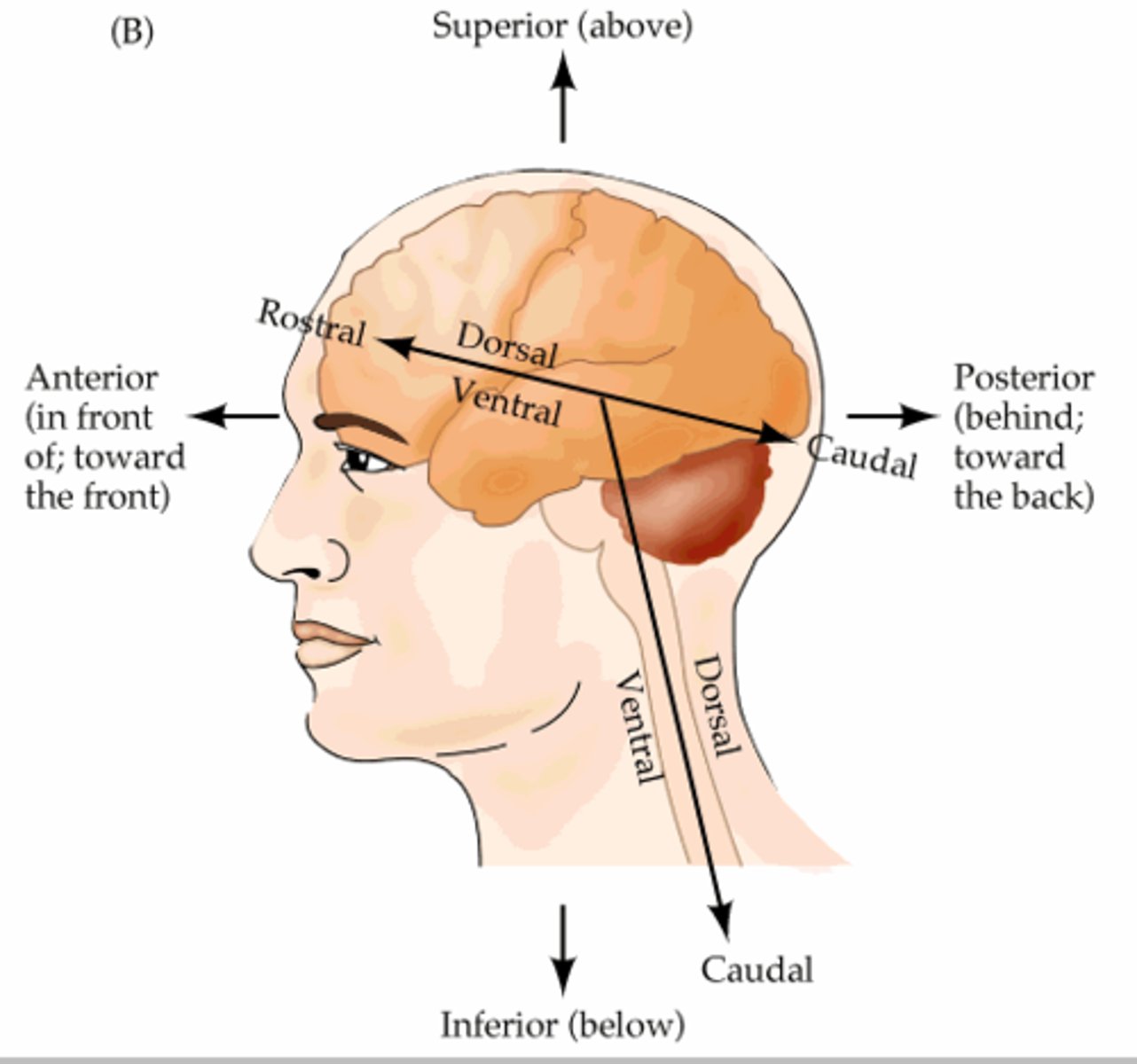
Medial
closer to the midline of the brain
Lateral
further away from the midline
Medulla
The lower part of the brainstem that controls vital autonomic functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
Pons
A part of the brainstem that relays signals between the medulla and higher brain areas; involved in sleep, respiration, and sensory processing.
Cerebellum
"little brain" ; A structure at the back of the brain involved in motor control, coordination, and balance.
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
Superior Colliculus/ Optic Tectum
receives visual sensory input
Inferior Colliculus
a midbrain nucleus in the auditory pathway
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Pituitary
at the base of the brain; stimulates growth and controls functions of other glands
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
Basal Ganglia
a set of subcortical structures that directs intentional movements
Occipital Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
Temporal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
Parietal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
Frontal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Terminal
Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons
Dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
Presynaptic side of synapse
The axon terminal contains synaptic vesicles that contain neurotransmitter.
Axon Hillock
the cone-shaped area on the cell body from which the axon originates
Myelin Sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
Glia Cell
special type of cell found in the nervous system that forms the myelin sheath, which increases the speed of neural conduction by providing insulation of the axons
IPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential; a slight hyperpolarization of the postysynaptic cell, moving the membrane potential of that cell further from threshold.
Action Potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Psuedobipolar cell
A neuron that possesses two connections but sends a signal only one way
Neurotransmitter
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Glutamate
The most common neurotransmitter in the brain. Excitatory.
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.