IB BIO - U1 L4 - CELL DIFFERENTIATION AND STEM CELLS
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are Emergent Properties?
Multicellular organisms are capable of completing functions that unicellular organisms can’t
Collective actions of individual cells combining to create new synergistic effects
Levels of organisation
Specialised Cell
Tissue
Organ
Organ System
Organism
Cellular Differentiation
Process by which a cell becomes specialised to perform a specific function via activation of some genes by chemical signals and not others.
What are specialised cells?
cells designed to carry out a particular role in the body
Gene Packing
Differentiated cells have different regions of DNA packaged as euchromatin and heterochromatin Euchromatin-
Euchromatin:
Expanded form that is accessible for transcription (active gene).
Heterochromatin:
Condensed form that is not accessible for transcription (inactive gene)
Stem Cells
animal cell that can differentiate into many types and continually replicate
Stem Cell Origins
Embryos
Umbilical Cord
Blood Adult Tissues
Types of Stem Cells:
Totipotent
Pluripotent
Multipotent
Unipotent
Totipotent Stem Cells
Form any cell type and develop into entirely new organisms (ex- zygote)- embryonic
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Form any cell type arising from 3 germ layers (ex- inner mass of blastocyst)- embryonic.
Multipotent Stem Cells
Only form closely related cell types (ex-bone marrow) adult
Unipotent Stem Cells
Can only regenerate themselves, cannot differentiate.
What are Stem Cell Niches?
Sites within body where pool of adult stem cells are maintained.
Where are Stem Cell Niches located?
Bone Marrow
Hair follicles
Heart
Intestines
Brain
These are all multipotent (can only differentiate into similar cells/closely related cell types)
Uses of Stem Cells.
Necessary for embryonic development.
undifferentiated cell source from which all other cell types may be derived.
Viable therapeutic option.
when adult tissues become damaged and cannot be regenerated.
Examples of Therapeutic Stem Cells Use
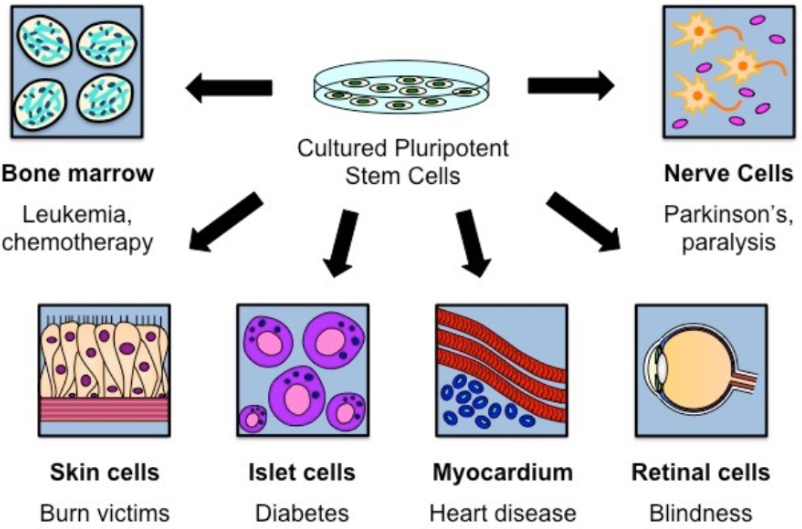
Stem Cell Therapy
Stargardt’s Disease
inherited form of juvenile macular degeneration that causes progressive vision loss to point of blindness
Caused by gene mutation that impairs energy transport in retinal photoreceptor cells, cousin them to degenerate
Treated by replacing dead cells in retina with functioning ones derived from stem cells.
Ethics
Multipotent
Effective for certain conditions, but is limited in its scope of application (lower potency)
Pluripotent
Greatest yield from embryos, but requires destruction of a potential living organisms (greatest potency) This is where ethical consideration comes in
Umbilical Cord Blood
Stored and preserved at cost
Raises ethical concerns of availability and access; fairness
Artificial Stem Cell Techniques
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT)
Nuclear Reprogramming
What is a Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT)?
Creation of embryonic clones by fusing a diploid nucleus with an enucleated egg cell (therapeutic cloning)
What is Nuclear Reprogramming?
Induce change in gene expression to transform it into different cell type (transdifferentiation)